Newton is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. It is approximately 7 miles (11 km) west of downtown Boston. Newton resembles a patchwork of thirteen villages, without a city center. At the 2020 U.S. census, the population of Newton was 88,923.
| Name: | Newton city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Massachusetts |
| County: | Middlesex County |
| Elevation: | 100 ft (30 m) |
| Total Area: | 18.16 sq mi (47.03 km²) |
| Land Area: | 17.83 sq mi (46.17 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.33 sq mi (0.86 km²) |
| Total Population: | 88,923 |
| Population Density: | 4,987.83/sq mi (1,925.84/km²) |
| Area code: | 617/857 |
| FIPS code: | 2545560 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0617675 |
| Website: | www.newtonma.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Newton location map. Where is Newton city?
History
Newton was settled in 1630 as part of “the newe towne”, which was renamed Cambridge in 1638. Roxbury minister John Eliot persuaded the Native American people of Nonantum, a sub-tribe of the Massachusett led by a sachem named Waban, to relocate to Natick in 1651, fearing that they would be exploited by colonists. Newton was incorporated as a separate town, known as Cambridge Village, on December 15, 1681, then renamed Newtown in 1691, and finally Newton in 1766. It became a city on January 5, 1874. Newton is known as The Garden City.
In Reflections in Bullough’s Pond, Newton historian Diana Muir describes the early industries that developed in the late 18th and early 19th centuries in a series of mills built to take advantage of the water power available at Newton Upper Falls and Newton Lower Falls. Snuff, chocolate, glue, paper and other products were produced in these small mills but, according to Muir, the water power available in Newton was not sufficient to turn Newton into a manufacturing city, although it was, beginning in 1902, the home of the Stanley Motor Carriage Company, the maker of the Stanley Steamer.
Newton, according to Muir, became one of America’s earliest commuter suburbs. The Boston and Worcester, one of America’s earliest railroads, reached West Newton in 1834. Wealthy Bostonian businessmen took advantage of the new commuting opportunity offered by the railroad, building gracious homes on erstwhile farmland of West Newton hill and on Commonwealth street. Muir points out that these early commuters needed sufficient wealth to employ a groom and keep horses, to drive them from their hilltop homes to the station.
Further suburbanization came in waves. One wave began with the streetcar lines that made many parts of Newton accessible for commuters in the late nineteenth century. The next wave came in the 1920s when automobiles became affordable to a growing upper middle class. Even then, however, Oak Hill continued to be farmed, mostly market gardening, until the prosperity of the 1950s made all of Newton more densely settled.
Two of the 9/11 hijackers stayed in Newton the night before the attack. The hijackers of American Airlines Flight 11 spent their last night in Newton’s Park Inn, an economy motel across the street from the Chestnut Hill Mall and within walking distance of The Atrium.
Each April on Patriots’ Day, the Boston Marathon is run through the city, entering from Wellesley on Route 16 (Washington Street) where runners encounter the first of the four infamous Newton Hills. It then turns right onto Route 30 (Commonwealth Avenue) for the long haul into Boston. There are two more hills before reaching Centre Street, and then the fourth and most noted, Heartbreak Hill, rises shortly after Centre Street. Residents and visitors line the race route along Washington Street and Commonwealth Avenue to cheer the runners.
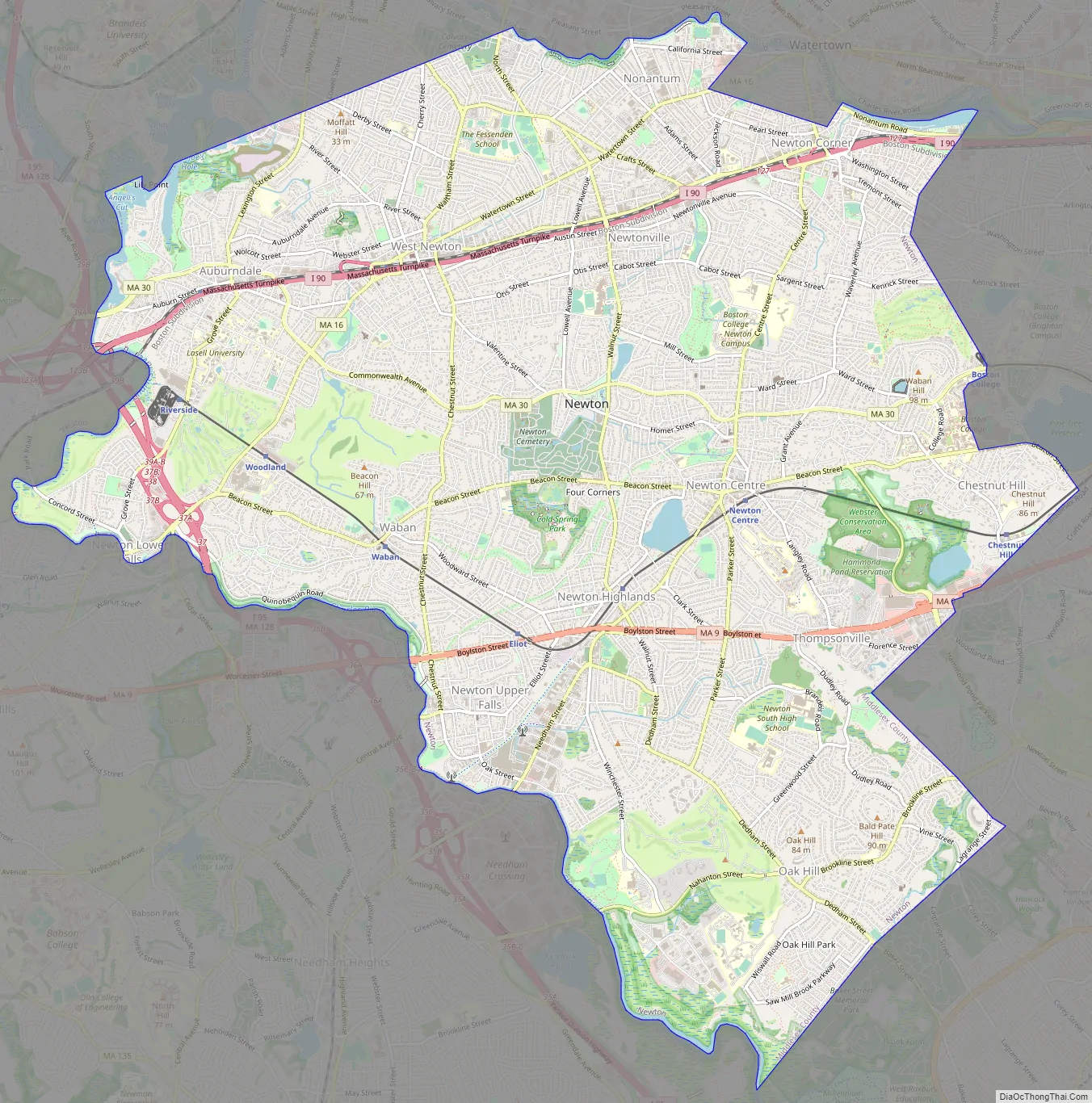
Newton Road Map
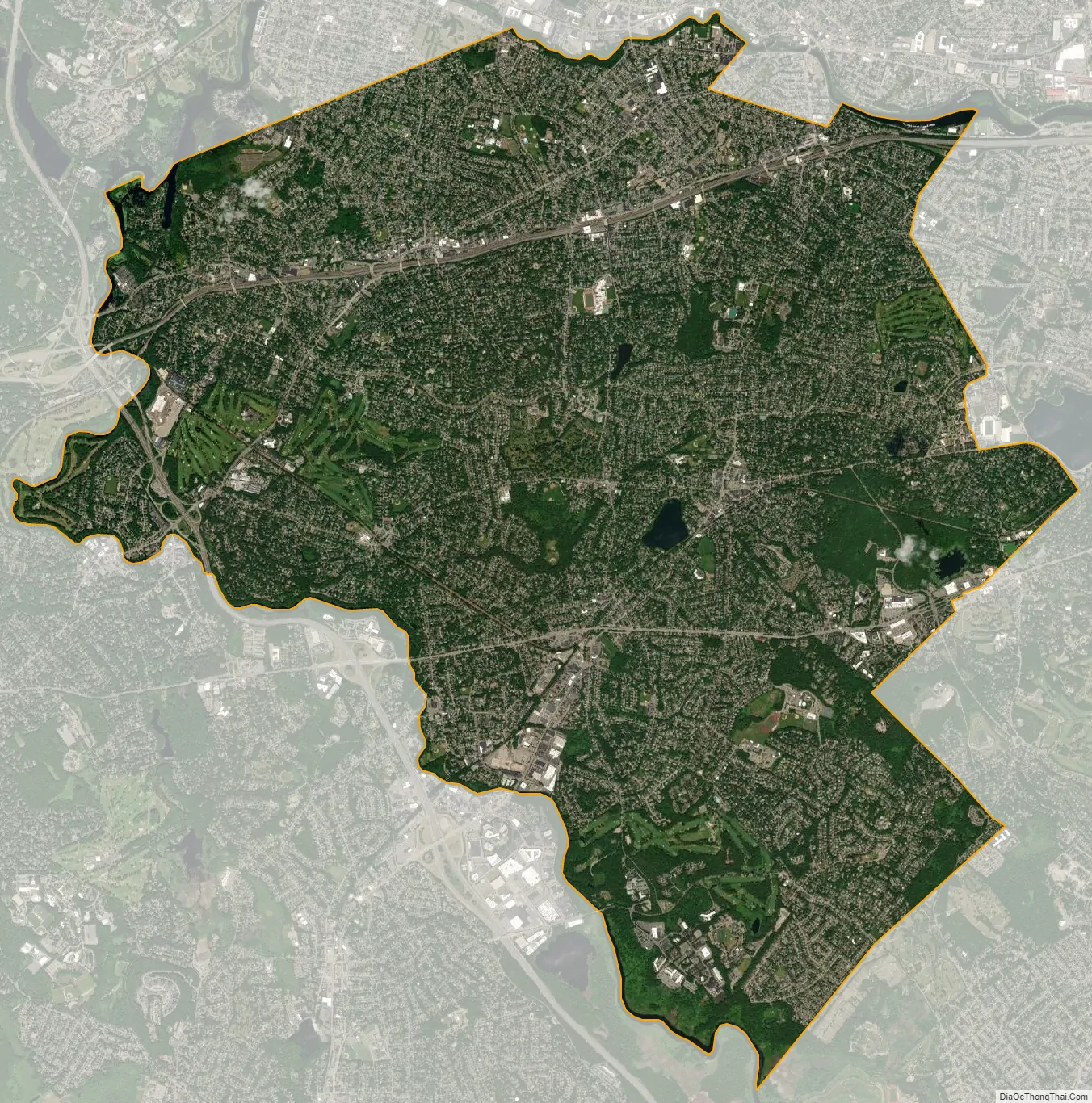
Newton city Satellite Map
Geography
Newton is a suburban city approximately 7 mi (11 km) from downtown Boston, in Middlesex County, Massachusetts. It is also bordered by Waltham and Watertown on the north, Needham and the West Roxbury neighborhood of Boston on the south, Wellesley and Weston on the west, and Brookline and the Brighton neighborhood of Boston on the east.
The Charles River flows along the north and west parts of Newton, and Route 128 passes through the west part of the city.
The Massachusetts Turnpike goes through the more urbanized northern section of the city before heading into Boston. Additional major highways in Newton include Route 9, serving the southern parts of the city, and Hammond Pond Parkway, which is the main north–south route through Chestnut Hill and provides access to Brookline and West Roxbury.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 18.2 square miles (47.1 km), of which 18.0 square miles (46.6 km) is land and 0.2 square miles (0.5 km) (0.82%) is water.
Geological history
Geologically Newton located within topographic lowland the Boston Basin of the Appalachian Mountain chain. This lowland is surrounded by a ring of highland drumlins which were left after the last glaciation twelve thousand years ago.
There are several unique outcroppings of rocks around Newton where geologic history revealing of how territory have formed and has changed over the past hundreds millions of years of drift supercontinents and ancient oceans, earthquake activity associated with volcanism and related faulting activity and changing climate. There are mainly three types of bedrock: Roxbury Conglomerate, Cambridge Argillite or Slate, and Brighton Volcanics and the Mattapan Volcanics pre-Cambrian foundation of Dedham Granodiorite. The Boston Border Fault and the Shawmut anticline of Newton formed as the alpine mountains of east-central Massachusetts were created. Unique outcroppings rocks exposure has steadily declined as Newton area has become increasingly developed.
Topography
Newton has grown around a formation of seven hills. “The general features of Newton are not without interest. Seven principal elevations mark its surface, like the seven hills of ancient Rome, with the difference that the seven hills of Newton are much more distinct than the seven hills of Rome: Nonantum Hill, Waban Hill, Chestnut Hill, Bald Pate Hill, Oak Hill, Institution Hill and Mount Ida.”
Villages
Rather than having a single city center, Newton is a patchwork of thirteen villages, many boasting small downtown areas of their own. The 13 villages are: Auburndale, Chestnut Hill, Newton Centre, Newton Corner, Newton Highlands, Newton Lower Falls, Newton Upper Falls (both on the Charles River, and both former small industrial sites), Newtonville, Nonantum (also known as Silver Lake or “The Lake”), Oak Hill, Thompsonville, Waban and West Newton. Oak Hill Park is a place within the village of Oak Hill that itself is shown as a separate and distinct village on some city maps (including a map dated 2010 on the official City of Newton website), and Four Corners is also shown as a village on some city maps. Although most of the villages have a post office, they have no legal definition and no firmly defined borders. This village-based system often causes some confusion with addresses and for first-time visitors.
Climate
The record low temperature was −21 °F (−29 °C) in February 1934; the record high temperature was 101 °F (38 °C) in August 1975.
See also
Map of Massachusetts State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming