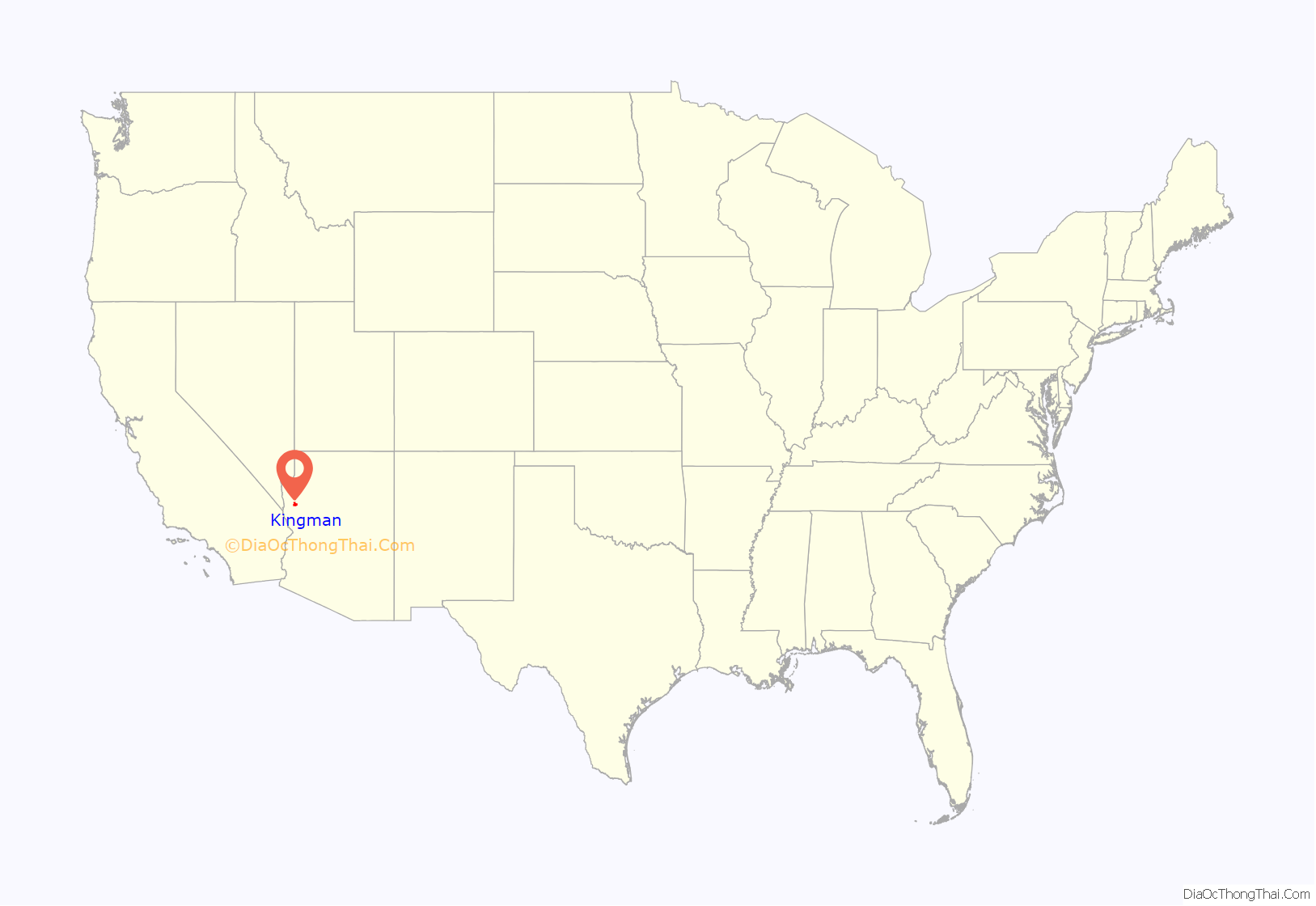
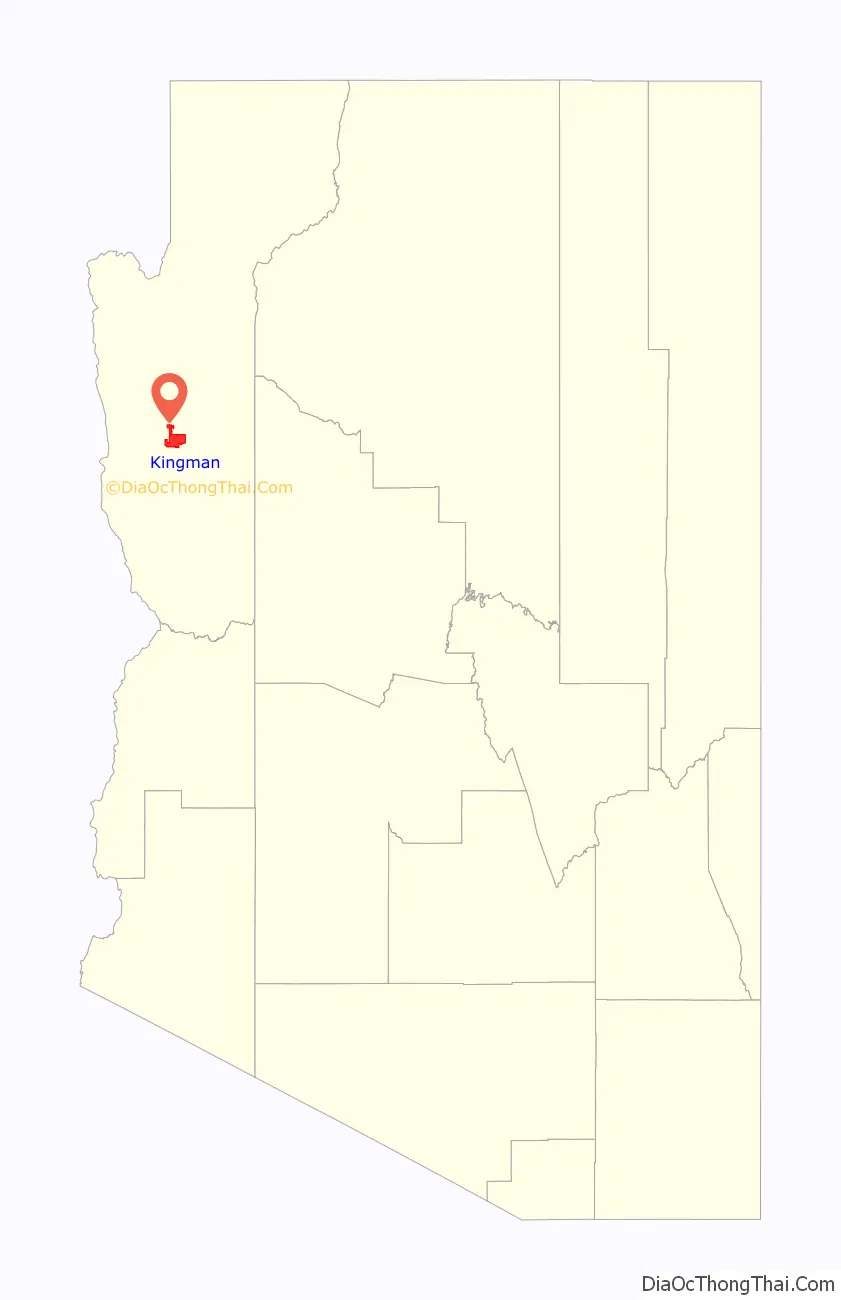
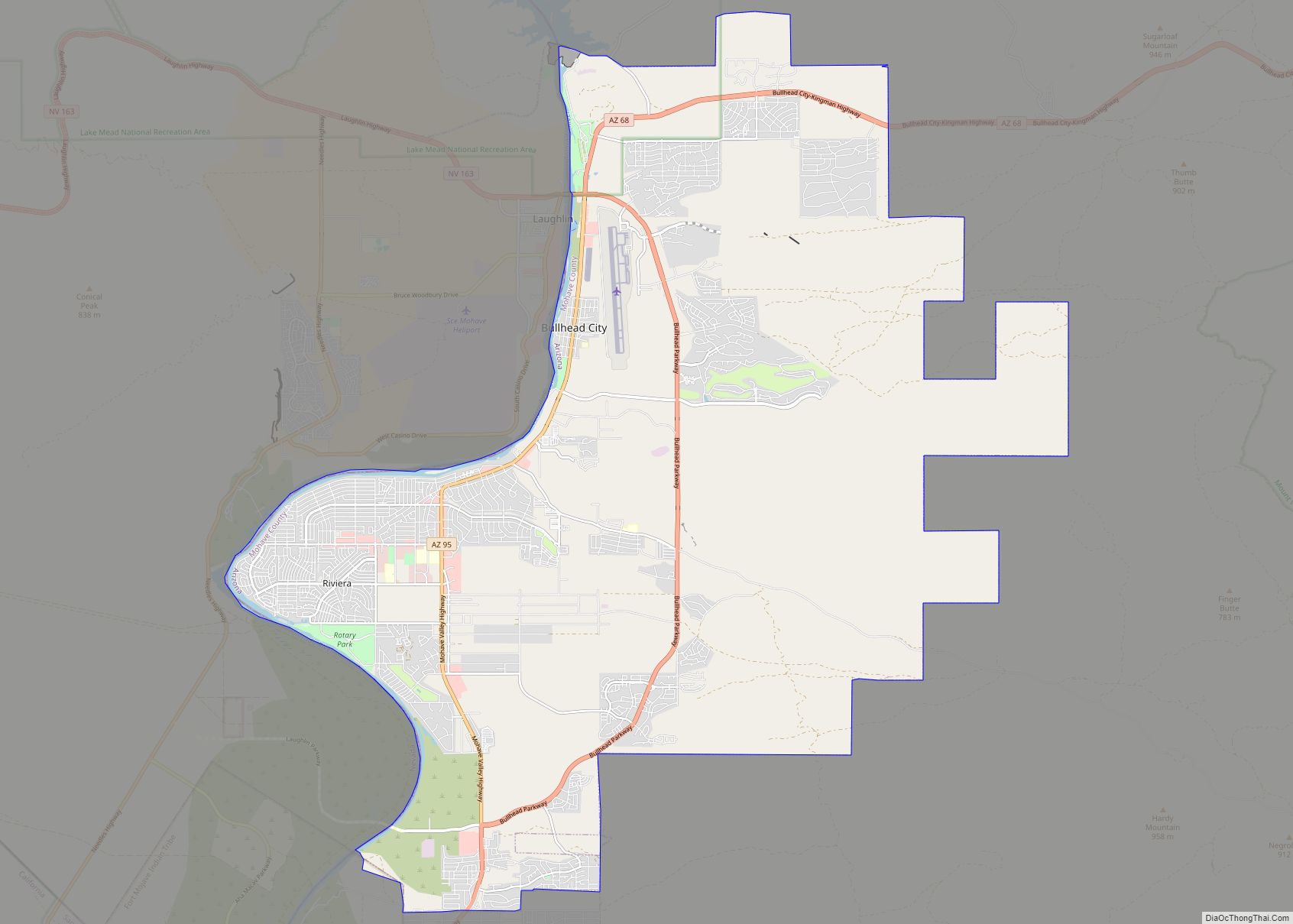
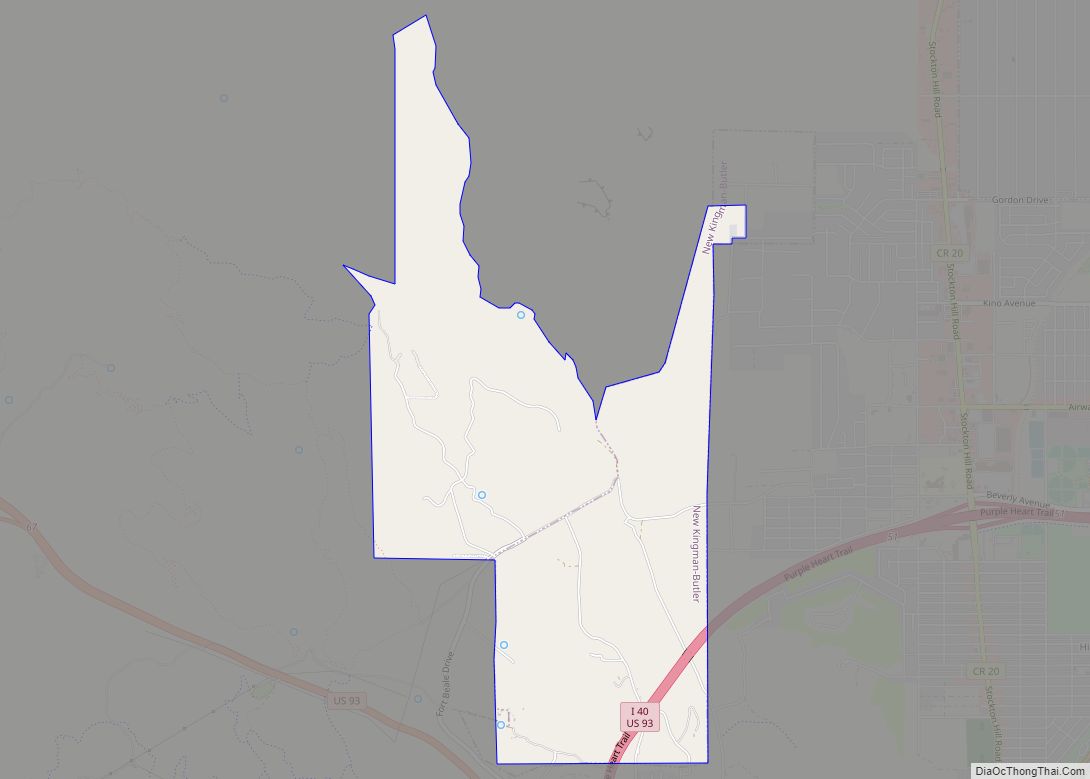
Kingman is a city in, and the county seat of, Mohave County, Arizona, United States. It is named after Lewis Kingman, an engineer for the Atlantic and Pacific Railroad. It is located 105 miles (169 km) southeast of Las Vegas, Nevada, and 180 miles (290 km) northwest of Arizona’s state capital, Phoenix. The population was 32,689 at the 2020 census.
| Name: | Kingman city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Arizona |
| County: | Mohave County |
| Incorporated: | 1882 |
| Elevation: | 3,333 ft (1,016 m) |
| Total Area: | 37.55 sq mi (97.25 km²) |
| Land Area: | 37.55 sq mi (97.25 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 32,689 |
| Population Density: | 870.62/sq mi (336.14/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 86401, 86402, 86409 |
| Area code: | 928 |
| FIPS code: | 0437620 |
| Website: | www.cityofkingman.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
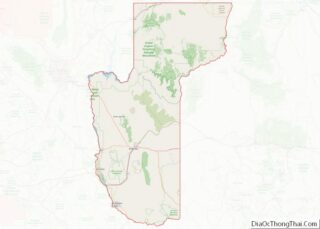
Kingman location map. Where is Kingman city?
History
Lt. Edward Fitzgerald Beale, a U.S. Navy officer in the service of the Army Corps of Topographical Engineers, was ordered by the U.S. War Department to build a federal wagon road across the 35th parallel. His secondary orders were to test the feasibility of the use of camels as pack animals in the Southwestern desert. Beale traveled through the present-day Kingman in 1857 surveying the road and in 1859 to build the road. Beale’s Wagon Road became part of U.S. Route 66 and later Interstate 40. Remnants of the wagon road can still be seen in White Cliffs Canyon in Kingman.
Kingman was founded in 1882 before statehood, in Arizona Territory. Situated in the Hualapai Valley between the Cerbat and Hualapai mountain ranges, Kingman had its modest beginnings as a simple railroad siding near Beale Springs. Civil engineer Lewis Kingman supervised the building of the railroad from Winslow to Beale Springs. This spring had been used by Native Americans living in the area for centuries.
The Mohave County seat was originally located in Mohave City from 1864 to 1867. In 1865, the portion of Arizona Territory west of the Colorado River was transferred to Nevada after Nevada’s statehood, and became part of Lincoln County, now Clark County, Nevada. The remaining territory of Pah-Ute County became part of Mohave County. Its seat was moved to Hardyville (now within Bullhead City) in 1867. The county seat transferred to the mining town of Cerbat in 1873, then to Mineral Park near Chloride. After some time, the county seat and all instruments were permanently moved to Kingman in 1887.
During World War II, Kingman was the site of a U.S. Army Air Force (USAAF) airfield. The Kingman Army Airfield was founded at the beginning of the war as an aerial gunnery training base. It became one of the USAAF’s largest, training some 35,000 soldiers and airmen. The airfield and Kingman played a significant role in this important era of America’s history. Following the war, the Kingman Airfield was one of the largest reclamation sites for obsolete military aircraft.
Postwar, Kingman experienced growth as several major employers moved into the vicinity. In 1953, Kingman was used to detain those men accused of practicing polygamy in the Short Creek raid, which was at the time one of the largest arrests in American history. In 1955, Ford Motor Company established a proving ground (now one of the Chrysler Proving Grounds) in nearby Yucca at the former Yucca Army Airfield. Several major new neighborhoods in Kingman were developed to house the skilled workers and professionals employed at the proving ground. Likewise, the development of the Mineral Park mine near adjacent Chloride, and construction of the Mohave Generating Station in nearby Laughlin, Nevada, in 1971 contributed to Kingman’s population growth. Also, the location of a General Cable plant at the Kingman Airport Industrial Park provided steady employment.
Kingman explosion
The Kingman Explosion, also known as the Doxol Disaster or Kingman BLEVE, was a catastrophic boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion (BLEVE) that occurred on July 5, 1973, during a propane transfer from a Doxol railroad car to a storage tank on the Getz rail siding near Andy Devine Avenue/Route 66.
Firefighters Memorial Park in Kingman is dedicated to the 11 firefighters who died in the blaze.
1980s and on
The 1915-built Mohave County Courthouse and the county’s somewhat older jail were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1983. The downtown and other areas of Kingman were evaluated for historic resources in a 1985 study, the Kingman Multiple Resources Area study. The study identified 63 historic resources in Kingman and led to many of them being listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1986. The county courthouse and jail, a 1928-built locomotive (the Santa Fe 3759), a World War II gunnery school radio tower, and about 50 various houses and other buildings in Kingman are listed on the National Register, comprising the majority of National Register listings in Mohave County.
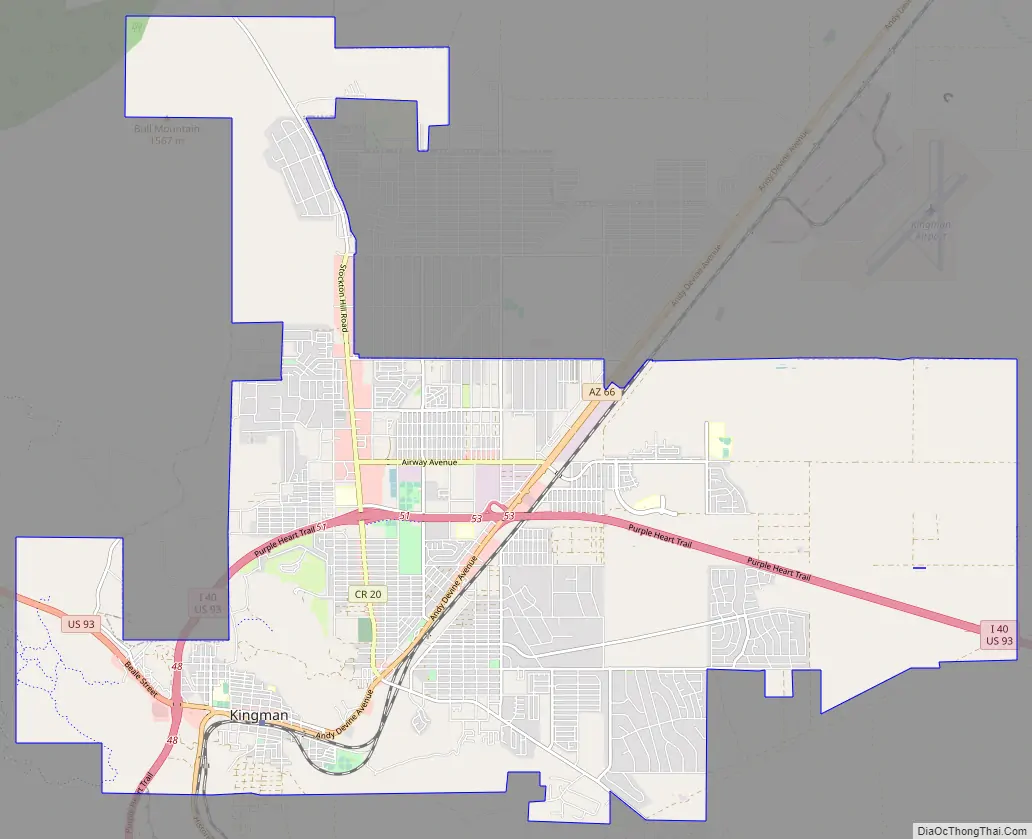
Kingman Road Map
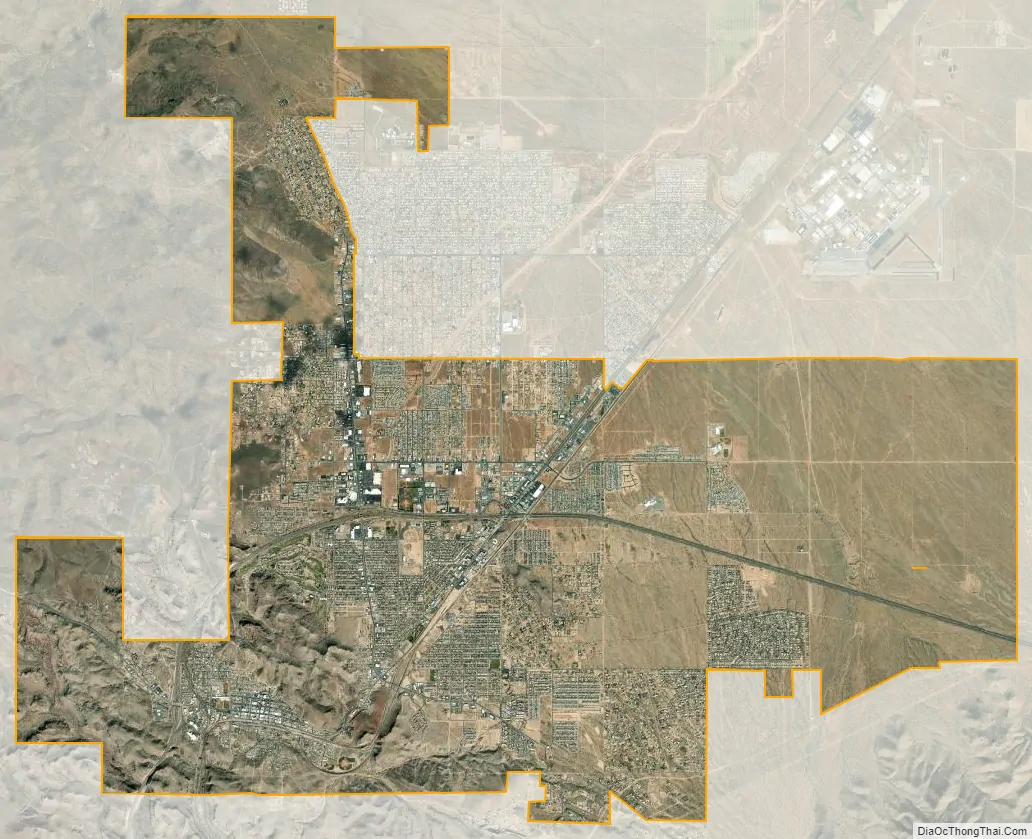
Kingman city Satellite Map
Geography
Kingman is in central Mohave County, along Interstate 40 and U.S. Route 93. The city is served by three exits on I-40, which leads east 147 miles (237 km) to Flagstaff and southwest 62 miles (100 km) to Needles, California. US-93 leads northwest 107 miles (172 km) to Las Vegas and southeast 130 miles (210 km) to Wickenburg, 54 miles (87 km) from Phoenix. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city of Kingman has a total area of 37.5 square miles (97 km), all land.
Climate
Kingman sits on the eastern edge of the Mojave Desert, but it is located in a cold desert climate (Köppen BWk) due to its plateau location. Kingman’s higher elevation and location between the Colorado Plateau and the Lower Colorado River Valley keeps summer high temperatures away from the extremes (115 °F (46 °C) or more) experienced by Phoenix and the Colorado River Valley. The higher elevation also contributes to winter cold and occasional snowfall. Summer daytime highs reach above 90 °F (32 °C) frequently, but rarely exceed 107 °F (42 °C). Summertime lows usually remain between 60 and 70 °F (16 and 21 °C). Winter highs are generally mild, ranging from around 50 to 60 °F (10 to 16 °C), but winter nighttime lows often fall to freezing, with significantly lower temperatures possible, and occasional snow.
The record low temperature in Kingman was set on January 9, 1937, at 6 °F (−14 °C), and the record high temperature occurred on June 20, 2017, at 113 °F (45 °C). The wettest year was 1919 with 21.22 inches (539 mm) and the driest year was 1947 with 3.58 inches (91 mm). The most rainfall in one month was 9.85 inches (250 mm) in September 1939. The most rainfall in 24 hours was 6.03 inches (153 mm) on November 28, 1919. The snowiest year was 1949 with 18.2 inches (0.46 m). The most snowfall in one month was 14.0 inches (0.36 m) in December 1932. On December 31, 2014 and January 1, 2015, Kingman received 6.5 inches of snow. The storm was so significant that it was a contributing factor for closing Interstate 40 at the US 93 Junction for 24 hours.
See also
Map of Arizona State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming