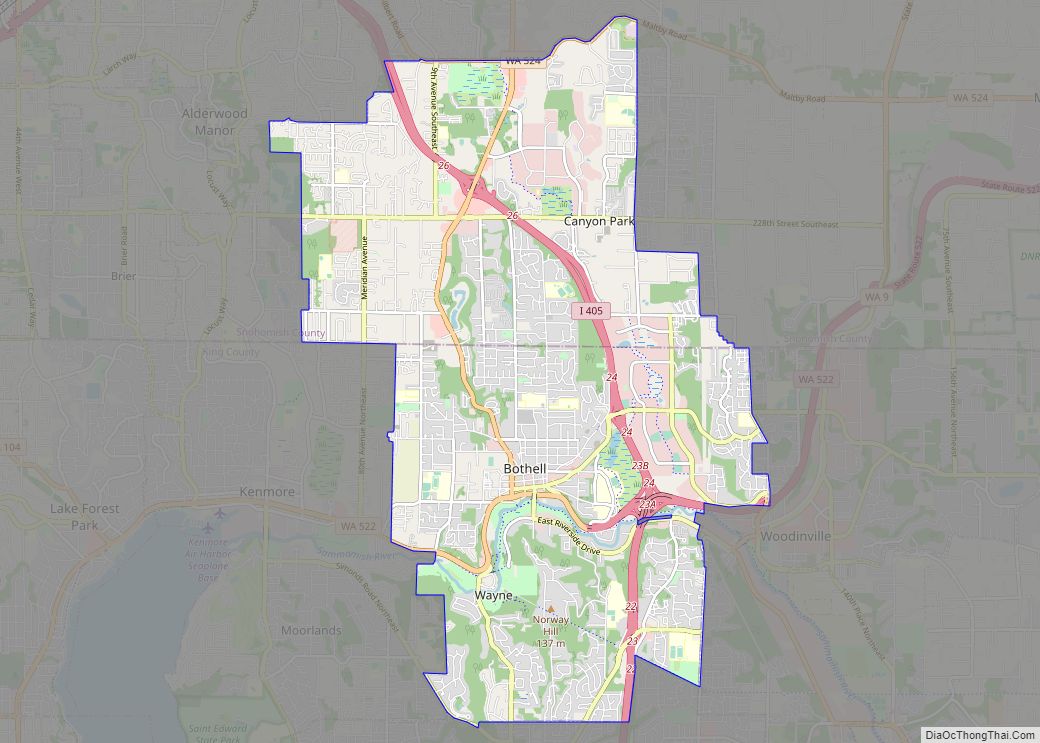
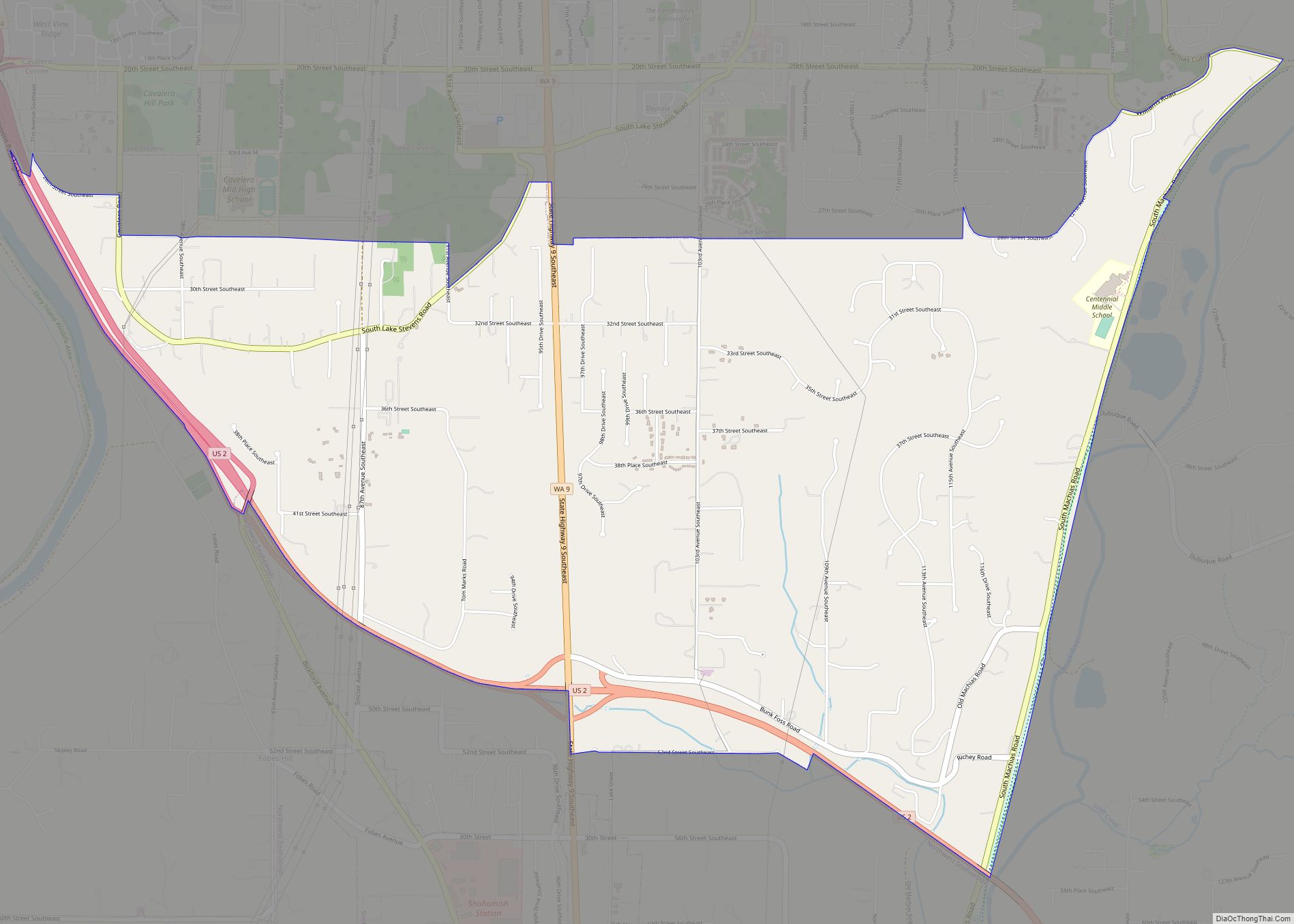
Snohomish is a city in Snohomish County, Washington, United States. The population was 9,098 at the 2010 census. It is located on the Snohomish River, southeast of Everett and northwest of Monroe. Snohomish lies at the intersection of U.S. Route 2 and State Route 9. The city’s airport, Harvey Airfield, is located south of downtown and used primarily for general aviation.
The city was founded in 1859 and named Cadyville after pioneer settler E. F. Cady and renamed to Snohomish in 1871. It served as county seat of Snohomish County from 1861 to 1897, when the county government was relocated to Everett. Snohomish has a downtown district that is renowned for its collection of antique shops and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
| Name: | Snohomish city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Washington |
| County: | Snohomish County |
| Founded: | 1859 |
| Incorporated: | June 26, 1890 |
| Elevation: | 66 ft (20 m) |
| Total Area: | 3.72 sq mi (9.64 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3.52 sq mi (9.12 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.20 sq mi (0.52 km²) 4.44% |
| Total Population: | 9,098 |
| Population Density: | 2,883.84/sq mi (1,113.35/km²) |
| Area code: | 360 |
| FIPS code: | 5365170 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1531910 |
| Website: | snohomishwa.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Snohomish location map. Where is Snohomish city?
History
The Snohomish River Valley was originally inhabited by the Snohomish people, a Coast Salish tribe who lived between Port Gardner Bay and modern-day Monroe. An archaeological site near the confluence of the Snohomish and Pilchuck Rivers has indications of human habitation that began as early as 8,000 years before present. The Snohomish had contact with white explorers in the early 19th century, with their name recorded as “Sinnahamis” by John Work of the Hudson’s Bay Company, among the first to also use the name to describe the river. The Snohomish were signatories of the Point Elliott Treaty in 1855, which relocated the tribe to the Tulalip Indian Reservation. In the early 1850s, the territorial government planned to construct a military road connecting Fort Steilacoom to Fort Bellingham, with a ferry crossing of the Snohomish River at Kwehtlamanish, a winter village of the Snohomish people. The road, proposed in the wake of the Pig War, was intended to be built far enough inland to be safe from British naval attacks.
The confluence of the Snohomish and Pilchuck rivers, located near Kwehtlamanish, was sought by several American settlers from Steilacoom who arrived in 1859 to file homestead claims. Edson F. Cady and Heil Barnes, representing carpenter Emory C. Ferguson, settled near the proposed ferry landing, while Egbert H. Tucker filed a claim for a plot on the other side of the Snohomish River. The settlement was originally known as “Cadyville” and changed its name to Snohomish City in 1871. The name Snohomish comes from the name of the dominant local Native American tribe “sdoh-doh-hohbsh” ([sduhúbʃ]), whose meaning is widely disputed.
Although the military road was never completed, Snohomish quickly became a center of commerce in the expanding region. In 1861, Snohomish County separated from Island County and the Village of Snohomish was voted the county seat. It remained so until 1897 when the county seat was relocated to the larger, yet much newer neighboring city of Everett, Washington after a controversial and contested county-wide vote.
Snohomish’s first school was organized in either 1867 or 1869. The Village of Snohomish was incorporated in 1888 and re-incorporated as a city in 1890 due to the transition from territory to state. Hyrcanus Blackman was elected mayor, having already been Police Chief for two years. 1893 saw the construction of a roller skating rink and 1894 the first graduations from Snohomish High School. By 1899 the city of Snohomish was a prosperous town with a population of 2,000, 25 businesses and 80 homes.
1901 brought Snohomish the first motor car in the county. In 1903 First Street was paved with brick. When it was finished, there was a three-day celebration, and for years afterward, the city’s residents remained so proud of the street that they washed it every week with a fire hose.
Emma C. Patric was appointed the town’s first librarian in 1901, an event that lead to the 1910 grand opening of the town’s first public library, The Carnegie Library. It is now the oldest remaining public building in the city. In 1911 a disastrous fire struck First Street and everything between Avenues B and C was destroyed. The fire began when a small blaze in the Palace Cafe on the South side of the street got out of control on Memorial Day, 1911 at about four a.m. Thirty-five business structures were put out of business, with $173,000 worth of goods destroyed. Despite the disaster the town continued to grow and by 1920 the population grew to a little over 3,000. The population would remain relatively stable for the next 40 years. The city was connected to Everett by an interurban railway that ceased operations in 1921 after a trestle was damaged during a major flood.
The Great Depression was not acutely felt in Snohomish due to its economy being mostly agrarian with many family farms. One of the town’s largest employers, Bickford Ford, was founded in 1934 by Lawrence Bickford; the dealership flourished in a period when many auto dealerships failed. The 1930s brought Snohomish national notice as the hometown of baseball great Earl Averill, the first Washingtonian elected to the Baseball Hall of Fame. Averill played from 1929 to 1941, mostly with the Cleveland Indians.
The 1960s saw the city of Snohomish enter a period of decline. As the Boeing Company fell on hard times, many people were laid off and had to move away to seek other work. A commonly heard phrase was, “Will the last person out of Seattle please turn off the lights?” Snohomish fought back with a redevelopment plan in 1965 that proposed the destruction of the historic structures along First Street to make way for an enclosed mall. The plan was not carried out due to lack of funds, and the area remains today as it has through much of its history.
The town’s economic malaise continued throughout much of the ’70s, with the downtown area given over to mostly bars and small shops. In 1973 the city adopted a Historic District Ordinance protecting historic buildings and structures from inappropriate alterations and demolitions and encouraging the design of new construction in keeping with the district’s historic character. In 1974, the Historic Business District, a 36-block area, was placed on the National Register of Historic Places. Larger stores moved away from First Street into newer developments and strip malls that spread out along Second Street and Avenue D.
In 1974 the Seattle-Snohomish mill was gutted by fire and rebuilt by its owners. In 1975 a severe flood struck the area, damaging over 300 homes and killing 3,500 head of livestock, but the community rallied to support those who were affected.
The 1980s saw renewed vigor in Snohomish when, along with other developments, two 7-Eleven convenience stores and a McDonald’s franchise opened during the first part of the decade. Around 1985, the U.S. Route 2 bypass was completed, allowing traffic which had until then been forced to pass through the town to circumvent the city.
In the 1990s, First Street was redeveloped to take advantage of its historic buildings as a tourist attraction. Its sidewalks were rebuilt and public restrooms added. The city hall and police station were moved away from First Street and a new fire station was built, allowing those historic buildings to be renovated as well.
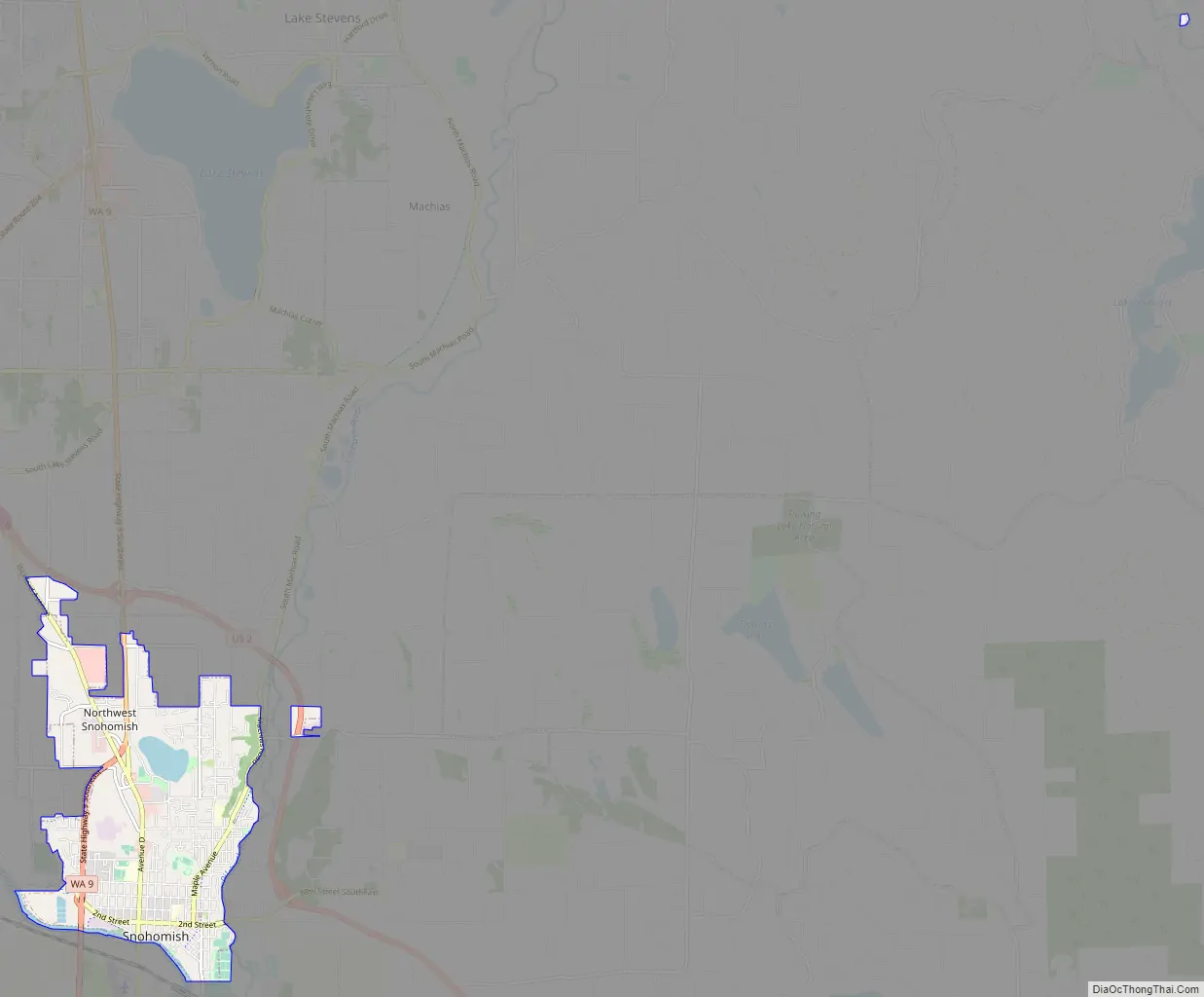
Snohomish Road Map
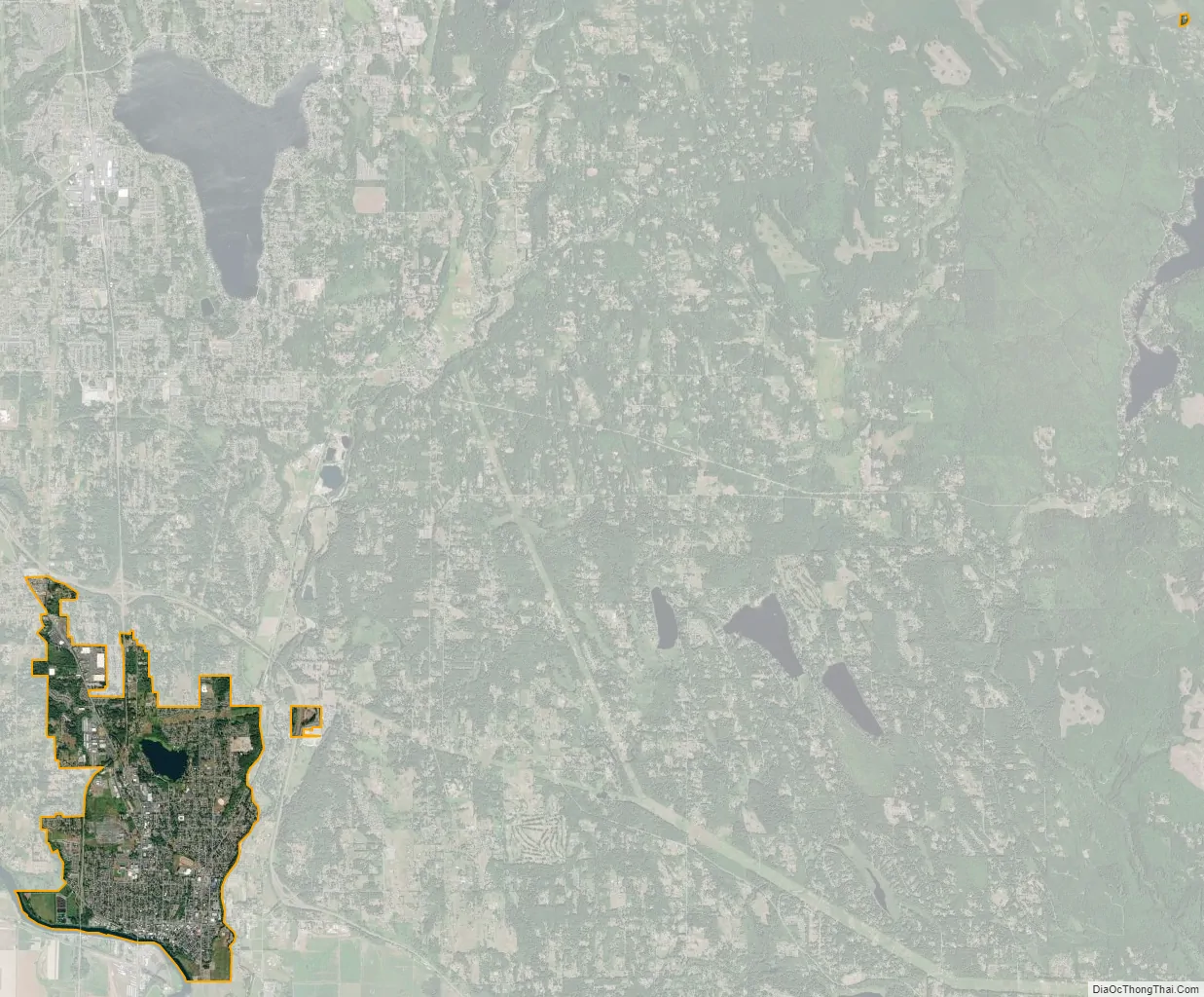
Snohomish city Satellite Map
Geography
Snohomish is located along the north bank of the Snohomish River near where it is joined by the Pilchuck River. The city lies on the Getchell Hill Plateau, a low hill in the Snohomish River Valley that interrupts the wide, flat river valley. Some neighborhoods of the city are on a ridge that is west of the Pilchuck River, as well as Dutch Hill on the opposite bank. Blackmans Lake (formerly Stillaguamish Lake) is located north of downtown Snohomish and has a boat launch maintained by the city government. The river valley was formed approximately 14,000 years before present by the outflow of a glacial lake during the Vashon Glaciation event. The river itself floods during the winter season, occasionally breaching the dikes in Downtown Snohomish.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 3.60 square miles (9.32 km), of which, 3.44 square miles (8.91 km) is land and 0.16 square miles (0.41 km) is water. Snhoomish’s city limits are generally defined by the Snohomish River to the south, Fobes Hill to the west, several city streets to the north, and the Pilchuck River to the east. The city also has an urban growth area that extends north towards U.S. Route 2 and south of the Snohomish River to include Harvey Airfield.
The historic business and residential center of the town constitutes the Snohomish Historic District, which is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Many houses bear plaques with the year the house was built and the name of the people who originally occupied it. Each year the city gives tours of the historic houses; one of them, the Blackman House, is a year-round museum.
See also
Map of Washington State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Asotin
- Benton
- Chelan
- Clallam
- Clark
- Columbia
- Cowlitz
- Douglas
- Ferry
- Franklin
- Garfield
- Grant
- Grays Harbor
- Island
- Jefferson
- King
- Kitsap
- Kittitas
- Klickitat
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Mason
- Okanogan
- Pacific
- Pend Oreille
- Pierce
- San Juan
- Skagit
- Skamania
- Snohomish
- Spokane
- Stevens
- Thurston
- Wahkiakum
- Walla Walla
- Whatcom
- Whitman
- Yakima
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming