Payson is a city in Utah County, Utah, United States. It is part of the Provo–Orem Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 21,101 at the 2020 census.
| Name: | Payson city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Utah |
| County: | Utah County |
| Founded: | October 20, 1850 |
| Incorporated: | January 21, 1853 |
| Elevation: | 4,700 ft (1,418 m) |
| Total Area: | 13.05 sq mi (33.81 km²) |
| Land Area: | 13.04 sq mi (33.78 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.01 sq mi (0.02 km²) |
| Total Population: | 21,101 |
| Population Density: | 1,618.17/sq mi (624.66/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 84651 |
| Area code: | 385, 801 |
| FIPS code: | 4958730 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1444252 |
| Website: | http://www.paysonutah.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
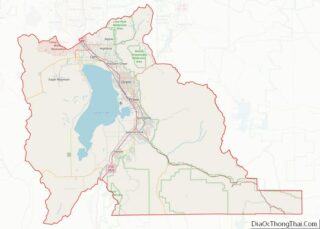
Payson location map. Where is Payson city?
History
Pioneers from the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints led by James Edward Pace Jr. first settled what is now Payson, Utah. On Sunday, October 20, 1850, Pace with his family and the families of John Courtland Searle and Andrew Jackson Stewart, totaling 16 settlers in all, arrived at their destination on Peteetneet Creek.
The settlement was originally named Peteetneet Creek, after which Chief Peteetneet was named. Peteetneet is the anglicized approximation of Pah-ti’t-ni’t, which in the Timpanogos dialect of the Southern Paiute language means “our water place”. Chief Peteetneet was the clan leader of a band of Timpanogos Indigenous Americans whose village was on a stretch of the creek about a mile northwest of Payson’s present city center. The village, when fully occupied, housed more than 200 of Chief Peteetneet’s clan and near kinsmen. It served as a base from which seasonal hunting and foraging parties moved to the mountains each summer and fall.
Five months later, on the morning of March 23, 1851, Brigham Young, having lost confidence in the leadership of James Pace, released him from his calling and reorganized the community under Bishop Benjamin Cross. Then, in the afternoon, in a secular meeting, Brigham Young acting as Territorial Governor, designated the settlement on Peteetneet Creek as Payson, Utah County, Utah Territory. He acknowledged naming the town after Payson, Illinois, a small town in Adams County near Quincy where kind citizens had taken in the Young family after they were driven from Missouri in 1839.
In January 1853, Territorial Governor Brigham Young submitted a bill to the Second Utah Territorial Legislature to incorporate Payson as a city. On January 21, 1853, on the last day of the legislative session, the legislature passed the act. Brigham Young signed it. And Payson became an incorporated city within a strip of territory two miles wide on either side of Peteetneet Creek, extending from the shore Utah Lake to the top of the mountains to the south. On April 12, 1853, Payson voters elected a city council composed of aldermen and councilmen, the distinction between the two being uncertain. The voters also elected as the town’s first mayor, David Crockett who had returned to Payson after James Pace’s fall from power. He would serve as Mayor for 2 additional two-year terms and as an alderman until 1860.
On March 6, 1854, the LDS Church organized the Payson Ward as part of the Utah Stake with C. B. Hancock as Bishop and James McClellan and John Fairbanks as counselors. Bishop Cross, who was in declining health died on December 31 at age 65.
The Payson Tabernacle of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints was dedicated by Wilford Woodruff in 1872.
In 1873 the Payson independent school District established a high school, the first such institution in Utah south of Salt Lake City. It closed in 1876 after Brigham Young Academy opened in Provo, and a Presbyterian mission school offering education through grade 12 was established under Rev. Wildman Murphy. An opera house was built in Payson in 1883. In the late 1800s, a factory making horse collars operated in Payson.
When the Strawberry Valley Reclamation Project was completed in 1912, the Utah-Idaho Sugar Company decided to place a sugar beet processing factory in the area. The plant was completed in October 1913. By 1915, the biggest year for the factory, 5,014 acres (20.29 km) were planted, yielding 36,915 tons of sugar beets, which were processed into 7,722 tons of sugar.
In 1897, the beet leafhopper, Circulifer tenellus, the only known vector of the beet curly top virus (BCTV), invaded Utah County. Its transmission of the disease caused serious crop losses in Payson, Lehi and other areas of the county. As the disease grew worse, Payson farmers reduced beet acreage and planted other crops. Those willing to take a chance with beet contracts experienced declining yields. In 1924, beet growers all over Utah County experienced a complete crop failure. The result was that in 1924, Utah-Idaho Sugar closed its Payson and Lehi sugar factories. The factory was dismantled and demolished in 1940, leaving only the sugar warehouse. Beet contracts continued to be signed in the Payson area, and harvests were processed in the Utah-Idaho Sugar factory in Spanish Fork.
In 1940, the sugar factory property, which included only the sugar warehouse, was sold to the Utah Poultry Producers Co-operative Association (now Intermountain Farmers Association = IFA Country Stores), which used the building for grain storage until 1978. In 1979, this property located at 10460 South 4400 West in Payson became the present IFA fertilizer storage, blending, packaging and distribution facility.
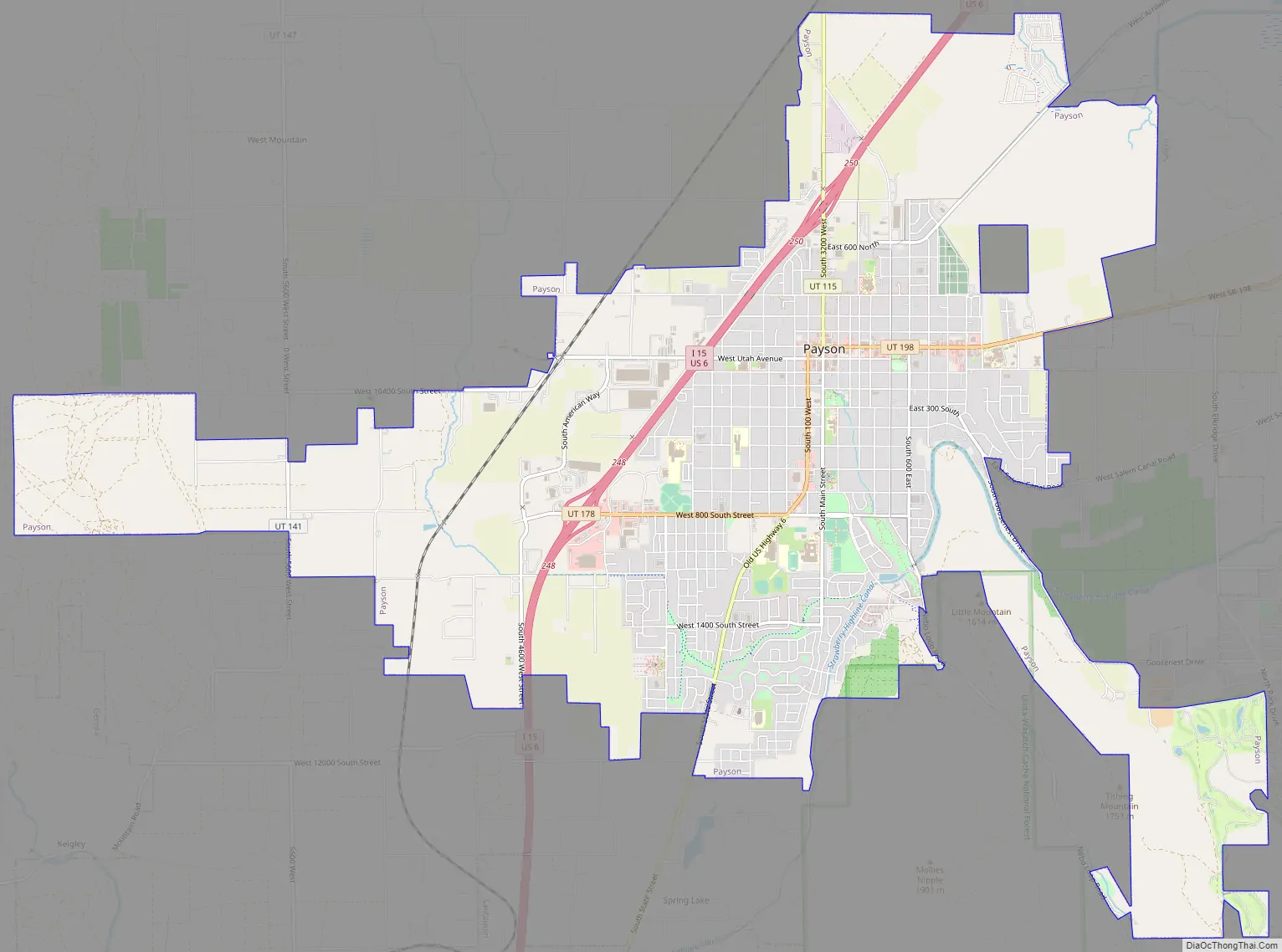
Payson Road Map
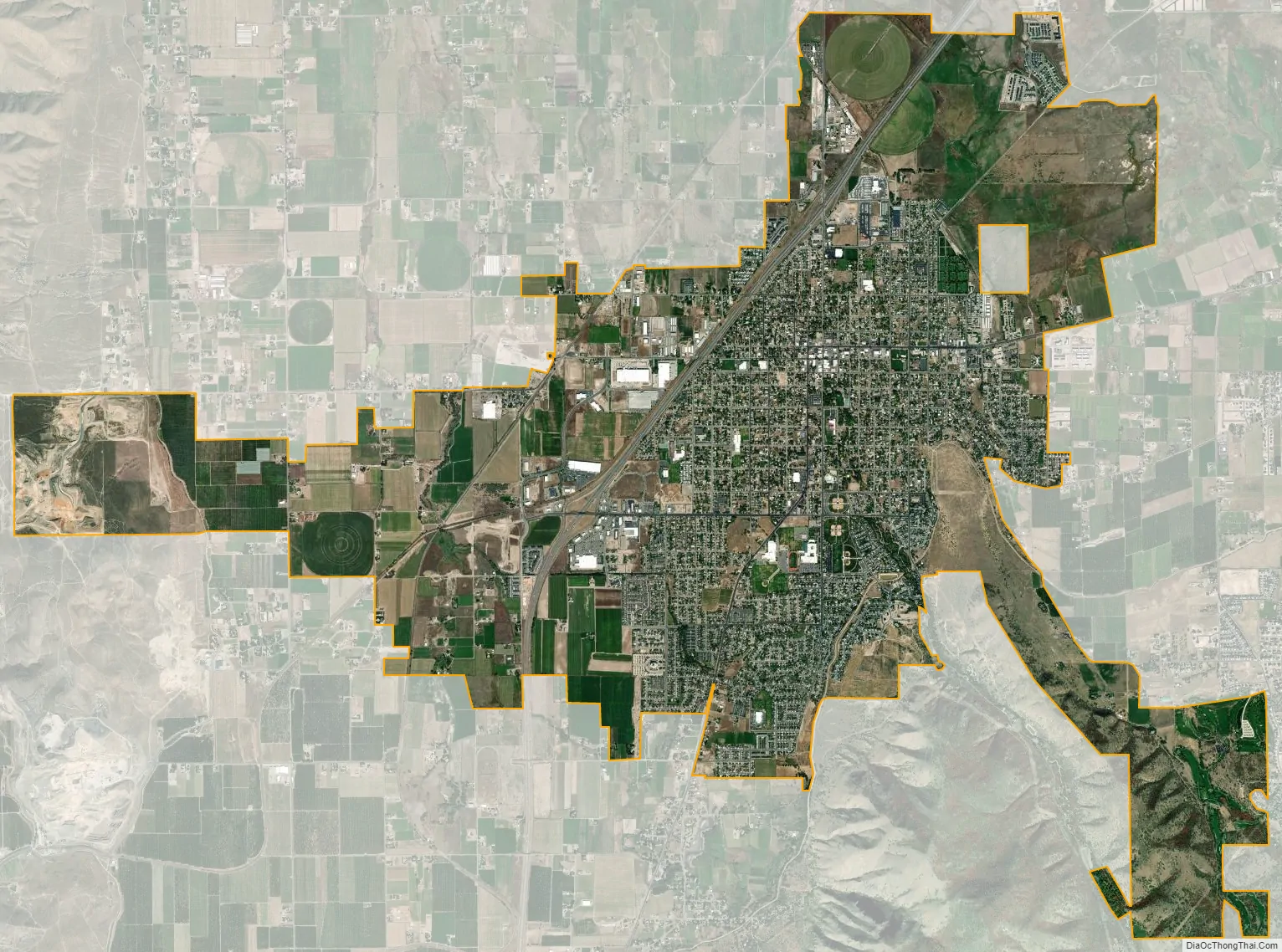
Payson city Satellite Map
See also
Map of Utah State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming