College Park is a city in Prince George’s County, Maryland, United States, and is approximately four miles (6.4 km) from the northeast border of Washington, D.C. The population was 34,740 at the 2020 United States census. College Park is best known as the home of the University of Maryland, College Park.
Since 1994, the city has also been home to the National Archives at College Park, a facility of the U.S. National Archives, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Center for Weather and Climate Prediction (NCWCP), and the Food and Drug Administration’s Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition (CFSAN).
| Name: | College Park city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
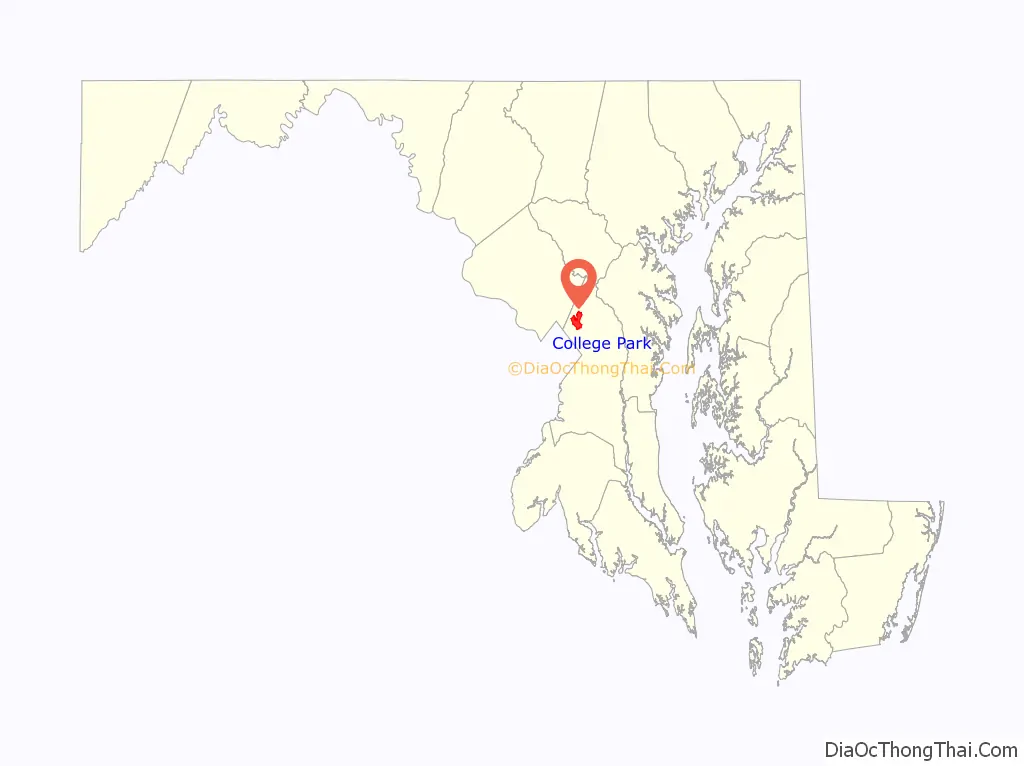
| State: | Maryland |
| County: | Prince George’s County |
| Founded: | 1856 |
| Incorporated: | 1945 |
| Elevation: | 69 ft (21 m) |
| Total Area: | 5.68 sq mi (14.72 km²) |
| Land Area: | 5.61 sq mi (14.53 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.07 sq mi (0.18 km²) |
| Total Population: | 34,740 |
| Population Density: | 6,191.41/sq mi (2,390.37/km²) |
| Area code: | 301, 240 |
| FIPS code: | 2418750 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 2390578 |
| Website: | www.collegeparkmd.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
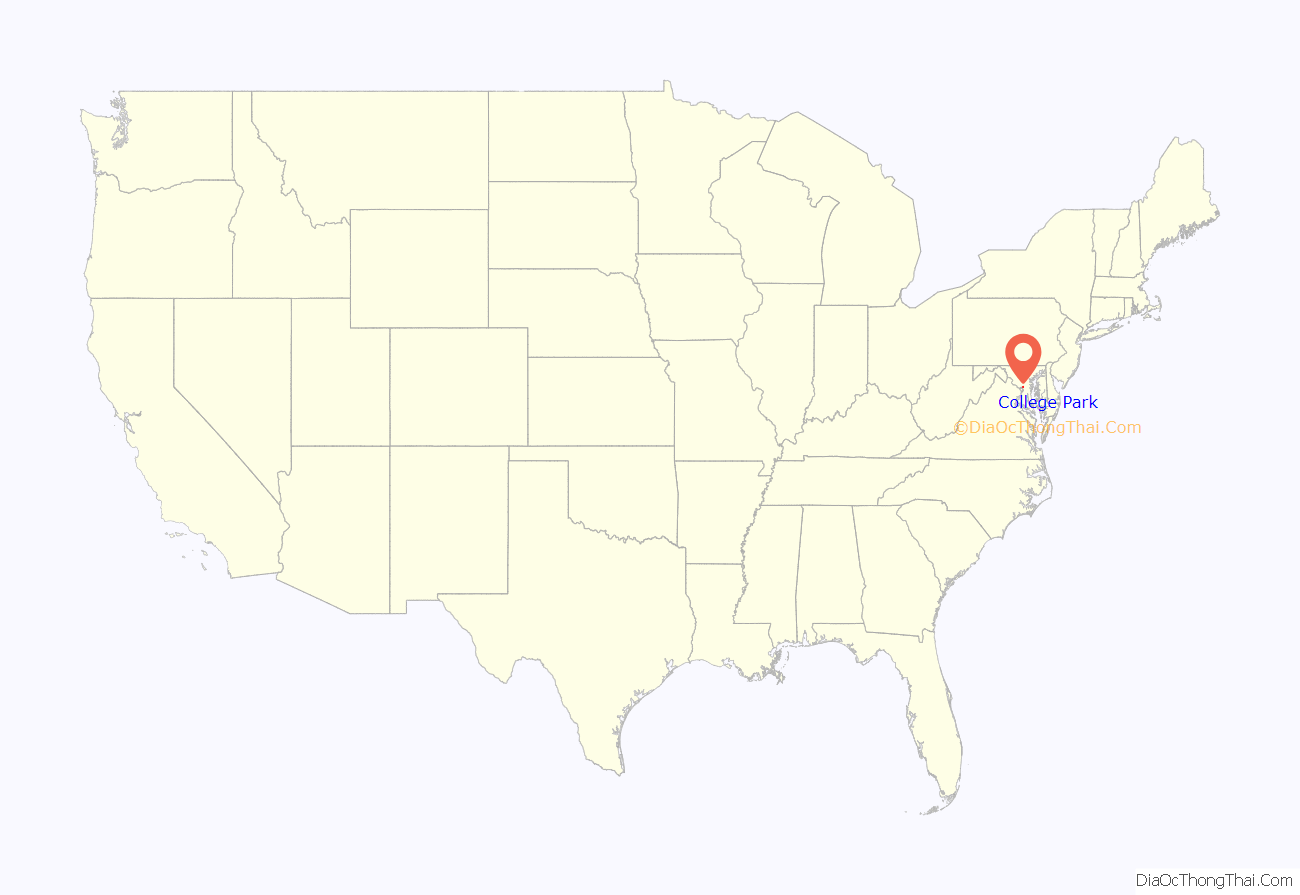
College Park location map. Where is College Park city?
History
19th century
College Park was developed beginning in 1889 near the Maryland Agricultural College (later the University of Maryland) and the College Station stop of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. The suburb was incorporated in 1945 and included the subdivisions of College Park, Lakeland, Berwyn, Oak Spring, Branchville, Daniel’s Park, and Hollywood.
The original College Park subdivision was first platted in 1872 by Eugene Campbell. The area remained undeveloped and was re-platted in 1889 by John O. Johnson and Samuel Curriden, Washington real estate developers. The original 125-acre (0.51 km) tract was divided into a grid-street pattern with long, narrow building lots, with a standard lot size of 50 feet (15 m) by 200 feet (61 m). College Park developed rapidly, catering to those who were seeking to escape the crowded Washington, D.C., as well as to a rapidly expanding staff of college faculty and employees.
College Park originally included single-family residences constructed in the Shingle, Queen Anne, and Stick styles, as well as modest vernacular dwellings. Commercial development increased in the 1920s, aided by the increased automobile traffic and the growing campus along Baltimore Avenue/Route 1.
20th century
By the late 1930s, most of the original subdivision had been partially developed. Several fraternities and sororities from the University of Maryland built houses in the neighborhood. After World War II, construction consisted mostly of infill of ranch and split-level houses. After incorporation in 1945, the city continued to grow, and a municipal center was built in 1959.
The Lakeland neighborhood was developed beginning in 1890 around the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, whose Branchville and Calvert Road depots were located approximately one mile to the north and south, respectively. Lakeland was created by Edwin Newman, who improved the original 238 acres (0.96 km) located to the west of the railroad. He also built a number of the original homes, a small town hall, and a general store. The area was originally envisioned as a resort-type community. However, due to the flood-prone, low-lying topography, the neighborhood became an area of African-American settlement. Around 1900, the Baltimore Gold Fish Company built five artificial lakes in the area to spawn goldfish and rarer species of fish. By 1903 Lakeland was an established African-American community with a school and two churches. Lakeland was central in a group of African American communities located along Route One through Prince Georges County. Lakeland High School opened in 1928 with funding from the Rosenwald Fund, the African American community and the county. Lakeland High served all African American students in the northern half of the county until 1950 when it was converted to a facility for lower grades. The community’s first Rosenwald school was a new elementary which opened in 1925.
The Berwyn neighborhood was developed beginning about 1885 adjacent to the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. It was created by Francis Shannabrook, a Pennsylvanian who purchased a tract of land between Baltimore Avenue and the railroad tracks. Shannabrook established a small depot, built a general store, and erected approximately 15 homes in the area to attract moderate-income families looking to move out of Washington. The neighborhood began to grow after 1900 when the City and Suburban Electric Railway entered the area. By 1925, approximately 100 single-family homes existed, mostly two-story, wood-frame buildings. The community housing continued to develop in the 1930s and 1940s with one story bungalows, Cape Cods, and Victorians and, later, raised ranches and split-level homes.
The Daniels Park neighborhood was developed, beginning in 1905 on the east and west sides of the City and Suburban Electric Railway in north College Park. Daniels Park was created by Edward Daniels on 47 acres (19 ha) of land. This small residential subdivision was improved with single-family houses arranged along a grid pattern of streets. The houses—built between 1905 and the 1930s—range in style from American Foursquares to bungalows.
The Hollywood neighborhood was developed in the early 20th century along the City and Suburban Electric Railway. Edward Daniels, the developer of Daniels Park, planned the Hollywood subdivision as a northern extension of that earlier community. Development in Hollywood was slow until after World War II, when Albert Turner acquired large tracts of the northern part of the neighborhood in the late 1940s. Turner was able to develop and market brick and frame three-bedroom bungalows beginning in 1950. By 1952, an elementary school had been built. Hollywood Neighborhood Park, a 21-acre (8.5 ha) facility along the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad line, is operated by the Maryland-National Capital Park and Planning Commission.
In 1943, due to World War II efforts to conserve rail transport, the Washington Senators relocated their spring training camp to College Park. The locations of 1943 Major League Baseball spring training camps were limited to an area east of the Mississippi River and north of the Ohio River.
During the 1960s through the 1980s an Urban Renewal Project took place within the historic African American community of Lakeland. This project was carried out in the face of the opposition of the community’s residents and resulted in the redevelopment of approximately two thirds of the community. It displaced 104 of Lakeland’s 150 households.
21st century
On September 24, 2001, a multiple-vortex F3 tornado hit the area. This storm moved at peak intensity through the University of Maryland College Park campus, and then moved north parallel to I-95 to the Laurel area, where F3 damage was also noted. The damage path from the storm was measured at 17.5 miles (28.2 km) in length. The tornado caused two deaths and 55 injuries and $101 million in property damage. The two deaths were sisters who died when their car was picked up and hurled over a building before being slammed to the ground. Both young women were University of Maryland students. This tornado was part of the Maryland, Virginia, and Washington, D.C., tornado outbreak of 2001, one of the most dramatic recent tornado events to directly affect the Baltimore-Washington metropolitan area.
By the turn of the 21st century, College Park began experiencing significant development pressure. Both students and city residents acknowledged the city’s lack of amenities and poor sense of place. In 2002, the city and county passed the Route 1 Sector Plan, which allowed and encouraged mixed use development along College Park’s main roadway. Recent projects—like the East Campus Redevelopment Initiative, The University View, The Varsity, and Landmark student apartments and the Northgate Condos—give many in the community hope that the city, like other notable American college towns, might one day have a vibrant downtown and a diverse population. In 2004, College Park annexed 72 acres (29 ha) that were previously considered to be in Beltsville, an unincorporated area; this tract included a Holiday Inn and an IKEA.
The University of Maryland’s Student Government Association sponsored a design charrette in April 2006 to envision the future of College Park. In July 2006, a group of students created Rethink College Park—a community group providing a website to share information about development and to encourage public dialogue.
Since 2009, other notable architectural additions to College Park have been: a parking garage (with The Ledo Restaurant on ground level) in downtown near the intersection of Route 1 and Knox Road; The University View and The Varsity student apartment towers with ground floor retail businesses; graduate school apartment towers adjacent to The View apartments; and The Hotel at the University of Maryland.
As of 2020, the University of Maryland is undergoing many major construction projects on campus. Construction includes a $13.7 million addition of four new wings to the chemistry building, a $195.7 million sports and medicine complex for Cole Field House, a new public policy school building at about $52.4 million between the Lee Building and Rossborough Inn, a $60 million IDEA (Innovate, Design and Engineer for America) Factory, and a $14.5 million replacement of all mechanical equipment in wing 2 of the H.J. Patterson Hall.
On June 9, 2020, the city government passed a “Resolution of the Mayor and Council of the City of College Park Renouncing Systemic Racism and Declaring Support of Black Lives” which recognized harm done to the historic African American community of Lakeland. In it, “the Mayor and Council acknowledge and apologize for our city’s past history of oppression, particularly with regards to the Lakeland community, and actively seek opportunities for accountability and truth-telling about past injustice, and aggressively seek opportunities for restorative justice”.
On March 2, 2023, College Park Mayor Patrick Wojahn, who had served as Mayor since 2015, resigned after being arrested on child pornography charges involving 40 counts of possession of child exploitative material and 16 counts of distribution of child exploitative material.
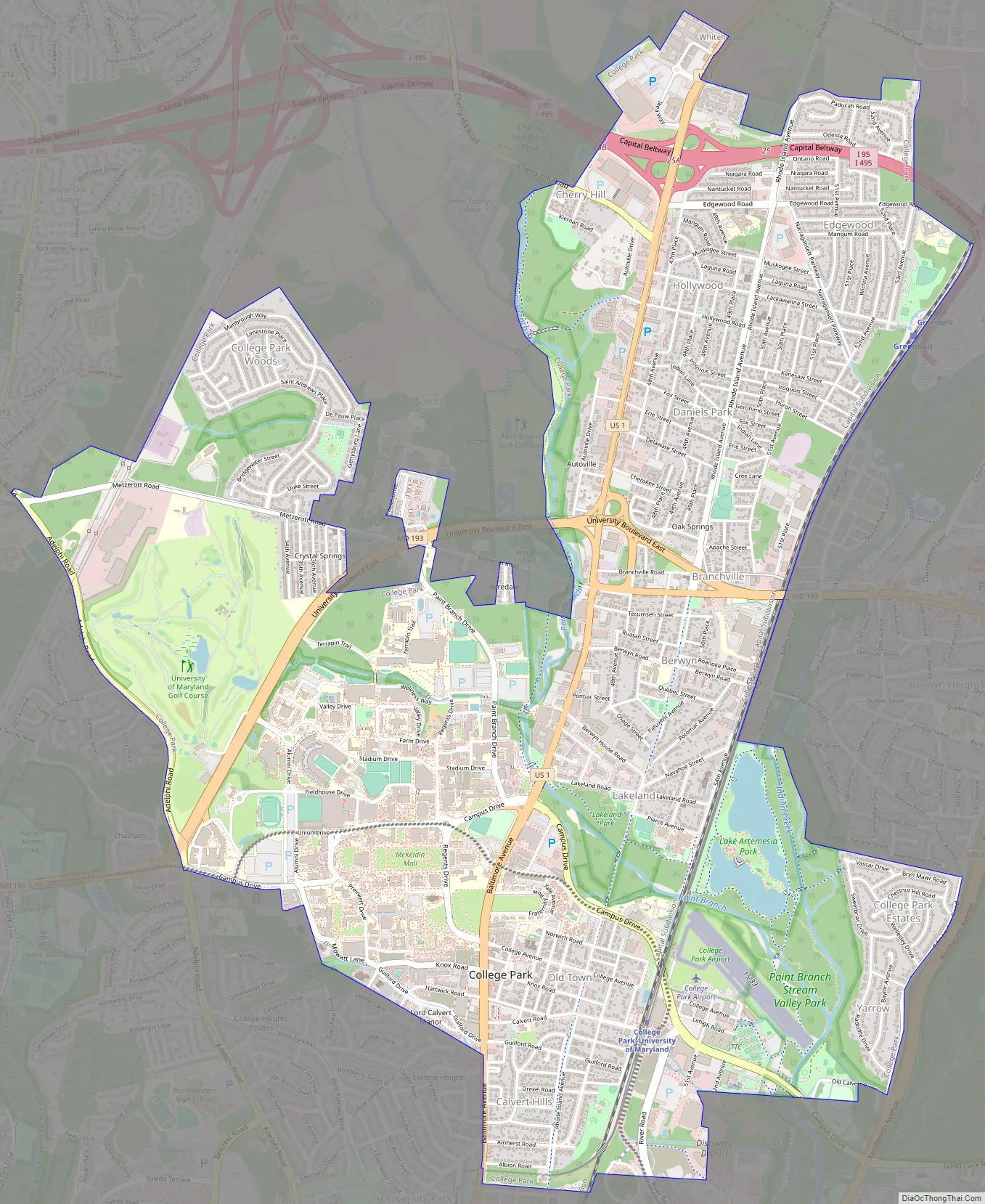
College Park Road Map
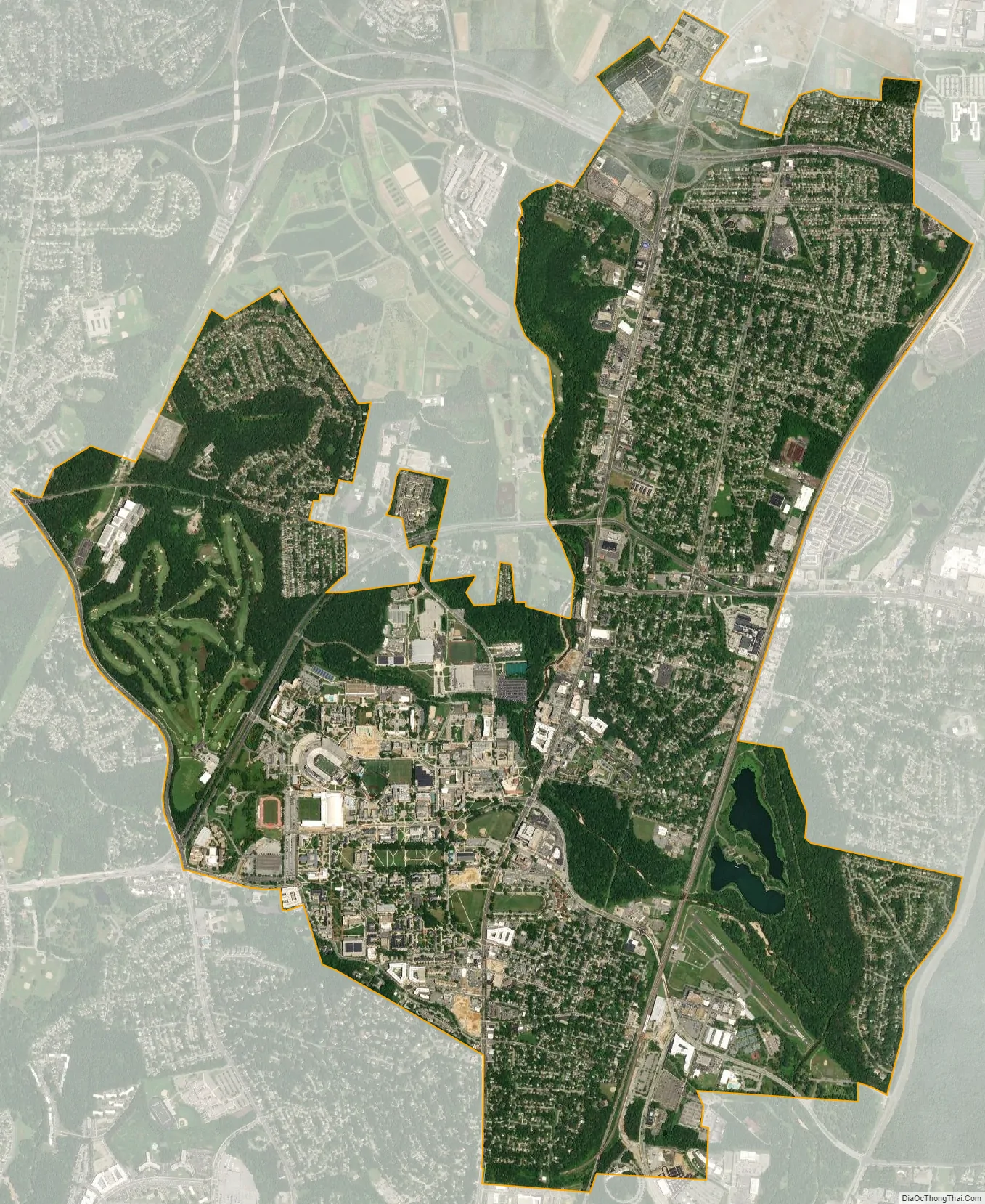
College Park city Satellite Map
Geography
College Park is located at 38°59′48″N 76°55′39″W / 38.99667°N 76.92750°W / 38.99667; -76.92750 (38.996560, -76.927509).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 5.68 square miles (14.71 km), of which 5.64 square miles (14.61 km) is land and 0.04 square miles (0.10 km) is water.
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen climate classification system, College Park has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated “Cfa” on climate maps.
Neighborhoods
- Autoville/Cherry Hill
- Berwyn
- Branchville
- Calvert Hills
- College Park Woods
- Crystal Springs/Patricia Court
- Daniels Park
- Hollywood
- Lakeland
- North College Park
- Old Town
- Sunnyside
- Yarrow
Adjacent areas
- Beltsville (North)
- Berwyn Heights (East)
- University Park (Southwest)
- Riverdale Park (South)
- Adelphi (West)
- Hyattsville (Southwest)
See also
Map of Maryland State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming