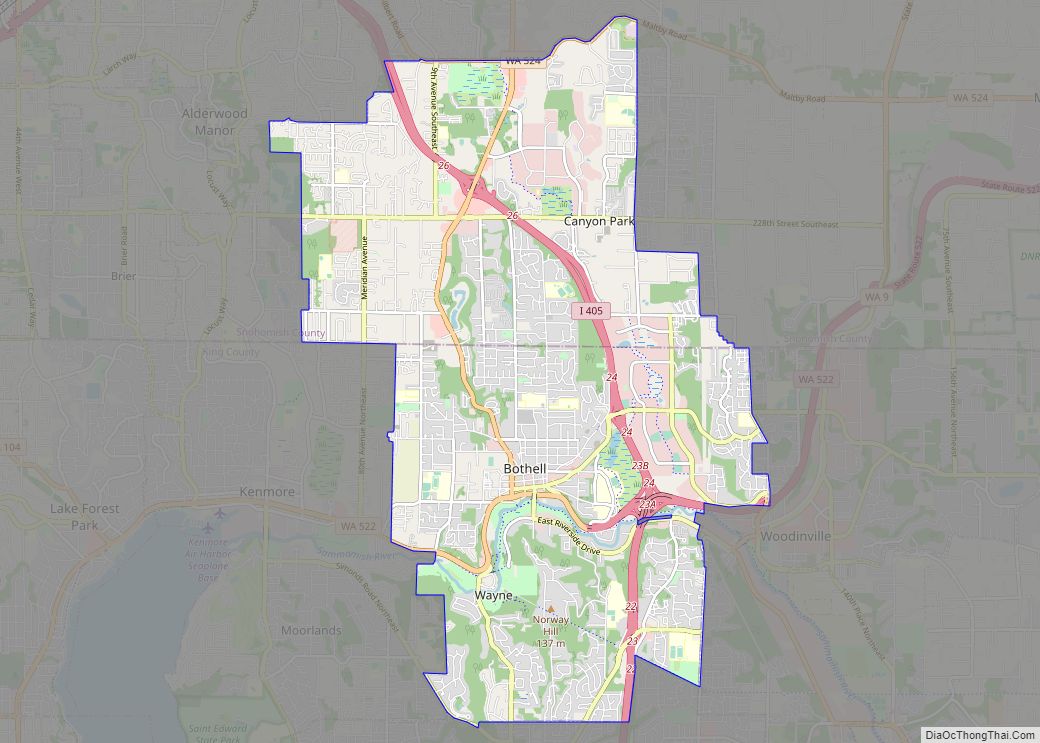
Everett (/ˈɛvərɪt/) is the county seat and largest city of Snohomish County, Washington, United States. It is 25 miles (40 km) north of Seattle and is one of the main cities in the metropolitan area and the Puget Sound region. Everett is the seventh-largest city in the state by population, with 110,629 residents as of the 2020 census. The city is primarily situated on a peninsula at the mouth of the Snohomish River along Port Gardner Bay, an inlet of Possession Sound (itself part of Puget Sound), and extends to the south and west.
The Port Gardner Peninsula was historically inhabited by the Snohomish people, who had a winter village named Hibulb near the mouth of the river. Modern settlement in the area began with loggers and homesteaders arriving in the 1860s, but plans to build a city were not conceived until 1890. A consortium of East Coast investors seeking to build a major industrial city acquired land in the area and filed a plat for “Everett”, which they named in honor of Everett Colby, the son of investor Charles L. Colby. The city was incorporated in 1893, shortly after the arrival of the Great Northern Railway, and prospered as a major lumber center with several large sawmills. Everett became the county seat in 1897 after a dispute with Snohomish contested over several elections and a Supreme Court case. The city was the site of labor unrest during the 1910s, which culminated in the Everett massacre in 1916 that killed several members of the Industrial Workers of the World.
The area was connected by new interurban railways and highway bridges in the 1920s, transforming it into a major commercial hub, and gained an airport at Paine Field in 1936. The city’s economy transitioned away from lumber and towards aerospace after World War II, with the construction of Boeing’s aircraft assembly plant at Paine Field in 1967. Boeing’s presence brought additional industrial and commercial development to Everett, as well as new residential neighborhoods to the south and west of the peninsula that was annexed by the city. Boeing remains the city’s largest employer, alongside the U.S. Navy, which has operated Naval Station Everett since 1994.
Everett remains a major employment center for Snohomish County, but has also become a bedroom community for Seattle in recent decades. It is connected to Seattle by Interstate 5 and various public transit services at Everett Station, including the Sounder commuter train, Amtrak, and commuter buses. Everett stages several annual festivals and is also home to minor league sports teams, including the Everett Silvertips at Angel of the Winds Arena and Everett Aquasox at Funko Field.
| Name: | Everett city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Washington |
| County: | Snohomish County |
| Incorporated: | May 4, 1893 |
| Land Area: | 33.19 sq mi (85.96 km²) |
| Water Area: | 14.71 sq mi (38.11 km²) |
| Population Density: | 3,358.6/sq mi (1,296.76/km²) |
| Area code: | 425 |
| FIPS code: | 5322640 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1512198 |
| Website: | everettwa.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
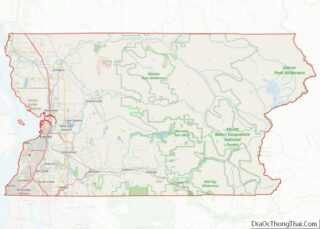
Everett location map. Where is Everett city?
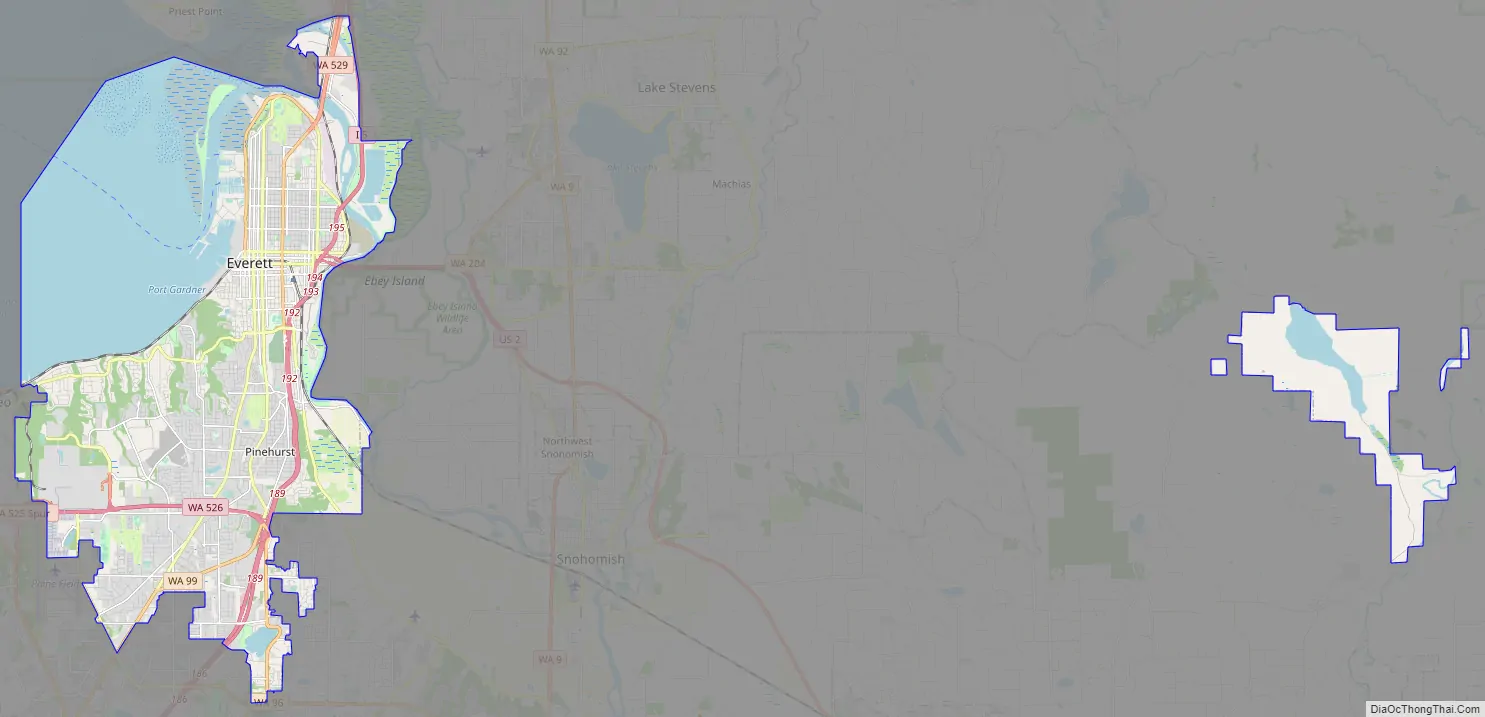
Everett Road Map
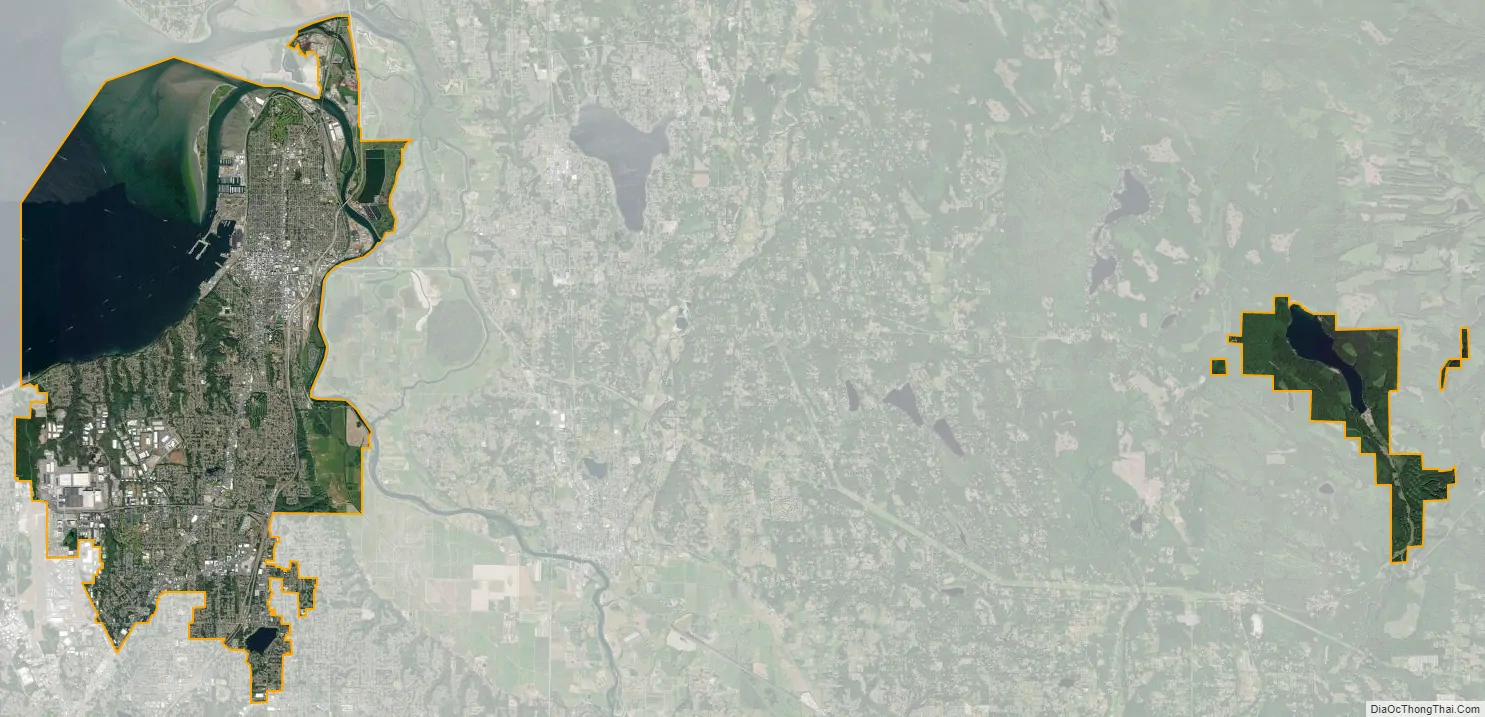
Everett city Satellite Map
Geography
Everett is one of the core cities comprising the Seattle metropolitan area and is 25 miles (40 km) north of Seattle. It is primarily situated on the Port Gardner Peninsula, bordered to the west by Port Gardner Bay (part of Possession Sound in the Puget Sound estuary), and to the north and east by the Snohomish River delta. The city also encompasses suburban and industrial areas to the south and southwest of the peninsula, which were annexed during the mid-to-late 20th century. Everett has 11 miles (18 km) of freshwater shoreline and 11 miles (18 km) of saltwater shoreline, including public access points at parks and boat ramps on Port Gardner Bay and the Snohomish River. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 48.49 square miles (125.59 km), of which 33.45 square miles (86.64 km) is land and 15.04 square miles (38.95 km) is water.
The city’s western boundary with Mukilteo is generally defined by Japanese Gulch on the edge of the Boeing Everett Assembly Plant and its auxiliary buildings. The southwestern edge of Everett borders an unincorporated area that includes Paine Field and the Lake Stickney/Mariner neighborhoods, which are part of the city’s designated urban growth area that extends south towards Lynnwood. The southern boundary wraps around Silver Lake and follows State Route 527 to State Route 96 at Murphy’s Corner, where it borders Mill Creek. Everett’s boundaries follow various housing subdivisions in the Eastmont area before reaching the Snohomish River, which forms the primary eastern border. The northeastern boundary includes portions of Smith Island in the river delta reaching towards Marysville; a series of highway bridges connect Everett to Marysville to the north and Lake Stevens to the east by crossing the Snohomish River delta. The city boundaries also include 3,729 acres (1,509 ha) of forest surrounding Lake Chaplain, a reservoir in the Cascade Mountains that provides part of the municipal water supply.
The Port Gardner Peninsula was formed during the northward retreat of Vashon Glaciation during an ice age 14,000 years before present. The underlying soil is generally loamy and includes gravelly sand in the glacial outwash. Everett is near the Southern Whidbey Island Fault, a shallow earthquake fault zone that runs near the western edge of the city and was discovered in 1994. In the 1990s, local geologists also found evidence of a tsunami and soil liquefaction in deposits under the Snohomish River delta that were not directly connected to the South Whidbey Island Fault. The city government established its emergency management and preparedness office in 2002 and conducts regular disaster drills to simulate a potential response. The southwestern neighborhoods of Everett include several ravines formed by local creeks that drain into Port Gardner Bay. The area is also prone to mudslides that interrupt passenger and freight service on the railroad that runs along the coastline of the bay. Other areas of the city drain into the watersheds of the Snohomish River and Lake Washington.
Cityscape and neighborhoods
The city of Everett maintains an Office of Neighborhoods which facilitates communication between the city and recognized neighborhood associations. The neighborhood associations are independent from the city and have elected leaders. Various neighborhoods in Everett have views of the Cascade and Olympic mountains, including Mount Baker and Mount Rainier.
As of 2019, Everett’s 19 recognized neighborhood associations are:
- Bayside, which includes most of Downtown Everett, the Port of Everett, and Naval Station Everett, and surrounding residential areas.
- Boulevard Bluffs, a primarily residential area of the city bordering Mukilteo
- Cascade View, a residential area in South Everett, north of Everett Mall
- Delta, a primarily residential area north of Downtown Everett
- Evergreen, a primarily residential area in South Everett
- Glacier View, an older residential area south of downtown
- Harborview–Seahurst–Glenhaven, consisting of older residential areas south of downtown
- Holly, a mix of residential, commercial, and industrial areas on the southern edge of the city
- Lowell, a primarily residential area southeast of downtown and formerly an independent town founded in 1863
- Northwest Everett, which includes older residential areas northwest of downtown, a historic district, and the Everett Community College campus
- Pinehurst–Beverly Park, a mix of residential and commercial areas in South Everett
- Port Gardner, which includes parts of Downtown Everett and residential areas on Rucker Hill, a historic district
- Riverside, includes residential areas northeast of downtown and a historic district
- Silver Lake, includes residential and commercial areas surrounding Silver Lake in the extreme southeastern part of the city
- South Forest Park, a residential neighborhood near downtown
- Twin Creeks, which includes the area surrounding Everett Mall and a mix of residential and commercial areas.
- Valley View–Sylvan Crest–Larimer Ridge, residential areas in southeast Everett
- View Ridge–Madison, residential areas west and southwest of Forest Park
- Westmont, a primarily multi-family housing area in the southwestern part of the city
Downtown Everett is generally defined as the area north of Pacific Avenue, east of West Marine View Drive, south of Everett Avenue, and west of Broadway. It is home to city and county government offices, high-rise office buildings, hotels, and apartment buildings. The Angel of the Winds Arena is on the west side of Broadway, anchoring a small historic district on Hewitt Avenue. Several downtown streets are named for the founders of the Everett Land Company and their associates, including John D. Rockefeller, the Rucker Brothers, Charles L. Colby, and shipbuilder Alexander McDougall.
The city government approved plans in 2018 to allow for high-rise buildings as tall as 25 stories and with reduced parking requirements to encourage denser development in anticipation of a future Link light rail station. In the early 2020s, several apartment buildings with a combined 650 units were completed in downtown and the waterfront district.
Climate
Everett generally has an oceanic climate similar to most of the Puget Sound lowlands, with year-round moderate temperatures influenced by marine air masses. The variation of normal weather between seasons is less extreme than inland areas, with dry summers and mild, rainy winters due to the proximity of the Pacific Ocean. Under the Köppen climate classification system, Everett is described as having a warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Csb). The city marks the north end of the Puget Sound Convergence Zone, a local weather phenomenon caused by colliding air currents from the region’s mountain ranges that produces heavier rain and stronger winds than the rest of the region.
The warmest month for Everett is August, with average high temperatures of 72.7 °F (22.6 °C), while January is the coolest, at an average high of 44.9 °F (7.2 °C). The highest recorded temperature at Paine Field, 100 °F (38 °C), first occurred on July 29, 2009; it was tied on August 16, 2020, and tied again on June 28, 2021, during a regional heat wave. The lowest, 0 °F (−18 °C), occurred on November 11, 1993. The city receives 35.71 inches (907 mm) of annual rainfall, which mostly falls from October to March and peaks in December. Everett rarely receives significant snowfall and its highest total, 26.6 inches (68 cm), occurred in 1965.
See also
Map of Washington State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Asotin
- Benton
- Chelan
- Clallam
- Clark
- Columbia
- Cowlitz
- Douglas
- Ferry
- Franklin
- Garfield
- Grant
- Grays Harbor
- Island
- Jefferson
- King
- Kitsap
- Kittitas
- Klickitat
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Mason
- Okanogan
- Pacific
- Pend Oreille
- Pierce
- San Juan
- Skagit
- Skamania
- Snohomish
- Spokane
- Stevens
- Thurston
- Wahkiakum
- Walla Walla
- Whatcom
- Whitman
- Yakima
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming