Richland (/ˈrɪtʃlənd/) is a city in Benton County, Washington, United States. It is located in southeastern Washington at the confluence of the Yakima and the Columbia Rivers. As of the 2020 census, the city’s population was 60,560. Along with the nearby cities of Pasco and Kennewick, Richland is one of the Tri-Cities, and is home to the Hanford nuclear site.
| Name: | Richland city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Washington |
| County: | Benton County |
| Elevation: | 384 ft (117 m) |
| Land Area: | 39.22 sq mi (101.59 km²) |
| Water Area: | 3.39 sq mi (8.79 km²) |
| Population Density: | 1,345.5/sq mi (519.5/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 99352, 99353, 99354 |
| Area code: | 509 |
| FIPS code: | 5358235 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1513395 |
| Website: | Ci.Richland.WA.US |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
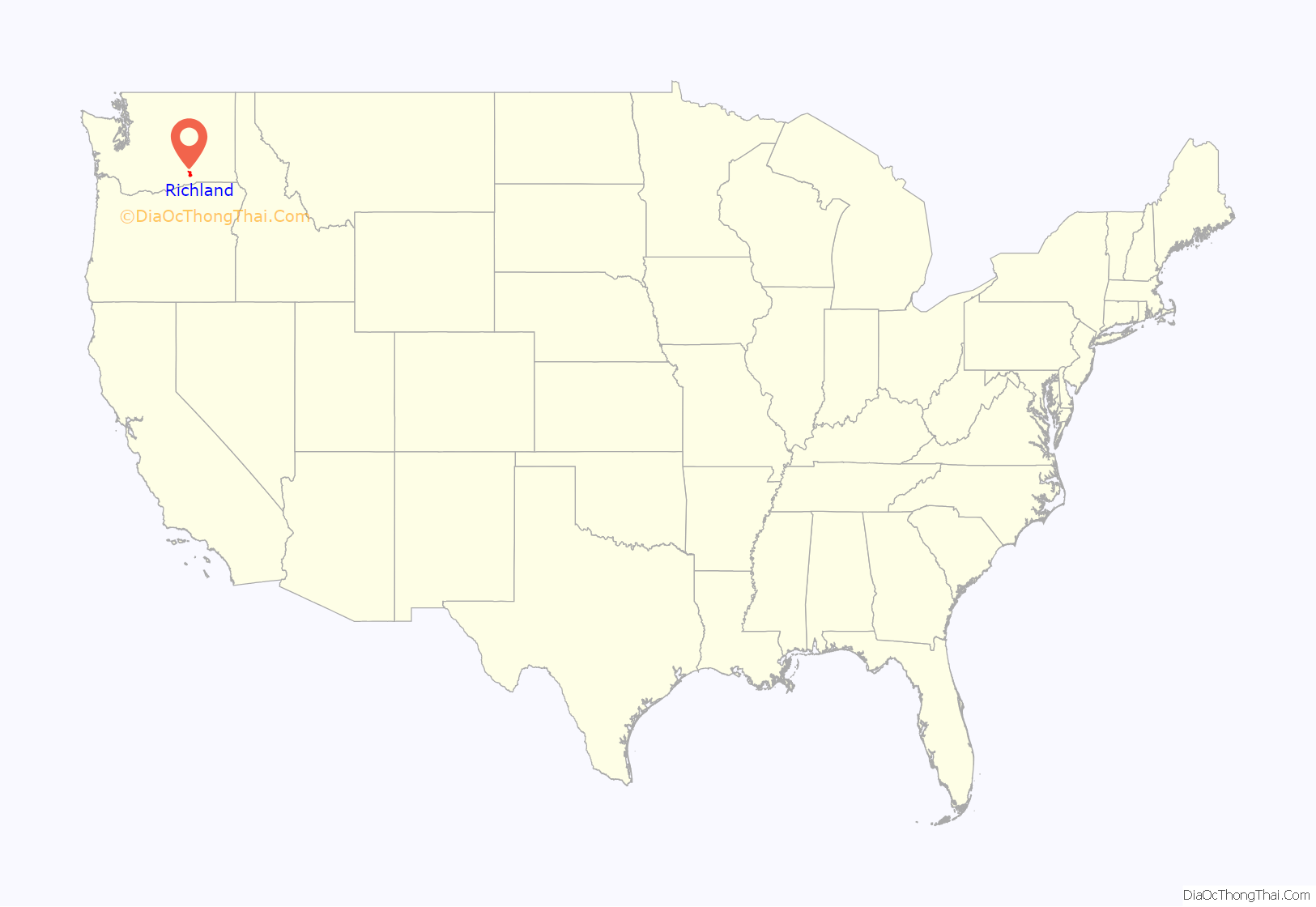
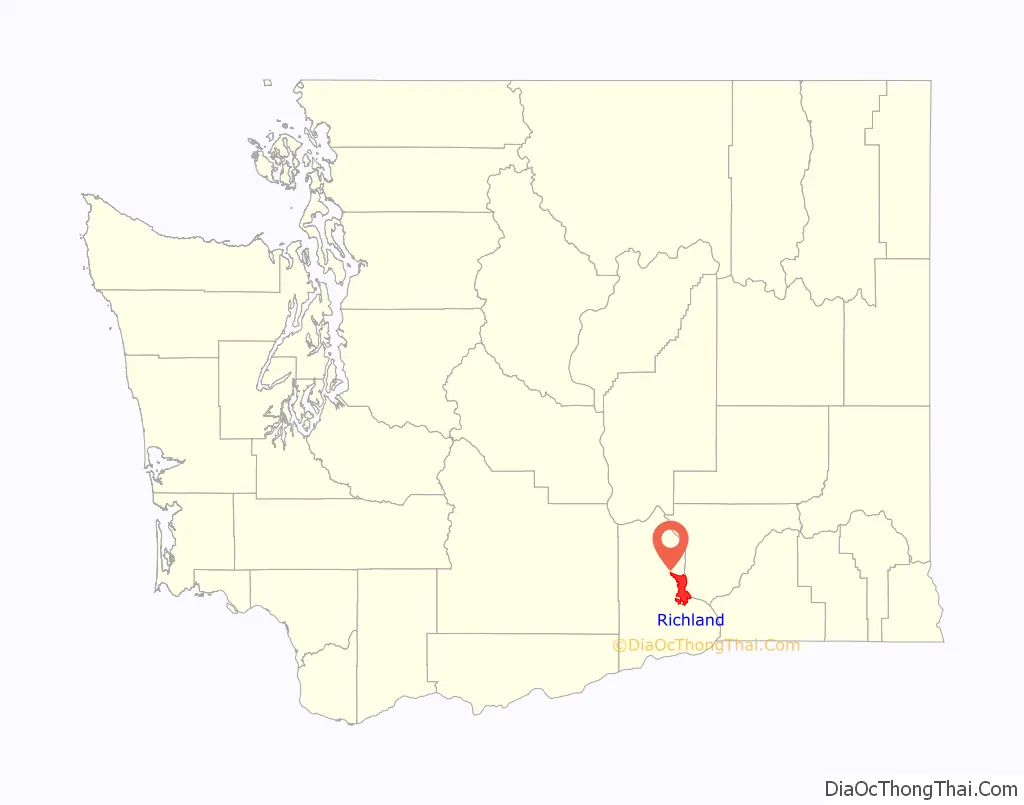
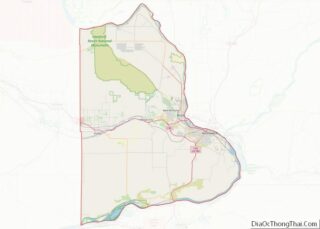
Richland location map. Where is Richland city?
History
For centuries, the village of Chemna stood at the mouth of the current Yakima River. Today that village site is called Columbia Point. From this village, the Wanapum, Yakama and Walla Walla Indians harvested the salmon runs entering the Yakima River. Captain William Clark of the Lewis and Clark Expedition visited the mouth of the Yakima River on October 17, 1805.
Formative years
In 1904–1905, W.R. Amon and his son Howard purchased 2,300 acres (9 km) and proposed a town site on the north bank of the Yakima River. Postal authorities approved the designation of this town site as Richland in 1905, naming it for Nelson Rich, a state legislator and land developer. In 1906, the town was registered at the Benton County Courthouse. It was incorporated on April 28, 1910, as a Washington Fourth Class City.
World War II
Richland was a small farm town until the U.S. Army purchased 640 sq mi (1,660 km) of land – half the size of Rhode Island – along the Columbia River during World War II, evicting the 300 residents of Richland as well as those of the now vanished towns of White Bluffs and Hanford just upriver. The army turned it into a bedroom community for the workers on its Manhattan Project facility at the nearby Hanford Engineering Works (now the Hanford site). The population increased from 300 in July and August 1943 to 25,000 by the end of World War II in August 1945. All land and buildings were owned by the government. Housing was assigned to residents, and token rent was collected; families were assigned to houses or duplexes; single people were placed in apartments or barracks. Everything necessary was provided, from free bus service to light bulbs, and trees were planted in people’s yards by the government. Much of the city was planned by Spokane architect Gustav Albin Pherson and overseen by the Army Corps of Engineers. While there were dormitories and barracks built at the time, prefabricated duplexes and single-family homes are all that survive today. Because homes were allocated based on family size and need, there were a number of floorplans available. These were each identified by a letter of the alphabet, and so came to be known as alphabet houses.
In 1954 Harold Orlando Monson was elected the first mayor of Richland and traveled to Washington, D.C., to negotiate increased rights (such as private home ownership) for citizens in military cities across the country.
Richland’s link to the Army Engineers is suggested by its street nomenclature; many of the streets are named after famous engineers. The main street (George Washington Way) is named after the first president, who was a surveyor; Stevens Drive is named after John Frank Stevens, chief engineer of the Panama Canal and Stevens Pass; Goethals Drive is named after George W. Goethals, designer of the Panama Canal; and Thayer Drive is named after Sylvanus Thayer, superintendent of West Point and later founder of the Thayer School of Engineering at Dartmouth College. The rule is that if alphabet houses reside on a given street, they are named after an engineer or a type of tree.
The end of the war
With the end of the war, the Hanford workers’ camp, originally located fifteen miles (24 km) north of Richland at the old Hanford town site, was closed down. Although many of the workers moved away as the war effort wound down, some of them moved to Richland, offsetting the depopulation that might otherwise have occurred.
The Cold War boom
Fears that the Soviet Union’s intentions were aggressive set off the Cold War in 1947. The capacity to produce plutonium was increased beginning in 1947. When the Soviet Union developed and tested its first nuclear weapon in 1949, the U.S. nuclear program was reinvigorated. A second post-WWII expansion began in 1950 due to the war in Korea. Richland’s Cold War construction boom resulted in Richland’s population growing to 27,000 people by 1952. Many of these people lived in a construction camp of trailers located in what is now north Richland. With time, these trailers were vacated and the core city grew. Others lived at Camp Columbia near Horn Rapids until the camp was closed in 1950. In 2005 several dozen houses built in the northern part of the core city during this boom were added to the National Register of Historic Places as the Gold Coast Historic District.
Transition to private property
The government got out of the landlord business in 1957 when the real estate was sold to the residents. Most of the people lived in duplexes; senior tenants were given the option to purchase the building; junior tenants were given the option to purchase lots in a newly platted area of north Richland. Richland was incorporated in 1958 as a chartered First Class City, an open self-governed city. As part of the transition, large areas of undeveloped land became city property. Richland’s financial dependency on the federal Hanford facility changed little at this time because Hanford’s mission as a weapons materials production site continued during the Cold War years.
Unclassified Hanford
At some point, documents and photographs of the Hanford military facilities became declassified by the U.S. government. Those digitized records are considered to be in the public domain, and are hosted on the online Hanford Document Retrieval System. Historical events, such as a visit to the property by President Richard Nixon, are also stored on the database.
After the production boom
With the shutdown of the last production reactor in 1987, the area transitioned to environmental cleanup and technology. Now, many Richland residents are employed at the Hanford site in its environmental cleanup mission.
Richland High School’s sports teams are called the Bombers, complete with a mushroom cloud logo. Some of the streets platted after 1958 are named after U.S. Army generals (such as Patton Street, MacArthur Street, Sherman Street, and Pershing Avenue) and after various nuclear themes (Einstein Avenue, Curie Street, Proton Lane, Log Lane, and Nuclear Lane). A local museum, the Reach Museum, tells the story of the cultural, natural, and scientific history of the Hanford Reach and Columbia Basin area; it replaced the now closed Columbia River Exhibition of History, Science, and Technology (CREHST) in 2014.
Washington State University, Tri-Cities was founded in northern Richland in 1989, growing out of a former Joint Graduate Center which had been affiliated with the University of Washington, Oregon State University, and Washington State University. Richland is also home to Kadlec Regional Medical Center. Columbia Basin College’s Medical Training Center is near Kadlec Regional Medical Center.
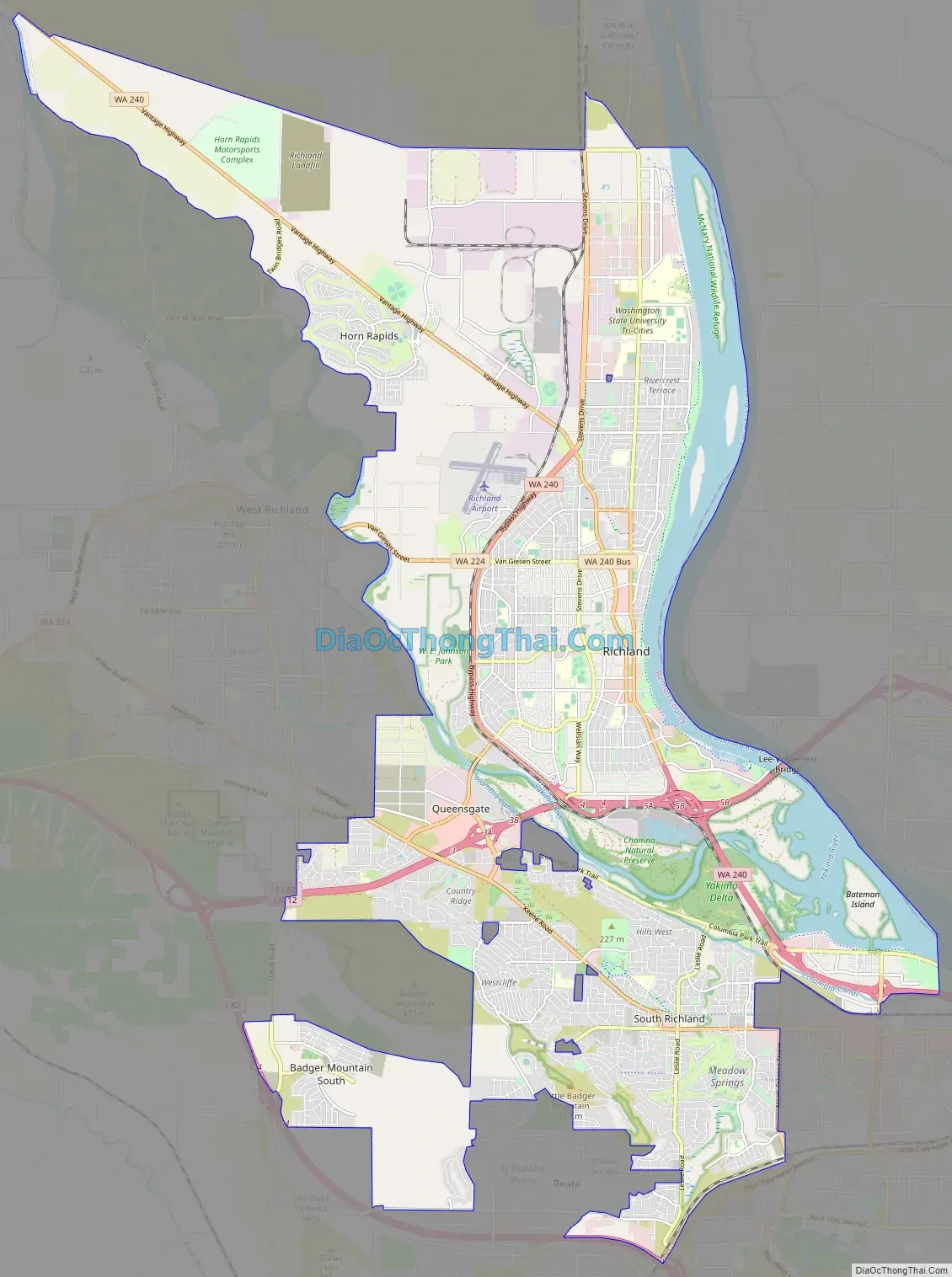
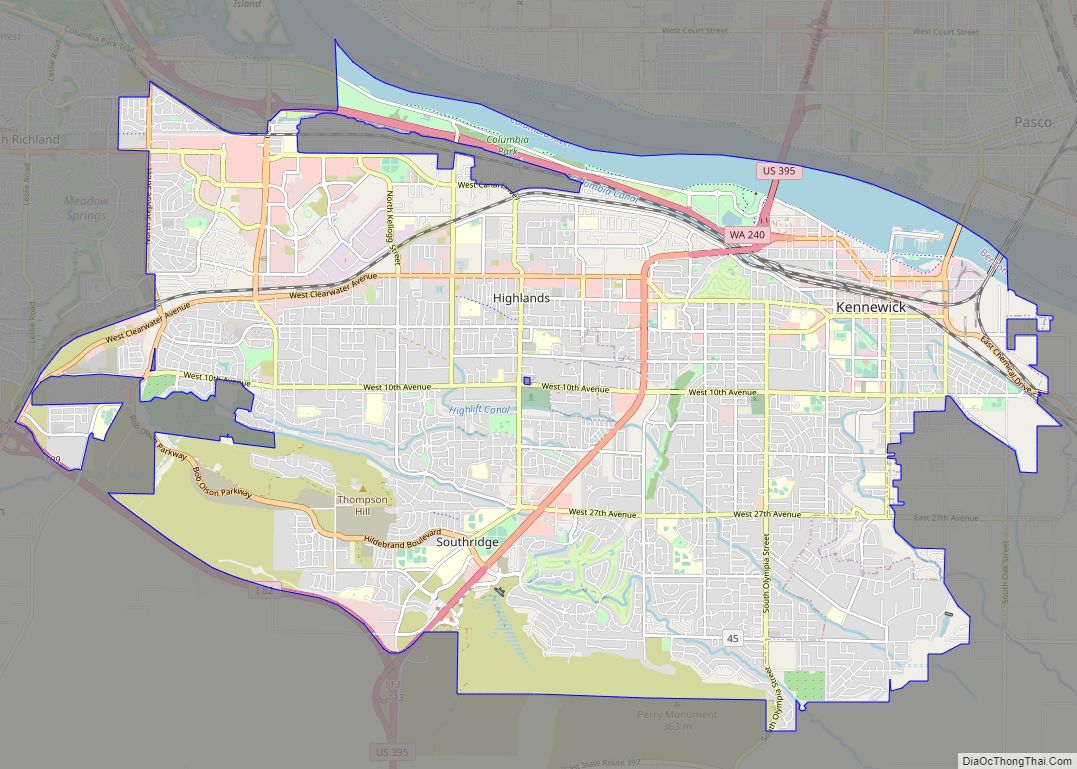
Richland Road Map
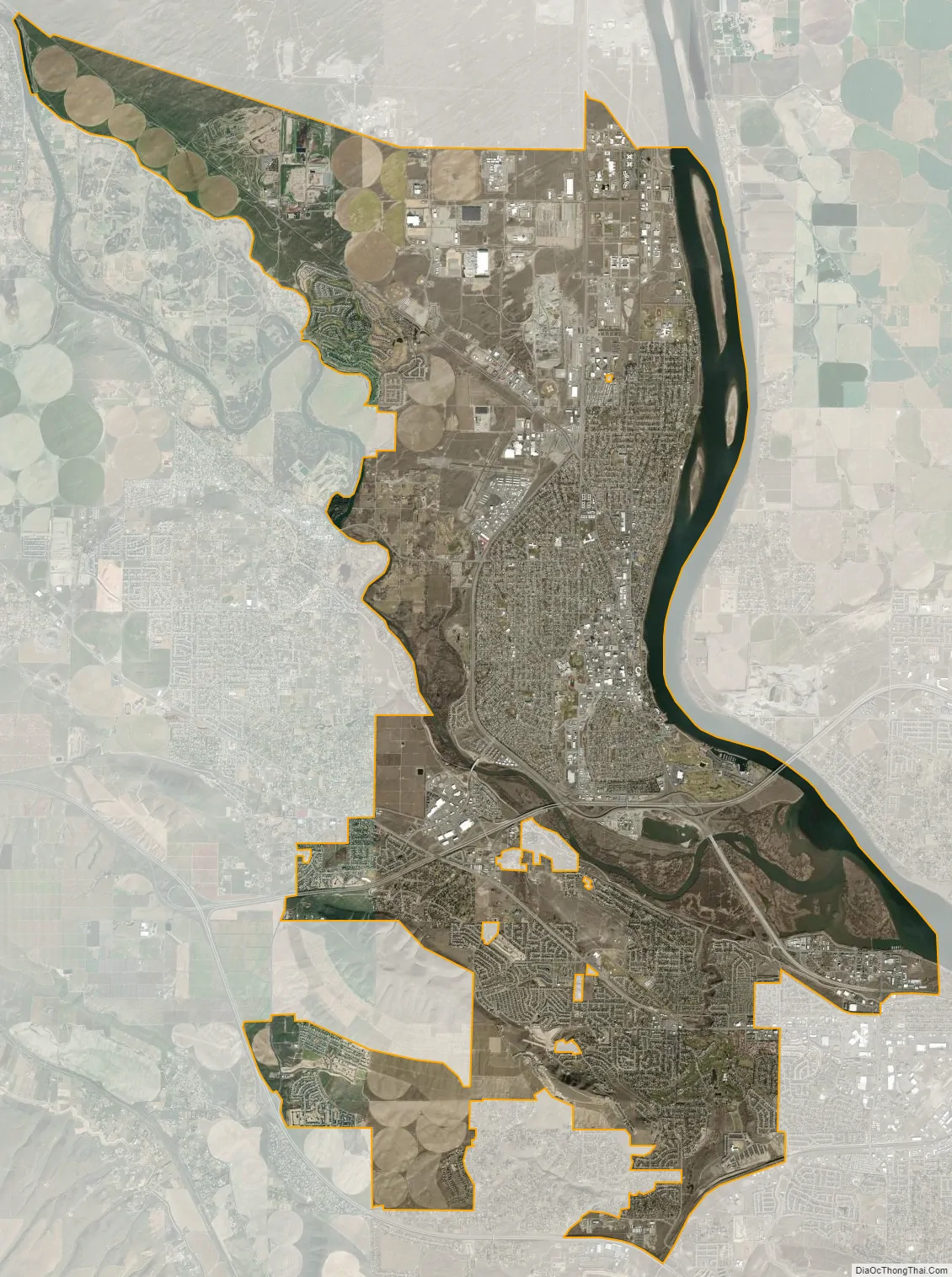
Richland city Satellite Map
Geography
Richland is located at 46°16′47″N 119°16′53″W / 46.27972°N 119.28139°W / 46.27972; -119.28139 (46.279657, −119.281377).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 39.11 square miles (101.29 km), of which, 35.72 square miles (92.51 km) is land and 3.39 square miles (8.78 km) is water. Elevation at the airport is 120 m (390 ft).
In the late 1970s, Richland sought to annex 5 square miles (13 km) of unincorporated land in Franklin County on the east side of the Columbia River, anticipating development following the construction of Interstate 182. The move was blocked by Pasco, who had planned to annex much of the area themselves. The Richland city government filed an appeal against the Franklin County Boundary Review Board in 1983 following their approval of Pasco’s claim; the Washington Supreme Court affirmed the Franklin County decision.
Climate
Richland receives about 7 inches (180 mm) of precipitation per year, giving it a semi-arid desert climate and resulting in a shrub-steppe environment. Summers are hot with infrequent thunderstorms, while winters are milder than all of Eastern Washington with snow falling only occasionally. During the 2021 Western North America heat wave, the maximum temperature of 118 °F (48 °C) was recorded in Richland which tied the previous all-time record high temperature in the state of Washington. Nearby, the Hanford Site recorded a high of 120 °F (49 °C), the new state record.
See also
Map of Washington State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Asotin
- Benton
- Chelan
- Clallam
- Clark
- Columbia
- Cowlitz
- Douglas
- Ferry
- Franklin
- Garfield
- Grant
- Grays Harbor
- Island
- Jefferson
- King
- Kitsap
- Kittitas
- Klickitat
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Mason
- Okanogan
- Pacific
- Pend Oreille
- Pierce
- San Juan
- Skagit
- Skamania
- Snohomish
- Spokane
- Stevens
- Thurston
- Wahkiakum
- Walla Walla
- Whatcom
- Whitman
- Yakima
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming