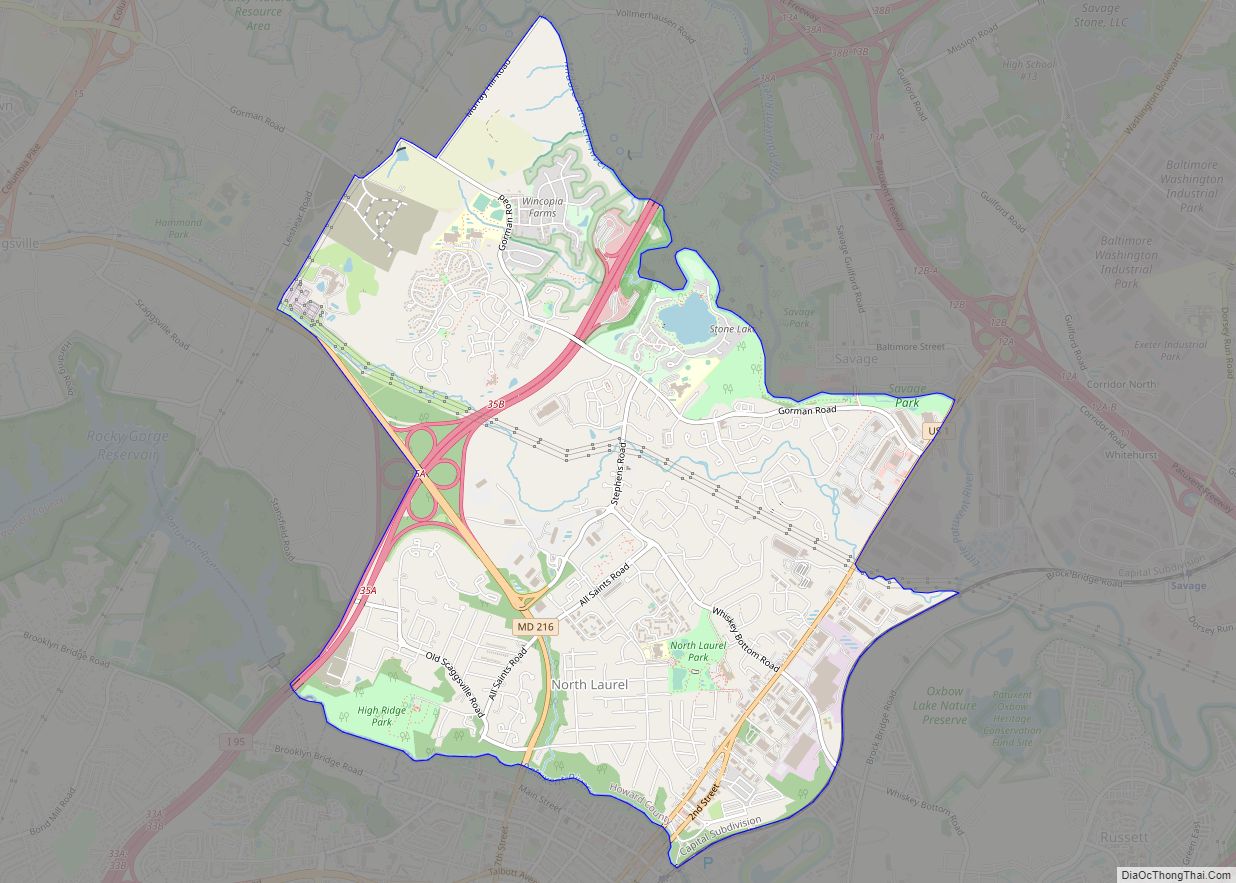
North Laurel is a census-designated place (CDP) in Howard County, Maryland, United States. The published population was 4,474 at the 2010 census. This population was substantially less than the CDP’s population in 2000, and was the result of an error in defining the boundary prior to tabulation and publication of 2010 Census results. The corrected 2010 Census population is 20,259. North Laurel is adjacent to the City of Laurel, which is located across the Patuxent River in Prince George’s County.
| Name: | North Laurel CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | Maryland |
| County: | Howard County |
| Elevation: | 299 ft (91 m) |
| Total Area: | 6.54 sq mi (16.93 km²) |
| Land Area: | 6.48 sq mi (16.79 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.06 sq mi (0.15 km²) |
| Total Population: | 25,379 |
| Population Density: | 3,915.30/sq mi (1,511.79/km²) |
| FIPS code: | 2456725 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1867298 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
North Laurel location map. Where is North Laurel CDP?
History
Prehistoric times
The edge of the Arundel Formation underlies the North Laurel area. The astrodon, a herbivorous sauropod, was present about 112 million years ago. Prior to 10,700 B.C. North Laurel was a spruce forest evolving into a boreal forest occupied by mammals ranging from mastodon to sloth. By 3000 B.C. the vegetation was similar to modern plant life. Humans have lived along the Patuxent River since at least 6500 B.C. By the time of European contact, the lands in the region were occupied by various tribes of Algonquin speaking Native Americans.
Recent history
The Patuxent River was first named (“Pawtuxunt”) on the detailed map resulting from the 1608 voyage upriver by Jamestown settler John Smith. The early English settlers progressively explored further northward from the mouth of the river, eventually reaching the area that is now North Laurel. In the 1620s the Susquehannocks pushed the Piscataway tribes out to the southeast to reduce competition occupying the area as far south as the Potomac River. The Susquehannocks were well armed hunters and profited from beaver trading with the English. By 1632 Lord Baltimore had claimed title to issue land grants in Maryland through Charles I of England. In 1652, the Susquehannocks made a treaty with Marylanders to keep trade flowing and receive arms to use against the Iroquois to the north. By 1675, efforts were underway to eliminate the Susquehannocks from the region.
The North Laurel region was surveyed into land grants with colorful names in the mid-1700s. The largest grant was Warfield’s Range, followed by Wincopion Neck. Smaller grants in the area include (from north to south) The Addition, Ridgley’s Neck, Bare Hills, Poplar Range, Grover’s Lot, Poplar Bottom, Holland’s Chance, Snowden’s Intent, Clark’s Walks, Snowden’s New Birmingham, Brother’s Partnership, Warfields Neglect, Sappington’s Sweep, Nellsons Rainbow, Lasswells Hopewell, and Davis’s Hills. The oldest structure in Howard County was situated on Warfield’s Range. The log cabin built in 1696 was moved to Elkridge to accommodate a Newburn development, and was destroyed by arson. The post road from Washington to Baltimore was constructed in 1740, which ran along its eastern boundary. Used by George Washington regularly, the road would remain the principle route between Baltimore and Washington for 200 years.
By the 1800s tobacco farming was the primary crop in North Laurel. Soil conservation was poor, leaving farms to switch crops or abandon farms. The founding of the Laurel grist mill in 1811 and the Savage Mill in 1822 brought an industrial economy to the area. Slavery was a common practice among the farmers in North Laurel until after emancipation. Runaway slave ads were regularly placed in the Baltimore Sun newspaper.
In the summer of 1834, Irish (Corkians) and German (Fardown) workers clashed at the B&O construction site at North Laurel. Fardowns burned shanties used by Corkian workers. A militia of 60 men were led by General Ridgley to keep the peace between the rival factions. In 1835 the rail line between Baltimore and Washington was completed next to the post road.
North Laurel was located in Anne Arundel County until 1860, when it became part of the newly subdivided Howard County.
In 1890, a syndicate purchased portions of the Burr, Brightwood, Kennedy, and Wheeler farms next to the B&O track to form a town named “North Laurel” adjacent, which did not materialize. The Patuxent Springs became a small tourist destination at the turn of the century.
In 1901, Ernest Lyon founded the Maryland Industrial and Agricultural Institute for Colored Youths near the Patuxent River to serve African Americans during the era of racial segregation in the United States.
In 1910, the Southern Real Estate Company of Pittsburgh bought one of Gustuavas Ober’s North Laurel farms totaling 550 acres (220 ha) for $70,000. The lots were subdivided to form Laurel Park. Many of the lots remained undeveloped for over 100 years. Several remaining lots were purchased with eminent domain and exchanged with Cornerstone Homes to consolidate enough land to build the North Laurel Civic Center and park. In 2013, Howard County sold the remaining wooded lots on the parkland to build Park Overlook.
The next year, Senator Arthur Pue Gorman’s daughter, Grace “Daisy”, built her home, Overlook, on 140 acres (57 ha) of land along Murray Hill Road inherited from her father. Her husband, R.W. Johnson, was the first manager of the Laurel race track. The property has been the home to land developer and ambassador Kingdon Gould Jr. since 1952.
In 1948, police raided Rocway Towers, putting an end to a short-lived effort to bring Washington-funded gambling casinos to Laurel. The Stucco Roadhouse built in the 1920s to resemble a mission house was the site of a 1948 gangland murder and prostitution into the 1970s. It remains in operation today as a used car dealership. The same year, Freestate Raceway, a second racetrack featuring harness racing, was opened.
In 1959 the plan was announced that Interstate 95 would be built through the farms of eastern Howard County. In October 1962, 47 acres (190,000 m) were rezoned for apartments at the corner of Whiskey Bottom Road and All Saints Road to take advantage of the future highway exit in North Laurel. An additional 27 acres (11 ha) of land was given to the county in school exchange for approving such a dense development. To the north, school board member Rob Moxley was secretly buying and swapping 10,000 acres (4,000 ha) of farmland for Howard Research and Development to build Columbia. On 21 September 1963, the Laurel Planning and Redevelopment Corporation took out $520,000 in loans to buy 100 acres (40 ha) of the land to build Whiskey Bottom Apartments, which was resold to Whiskey Bottom Properties in 1966 for $1,000,000. The loan officer Ralph Lublow was tried for taking secret bonuses for the project, and in 1978 was released due to insanity after ordering hitmen to murder fellow businessmen Morton Hollander and Alvin Blum. On June 17, 1964, the Howard County Public School system applied for a P.L. 815 federal loan intended to fund schools for the children of federal workers that were being relocated to support Cold-War buildups. The project that would support the rapid population increase from the Whiskey Bottom development would become Whiskey Bottom Road Elementary School.
By 1963, the county anticipated growth from 44,000 to nearly 260,000 by the year 2000 (a mark reached by 2004). It also anticipated that despite the massive growth in population from the new 100,000-person “planned city” of Columbia, the Sixth Election District would be the most populated section of Howard County after 1975.
In 1991, Freestate Racetrack was targeted for development. The Coca-Cola company sought the site for a bottling plant that was eventually built in Hanover, Maryland. On 8 September 1992, a man and a teenager attempted a series of failed carjackings starting at the southbound rest stop at I-95 through the Bolling Brook subdivisions. The men carjacked the vehicle of Dr. Pam Basu and her 22-month-old daughter at a stop at Horsham and Kightsbridge road. Basu attempted to retrieve her daughter, and was dragged to death along Gorman Road. The suspects were caught in western Howard County after a police chase. As a direct result of the violent incident, the Federal Anti-Car Theft Act of 1992 (FACTA) was created, the first federal carjacking law. The 1992 act, codified at 18 U.S.C. § 2119, took effect on October 25, 1992.
In 2006, the Rouse Company developed luxury townhomes at Stone Lake, a former quarry. The quarry was trash dump in the 1950s and closed in 1973. In 1976, Rouse proposed using the site for the profitable commercial landfill operations requiring dumping fees in competition with the Alpha Ridge Landfill. The site filled with rain and groundwater becoming the location of multiple drownings.
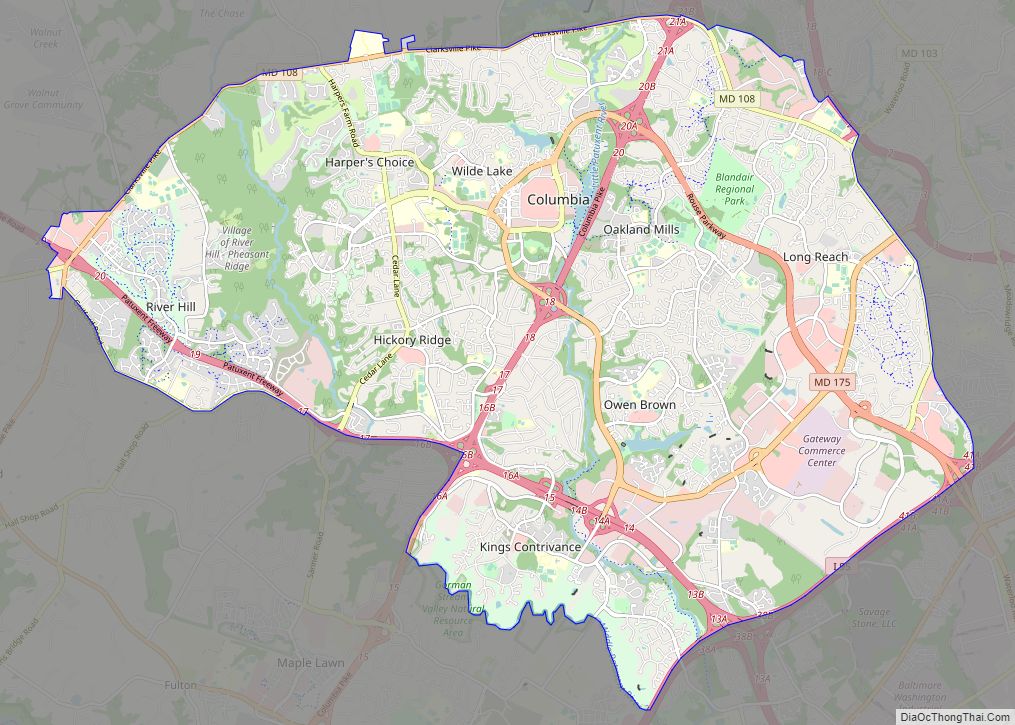
North Laurel Road Map
North Laurel city Satellite Map
Geography
North Laurel is located in the southern corner of Howard County at 39°8′4″N 76°51′46″W / 39.13444°N 76.86278°W / 39.13444; -76.86278 (39.134343, −76.862690). It is bordered to the north by Savage and Columbia, to the west by Scaggsville, to the south in Prince George’s County by the city of Laurel, and to the southeast in Anne Arundel County by Maryland City. The southern boundary of the CDP is defined by the Patuxent River, which is also the Howard County/Prince George’s County line.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the North Laurel CDP has a total area of 6.3 square miles (16.4 km), of which 6.3 square miles (16.3 km) is land and 0.039 square miles (0.1 km), or 0.6%, is water. (these area measurements differ from those initially published by the Census Bureau.
See also
Map of Maryland State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming