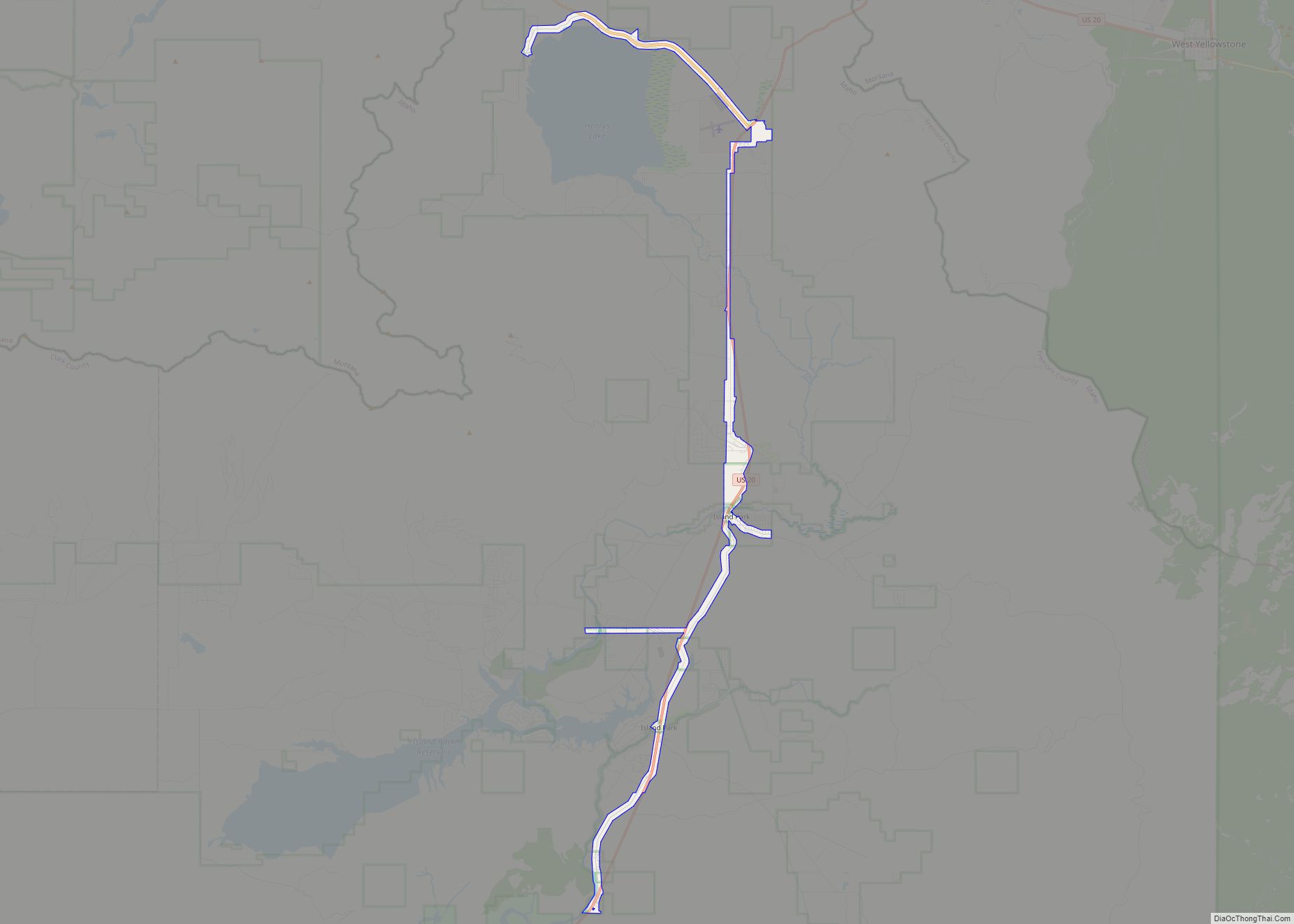
Island Park is a city in Fremont County, Idaho, United States. The city’s population was 286 at the 2010 census, up from 215 in 2000. The city was incorporated by owners of the many lodges and resorts along U.S. Route 20 in 1947, primarily to circumvent Idaho’s liquor laws that prohibited the sale of liquor outside of city limits. It is only 500 feet (150 m) wide in most locations yet, at 33 miles (53 km), claims to have the longest “Main Street” in the world.
Island Park is part of the Rexburg Micropolitan Statistical Area.
| Name: | Island Park city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
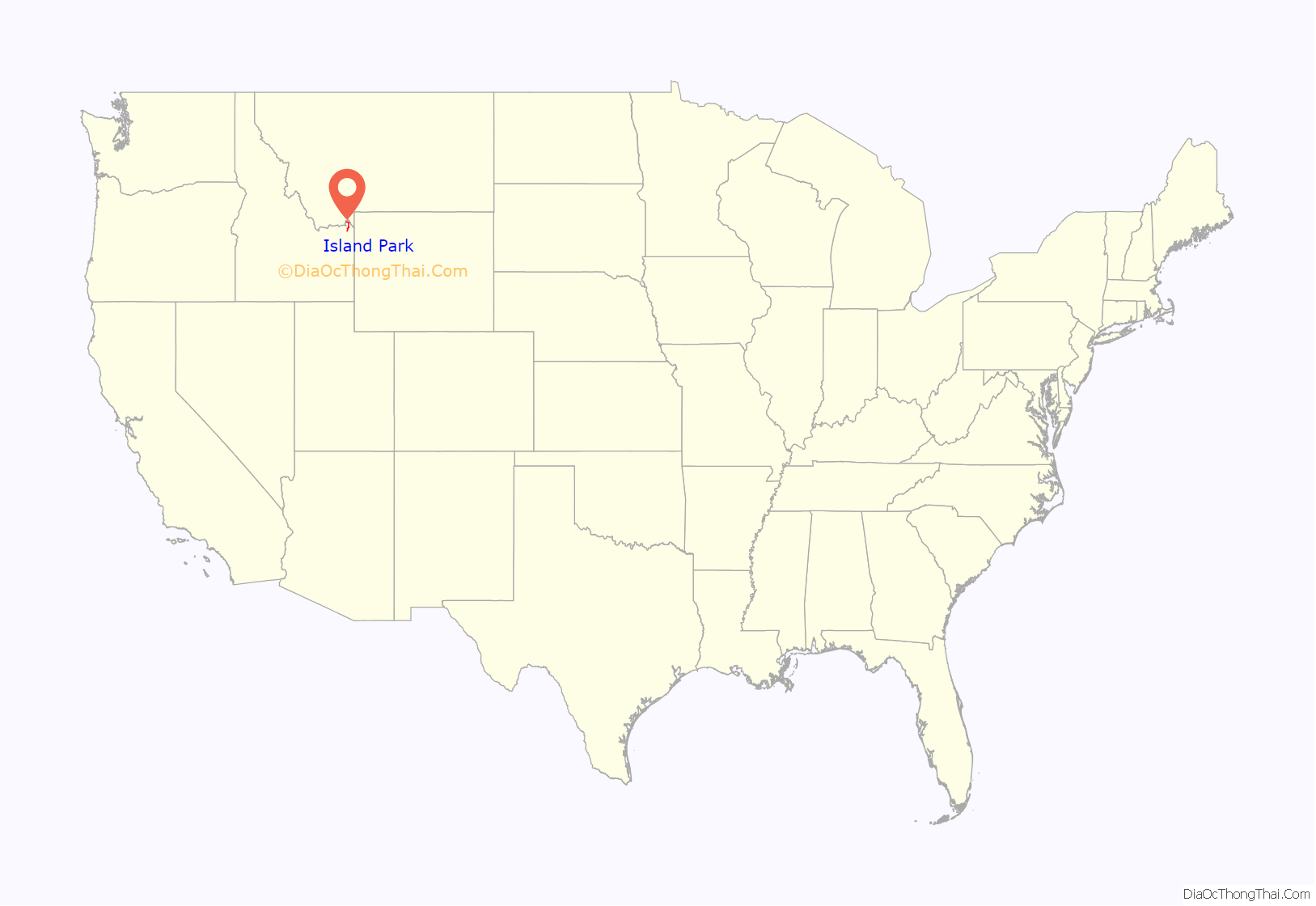
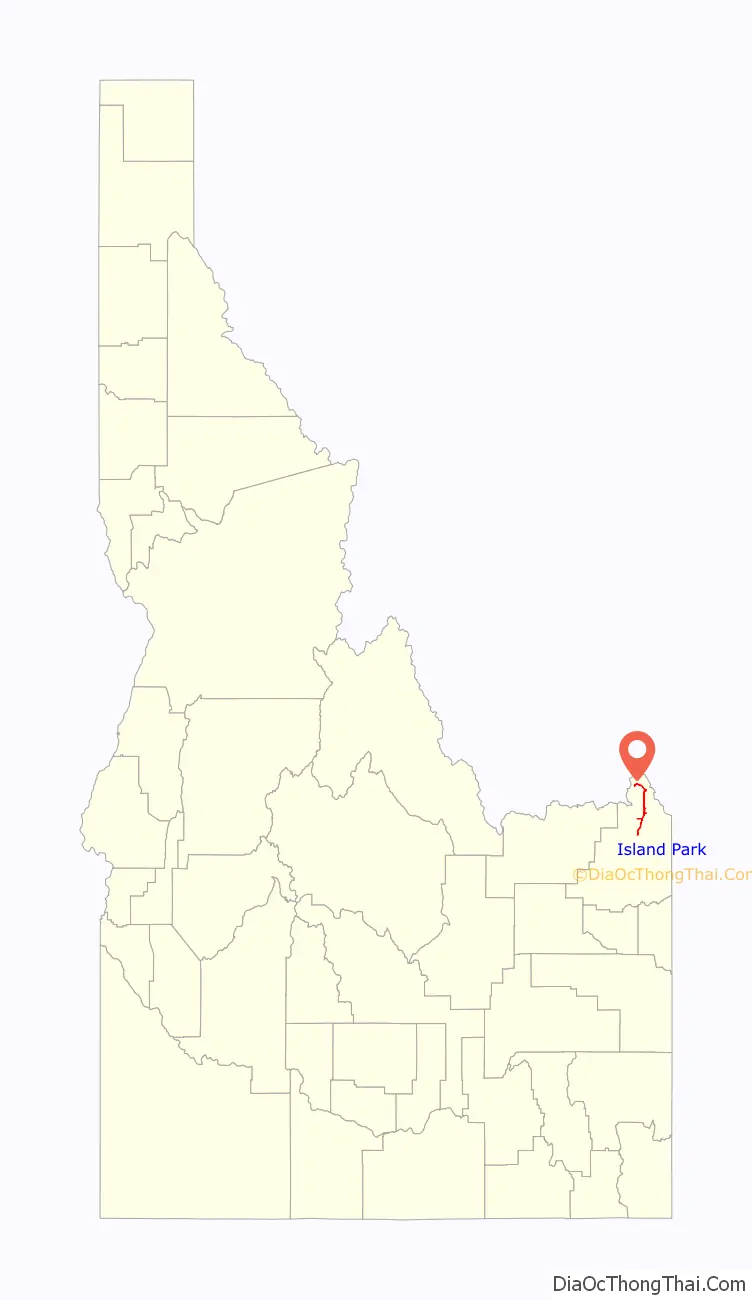
| State: | Idaho |
| County: | Fremont County |
| Elevation: | 6,293 ft (1,918 m) |
| Total Area: | 6.19 sq mi (16.03 km²) |
| Land Area: | 6.08 sq mi (15.75 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.11 sq mi (0.28 km²) |
| Total Population: | 286 |
| Population Density: | 43.74/sq mi (16.89/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 83429, 83433 |
| Area code: | 208 |
| FIPS code: | 1640600 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 2410121 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Island Park location map. Where is Island Park city?
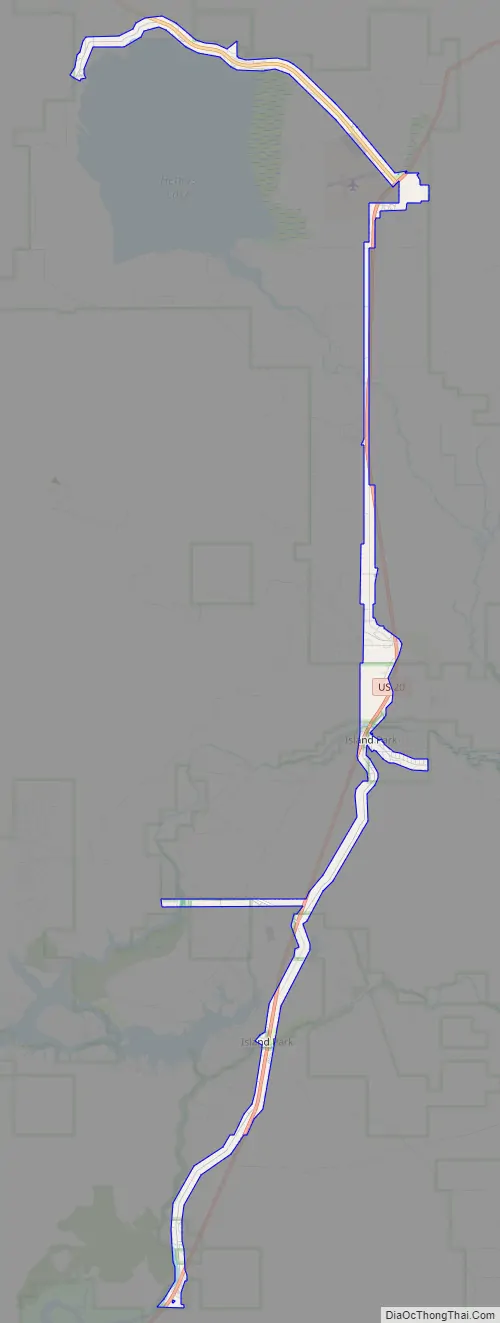
Island Park Road Map
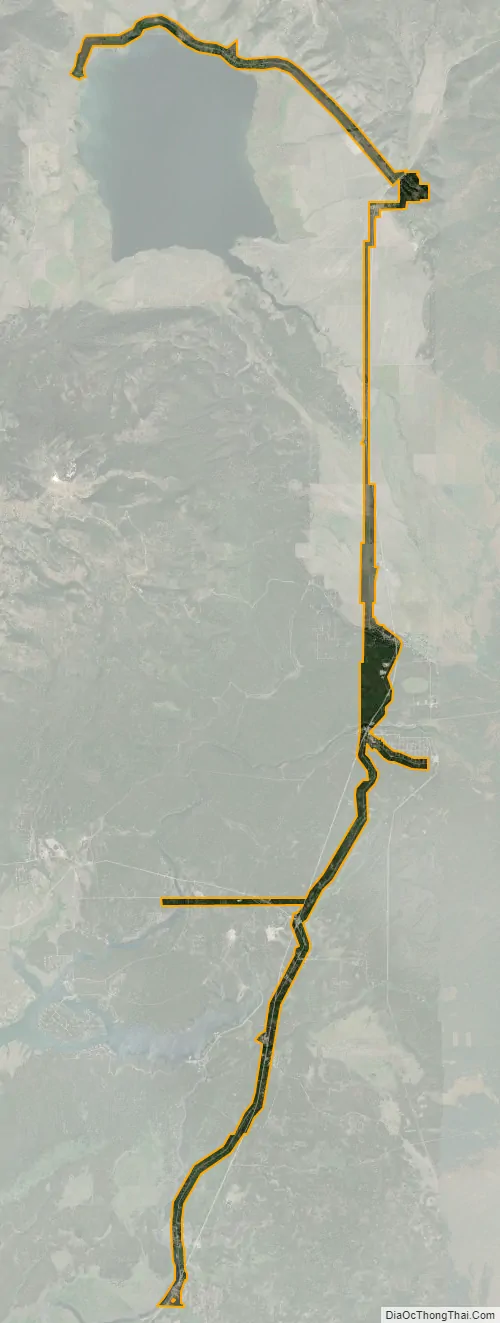
Island Park city Satellite Map
Geography
City geography
Island Park is located at 44°29′59″N 111°20′19″W / 44.49972°N 111.33861°W / 44.49972; -111.33861 (44.4996, −111.3387), at an elevation of 6,293 feet (1,918 m) above sea level, making it the highest city in Idaho.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 6.77 square miles (17.53 km), of which, 6.64 square miles (17.20 km) is land and 0.13 square miles (0.34 km) is water.
Regional geography
The area was known as Island Park long before the 33-mile (53 km)-long town was incorporated. The area known as Island Park is mostly a large crater or caldera named the Henry’s Fork Caldera that was created by the same hotspot that created the earlier Island Park Caldera and the later Yellowstone Caldera.
In addition to the portion which lies on the Henry’s Fork Caldera, about a third of what is known as Island Park is north of the caldera, extending across Henry’s Lake Flat and Henry’s Lake towards the Idaho/Montana border. Henry’s Lake Flat is a flat bottomed valley between high mountain ranges, with Henrys Lake at the northwest end of the flats. Mount Jefferson, south of Henry’s Lake, is 10,203 feet (3,110 m) high and Targhee Peak, north of Henrys Lake is 10,240 feet (3,121 m) high. The most famous of Island Park’s peaks, however, is the 9,886-foot (3,013 m) Sawtell Peak, south of Henrys Lake near Mount Jefferson. The peak is known for its beauty and is named for a perceived resemblance to a Native American chief’s profile while napping. The peak has also been called Chief Rains in the Face. Sawtell Peak is topped by a FAA radar dome and is visible from nearly anywhere in Island Park.
Although much smaller than either the Island Park Caldera or the Yellowstone Caldera, the Henry’s Fork Caldera is still one of the largest calderas in the world and is the only large caldera in the Yellowstone region that is plainly visible. It has a nearly level 20-mile (32 km) wide circular floor that slopes slightly towards the southeast. The caldera floor is at about 6,000 feet (1,830 m) of elevation with the rim generally being several hundred feet higher. The Henry’s Lake Flat area, north of the caldera, is a little higher. Henry’s Lake sits at about 6,500 feet (1,980 m), with the flats sloping slightly southward towards the caldera.
The Island Park area is mostly forested with many meadows and grasslands. It is mostly level, but is surrounded by forested hills and high mountains in the north. The Henrys Fork of the Snake River meanders through Island Park with its headwaters at Henry’s Lake and at Big Springs (Idaho). The Henry’s Fork is impounded by Island Park Dam to form Island Park Reservoir outside the north rim of the caldera. In fact, the entire south bank of Island Park Reservoir is formed by the northern slope of the caldera. The Henry’s Fork crosses through the caldera and then cascades off from it at Upper and Lower Mesa Falls.
The geography of Island Park is actually unique and distinctive. It is largely flat and it has unusually high precipitation. Island Park is at the same 6,000 feet (1,830 m) elevation as Teton Valley, Idaho, Jackson Hole, Wyoming, or the Centennial Valley, Montana; yet while these nearby areas are semi-arid prairie or even desert areas receiving less than 12 inches (30 cm) of precipitation annually, Island Park is forested and green with many streams, ponds, lakes, and meadows. Island Park receives well over 30 inches (76 cm) of precipitation annually, with parts receiving over 50 inches (127 cm). That is, Island Park has three times the rainfall and snowfall as nearby areas of the same elevation.
The Snake River Plain that was also formed by the Yellowstone hotspot aligns with the gap between the Sierra Nevada and Cascade mountain ranges along the West Coast of the United States so that there is a moisture channel that extends from the distant Pacific Ocean, between the Cascades and Sierra Nevada, through the Rocky Mountains to Island Park.
This abundant precipitation in Island Park falls on the relatively level floor of the caldera, where it forms numerous meandering streams, ponds, marshes, and meadows. It also falls on the higher areas to the east along the Yellowstone Park border, where it percolates though the granular volcanic deposits to emerge as some of the largest springs in the world. Big Springs, Buffalo River Springs, and Warm River Springs all are 1st Magnitude springs, and they form some of the crystal clear meandering streams that the area is famous for.
See also
Map of Idaho State and its subdivision:- Ada
- Adams
- Bannock
- Bear Lake
- Benewah
- Bingham
- Blaine
- Boise
- Bonner
- Bonneville
- Boundary
- Butte
- Camas
- Canyon
- Caribou
- Cassia
- Clark
- Clearwater
- Custer
- Elmore
- Franklin
- Fremont
- Gem
- Gooding
- Idaho
- Jefferson
- Jerome
- Kootenai
- Latah
- Lemhi
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Madison
- Minidoka
- Nez Perce
- Oneida
- Owyhee
- Payette
- Power
- Shoshone
- Teton
- Twin Falls
- Valley
- Washington
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming