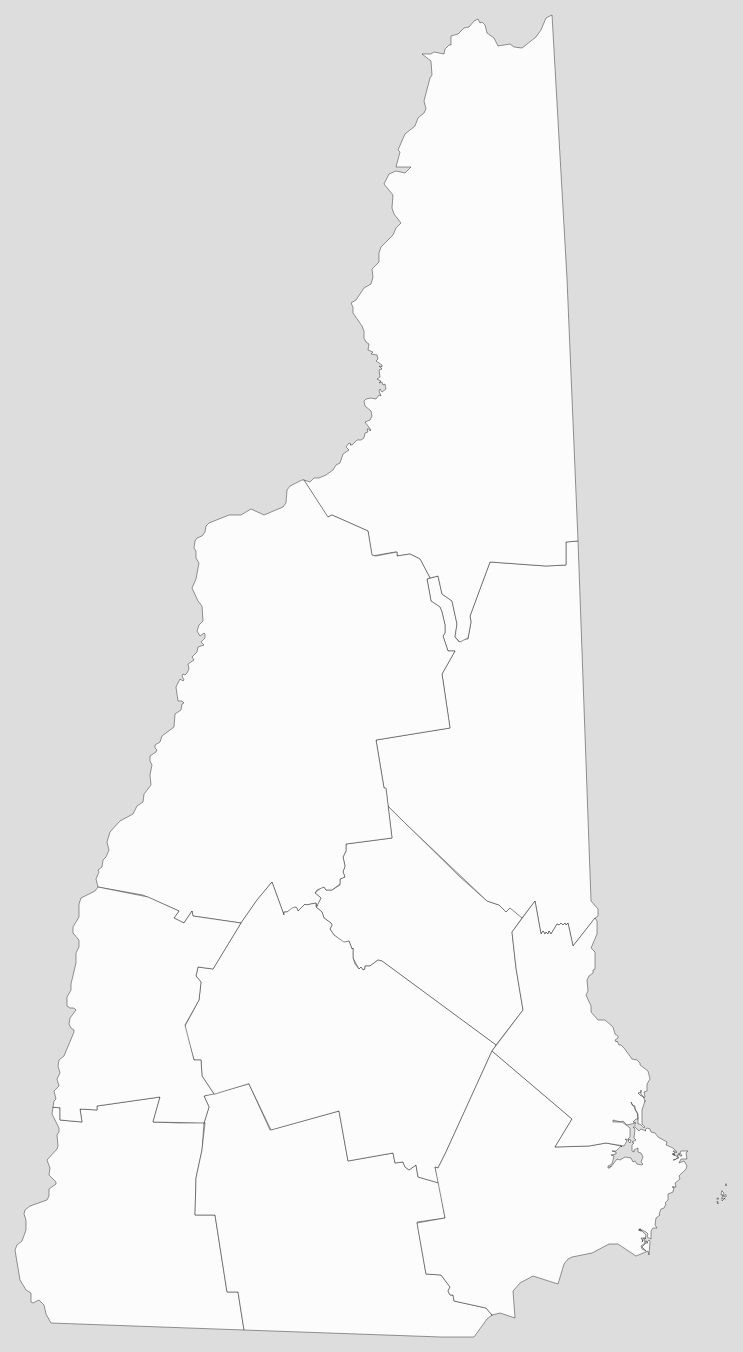
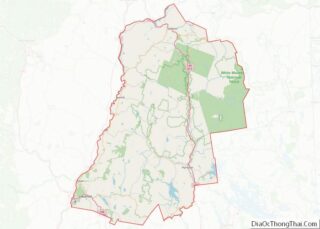
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the north. Of the 50 U.S. states, New Hampshire is the fifth smallest by area and the tenth least populous, with slightly more than 1.3 million residents as of the 2020 census. Concord is the state capital, while Manchester is the largest city. New Hampshire’s motto, “Live Free or Die”, reflects its role in the American Revolutionary War; its nickname, “The Granite State”, refers to its extensive granite formations and quarries. It is well known nationwide for holding the first primary (after the Iowa caucus) in the U.S. presidential election cycle, and for its resulting influence on American electoral politics.
New Hampshire was inhabited for thousands of years by Algonquian-speaking peoples such as the Abenaki. Europeans arrived in the early 17th century, with the English establishing some of the earliest non-indigenous settlements. The Province of New Hampshire was established in 1629, named after the English county of Hampshire. Following mounting tensions between the British colonies and the crown during the 1760s, New Hampshire saw one of the earliest overt acts of rebellion, with the seizing of Fort William and Mary from the British in 1774. In January 1776, it became the first of the British North American colonies to establish an independent government and state constitution; six months later, it signed the United States Declaration of Independence and contributed troops, ships, and supplies in the war against Britain. In June 1788, it was the ninth state to ratify the U.S. Constitution, bringing that document into effect.
Through the mid-19th century, New Hampshire was an active center of abolitionism, and fielded close to 32,000 soldiers for the Union during the U.S. Civil War. After the war, the state saw rapid industrialization and population growth, becoming a center of textile manufacturing, shoemaking, and papermaking; the Amoskeag Manufacturing Company in Manchester was at one time the largest cotton textile plant in the world. The Merrimack and Connecticut rivers were lined with industrial mills, most of which employed workers from Canada and Europe; French Canadians formed the most significant influx of immigrants, and today roughly a quarter of all New Hampshire residents claim French American ancestry, second only to Maine.
Reflecting a nationwide trend, New Hampshire’s industrial sector declined after the Second World War. Since 1950, its economy has heavily diversified to include financial and professional services, real estate, education, transportation and high-tech, with manufacturing still higher than the national average. Beginning in the 1950s, its population surged as major highways connected it to Greater Boston and led to more bedroom communities. In the 21st century, New Hampshire is among the wealthiest and most-educated states in the U.S., with the seventh-highest median household income and some of the lowest rates of poverty, unemployment, and crime. It is one of only nine states without an income tax and has no taxes on sales, capital gains, or inheritance while relying heavily on local property taxes to fund education; consequently, its state tax burden is among the lowest in the country.
New Hampshire ranks among the top ten states in metrics such as governance, healthcare, socioeconomic opportunity, and fiscal stability.
With its mountainous and heavily forested terrain, New Hampshire has a growing tourism sector centered on outdoor recreation. It has some of the highest ski mountains on the East Coast and is a major destination for winter sports; Mount Monadnock is among the most climbed mountains in the U.S. Other activities include observing the fall foliage, summer cottages along many lakes and the seacoast, motorsports at the New Hampshire Motor Speedway, and Motorcycle Week, a popular motorcycle rally held in Weirs Beach in Laconia. The White Mountain National Forest includes most of the Appalachian Trail between Vermont and Maine, and has the Mount Washington Auto Road, where visitors may drive to the top of 6,288-foot (1,917 m) Mount Washington.
| Before statehood: | Province of New Hampshire |
|---|---|
| Admitted to the Union: | June 21, 1788 (9th) |
| Capital: | Concord |
| Largest city: | Manchester |
| Largest metro and urban areas: | Greater Boston (combined and metro) Nashua (urban) |
| Elevation: | 1,000 ft (300 m) |
| Total Area: | 9,349 sq mi (24,214 km) |
| Area Rank: | 46th |
| Total Population: | 1,377,529 |
| Population Rank: | 41st |
| Population Density: | 150/sq mi (57/km) |
| Population Density Rank: | 21st |
| Median Household Income: | $73,381 |
| Income Rank: | 8th |
| Demonym(s): | Granite Stater New Hampshirite |
| USPS abbreviation: | NH |
| ISO 3166 code: | US-NH |
| Website: | www.nh.gov |
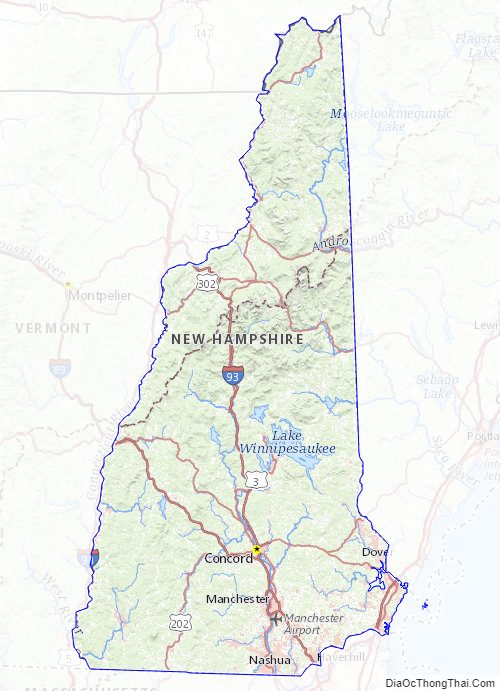
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
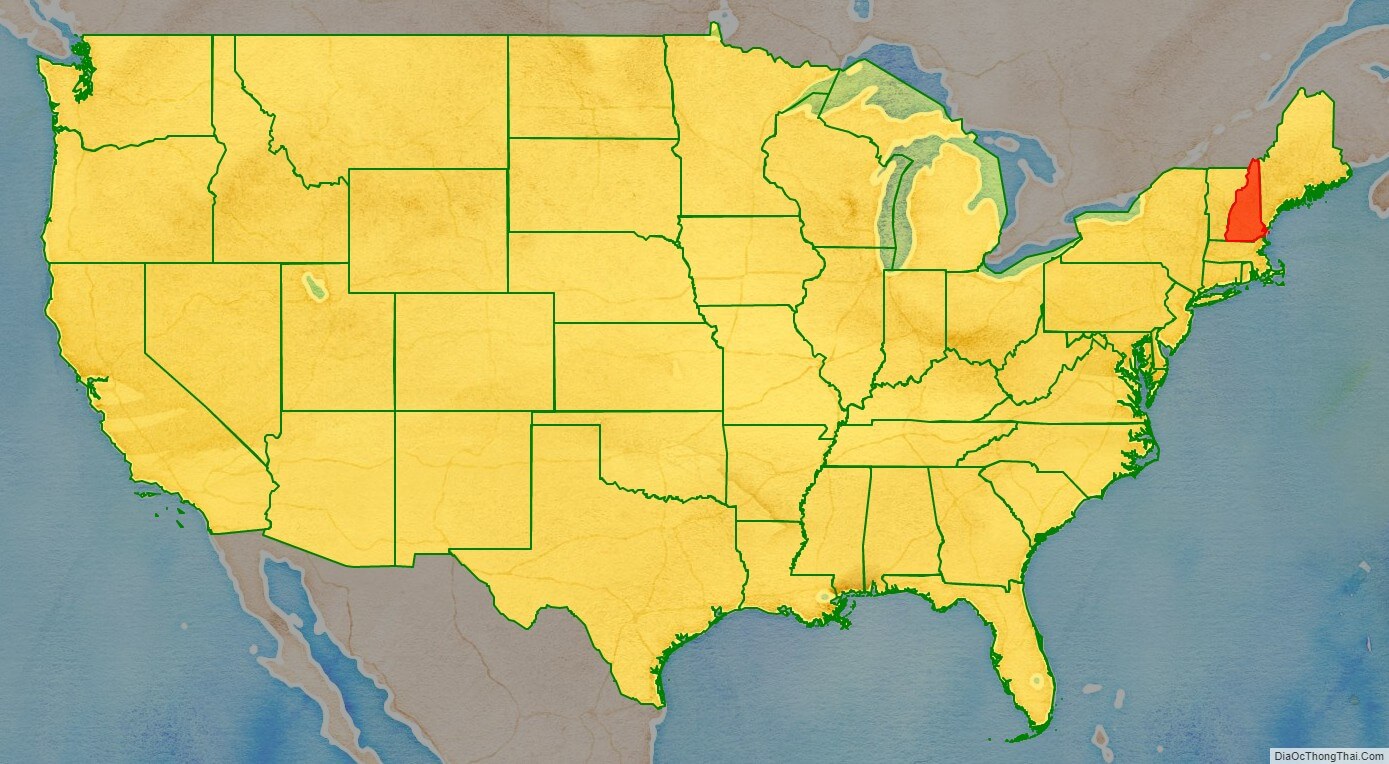
New Hampshire location map. Where is New Hampshire state?
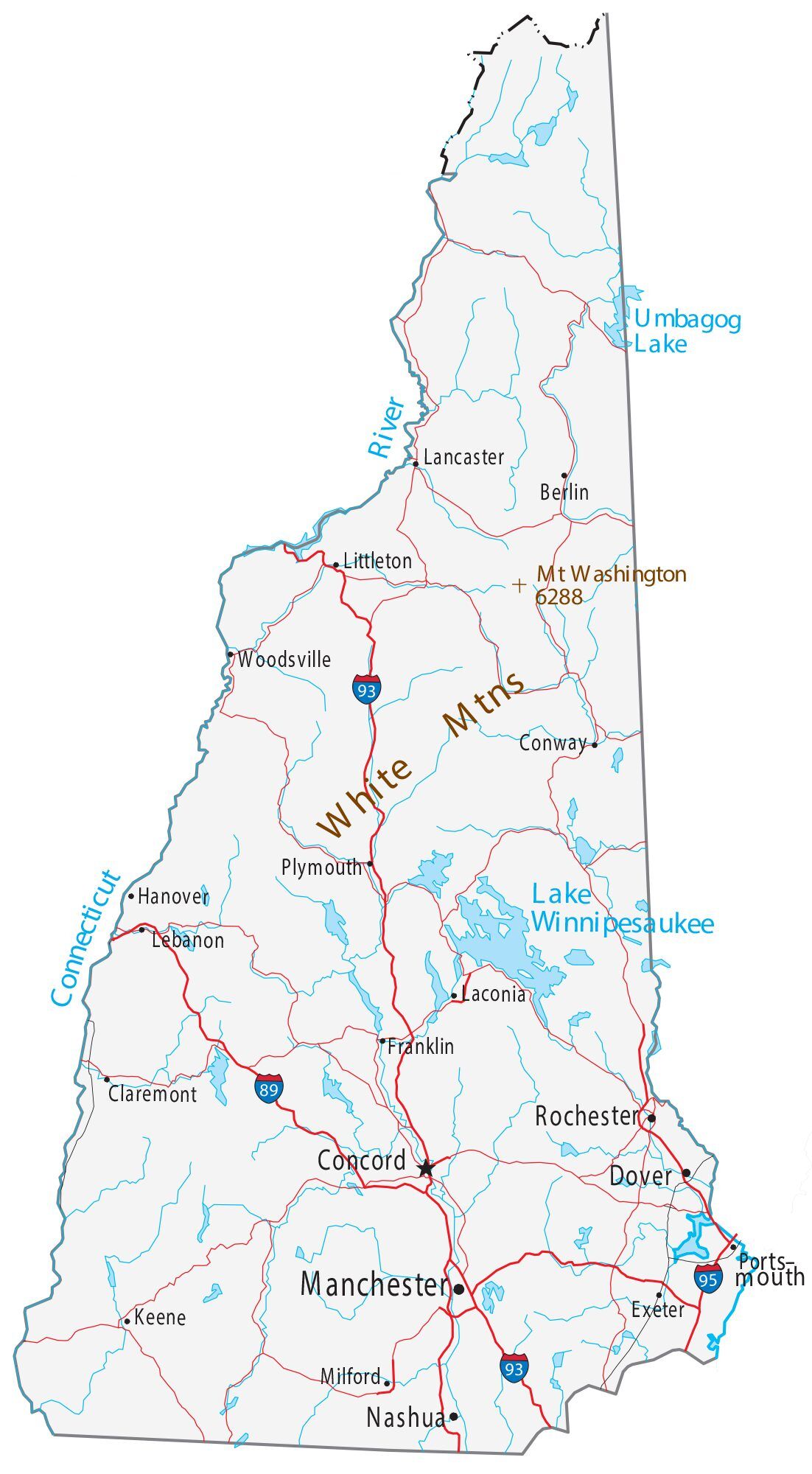
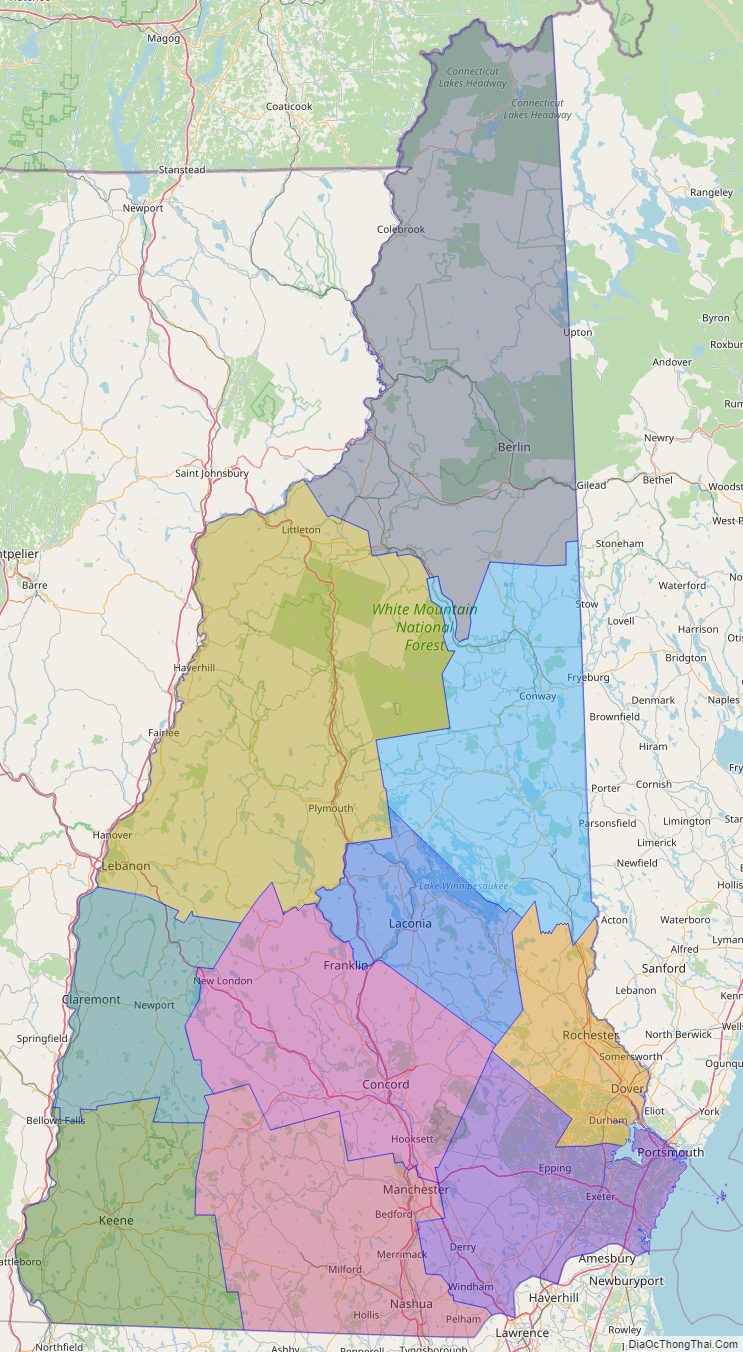
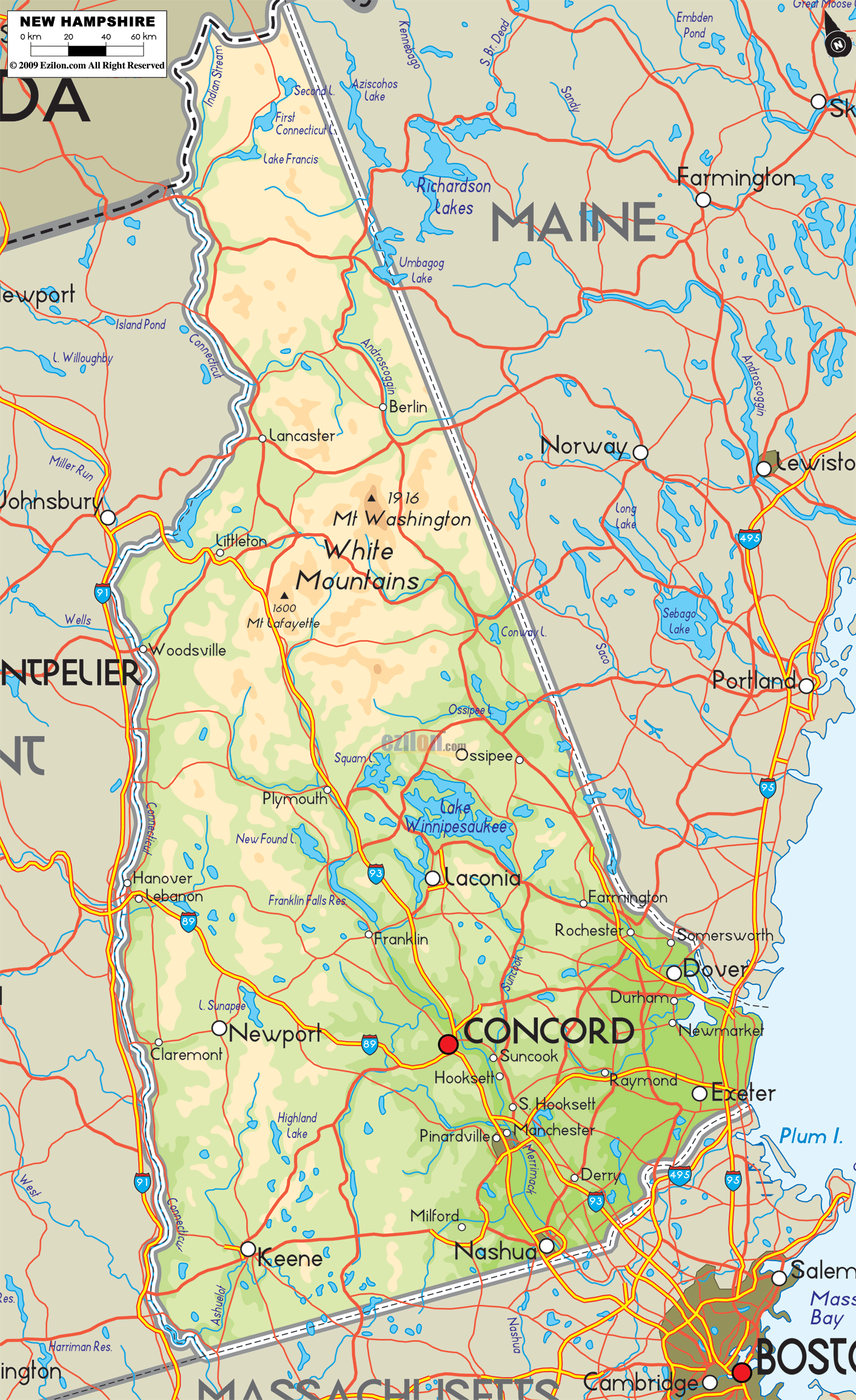
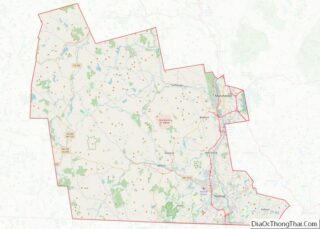
New Hampshire Road Map
New Hampshire Map – Roads & Cities
New Hampshire Street Map
History
Various Algonquian-speaking Abenaki tribes, largely divided between the Androscoggin and Pennacook nations, inhabited the area before European settlement. Despite the similar language, they had a very different culture and religion from other Algonquian peoples. English and French explorers visited New Hampshire in 1600–1605, and David Thompson settled at Odiorne’s Point in present-day Rye in 1623. The first permanent settlement was at Hilton’s Point (present-day Dover). By 1631, the Upper Plantation comprised modern-day Dover, Durham and Stratham; in 1679, it became the “Royal Province”. Father Rale’s War was fought between the colonists and the Wabanaki Confederacy throughout New Hampshire.
New Hampshire was one of the Thirteen Colonies that rebelled against British rule during the American Revolution. By the time of the American Revolution, New Hampshire was a divided province. The economic and social life of the Seacoast region revolved around sawmills, shipyards, merchants’ warehouses, and established village and town centers. Wealthy merchants built substantial homes, furnished them with the finest luxuries, and invested their capital in trade and land speculation. At the other end of the social scale, there developed a permanent class of day laborers, mariners, indentured servants and even slaves.
The only battle fought in New Hampshire was the raid on Fort William and Mary, December 14, 1774, in Portsmouth Harbor, which netted the rebellion sizable quantities of gunpowder, small arms, and cannon over the course of two nights. (General Sullivan, leader of the raid, described it as “remainder of the powder, the small arms, bayonets, and cartouche-boxes, together with the cannon and ordnance stores”.) This raid was preceded by a warning to local patriots the previous day, by Paul Revere on December 13, 1774, that the fort was to be reinforced by troops sailing from Boston. According to unverified accounts, the gunpowder was later used at the Battle of Bunker Hill, transported there by Major Demerit, who was one of several New Hampshire patriots who stored the powder in their homes until it was transported elsewhere for use in revolutionary activities. During the raid, the British soldiers fired upon the rebels with cannon and muskets. Although there were apparently no casualties, these were among the first shots in the American Revolutionary period, occurring approximately five months before the Battles of Lexington and Concord. On January 5, 1776, New Hampshire became the first colony to declare independence from Great Britain, almost six months before the Declaration of Independence was signed by the Continental Congress.
The United States Constitution was ratified by New Hampshire on June 21, 1788, when New Hampshire became the ninth state to do so.
New Hampshire was a Jacksonian stronghold; the state sent Franklin Pierce to the White House in the election of 1852. Industrialization took the form of numerous textile mills, which in turn attracted large flows of immigrants from Quebec (the “French Canadians”) and Ireland. The northern parts of the state produced lumber, and the mountains provided tourist attractions. After 1960, the textile industry collapsed, but the economy rebounded as a center of high technology and as a service provider.
Starting in 1952, New Hampshire gained national and international attention for its presidential primary held early in every presidential election year. It immediately became the most important testing ground for candidates for the Republican and Democratic nominations. The media gave New Hampshire and Iowa about half of all the attention paid to all states in the primary process, magnifying the state’s decision powers and spurring repeated efforts by out-of-state politicians to change the rules.
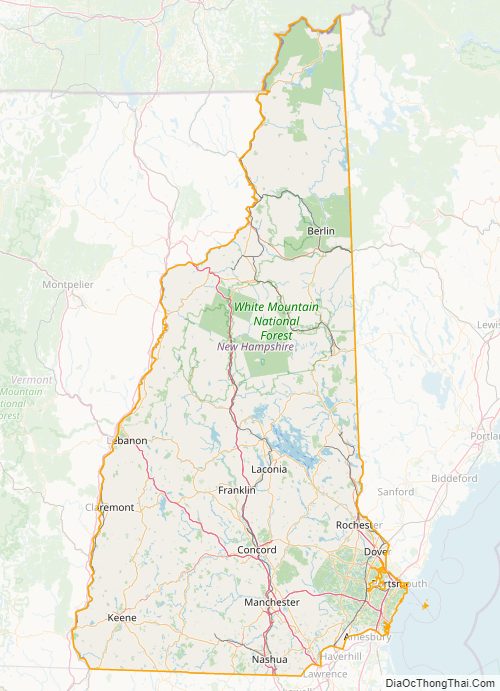
New Hampshire State Map – Places and Landmarks
New Hampshire Political Map
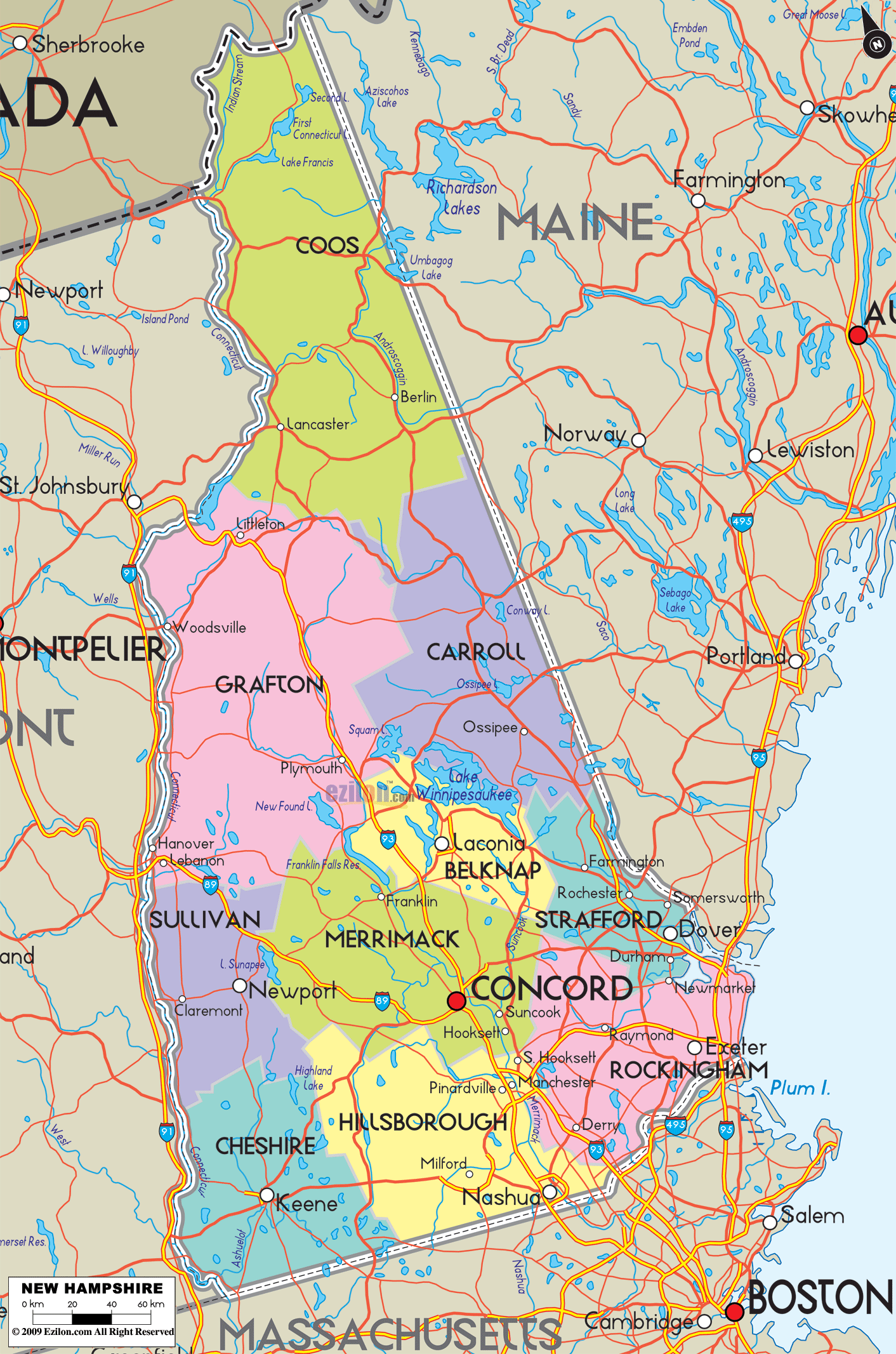
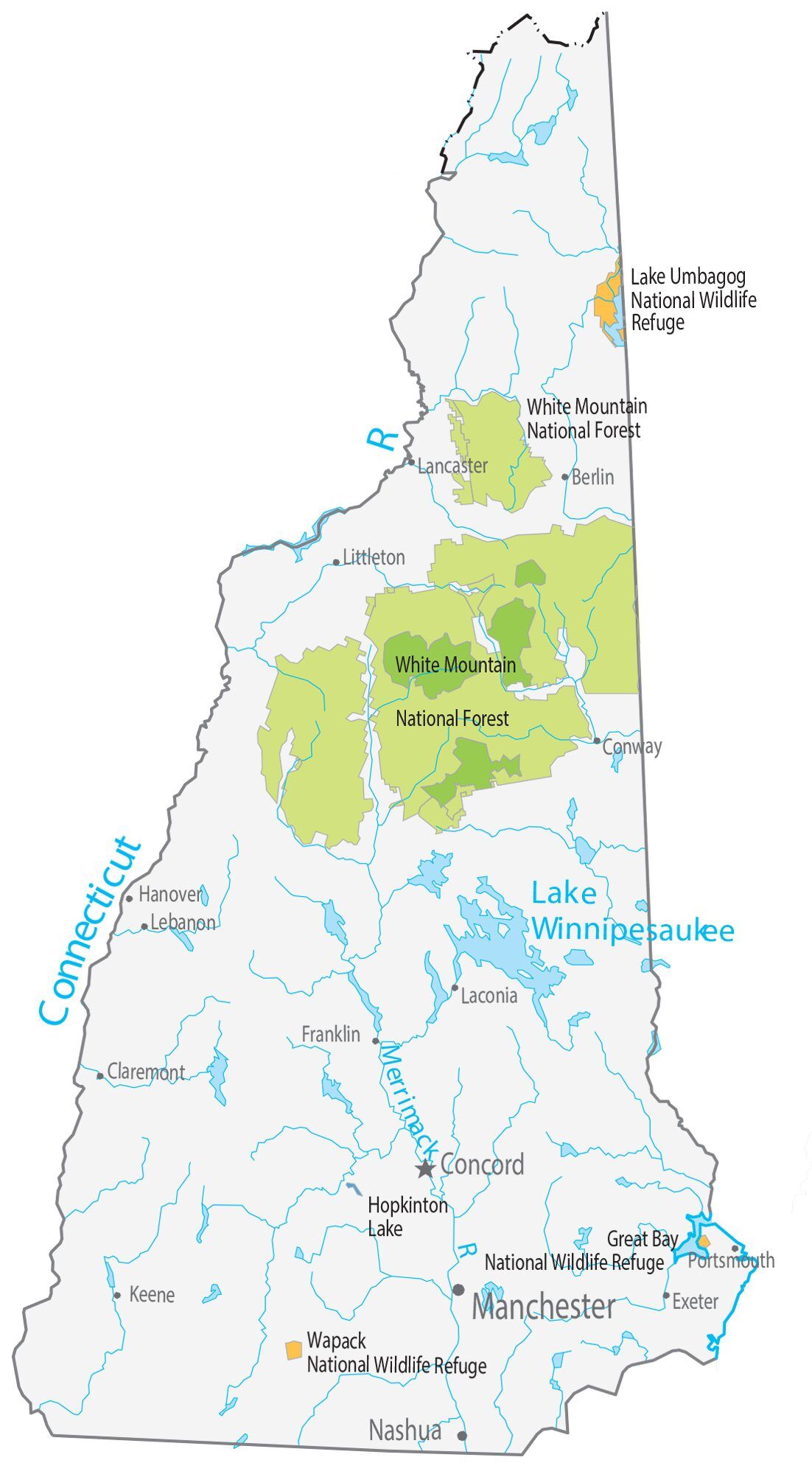
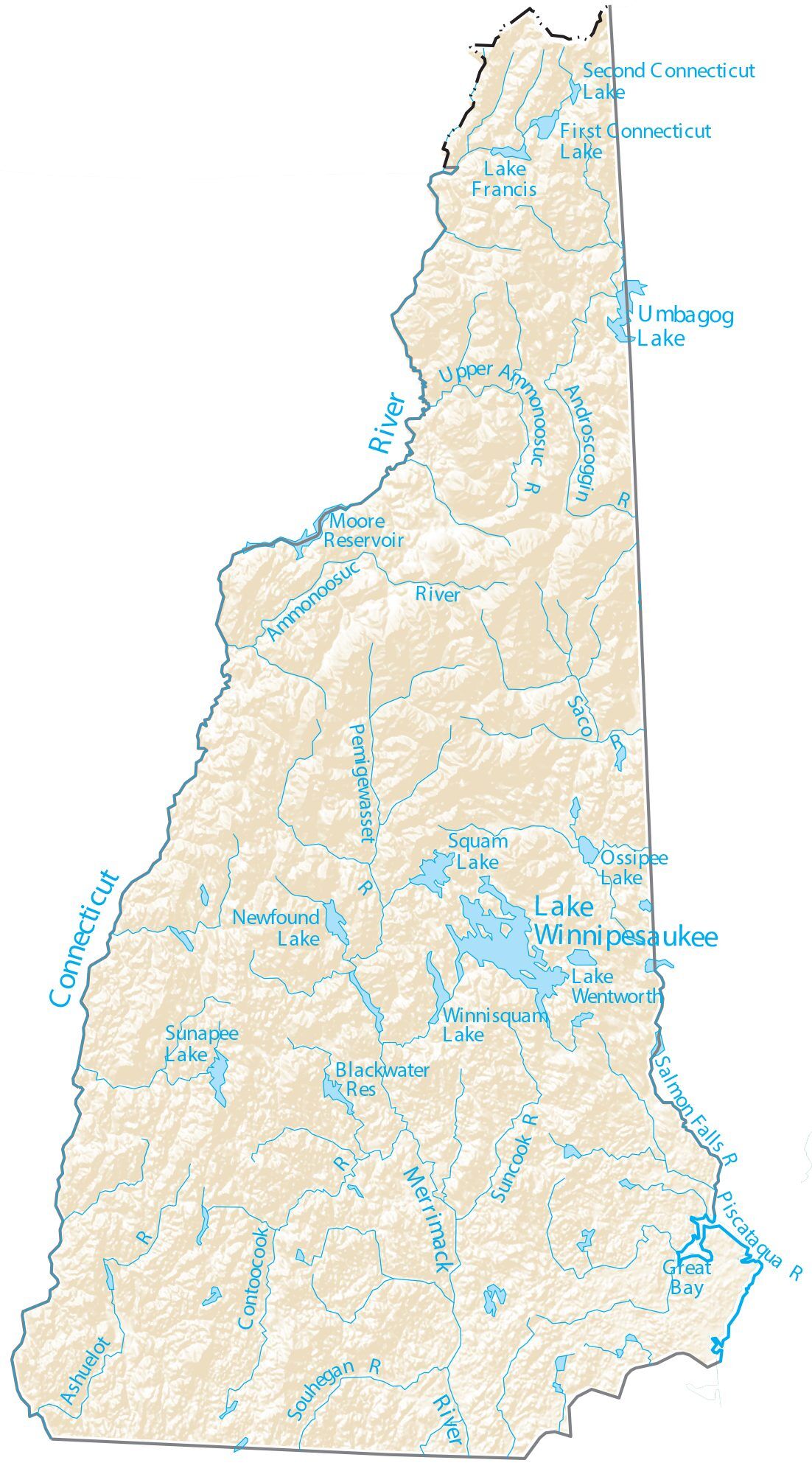
New Hampshire Lakes and Rivers Map
Geography
New Hampshire is part of the six-state New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bounded by Quebec, Canada, to the north and northwest; Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east; Massachusetts to the south; and Vermont to the west. New Hampshire’s major regions are the Great North Woods, the White Mountains, the Lakes Region, the Seacoast, the Merrimack Valley, the Monadnock Region, and the Dartmouth-Lake Sunapee area. New Hampshire has the shortest ocean coastline of any U.S. coastal state, with a length of 18 miles (29 km), sometimes measured as only 13 miles (21 km).
The White Mountains range in New Hampshire spans the north-central portion of the state. The range includes Mount Washington, the tallest in the northeastern U.S.—site of the second-highest wind speed ever recorded— as well as Mount Adams and Mount Jefferson. With hurricane-force winds every third day on average, more than a hundred recorded deaths among visitors, and conspicuous krumholtz (dwarf, matted trees much like a carpet of bonsai trees), the climate on the upper reaches of Mount Washington has inspired the weather observatory on the peak to claim that the area has the “World’s Worst Weather”. The White Mountains were home to the rock formation called the Old Man of the Mountain, a face-like profile in Franconia Notch, until the formation disintegrated in May 2003. Even after its loss, the Old Man remains an enduring symbol for the state, seen on state highway signs, automobile license plates, and many government and private entities around New Hampshire.
In southwestern New Hampshire, the landmark Mount Monadnock has given its name to a class of earth-forms—a monadnock—signifying, in geomorphology, any isolated resistant peak rising from a less resistant eroded plain.
Major rivers include the 110-mile (177 km) Merrimack River, which bisects the lower half of the state north–south before passing into Massachusetts and reaching the sea in Newburyport. Its tributaries include the Contoocook River, Pemigewasset River, and Winnipesaukee River. The 410-mile (660 km) Connecticut River, which starts at New Hampshire’s Connecticut Lakes and flows south to Connecticut, defines the western border with Vermont. The state border is not in the center of that river, as is usually the case, but at the low-water mark on the Vermont side; meaning the entire river along the Vermont border (save for areas where the water level has been raised by a dam) lies within New Hampshire. Only one town—Pittsburg—shares a land border with the state of Vermont. The “northwesternmost headwaters” of the Connecticut also define the part of Canada–U.S. border.
The Piscataqua River and its several tributaries form the state’s only significant ocean port where they flow into the Atlantic at Portsmouth. The Salmon Falls River and the Piscataqua define the southern portion of the border with Maine. The Piscataqua River boundary was the subject of a border dispute between New Hampshire and Maine in 2001, with New Hampshire claiming dominion over several islands (primarily Seavey’s Island) that include the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard. The U.S. Supreme Court dismissed the case in 2002, leaving ownership of the island with Maine. New Hampshire still claims sovereignty of the base, however.
The largest of New Hampshire’s lakes is Lake Winnipesaukee, which covers 71 square miles (184 km) in the east-central part of New Hampshire. Umbagog Lake along the Maine border, approximately 12.3 square miles (31.9 km), is a distant second. Squam Lake is the second largest lake entirely in New Hampshire.
New Hampshire has the shortest ocean coastline of any state in the United States, approximately 18 miles (29 km) long. Hampton Beach is a popular local summer destination. About 7 miles (11 km) offshore are the Isles of Shoals, nine small islands (four of which are in New Hampshire) known as the site of a 19th-century art colony founded by poet Celia Thaxter, and the alleged location of one of the buried treasures of the pirate Blackbeard.
It is the state with the highest percentage of timberland area in the country. New Hampshire is in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome. Much of the state, in particular the White Mountains, is covered by the conifers and northern hardwoods of the New England-Acadian forests. The southeast corner of the state and parts of the Connecticut River along the Vermont border are covered by the mixed oaks of the Northeastern coastal forests. The state’s numerous forests are popular among autumnal leaf peepers seeking the brilliant foliage of the numerous deciduous trees.
The northern third of the state is locally referred to as the “north country” or “north of the notches”, in reference to the White Mountain passes that channel traffic. It contains less than 5% of the state’s population, suffers relatively high poverty, and is steadily losing population as the logging and paper industries decline. However, the tourist industry, in particular visitors who go to northern New Hampshire to ski, snowboard, hike and mountain bike, has helped offset economic losses from mill closures.
Environmental protection emerged as a key state issue in the early 1900s in response to poor logging practices. In the 1970s, activists defeated a proposal to build an oil refinery along the coast and limited plans for a full-width interstate highway through Franconia Notch to a parkway.
Winter season lengths are projected to decline at ski areas across New Hampshire due to the effects of climate change, which is likely to continue the historic contraction and consolidation of the ski industry and threaten individual ski businesses and communities that rely on ski tourism.
Climate
New Hampshire experiences a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfa in some southern areas, Dfb in most of the state, and Dfc subarctic in some northern highland areas), with warm, humid summers, and long, cold, and snowy winters. Precipitation is fairly evenly distributed all year. The climate of the southeastern portion is moderated by the Atlantic Ocean and averages relatively milder winters (for New Hampshire), while the northern and interior portions experience colder temperatures and lower humidity. Winters are cold and snowy throughout the state, and especially severe in the northern and mountainous areas. Average annual snowfall ranges from 60 inches (150 cm) to over 100 inches (250 cm) across the state.
Average daytime highs are in the mid 70s°F to low 80s°F (24–28 °C) throughout the state in July, with overnight lows in the mid 50s°F to low 60s°F (13–15 °C). January temperatures range from an average high of 34 °F (1 °C) on the coast to overnight lows below 0 °F (−18 °C) in the far north and at high elevations. Average annual precipitation statewide is roughly 40 inches (100 cm) with some variation occurring in the White Mountains due to differences in elevation and annual snowfall. New Hampshire’s highest recorded temperature was 106 °F (41 °C) in Nashua on July 4, 1911, while the lowest recorded temperature was −47 °F (−44 °C) atop Mount Washington on January 29, 1934. Mount Washington also saw an unofficial −50 °F (−46 °C) reading on January 22, 1885, which, if made official, would tie the record low for New England (also −50 °F (−46 °C) at Big Black River, Maine, on January 16, 2009, and Bloomfield, Vermont on December 30, 1933).
Extreme snow is often associated with a nor’easter, such as the Blizzard of ’78 and the Blizzard of 1993, when several feet accumulated across portions of the state over 24 to 48 hours. Lighter snowfalls of several inches occur frequently throughout winter, often associated with an Alberta Clipper.
New Hampshire, on occasion, is affected by hurricanes and tropical storms—although, by the time they reach the state, they are often extratropical—with most storms striking the southern New England coastline and moving inland or passing by offshore in the Gulf of Maine. Most of New Hampshire averages fewer than 20 days of thunderstorms per year and an average of two tornadoes occur annually statewide.
The National Arbor Day Foundation plant hardiness zone map depicts zones 3, 4, 5, and 6 occurring throughout the state and indicates the transition from a relatively cooler to warmer climate as one travels southward across New Hampshire. The 1990 USDA plant hardiness zones for New Hampshire range from zone 3b in the north to zone 5b in the south.
Metropolitan areas
Metropolitan areas in the New England region are defined by the U.S. Census Bureau as New England City and Town Areas (NECTAs). The following is a list of NECTAs fully or partially in New Hampshire:
- Berlin
- Boston–Cambridge–Nashua
- Haverhill–Newburyport–Amesbury Town NECTA Division
- Lawrence–Methuen Town–Salem NECTA Division
- Lowell–Billerica–Chelmsford NECTA Division
- Nashua NECTA Division
- Claremont
- Concord
- Dover–Durham
- Franklin
- Keene
- Laconia
- Lebanon
- Manchester
- Portsmouth
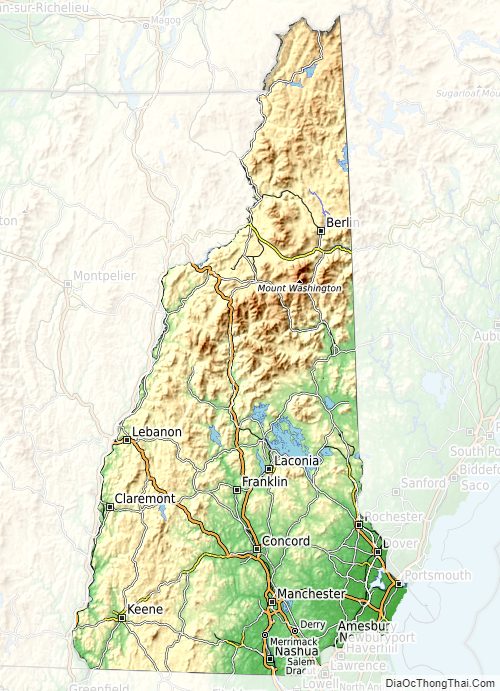
New Hampshire Physical Map
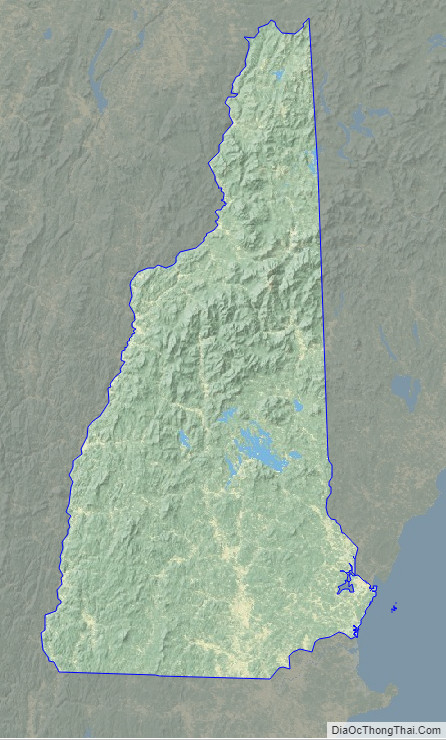
New Hampshire Topographic Map
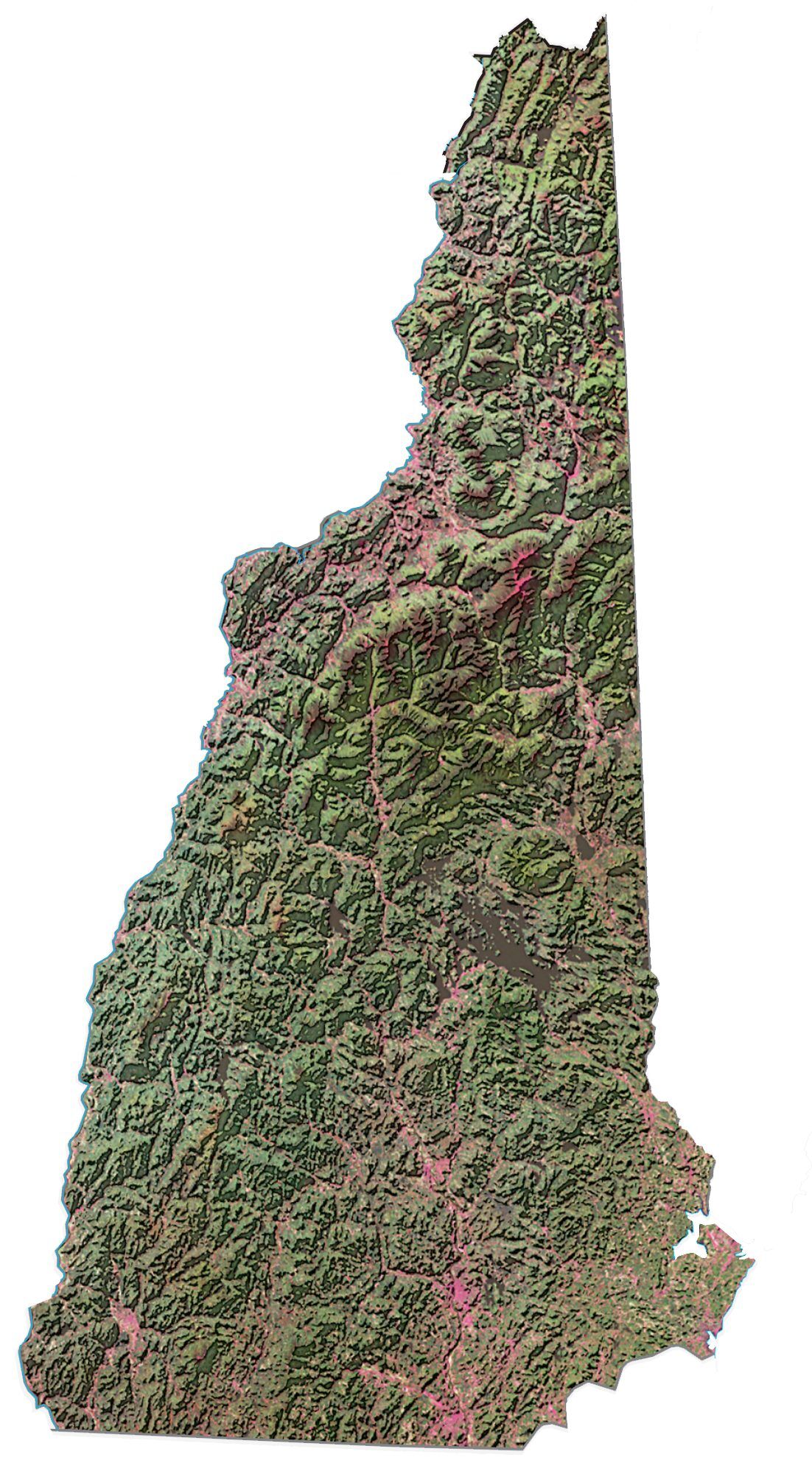
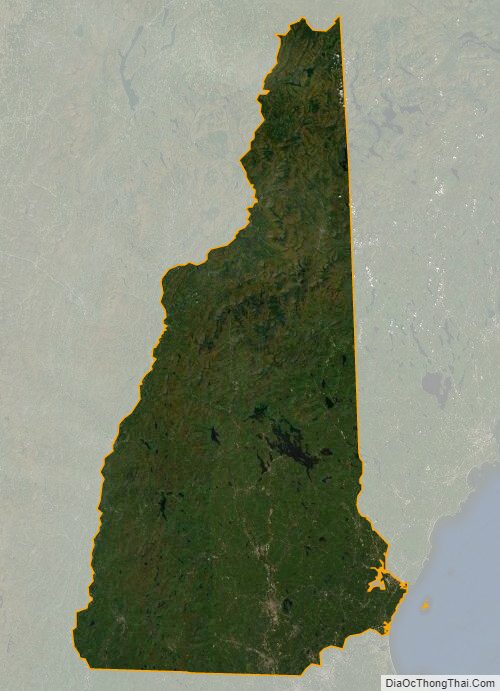
New Hampshire Satellite Map
Others printable maps
New Hampshire Outline Map
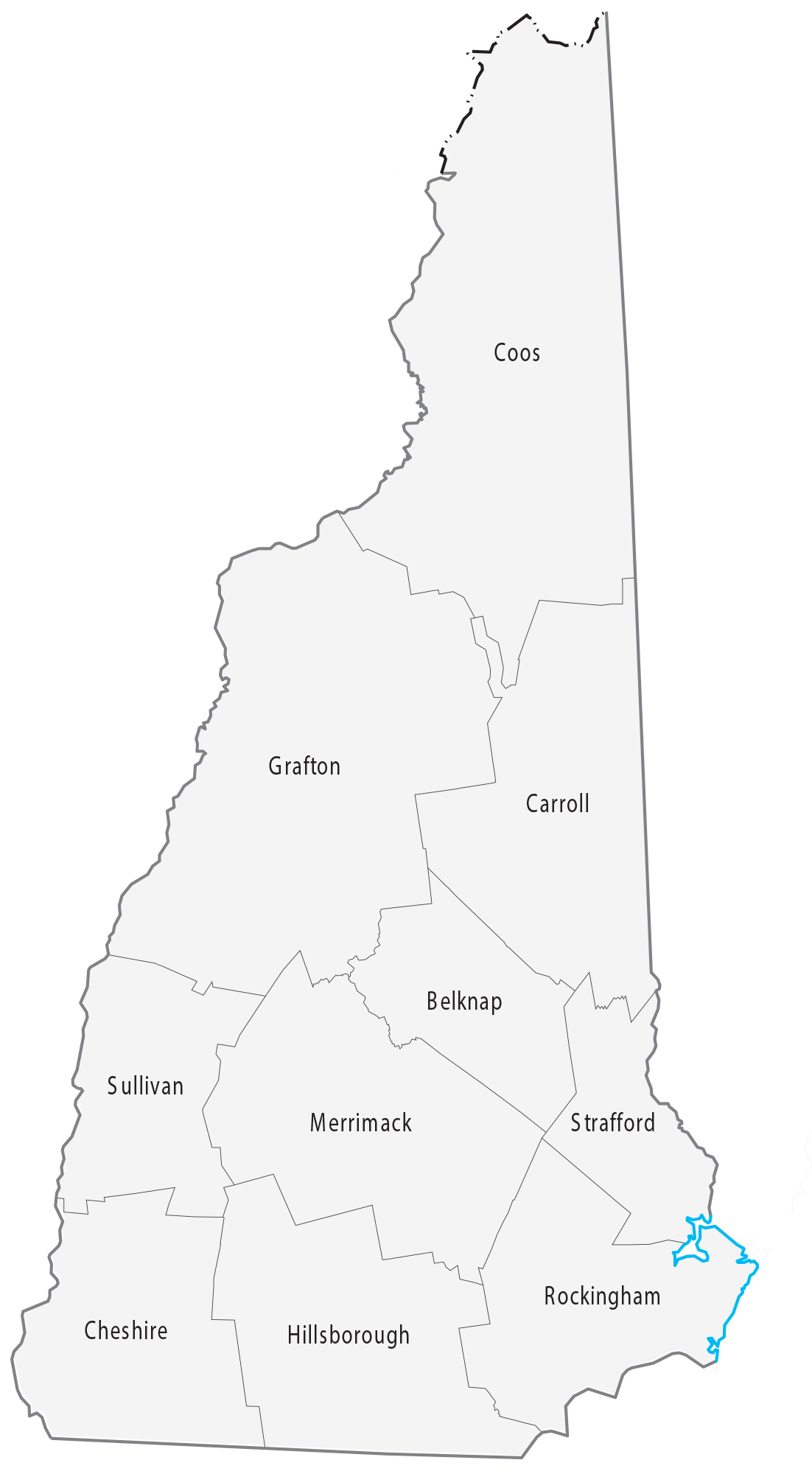
Blank New Hampshire County Map
See also
Map of New Hampshire State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming