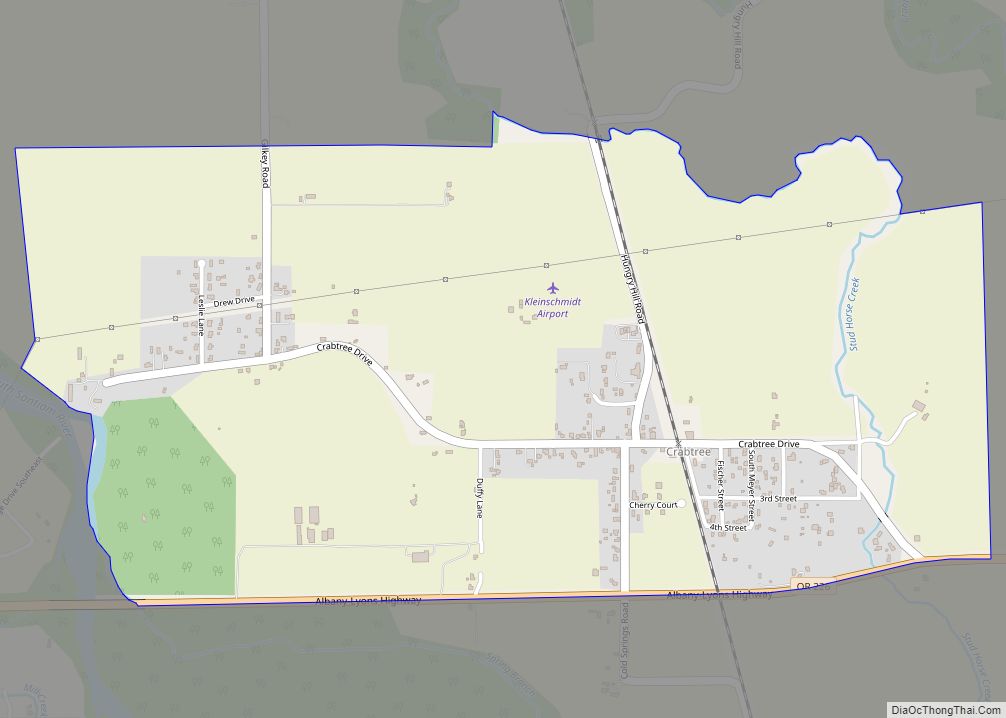
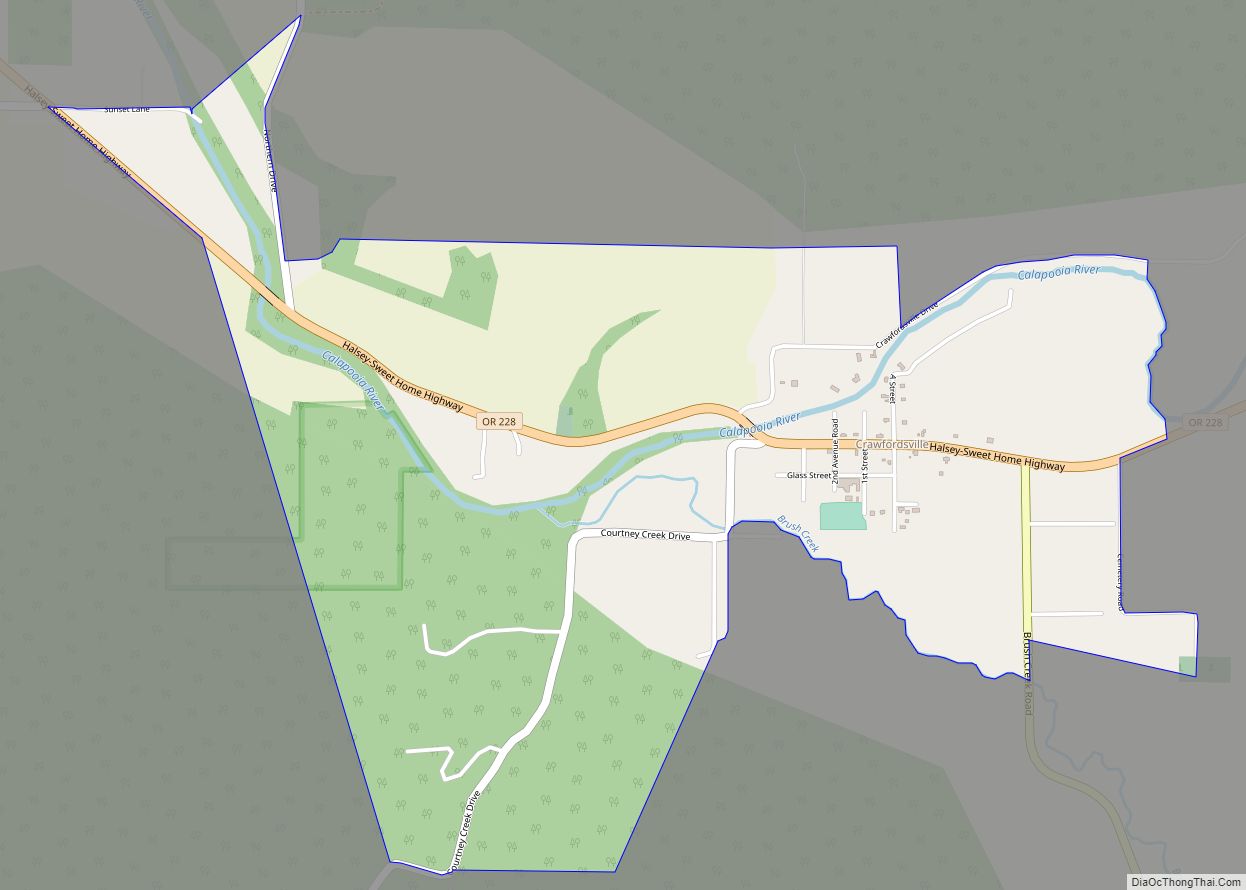
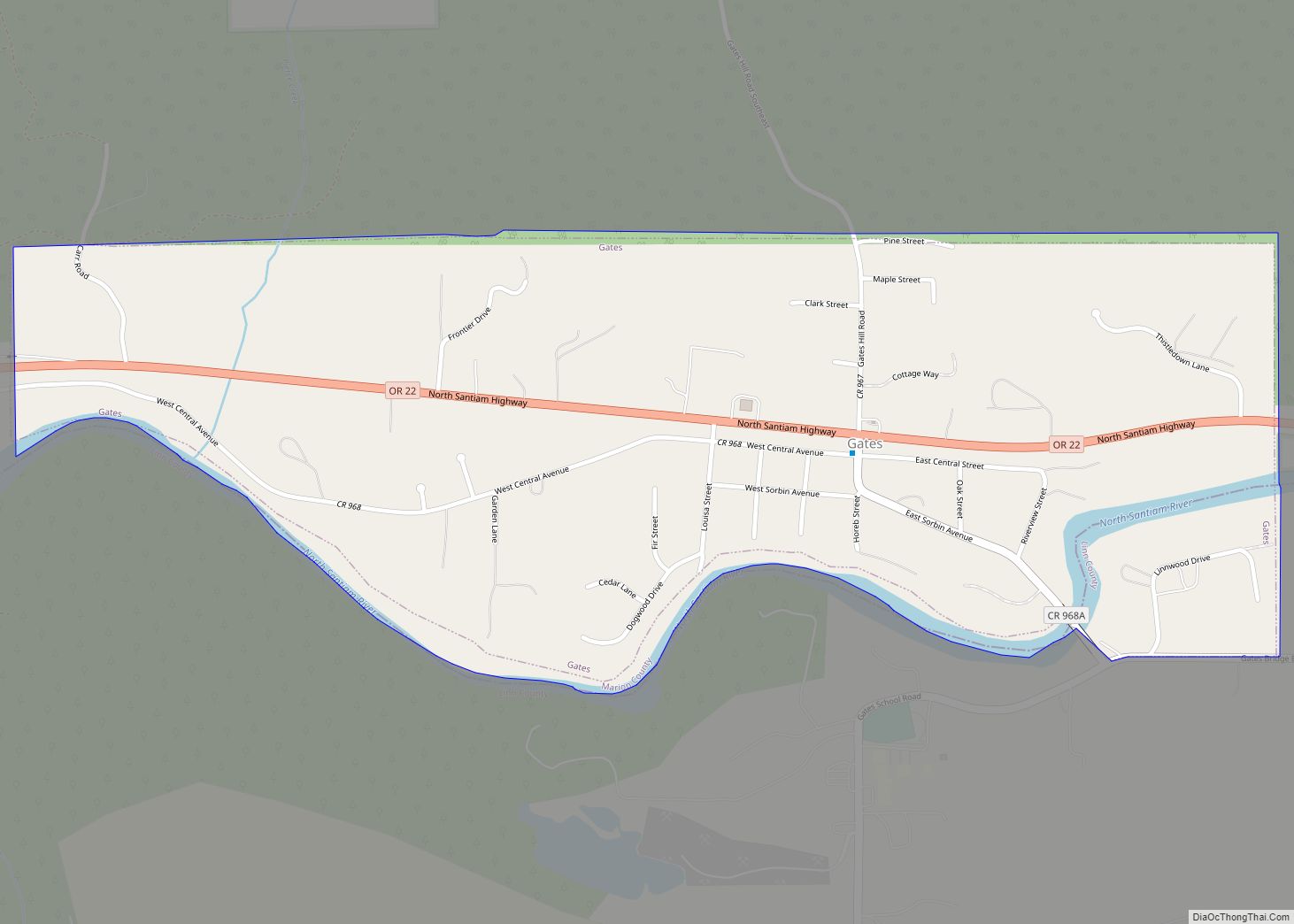
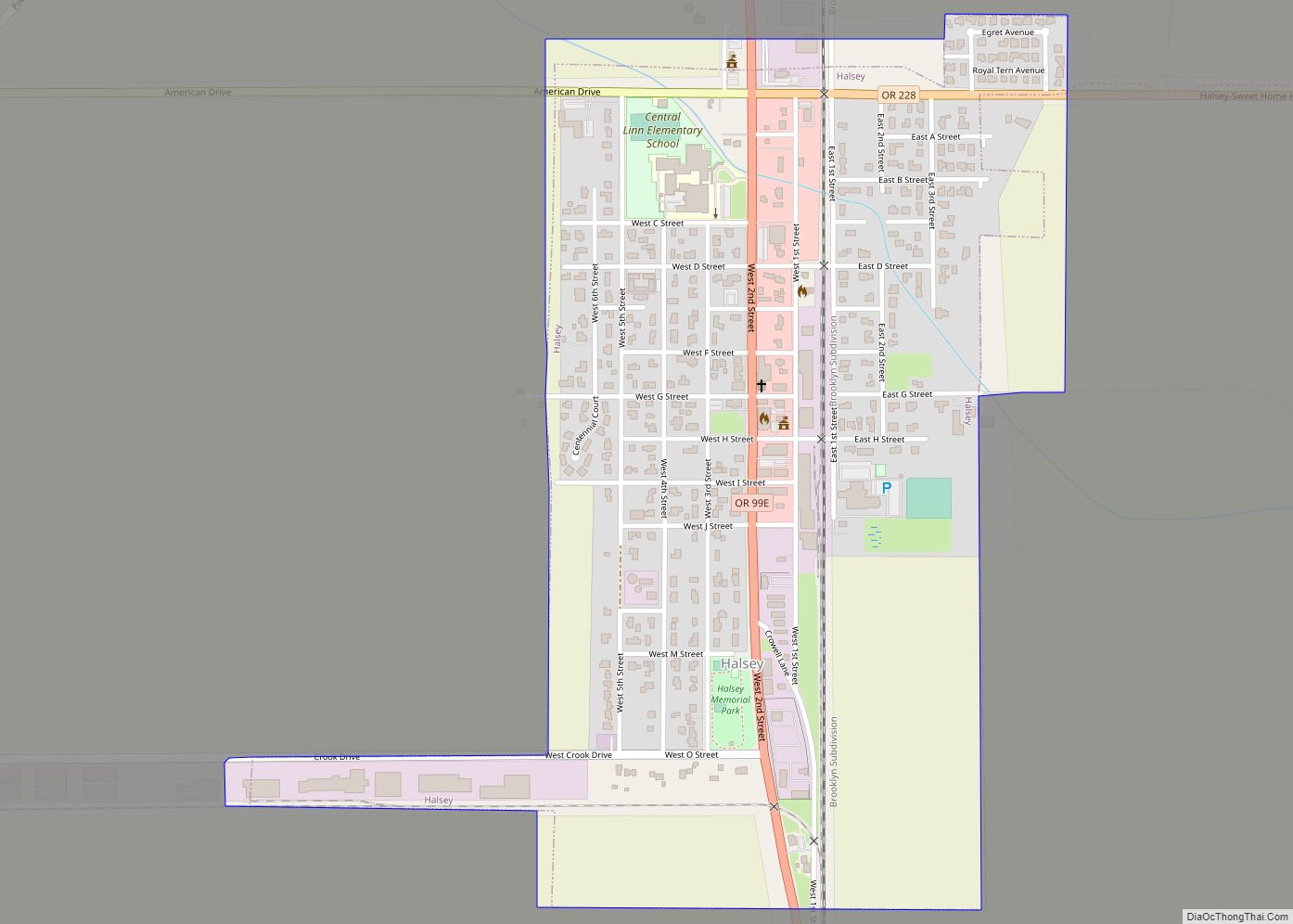
Lebanon (/ˈlɛbənən/ LEB-ən-ən) is a city in Linn County, Oregon, United States. Lebanon is located in northwest Oregon, southeast of Salem. The population was 19,690 at the 2020 census. Lebanon sits beside the South Santiam River on the eastern edge of the Willamette Valley, close to the Cascade Range and a 25-minute drive to either of the larger cities of Corvallis and Albany. Lebanon is known for its foot-and-bike trails, its waterside parks, and its small-town character.
| Name: | Lebanon city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Oregon |
| County: | Linn County |
| Incorporated: | 1878 |
| Elevation: | 351 ft (107 m) |
| Total Area: | 7.25 sq mi (18.79 km²) |
| Land Area: | 7.02 sq mi (18.19 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.23 sq mi (0.60 km²) |
| Total Population: | 19,690 |
| Population Density: | 2,626.66/sq mi (1,014.17/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 97355 |
| Area code: | 541 |
| FIPS code: | 4141650 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1136468 |
| Website: | www.ci.lebanon.or.us |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Lebanon location map. Where is Lebanon city?
History
In 1847, Jeremiah and Jemima Ralston bought a pioneers’ cabin, staked a claim, and built a log house on a low rise at what is now Ralston Park. Nearby, on today’s Main Street, they built a store. It soon became a stop for gold seekers on their way to California. A village grew up around the store, and in 1855 the couple filed a plat for the town, naming it for Jeremiah’s birthplace of Lebanon, Tennessee. They also donated land for the Santiam Academy, which the Methodist Episcopal Church operated until 1906.
Lebanon was established on the land of the Louis Band of the Santiam Kalapuya.Like other Kalapuya tribes, the Santiam had dwindled in number, from malaria and other diseases, before the Americans arrived. In 1855, the band sold the U.S. government their rights to the land and moved to a temporary reservation on a claim belonging to the Ralstons’ son, just south of their own. There the band awaited removal to the Grand Ronde Valley.
In 1859, local men in search of a way to drive cattle to central Oregon discovered the Santiam Pass. Soon Lebanon found itself on another essential trade route. Linn County stockmen incorporated the Willamette Valley and Cascade Mountain Road in 1864, and vacationers as well as stockmen came to rely on what came to be called the Santiam Wagon Road. This toll road was later replaced with U.S. Highway 20.
Transportation was often easier by water than land in the early decades of American settlement in the Willamette Valley. The South Santiam River was too shallow for large boats, so in 1872 construction began on a canal to carry barges laden with goods between Lebanon and Albany. But the water flowed too fast for upstream shipping, and the coming of the railroad curtailed downstream shipping. Today, however, the canal is still in use, running through Lebanon backyards to provide water for the people of Albany.
Railroads helped Lebanon provide its goods not only to Albany but to the world. The Albany–Lebanon Railroad, completed in 1880, was a branch of the Oregon and California Railroad’s north–south line through Albany. The Southern Pacific eventually took over these lines and, in 1910, rerouted the old Oregonian line through Lebanon.
From the 1890s on, a great variety of farming and food-processing industries flourished in the area. Eastern Oregon came to dominate in wheat growing, but Lebanon-area farmers produced orchard fruits, berries, walnuts, filberts, hops, flax, vegetables, forage crops, turkeys, mohair, honey, and flowers for florists. Lebanon had a cheese factory, a creamery, potato warehouses, a cannery, and prune and nut driers. In the 1920s, the local grass-seed industry got its start, and by the 1930s Linn County was the leading county in grass-seed production in the United States.
Lebanon’s most celebrated crop has been strawberries. By 1907, Lebanon was one of the leading strawberry-growing areas in the Willamette Valley. Lebanon’s Strawberry Festival – featuring, since 1931, “the World’s Largest Strawberry Shortcake” – has been an annual event since 1909. As of 2020, however, only one local strawberry field remains.
The local wood-products industry began to grow around 1900, which the supply of timber in the upper Midwest declined. The industry began to boom when the Oregon and Electric Railroad was completed, in 1932. New sawmills were built along the line in town as well as in the mountains. From 1937 to 1942, twenty new mills opened in the city; they made a great variety of wood products. The paper mill, which had originally made paper from wheat straw, doubled in size in 1936 to process logs that were floated down the South Santiam River. The local population swelled, and the Great Depression had little effect on the city.
In 1940, a still greater boom began. That year, Evans Products built what was purported to be the biggest plywood mill in the world. “Evansville” became a station on the Oregon and Electric line. World War II increased the demand for plywood, and women took men’s places in the mill. From 1940 to 1950, Lebanon’s population grew by 115 percent.
In 1952, the plywood plant, now called Cascade Plywood, began producing Lebanite, a hard composite board. Lebanon residents began calling themselves Lebanites. Cascade Plywood came to dominate Lebanon’s economy.
Lebanon’s economy began a slow decline in the 1970s. As overharvesting in the nearby forests made timber extraction more expensive, the mills began closing. Lebanon’s paper mill closed in 1980, the plywood mill in 1984, and the Lebanite hardwood plant in 2004. Weyerhaeuser shut down the last of the big mills in 2006 and 2007. Unemployment rocketed, and Main Street storefronts were left empty.
In the twenty-first century, the city’s economy has improved. The openings of the College of Osteopathic Medicine of the Pacific Northwest, in 2011, the Edward C. Allworth Veterans’ Home, in 2017, and Linn-Benton Community College’s HealthCare Occupations Center, in 2017, have sparked growth. Weyerhaeuser opened the state-of-the-art Santiam Lumber sawmill in 2008, only one year after closing down the old Bauman sawmill. Main Street storefronts and old houses are being renovated, and brewpubs, bakeries, and other new businesses are thriving.
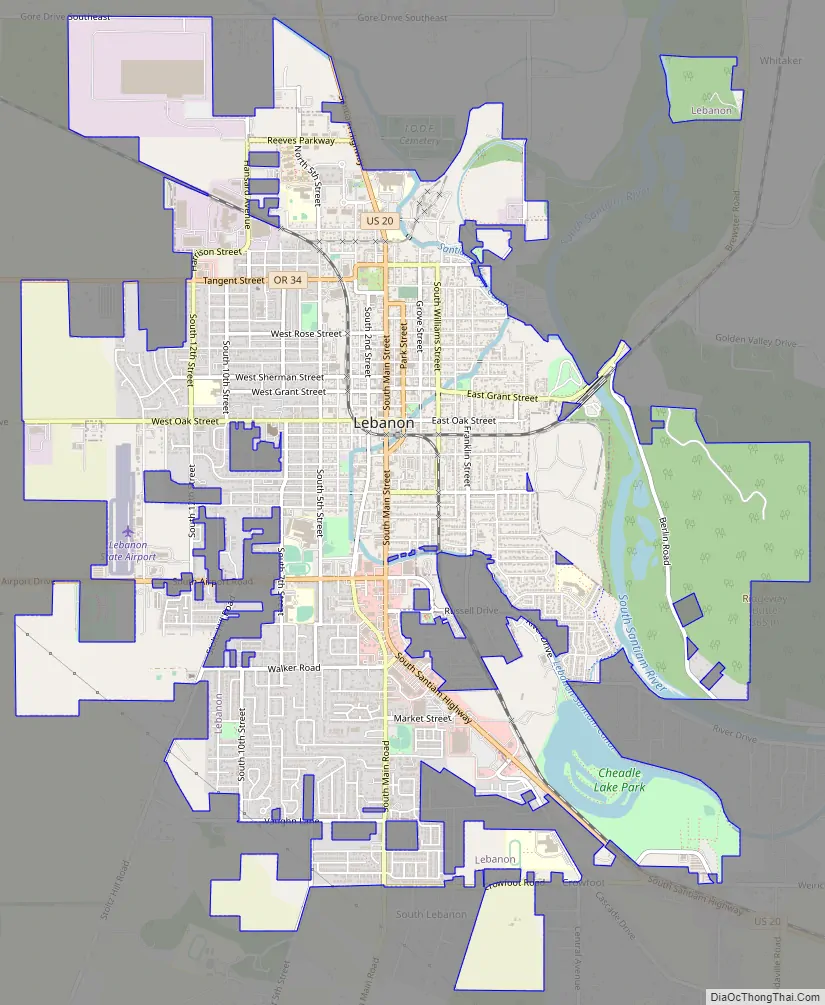
Lebanon Road Map
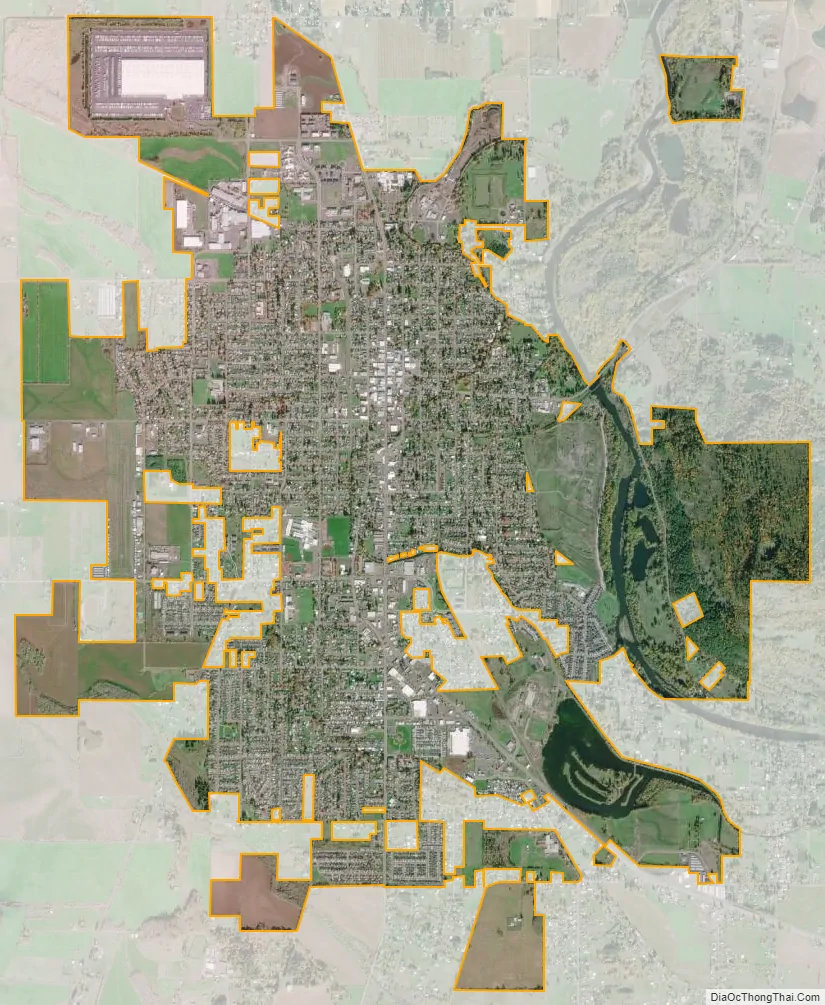
Lebanon city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 6.87 square miles (17.79 km), of which 6.67 square miles (17.28 km) is land and 0.20 square miles (0.52 km) is water.
Climate
This region experiences warm (but not hot) and dry summers, with no average monthly temperatures above 71.6 °F (22.0 °C). According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Lebanon has a warm-summer Mediterranean climate, abbreviated “Csb” on climate maps.
See also
Map of Oregon State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming