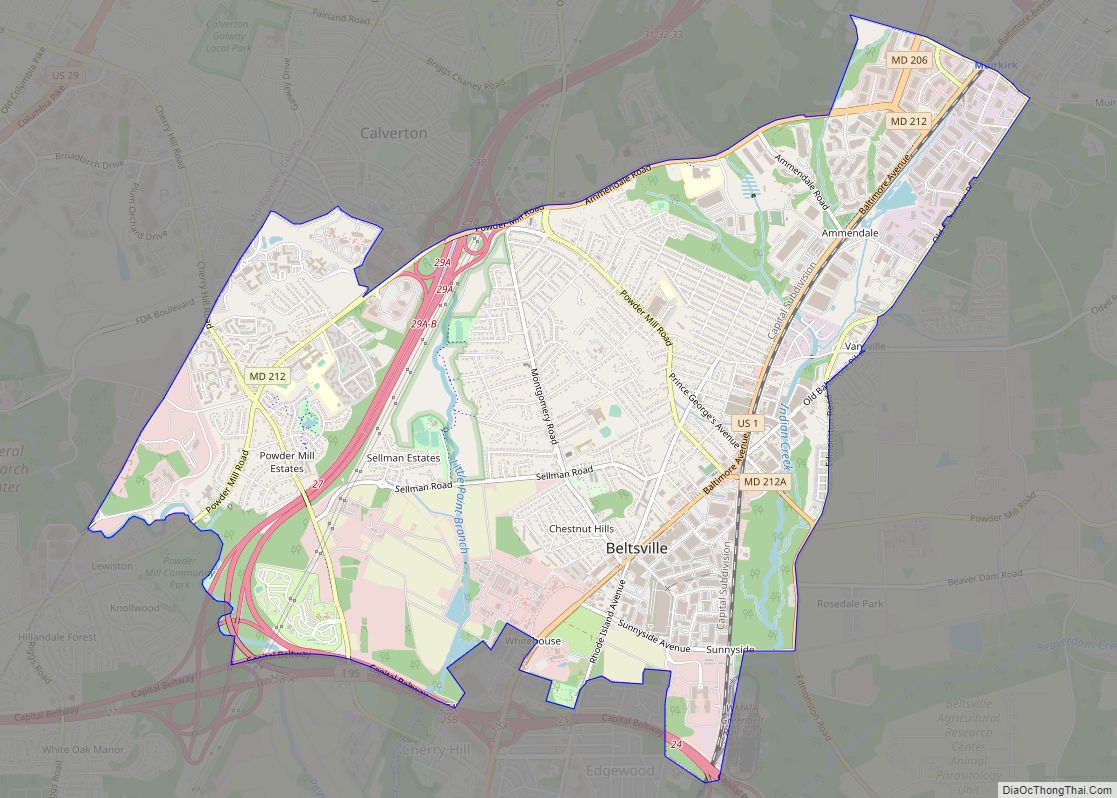
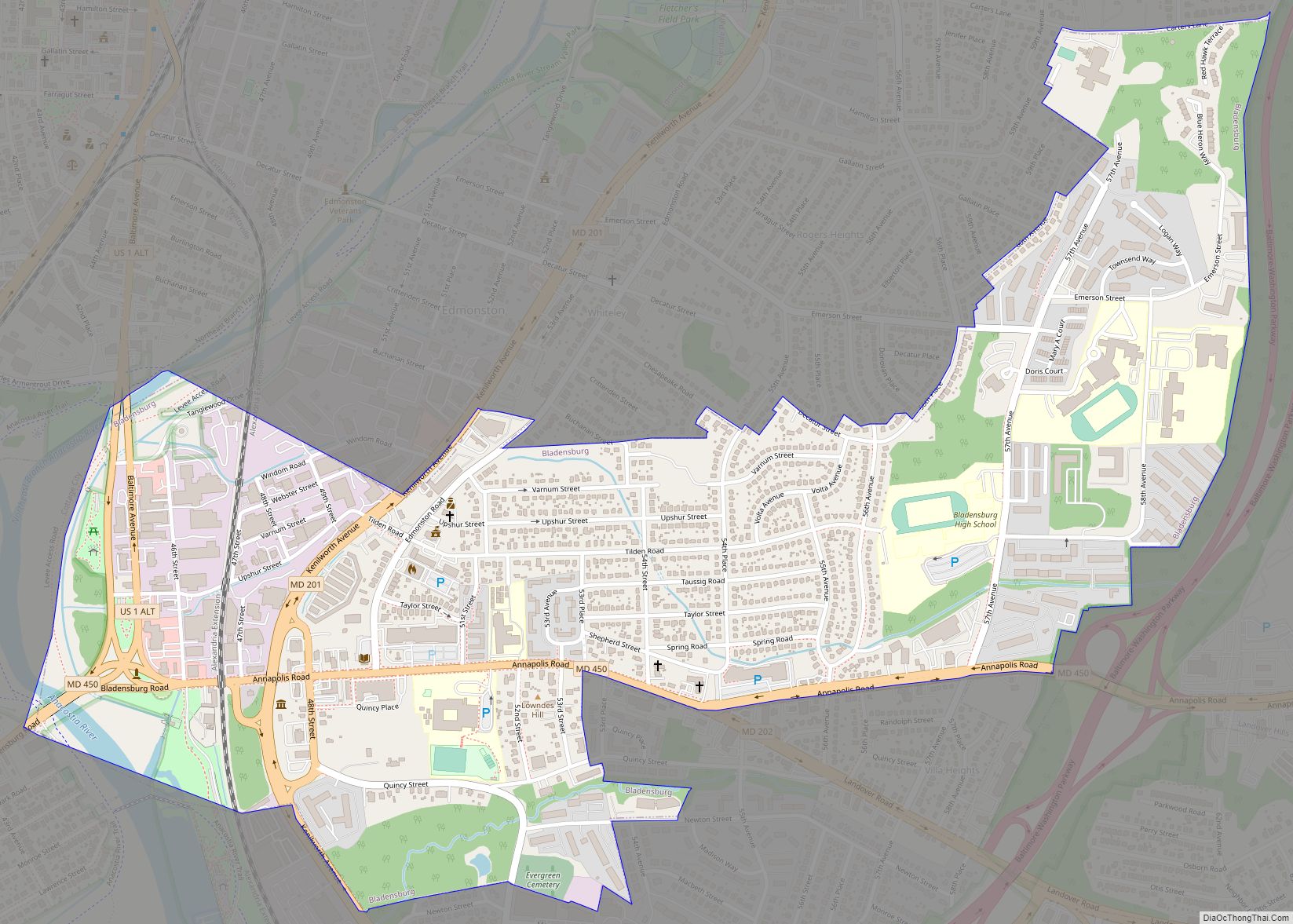
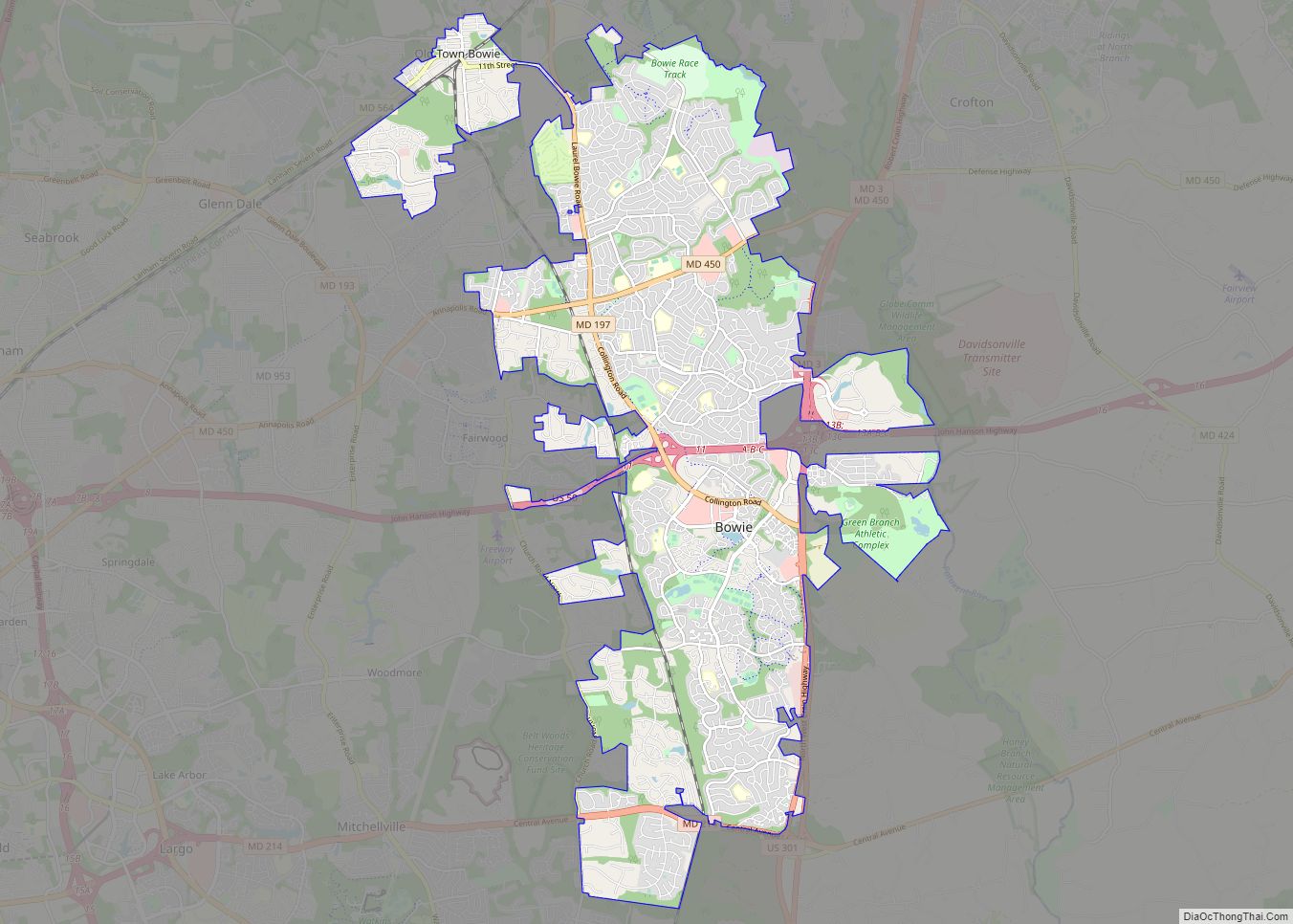
Beltsville is a census-designated place (CDP) in northern Prince George’s County, Maryland, United States. The community was named for Truman Belt, a local landowner. The 2020 census counted 20,133 residents. Beltsville includes the unincorporated community of Vansville.
| Name: | Beltsville CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | Maryland |
| County: | Prince George’s County |
| Elevation: | 135 ft (41 m) |
| Total Area: | 7.23 sq mi (18.73 km²) |
| Land Area: | 7.21 sq mi (18.66 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.03 sq mi (0.07 km²) |
| Total Population: | 20,133 |
| Population Density: | 2,793.92/sq mi (1,078.75/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 20704-20705 |
| FIPS code: | 2406400 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0597069 |
| Website: | www.beltsville.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Beltsville location map. Where is Beltsville CDP?
History
Beltsville’s history dates back to 1649, when the land was part of an 80,000-acre (324 km) land grant given to Richard Snowden I by Lord Baltimore of England. Snowden and his family were planters who established large plantations on which they built comfortable manor homes. Soon after, other settlers moved into the area, but they were farmers who could only afford a few acres of land and whose families lived in small cabins. The principal crop was tobacco, most of which was shipped to England. Because of the fertile soil and desirable growing conditions, the crops prospered.
Industry came to Beltsville in the early 18th century when iron ore was discovered in the area. The Muirkirk Iron Furnace on US 1 was established by Andrew and Elias Elliott, who learned their iron-making skills in Muirkirk, Scotland. They produced some of the best-quality pig iron in the country and supplied the U.S. Army with cannons, shot, wheels, and other iron products during the Revolutionary War and the Civil War.
By 1730, Post Road (now part of US 1) was the main thoroughfare through Beltsville. Though crude, it made stagecoach travel possible. In 1783, Gabriel Peterson Van Horn established a stage line and built the Van Horn Tavern on Odell Road, where passengers could spend the night as they traveled between Baltimore and Washington. The trip took one and one-half days.
Beltsville has a distinguished Revolutionary War hero as its native son. Brigadier General Rezin Beall, who was born on Turkey Flight Plantation on Old Gunpowder Road in 1723, prevented a British invasion at Drum Point on the Chesapeake Bay with only 100 men. He is credited with the fact that there are no Revolutionary War battlefields in Maryland.
In 1835 one of the first rail lines in the country, the Washington branch of the B&O Railroad (Baltimore & Ohio), was built through Prince George’s County. Coming from Baltimore, the line entered the county at Laurel and ran southwesterly to Bladensburg, then into Washington. B&O established a rail stop and freight depot on land purchased from a tobacco farmer named Trueman Belt, and they named the place after him. The new community of Beltsville was doubly blessed, for the Baltimore-Washington Turnpike crossed the rail line there. It soon became a thriving little trading center, eclipsing the older community of Vansville further north on the pike.
The original area developed haphazardly and consisted of a few residences, two churches, several small stores, a blacksmith, and a wheelwright. In 1891, the Beltsville Land Improvement Company was chartered and over the next thirty years developed the South Beltsville subdivision as a grid of streets. The developers sold the lots to individual owners and placed restrictive covenants on the deeds, including forbidding the manufacture or sale of alcohol and the sale of any property to an African American. Beltsville was marketed to professionals who wanted to escape the congestion of Washington and was developed with a mixture of Victorian-style houses and Colonial Revival houses. The community grew further when an electric railway was extended to Beltsville. The railway began as the Berwyn and Laurel Electric Railroad, but after suffering from financial difficulties it was acquired by the City and Suburban Railway. Located to the west of the railroad, along the line of present-day Rhode Island Avenue, the streetcar line served as the nucleus for additional subdivisions. These areas continued to develop slowly throughout the 1930s and 1940s with the construction of modest side-gable residences. Development continued after the introduction of the automobile, but it was not until after World War II that intensive development came to the Beltsville area.
As the federal government grew, in 1910 the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) began to purchase land in Beltsville for its Agricultural Research Service, the main in-house research arm of the USDA. The land now houses the Henry A. Wallace Beltsville Agricultural Research Center (BARC). The first parcel acquired was 375 acres (1.5 km) of the Walnut Grange Plantation with its historic “Butterfly House”. The Center eventually encompassed 14,600 acres (59 km) and became the largest and most prominent center of agricultural science research in the world.
There are a number of historic homes and buildings still standing in Beltsville. The oldest home was built in 1773. One of the largest of the older buildings, built in 1880, was the three-story Ammendale Normal Institute, which was destroyed by fire in 1998.
In 2003 Kevin Kennedy started a group which aimed to have Beltsville incorporate into its own municipality. By 2004 the 12-member group, named Committee to Incorporate Beltsville, advocated for getting the issue on the ballot. By late 2004 the group began efforts to collect 3,000 signatures on a petition so the issue can be put up for election; this would represent about one quarter of the persons in Beltsville who were registered to vote. By the deadline in March 2005 they failed to get sufficient signatures as they only had 2,000.
Historic sites
The following is a list of historic sites in Beltsville and identified by the Maryland-National Capital Park and Planning Commission: African-American Heritage Sites at nearby Rossville are listed at Muirkirk, Maryland.
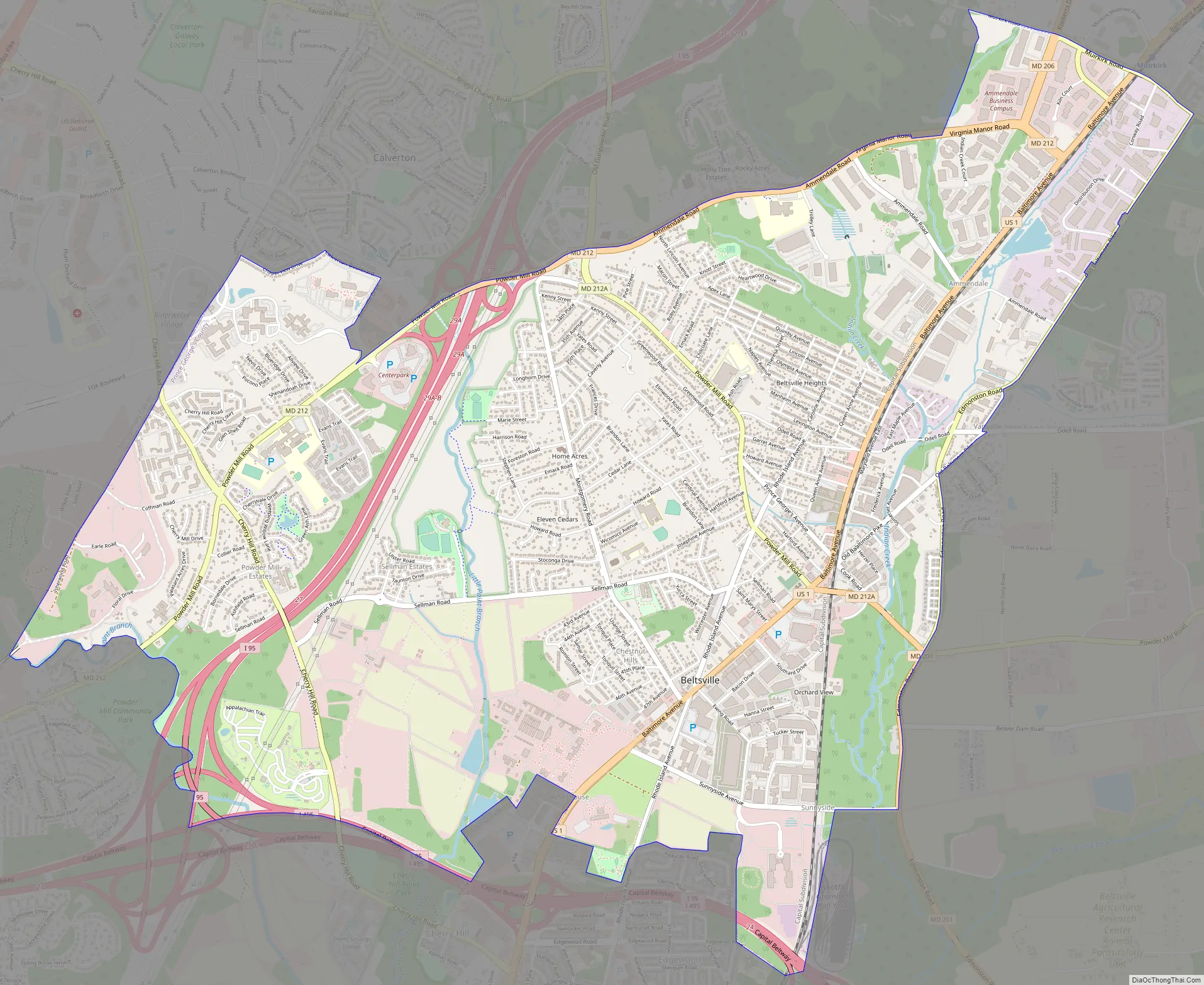
Beltsville Road Map
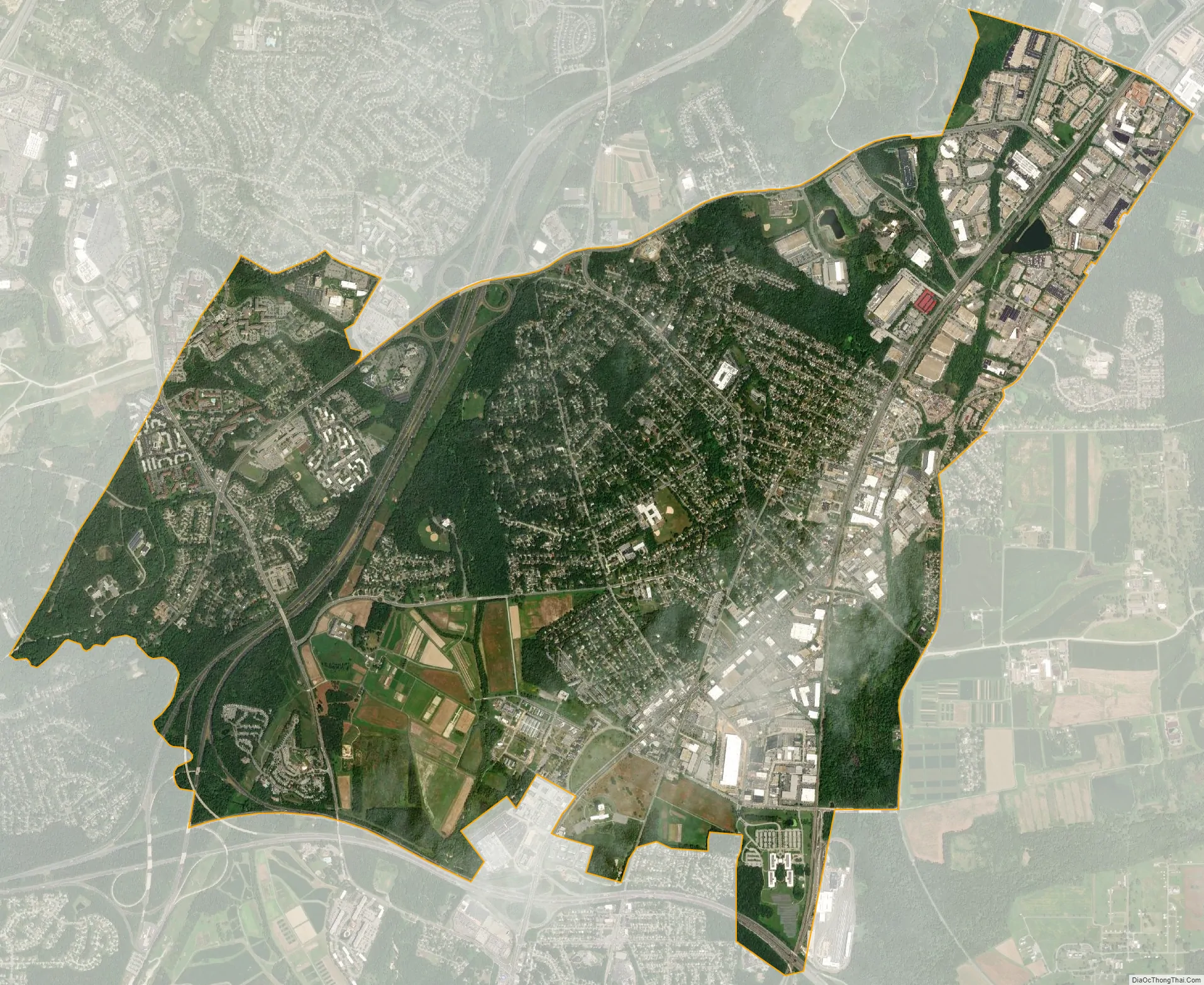
Beltsville city Satellite Map
Geography
Beltsville is located at 39°2′15″N 76°55′4″W / 39.03750°N 76.91778°W / 39.03750; -76.91778 (39.037509, −76.917847), adjacent to the Montgomery County – Prince George’s County line. It is approximately 7 miles (11 km) northeast of the Maryland border with Washington.
According to the United States Census Bureau, Beltsville has a total area of 7.2 square miles (18.6 km), of which 7.1 square miles (18.5 km) is land and 0.04 square miles (0.1 km), or 0.38%, is water.
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Beltsville has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated “Cfa” on climate maps.
See also
Map of Maryland State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming