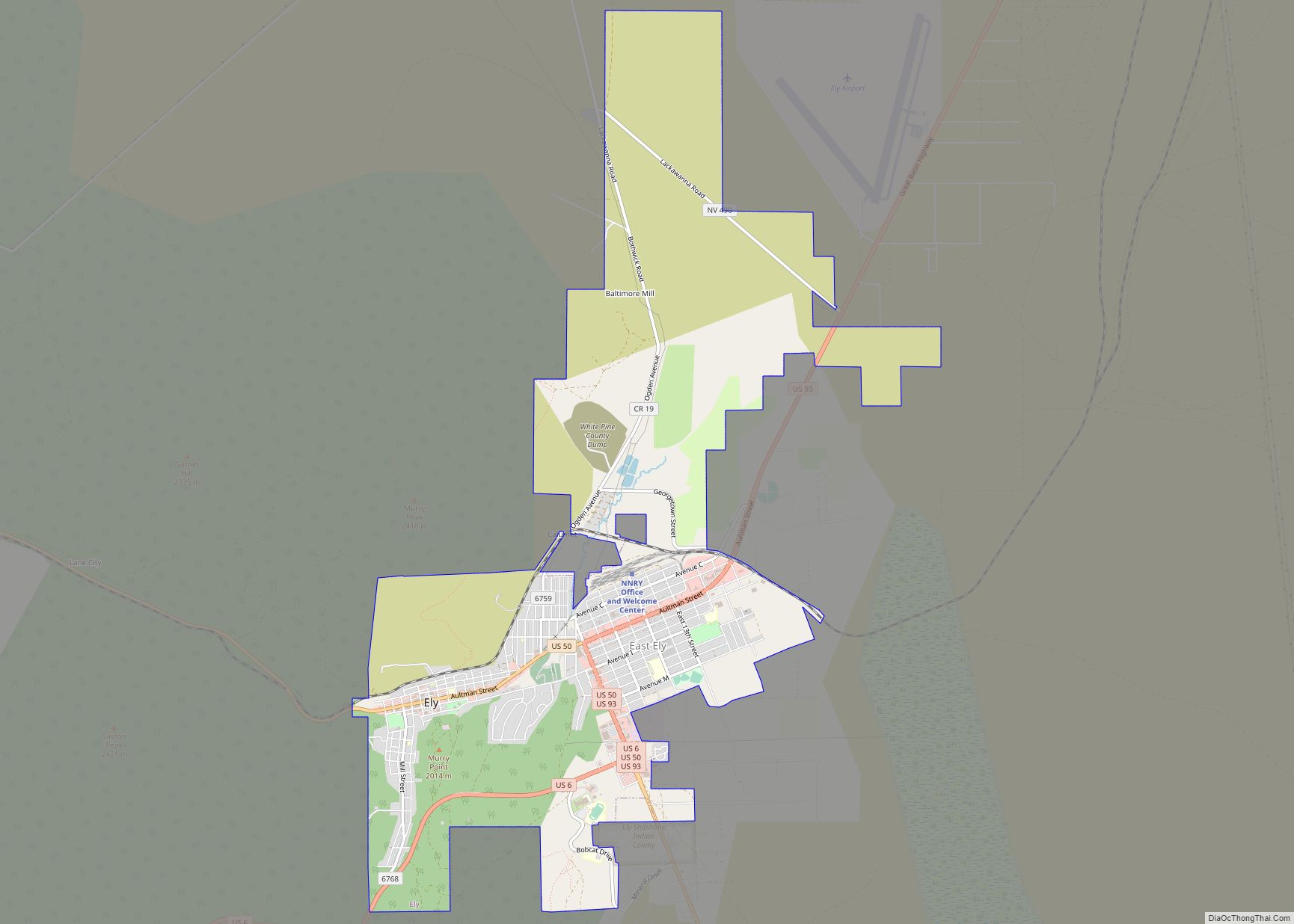
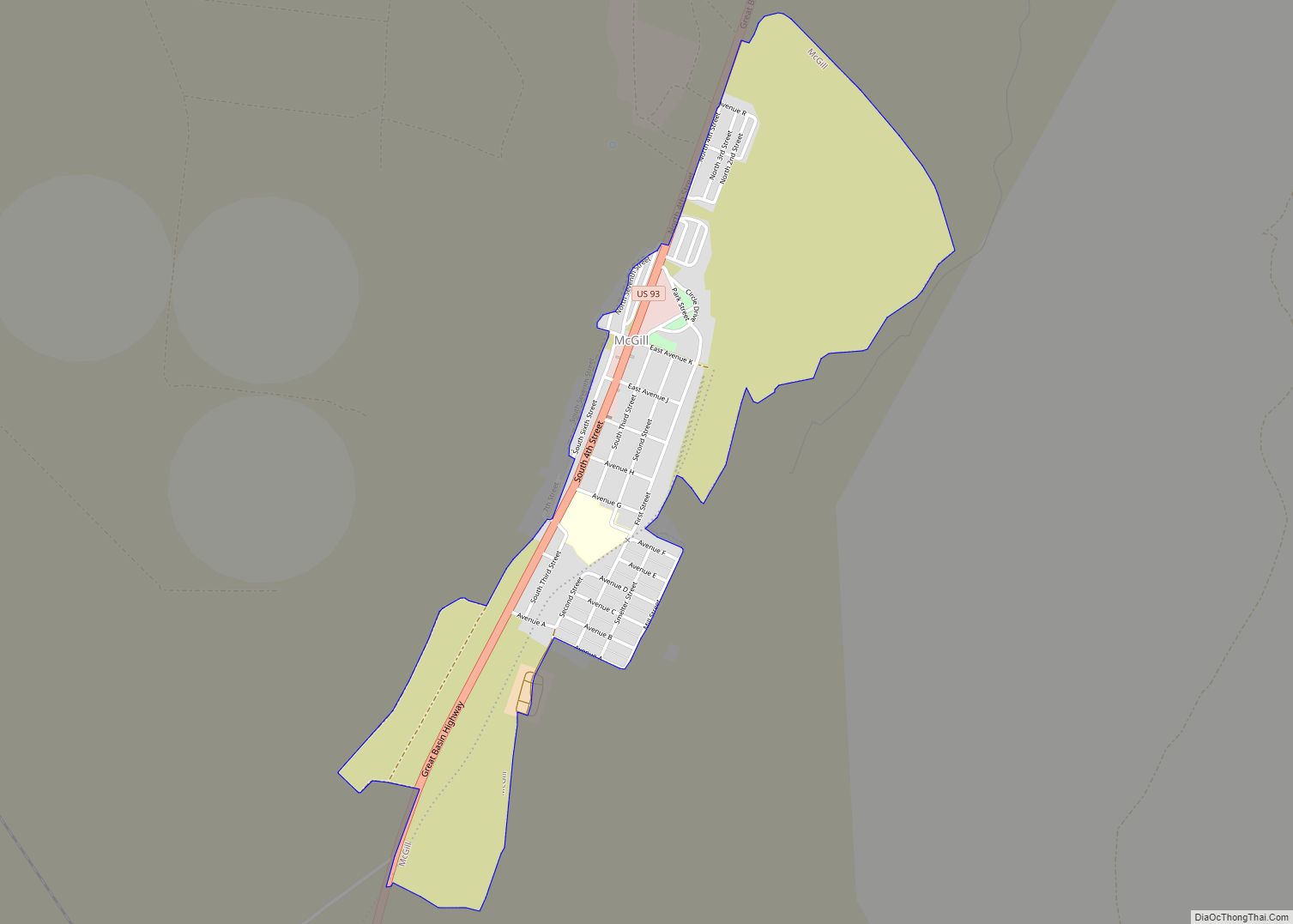
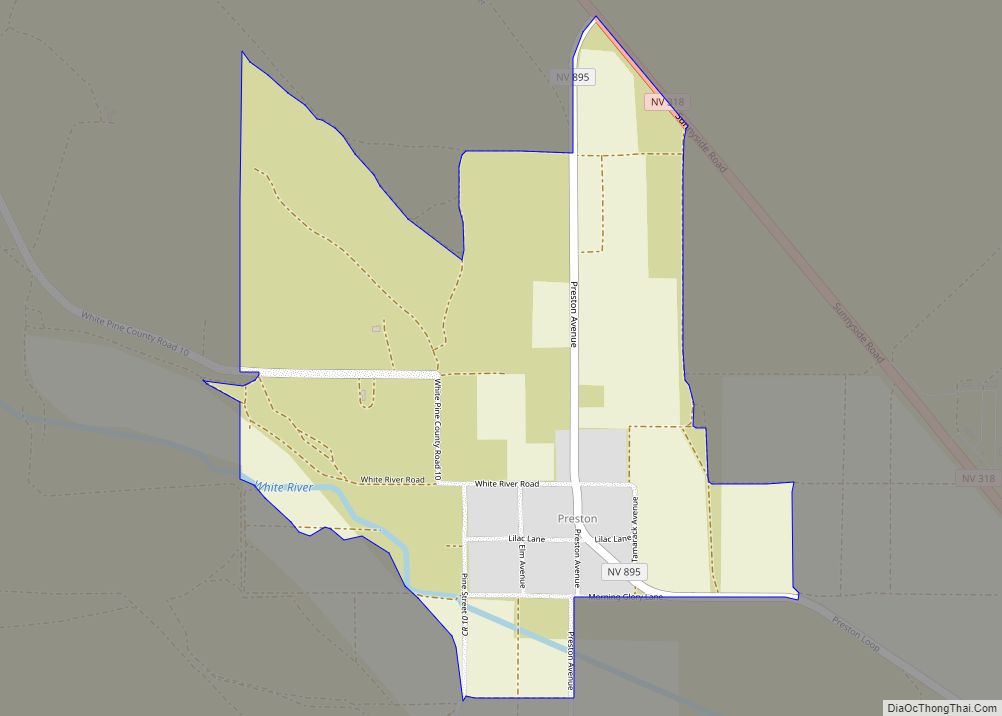
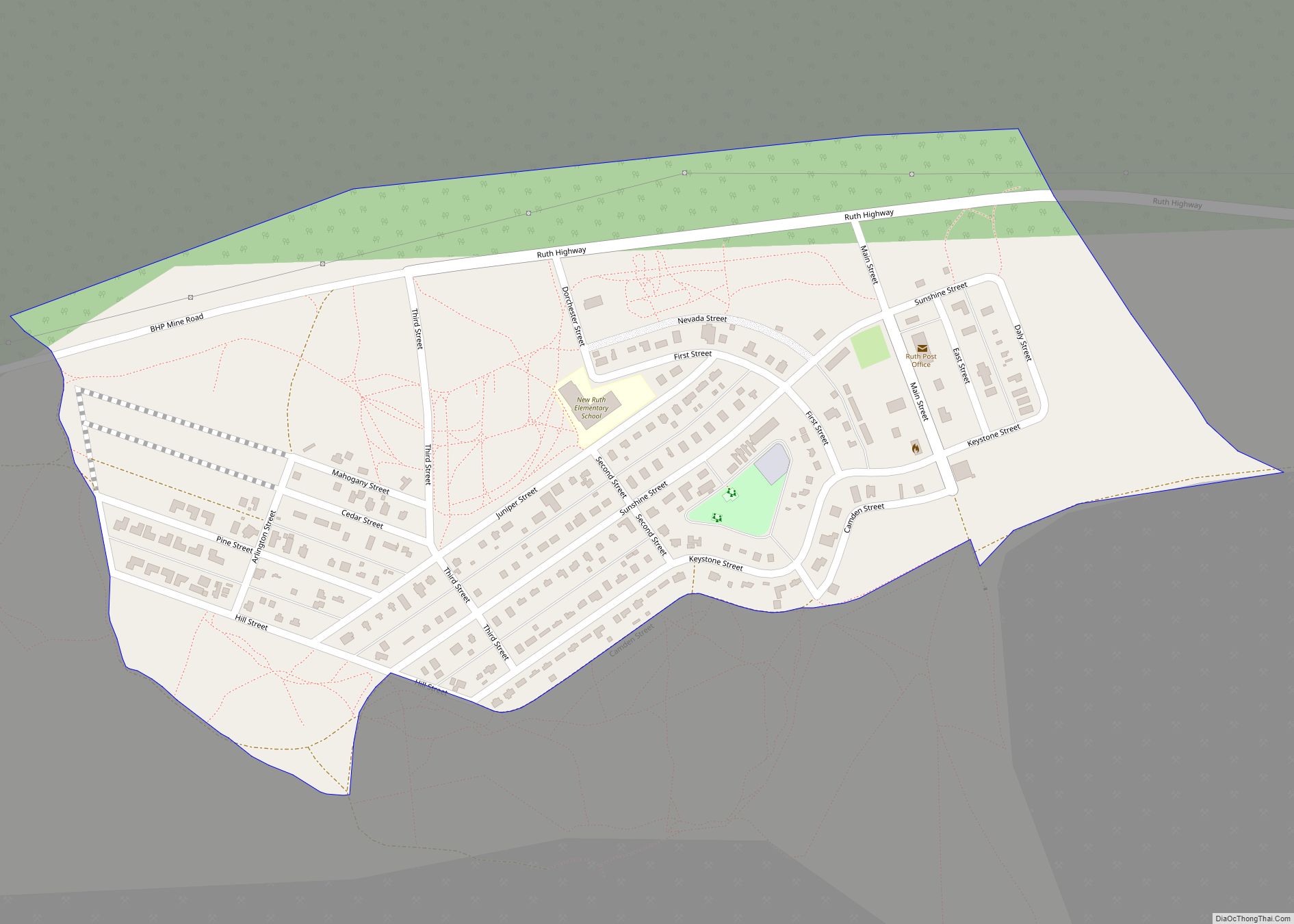
Ely (/ˈiːli/, EE-lee) is the largest city and county seat of White Pine County, Nevada, United States. Ely was founded as a stagecoach station along the Pony Express and Central Overland Route. In 1906 copper was discovered. Ely’s mining boom came later than the other towns along US 50. The railroads connecting the transcontinental railroad to the mines in Austin, Nevada and Eureka, Nevada have long been removed, but the railroad to Ely is preserved as a heritage railway by the Nevada Northern Railway and known as the Ghost Train of Old Ely. As of the 2020 census, the population was 3,924.
| Name: | Ely city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Nevada |
| County: | White Pine County |
| Elevation: | 6,437 ft (1,962 m) |
| Total Area: | 7.63 sq mi (19.75 km²) |
| Land Area: | 7.63 sq mi (19.75 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 3,924 |
| Population Density: | 514.56/sq mi (198.68/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 89301, 89315 |
| Area code: | 775 |
| FIPS code: | 3223500 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0859671 |
| Website: | www.cityofelynv.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Ely location map. Where is Ely city?
History
In 1878, Vermont resident J. W. Long came to White Pine County and soon set up a camp known as “Ely”, after discovering gold. The name “Ely” has been credited to several possible origins: Long’s hometown of Ely, Vermont; a New York Congressman with the surname Ely, who sent Long as a representative according to local historians; Smith Ely, a Vermont native who financed one of the city’s early mineral operations; and John Ely, an Illinois native who came to Nevada for mining.
Ely was founded as a stagecoach station along the Pony Express and Central Overland Route. Ely’s mining boom came later than the other towns along US 50, with the discovery of copper in 1906. This made Ely a mining town, suffering through the boom-and-bust cycles so common in the West. Originally, Ely was home to a number of copper mining companies, Kennecott Utah Copper being the most famous. With a crash in the copper market in the mid-1970s, Kennecott shut down and copper mining disappeared (temporarily).
With the advent of cyanide heap leaching—a method of extracting gold from what was previously considered very low-grade ore—the next boom was on. Many companies processed the massive piles of “overburden” that had been removed from copper mines, or expanded the existing open-pit mines to extract the gold ore. Gold mines as widespread as the Robinson project near Ruth, and AmSelco’s Alligator Ridge mine 65 miles (105 km) from Ely, kept the town alive during the 1980s and 1990s, until the recent revival of copper mining.
As Kennecott’s smelter was demolished, copper concentrate from the mine is now shipped by rail to Seattle, where it is transported to Japan for smelting. The dramatic increase in demand for copper in 2005 has once again made Ely a copper boom town.
The now-defunct BHP Nevada Railroad ran from the mining district south of Ruth through Ely to the junction with the Union Pacific at Shafter from 1996 to 1999.
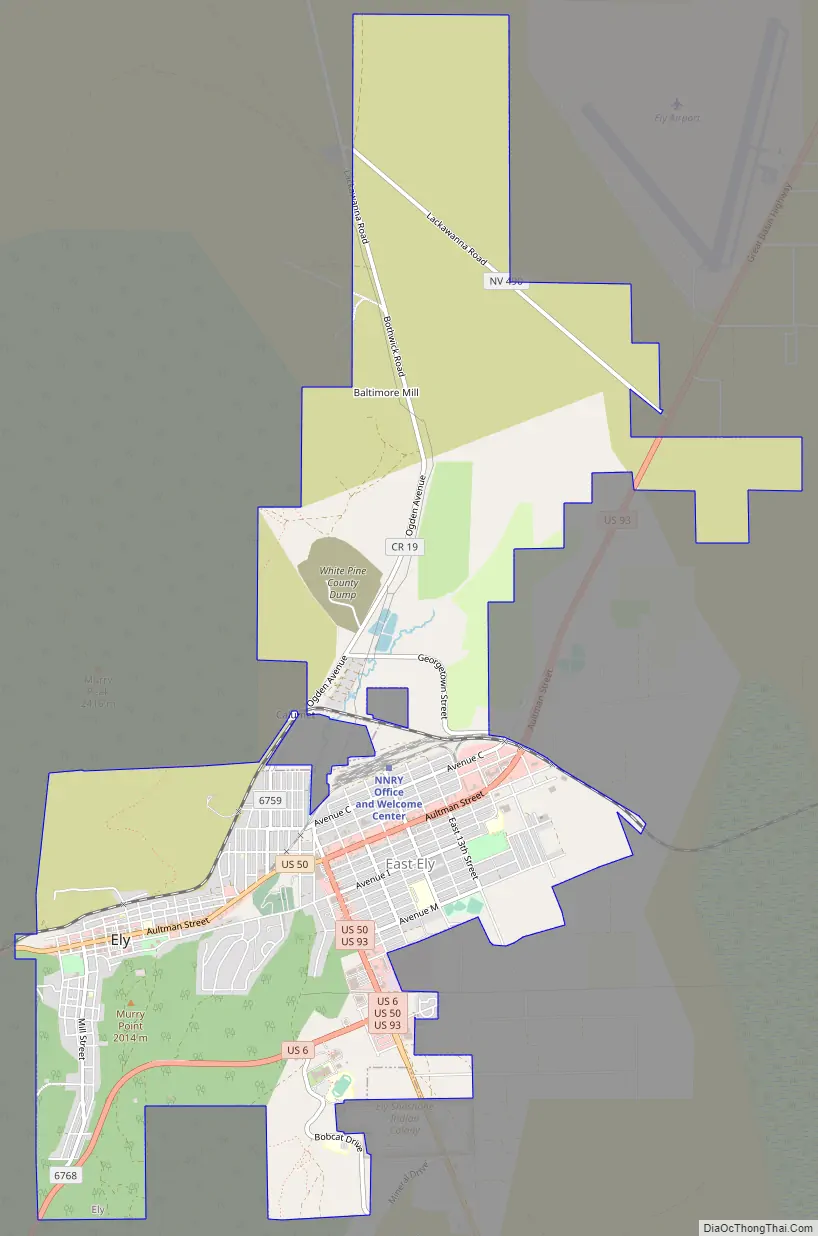
Ely Road Map
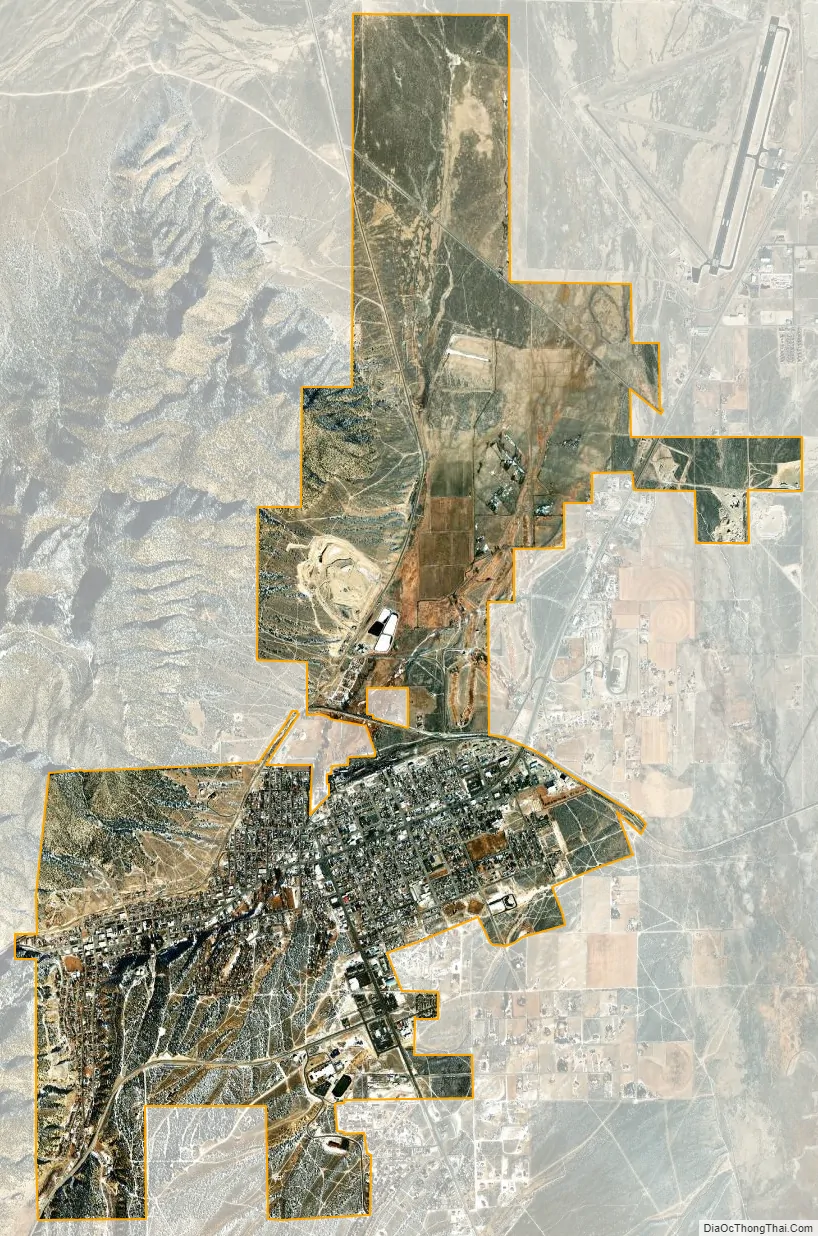
Ely city Satellite Map
Geography
Ely is 77 miles (124 km) east of Eureka, Nevada, 153 miles (246 km) west of Delta, Utah, 105 miles (169 km) north of Pioche, Nevada, 139 miles (224 km) south of Wells, Nevada, and 120 miles (190 km) south of West Wendover, Nevada.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 7.1 square miles (18 km), all of it land.
Ely experiences a semi-arid climate (Köppen BSk), and extreme day-night temperature differences year-round. Ely’s nighttime temperatures account for it being listed as one of the coldest places in the contiguous United States, with an average of 214.9 nights per year with a minimum temperature of 32 °F (0 °C) or less, 15.7 nights reaching 0 °F (−17.8 °C) or less, and 21.7 days when the high does not top freezing. On average, the first and last dates of freezing temperatures are September 8 and June 18, respectively, allowing a growing season of only 79 days. Frosts have occurred in every month, even July. The diurnal temperature range of Ely is so great due to its elevation, dry air, clear skies, and location in a valley, allowing for intense radiative cooling at sunset, even after hot summer days. The monthly mean temperature ranges from 26.7 °F (−2.9 °C) in January to 69.3 °F (20.7 °C) in July. High temperatures of 90 °F (32 °C) or higher occur on an average of 29.2 days annually, but, due to the elevation and aridity, the low very rarely manages to stay at or above 60 °F or 16 °C. Extreme temperatures ranged from 101 °F (38.3 °C) on July 18, 1998 down to −30 °F (−34.4 °C) on February 6, 1989.
On average, annual precipitation is 9.41 inches (239 mm), with 72.9 days of measurable precipitation annually. The wettest calendar year is 1897 with 17.20 inches (436.9 mm) and the driest 1974 with 4.22 inches (107.2 mm), though as much as 18.20 inches or 462.3 millimetres fell from July 1982 to June 1983. The most precipitation in one month was 5.52 inches (140.2 mm) in April 1900, and the most in 24 hours was 2.52 inches (64.0 mm) on September 26, 1982. Average annual snowfall is 54.1 inches (1.37 m), while the most snowfall in one month was 42.0 inches (1.07 m) in March 1894, and the greatest depth of snow on the ground 24 inches or 0.61 metres on January 23, 2010 – though data from neighboring Elko suggest greater depths in the winters of 1889/1890, 1915/1916 and 1931/1932. An average winter will see a maximum snow cover of 9 inches or 0.23 metres, though the severe winter of 1951/1952 had fifty days with snow cover over 10 inches or 0.25 metres. The most snowfall in a season has been 110.4 inches (2.80 m) from July 2010 to June 2011 and the least 12.1 inches (0.31 m) from July 1950 to June 1951.
See also
Map of Nevada State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming