Snoqualmie (/snoʊˈkwɔːlmi/ snoh-KWAWL-mee) is a city next to Snoqualmie Falls in King County, Washington, United States. It is 28 miles (45 km) east of Seattle. Snoqualmie city is home to the Northwest Railway Museum. The population was 10,670 at the 2010 census and an estimated 13,622 in 2019.
Many of the exterior shots for David Lynch’s Twin Peaks television series and movie (Fire Walk with Me) were filmed in Snoqualmie and in the neighboring towns of North Bend and Fall City. Movie actress Ella Raines was born on August 6, 1920, in Snoqualmie Falls, a mill town across the Snoqualmie River that is now part of Snoqualmie.
| Name: | Snoqualmie city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Washington |
| County: | King County |
| Elevation: | 427 ft (130 m) |
| Total Area: | 7.42 sq mi (19.22 km²) |
| Land Area: | 7.18 sq mi (18.59 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.24 sq mi (0.63 km²) |
| Total Population: | 10,670 |
| Population Density: | 1,898.01/sq mi (732.86/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 98065 |
| Area code: | 425 |
| FIPS code: | 5365205 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1526014 |
| Website: | www.snoqualmiewa.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Snoqualmie location map. Where is Snoqualmie city?
History
The second written record of the exploration of the Snoqualmie Valley comes from the notes of Samuel Hancock, who ventured up-river with the Snoqualmie tribe in 1851 in search of coal. Near the current location of Meadowbrook Bridge, Hancock was told by his guides that the land was known as Hyas Kloshe Illahee, or “good/productive land”. Hancock took this useful information back with him to the area now known as Tacoma. The area that is now Snoqualmie had been continuously occupied by members of the Snoqualmie Tribe and their ancestors for at least 13,000 years.
During the 1850s, tensions were very high between the native populations and the new settlers claiming the land as their own. In 1856, in response to these tensions, Fort Alden was built near a Snoqualmie village, in the area that would become Snoqualmie. After the Treaty War ended, Fort Alden was abandoned (along with other forts built around this time).
The most successful early pioneer in the Valley was Jeremiah Borst, who arrived in the spring of 1858 over the Cedar River trail from the eastern side of the mountains. He settled in the area that formerly held Fort Alden, and used his sales of pigs and apples in Seattle to buy out much of the surrounding land from other settlers.
As successful as farming was, other settlers had different methods of working the land. The very first lumber mill in the Snoqualmie Valley was established at the mouth of Tokul Creek around 1872 by Watson Allen. Within five years, there were 12 logging operations on the Snoqualmie River, providing lumber to the entire Seattle region. Within 15 years, logging and mill work was employing 140 men and sending millions of board feet of logs down the river.
In 1882, the Hop Growers Association was founded by three Puget Sound partners, who used land purchased on Snoqualmie Prairie from Jeremiah Borst to create a farm that would eventually cover 1,500 acres (6.1 km), 900 acres (3.6 km) of which was devoted solely to hops. This extremely successful venture (billed as “The Largest Hop Ranch in the World”) would fall prey to a combination of market and pest factors, and fell into relative obscurity by the end of the 1890s.
By the late 19th century, the Puget Sound region was growing, but bypassed by the major railways. In response, a group of Seattle entrepreneurs funded and built their own railway in an attempt to cross the Cascade Range. The Seattle, Lake Shore and Eastern Railway opened up the natural resources of the Snoqualmie Valley to the markets of the world, and brought in tourists to enjoy the natural beauty of the area and to marvel at the Falls.
The increased interest in the area led to a marked increase in speculation. Originally, the area that would become North Bend was platted as “Snoqualmie Prairie” in February 1889 by Will Taylor. The area that is currently Snoqualmie was platted in August of that same year as “Snoqualmie Falls” by investors from Seattle. The oral history of the area places the first residents of Snoqualmie as Edmund and Louisa Kinsey, who established the first hotel, livery, general store, dance hall, post office, and meat market – in addition to helping build the very first church in the town. Two of their sons (out of six children) are most famous for their photography documenting the early timber works in the region.
The Snoqualmie Falls Hydroelectric Plant, the first power plant at the Falls, was built in the late 1890s by Charles Baker, an investor from Seattle who had assisted in the platting of the city. This development provided both power and jobs to the region, and a small company town grew up near the falls to house the workers. More than 100 years later, Baker’s original generators are still in use by Puget Sound Energy.
The official vote for incorporation of “Snoqualmie Falls” as the city of Snoqualmie occurred in 1903. At the time, land prices had not decreased since initially set in 1889 — prices that did not reflect the financial reality of the region. In response to these high prices, people had created a large “squatting” community, building where they wanted regardless of land ownership or interests. The first challenge that the city council faced was lowering lot prices and migrating these buildings off the public right-of way, establishing the basic layout of the town that exists to this day.
In 1917, a new all-electric lumber mill (the second in the U.S.) opened across the river from Snoqualmie, along with the company town associated with it, Snoqualmie Falls. For the first half of the century, the timber industry provided the city and valley with a stable source of income and employment, even as World War I drew away workers and the Great Depression took its toll across the nation.
This prosperity was moderated during the Depression, and with the changes in culture and mobility in the latter half of the century, Snoqualmie and the majority of the valley stagnated. The city was bypassed when US-10 was built across the Cascades (now Interstate 90), and this led to a shift in commerce to the east (into North Bend) and west (into the Bellevue/Issaquah areas).
By the 1960s, the homes that had made up the company town of Snoqualmie Falls had been moved to other locations within the valley, and the city’s population had stabilized to a growth rate of roughly 11 people per year over the next 30 years (from 1,216 in 1960 to 1,546 in 1990).
This slow growth cycle continued until the mid-1990s, when the city annexed 1,300 acres (5.3 km) of undeveloped land that became the site of the current “master-planned” community of Snoqualmie Ridge, now referred to as Snoqualmie Ridge I. Snoqualmie Ridge I includes 2,250 dwelling units, a business park, a neighborhood center retail area and The Club at Snoqualmie Ridge, a private, PGA Tour-sanctioned golf course. Snoqualmie Ridge II, annexed in 2004, contains an additional 1,850 dwelling units, a hospital and a limited amount of additional retail.
The city council has continued to balance the desire to retain the rural and historical feel of Snoqualmie with the needs of a growing population. The city’s historic downtown underwent a major renovation to improve its infrastructure and make the area more attractive to visitors to the valley’s many natural attractions. As of 2023, Snoqualmie has continued to experience growth and development, with new residential and commercial projects being completed, including the Snoqualmie Hospital in 2015, the Snoqualmie Inn, new restaurants, and more townhomes. In addition, the city has continued to provide many parks and recreation facilities, including a network of trails and public spaces such as the Snoqualmie Community Park, built in 2009.
In 2012, the city of Snoqualmie annexed 593 acres (240 ha) of the former Weyerhaeuser mill site and mill pond (Borst Lake). The former mill office now hosts Dirtfish, an advanced rally car driver training school. The site is one of the largest undeveloped industrial zoned sites in King County, although significant planning and environmental review for potential future use remains to be done. The facility hosted a round of the 2014 Global RallyCross Championship.
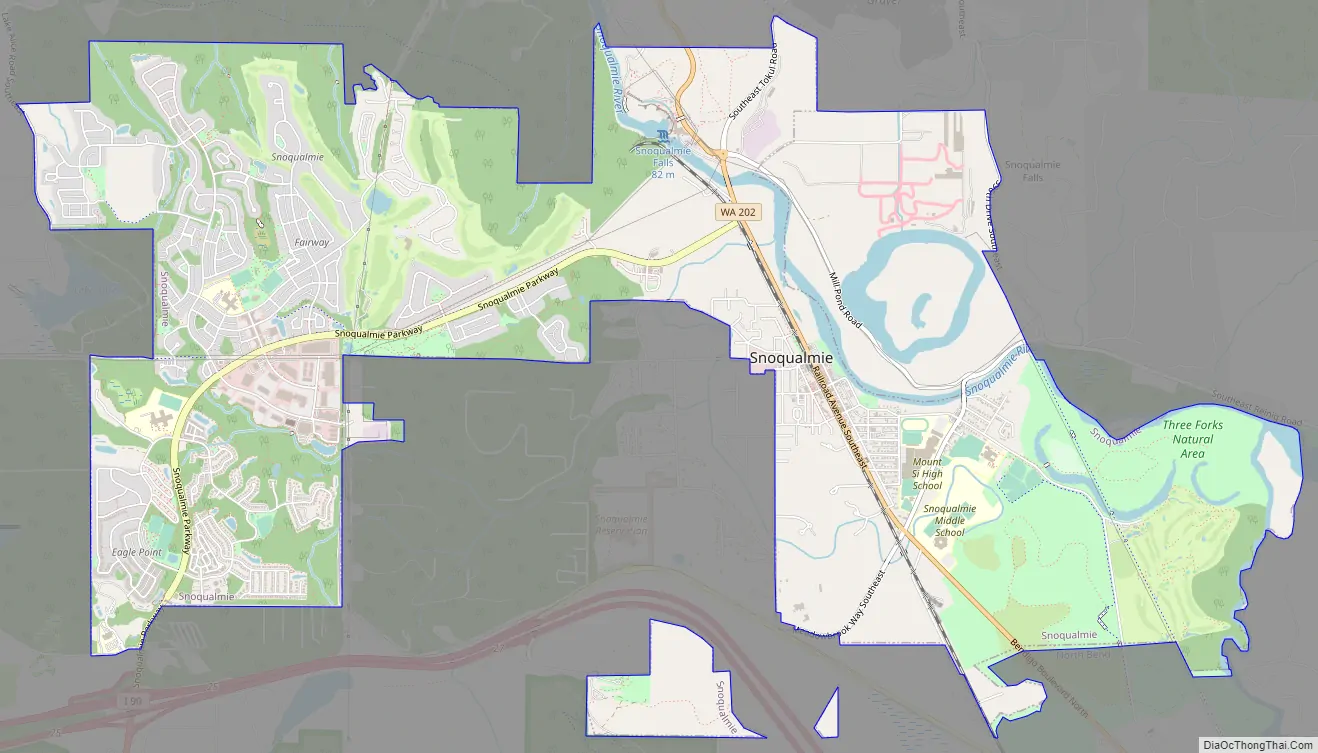
Snoqualmie Road Map
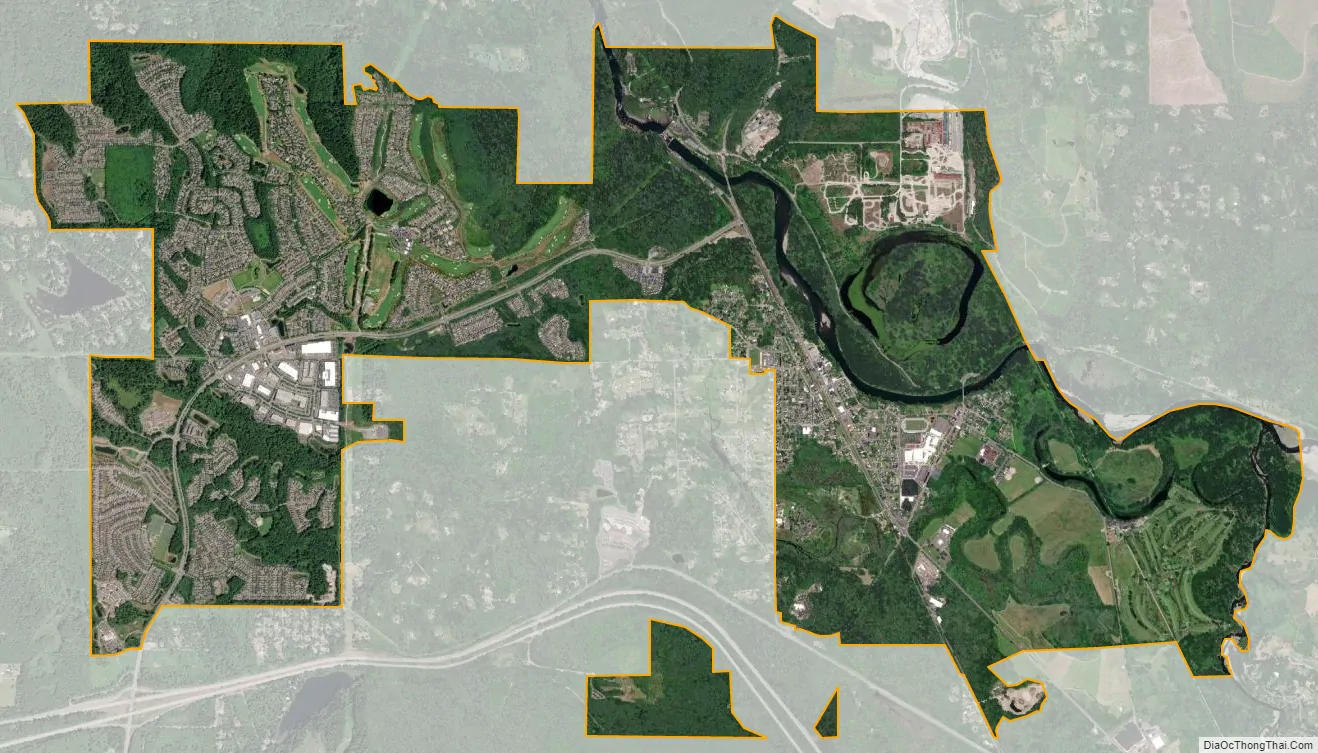
Snoqualmie city Satellite Map
Geography
Snoqualmie is located at 47°31′59″N 121°50′40″W / 47.53306°N 121.84444°W / 47.53306; -121.84444 (47.532934, -121.844341), at an elevation of 410 feet (120 m) above MSL.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 6.51 square miles (16.86 km), of which 6.40 square miles (16.58 km) are land and 0.11 square miles (0.28 km) are water.
Surrounding cities and communities
Climate
Snoqualmie has a cool summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen Csb).
See also
Map of Washington State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Asotin
- Benton
- Chelan
- Clallam
- Clark
- Columbia
- Cowlitz
- Douglas
- Ferry
- Franklin
- Garfield
- Grant
- Grays Harbor
- Island
- Jefferson
- King
- Kitsap
- Kittitas
- Klickitat
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Mason
- Okanogan
- Pacific
- Pend Oreille
- Pierce
- San Juan
- Skagit
- Skamania
- Snohomish
- Spokane
- Stevens
- Thurston
- Wahkiakum
- Walla Walla
- Whatcom
- Whitman
- Yakima
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming