Yakima (/ˈjækɪmɑː/ or /ˈjækɪmə/) is a city in and the county seat of Yakima County, Washington, United States, and the state’s 11th-largest city by population. As of the 2020 census, the city had a total population of 96,968 and a metropolitan population of 256,728. The unincorporated suburban areas of West Valley and Terrace Heights are considered a part of greater Yakima.
Yakima is about 60 miles (100 kilometers) southeast of Mount Rainier in Washington. It is situated in the Yakima Valley, a productive agricultural region noted for apple, wine, and hop production. As of 2011, the Yakima Valley produces 77% of all hops grown in the United States. The name Yakima originates from the Yakama Nation Native American tribe, whose reservation is located south of the city.
| Name: | Yakima city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Washington |
| County: | Yakima County |
| Incorporated: | December 10, 1883 |
| Elevation: | 1,066 ft (325 m) |
| Land Area: | 27.81 sq mi (72.02 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.46 sq mi (1.19 km²) 1.84% |
| Population Density: | 3,487/sq mi (1,346.4/km²) |
| Area code: | 509 |
| FIPS code: | 5380010 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1509643 |
| Website: | yakimawa.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
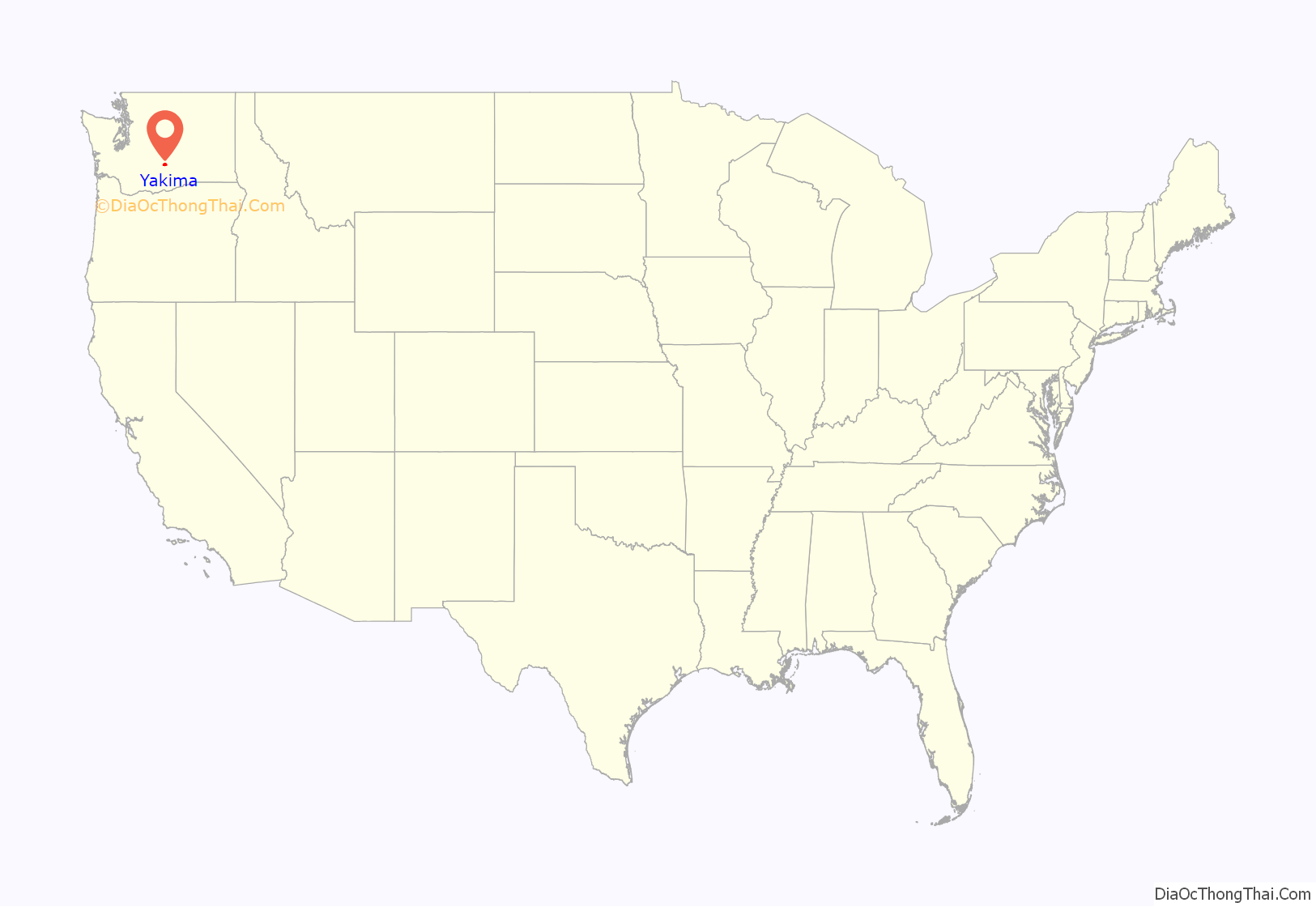
Yakima location map. Where is Yakima city?
History
The Yakama people were the first known inhabitants of the Yakima Valley. In 1805, the Lewis and Clark Expedition came to the area and discovered abundant wildlife and rich soil, prompting the settlement of homesteaders. A Catholic Mission was established in Ahtanum, southwest of present-day Yakima, in 1847. The arrival of settlers and their conflicts with the natives resulted in the Yakima War. The U.S. Army established Fort Simcoe in 1856 near present-day White Swan as a response to the uprising. The Yakamas were defeated and forced to relocate to the Yakama Indian Reservation.
Yakima County was created in 1865. When bypassed by the Northern Pacific Railroad in December 1884, over 100 buildings were moved with rollers and horse teams to the nearby site of the depot. The new city was dubbed North Yakima and was officially incorporated and named the county seat on January 27, 1886. The name was changed to Yakima in 1918. Union Gap was the new name given to the original site of Yakima.
On May 18, 1980, the eruption of Mount St. Helens caused a large amount of volcanic ash to fall on the Yakima area. Visibility was reduced to near-zero conditions that afternoon, and the ash overloaded the city’s wastewater treatment plant.
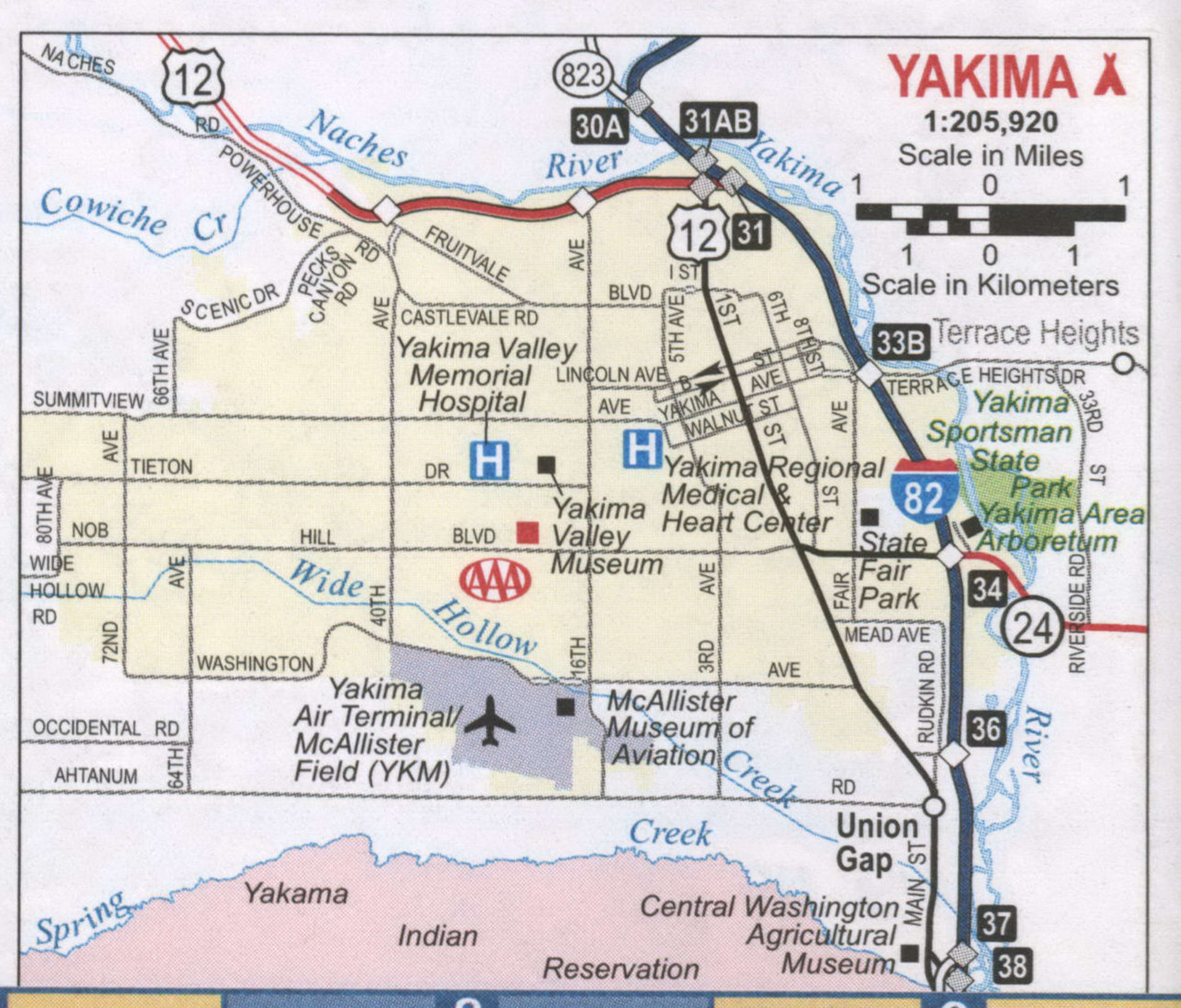
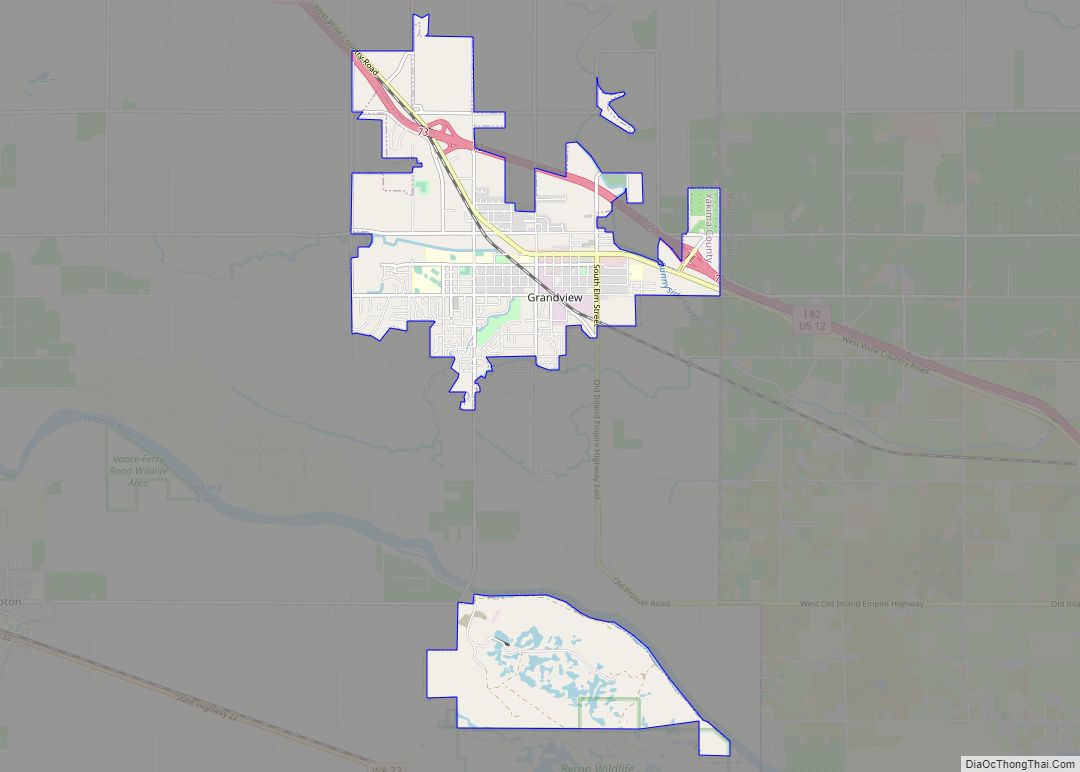
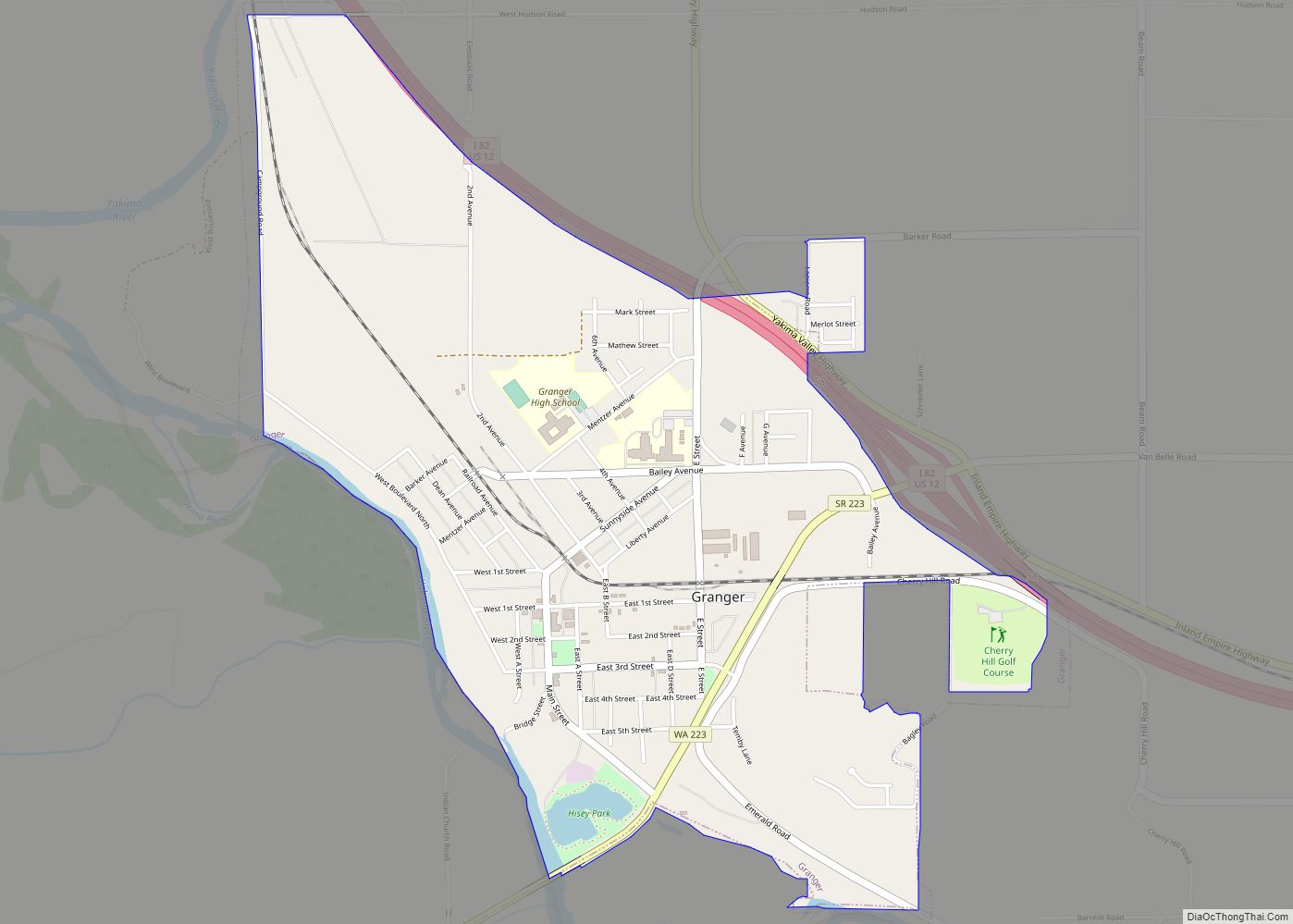
Yakima Road Map
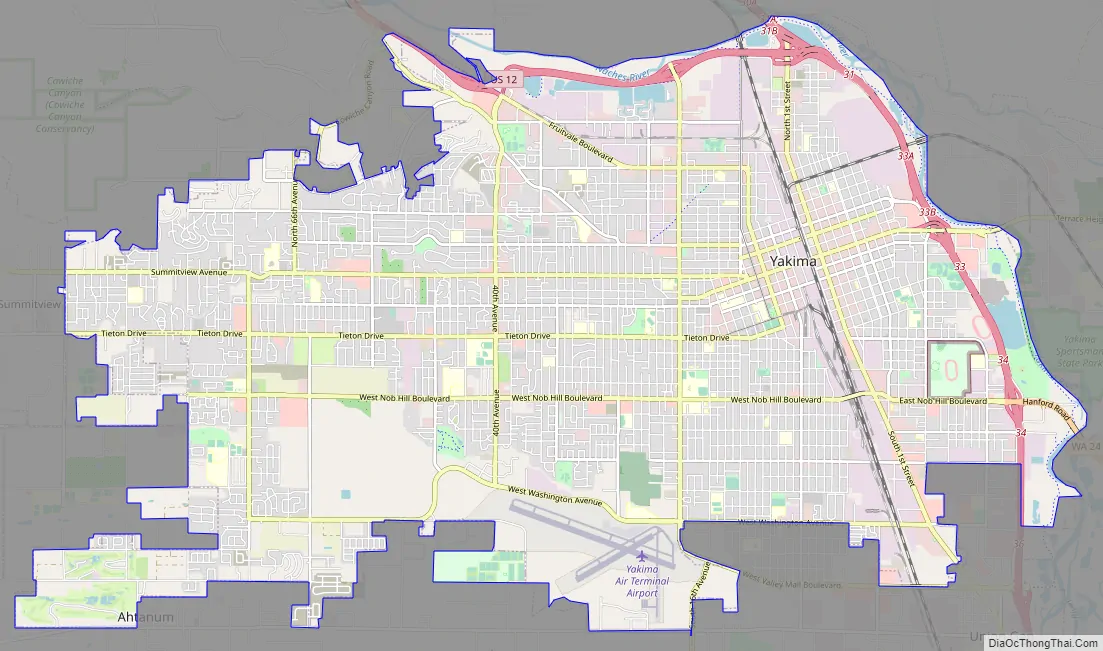
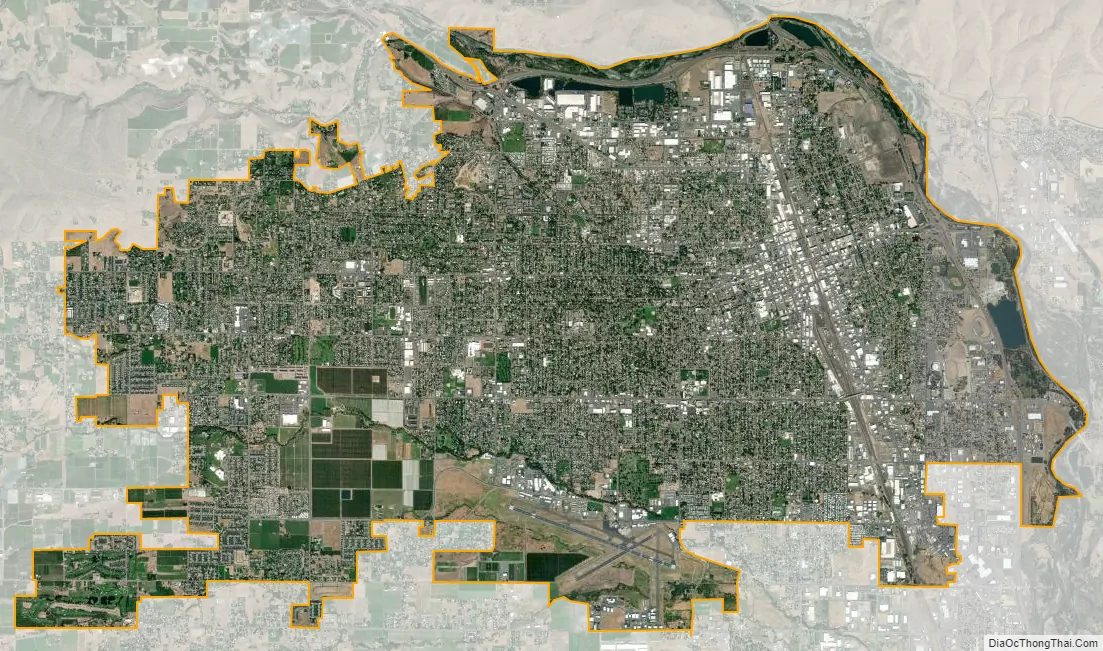
Yakima city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 27.69 sq mi (71.72 km), of which 27.18 sq mi (70.40 km) is land and 0.51 sq mi (1.32 km) is water. Yakima is 1095 feet above mean sea level.
Yakima region
The city of Yakima is located in the Upper Valley of Yakima County. The county is geographically divided by Ahtanum Ridge and Rattlesnake Ridge into two regions: the Upper (northern) and Lower (southern) valleys. Yakima is located in the more urbanized Upper Valley, and is the central city of the Yakima Metropolitan Statistical Area.
The unincorporated suburban areas of West Valley and Terrace Heights are considered a part of greater Yakima. Other nearby cities include Moxee, Tieton, Cowiche, Wiley City, Tampico, Gleed, and Naches in the Upper Valley, as well as Wapato, Toppenish, Zillah, Harrah, White Swan, Parker, Buena, Outlook, Granger, Mabton, Sunnyside, and Grandview in the Lower Valley.
Bodies of water
The primary irrigation source for the Yakima Valley, the Yakima River, runs through Yakima from its source at Lake Keechelus in the Cascade Range to the Columbia River at Richland. In Yakima, the river is used for both fishing and recreation. A 10-mile (16 km) walking and cycling trail, a park, and a wildlife sanctuary are located at the river’s edge.
The Naches River forms the northern border of the city. Several small lakes flank the northern edge of the city, including Myron Lake, Lake Aspen, Bergland Lake (private) and Rotary Lake (also known as Freeway Lake). These lakes are popular with fishermen and swimmers during the summer.
Climate
Yakima has a cold desert climate (Köppen BWk) with a Mediterranean precipitation pattern. Winters are cold, with December the coolest month, with a mean temperature of 28.5 °F (−1.9 °C). Annual average snowfall is 21.6 in (55 cm), with most occurring in December and January, when the snow depth averages 2 to 3 in (5.1 to 7.6 cm). There are 18.9 days per year in which the high does not surpass freezing, and 1.6 mornings where the low is 0 °F (−18 °C) or lower. Springtime warming is very gradual, with the average last freeze of the season May 13. Summer days are hot, but the diurnal temperature variation is large, averaging 34.9 °F (19.4 °C) in July, sometimes reaching as high as 50 °F (27.8 °C) during that season; there are 40.2 afternoons of maxima reaching 90 °F (32 °C) or greater annually and 5.7 afternoons of 100 °F (38 °C) maxima. Autumn cooling is very rapid, with the average first freeze of the season occurring on September 30. Due to the city’s location in a rain shadow, precipitation, at an average of 8.01 in (203 mm) annually, is low year-round, but especially during summer. Extreme temperatures have ranged from −25 °F (−32 °C) on February 1, 1950, to 113 °F (45 °C) on June 29, 2021.
See also
Map of Washington State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Asotin
- Benton
- Chelan
- Clallam
- Clark
- Columbia
- Cowlitz
- Douglas
- Ferry
- Franklin
- Garfield
- Grant
- Grays Harbor
- Island
- Jefferson
- King
- Kitsap
- Kittitas
- Klickitat
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Mason
- Okanogan
- Pacific
- Pend Oreille
- Pierce
- San Juan
- Skagit
- Skamania
- Snohomish
- Spokane
- Stevens
- Thurston
- Wahkiakum
- Walla Walla
- Whatcom
- Whitman
- Yakima
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming