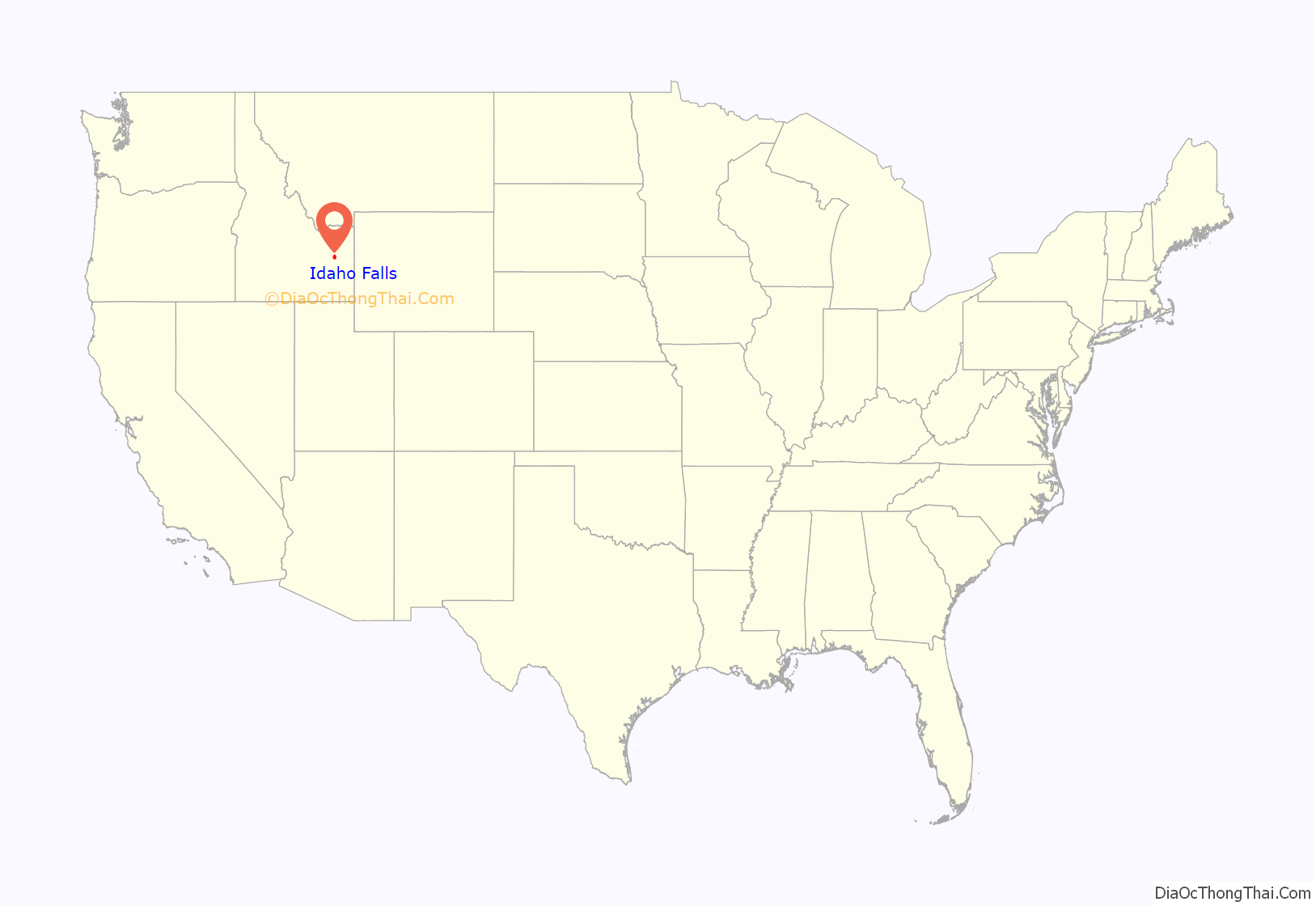
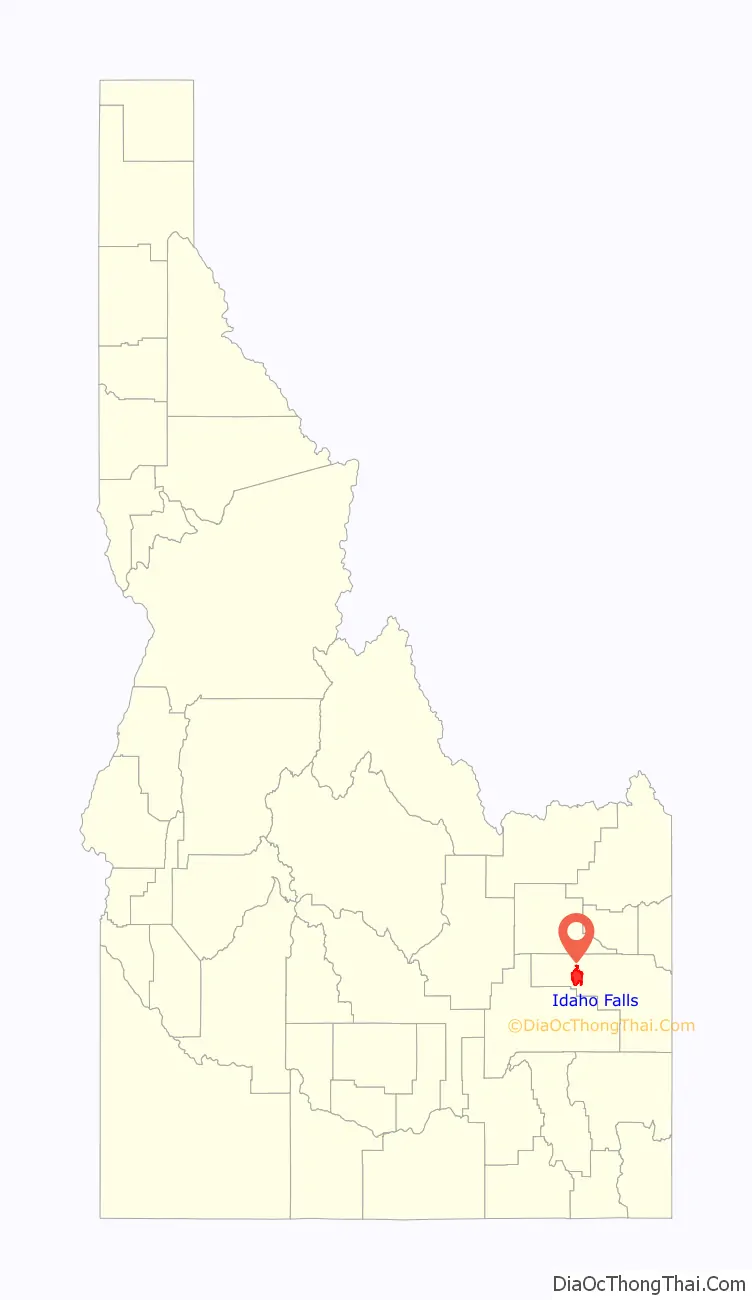
Idaho Falls is a city in and the county seat of Bonneville County, Idaho, United States. It is the state’s largest city outside the Boise metropolitan area. As of the 2020 census, the population of Idaho Falls was 64,818. In the 2010 census, the population of Idaho Falls was 56,813 (2019 estimate: 62,888), with a metro population of 133,265.
Idaho Falls serves as the commercial, cultural, and healthcare hub for Eastern Idaho, as well as parts of western Wyoming and southern Montana. It is served by the Idaho Falls Regional Airport and is home to the College of Eastern Idaho, Museum of Idaho, and the Idaho Falls Chukars minor league baseball team. It is the principal city of the Idaho Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Idaho Falls–Blackfoot-Rexburg, Idaho Combined Statistical Area.
| Name: | Idaho Falls city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Idaho |
| County: | Bonneville County |
| Founded: | 1864 |
| Incorporated: | 1891 |
| Elevation: | 4,705 ft (1,434 m) |
| Total Area: | 24.55 sq mi (63.59 km²) |
| Land Area: | 24.00 sq mi (62.16 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.56 sq mi (1.44 km²) |
| Total Population: | 64,818 |
| Population Density: | 2,700.75/sq mi (1,011.75/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 83401-83406, 83415 |
| Area code: | 208, 986 |
| FIPS code: | 1639700 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 396684 |
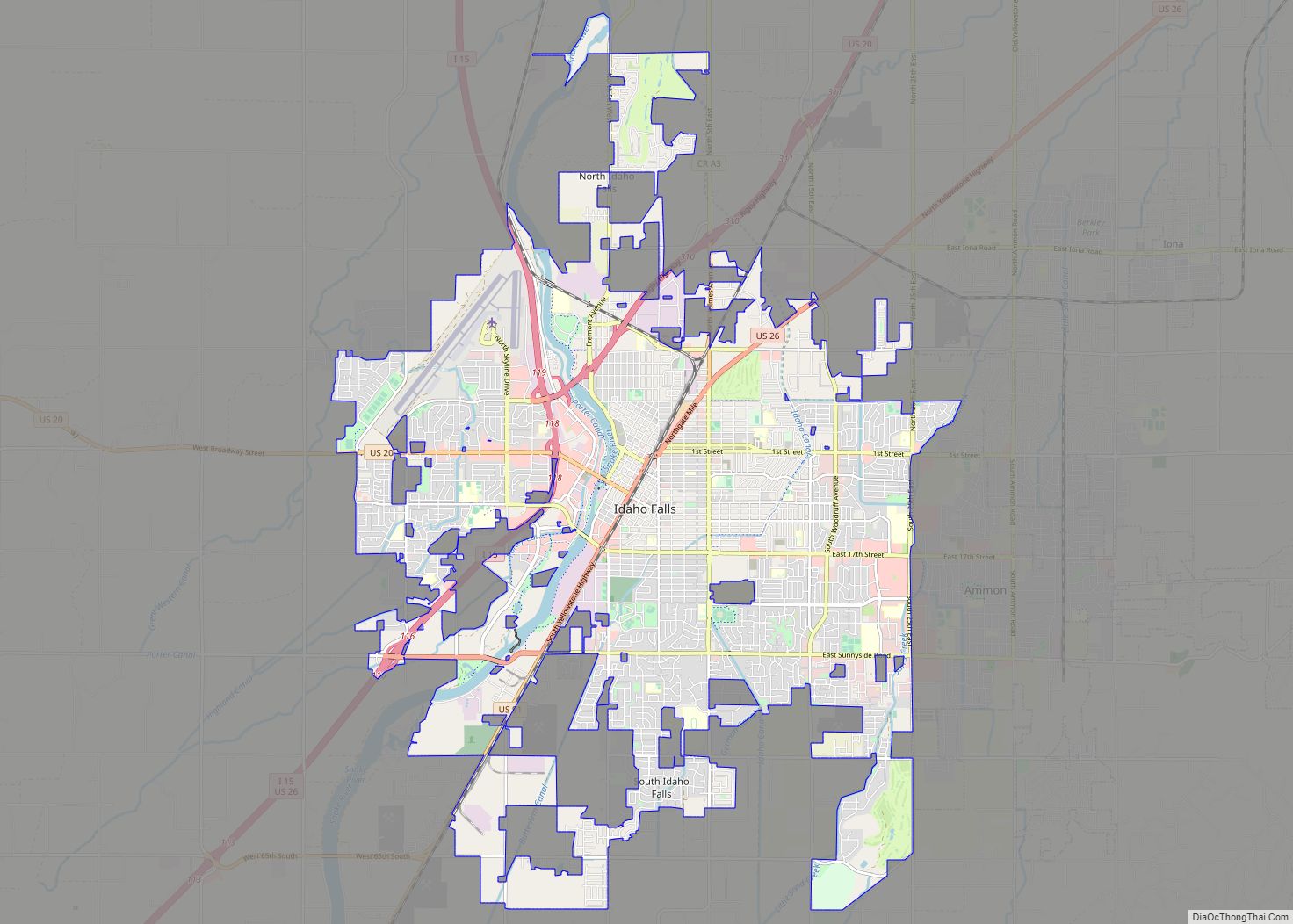
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Idaho Falls location map. Where is Idaho Falls city?
History
Montana Trail origins
The area around Idaho Falls was first sparsely settled by cattle and sheep ranchers. No significant development took place until 1864, when a man named Harry Rickets built and operated a ferry on the Snake River at 43°36.112′N 112°3.528′W / 43.601867°N 112.058800°W / 43.601867; -112.058800. The ferry served a new tide of westward migration and travel on the Montana Trail following the Bear River Massacre of Shoshone Indians in 1863.
The present-day site of Idaho Falls became a permanent settlement when freighter Matt Taylor built a timber-frame toll bridge across a narrow black basaltic gorge of the river 7 miles (11 km) downstream from the ferry. The bridge improved travel for settlers moving north and west, and for miners, freighters, and others seeking riches in the gold fields of Idaho and Montana—especially the boom towns of Bannack and Virginia City.
Eagle Rock
By the end of 1865, a private bank, small hotel, livery stable, eating house, post office, and stage station had sprung up near the bridge. The settlement was initially known as Taylor’s Crossing, but postmarks indicate that by 1866, the emerging town had become known as Eagle Rock. The name was derived from an isolated basalt island in the river near the ferry, where approximately twenty eagles nested.
In 1874, water rights were established on nearby Willow Creek and the first grain was harvested. Settlement was sparse, and consisted of only a couple of families and small irrigation ditches. The first child of European descent was born at Eagle Rock in 1874.
Soon, the Utah and Northern Railway (U&NR) was built, stretching north from Utah through Eagle Rock and crossing the Snake River at the same narrow gorge as Taylor’s bridge. The railway would eventually connect to the large new copper mines at Butte, Montana. The U&NR had the backing of robber baron Jay Gould, as Union Pacific Railroad had purchased it a few years prior. Grading crews reached Eagle Rock in late 1878, and by early 1879, a wild camp-town with dozens of tents and shanties had moved to Eagle Rock with a collection of saloons, dance halls, and gambling halls. The railroad company had 16 locomotives and 300 train cars working between Logan, Utah and the once-quiet stage stop. A new iron railroad bridge was fabricated in Athens, Pennsylvania at a cost of $30,000 and shipped by rail to the site, where it was erected in April and May 1879. The bridge was 800 feet (240 m) long and had two spans, with an island in the center. The camp-town moved on, but Eagle Rock now had regular train service and several U&NR buildings, shops, and facilities which expanded and transformed the town.
As soon as the railroad came through, settlers began homesteading the upper Snake River Valley in earnest. The first new settlers carved out homesteads to the north at Egin (near present-day Parker) and at Pooles Island (near present-day Menan). The Utah & Northern Railway provided easy access, especially to homesteaders from Utah, who soon populated much of the area surrounding Eagle Rock. Some of these men had initially worked building the railroad, then later returned with their families to stake out new farms. These Utah families brought irrigation know-how developed in Utah’s Great Basin settlements. Through their and others’ canal systems, water from the Snake River made the Upper Snake River Valley into one of the most successful irrigation projects in the Mountain West. Large-scale settlement ensued and within a decade, there appeared roads, bridges, and dams, which brought most of the Upper Snake River Valley under cultivation.
Then, in 1887, following the construction of the Oregon Short Line and a railroad workers’ strike in Eagle Rock, most of the railroad facilities were moved to Pocatello, where the new line branched off the U&NR. This caused a sharp and immediate drop in population, which nearly killed the town. In 1891, marketers convinced town leaders to change the name to Idaho Falls in reference to the rapids below the bridge. Some years later, the construction of a retaining wall for a hydroelectric power plant transformed the rapids into waterfalls. On June 22, 1895, the world’s then-largest irrigation canal, the Great Feeder (located 5 miles northeast of Ririe), began diverting water from the Snake River, helping to convert tens of thousands of more acres of desert into green farmland. The area grew sugar beets, potatoes, peas, grains, and alfalfa, and became one of the most productive agricultural regions of the United States. The city once again began to flourish, growing continuously into the 20th century.
Nuclear reactors
In 1949, the Atomic Energy Commission opened the National Reactor Testing Station (NRTS) in the desert west of Idaho Falls. On December 20, 1951, a nuclear reactor there produced useful electricity for the first time in history. There have been more than 50 unique reactors built at the facility for testing—only three remain active.
On January 3, 1961, NRTS became the scene of the only fatal nuclear reactor incident in U.S. history. The event occurred at an experimental U.S. Army plant known as the Argonne Low-Power Reactor, which the Army called the Stationary Low-Power Reactor Number One (SL-1). Due to poor design and maintenance procedures, a single control rod was manually pulled out too far from the reactor, causing the reactor to become prompt critical, leading to a destructive power excursion. Three trained military men had been working inside the reactor room when a mistake was made while reattaching a control rod to its motor assembly. With the central control rod nearly fully extended, the nuclear reactor rated at 3 MW rapidly increased power to 20 GW. This rapidly boiled the water inside the core. As the steam expanded, a pressure wave of water forcefully struck the top of the reactor vessel, upon which two of the men stood. The explosion was so severe that the reactor vessel was propelled nine feet into the air, striking the ceiling before settling back into its original position. One man was impaled by a shield plug and lodged into the ceiling, where he died instantly. The other men died from their injuries within hours. The three men were buried in lead coffins, and that entire section of the site was buried. The core meltdown caused no damage to the area, although some radioactive nuclear fission products were released into the atmosphere.
The site has since developed into the Idaho National Laboratory (INL), a national laboratory operated by the United States Department of Energy. INL and its contractors are a major economic engine for the Idaho Falls area, employing more than 8,000 people between the desert site and its research and education campus in Idaho Falls. Among other projects, INL operates and manages the world-famous Advanced Test Reactor (ATR).
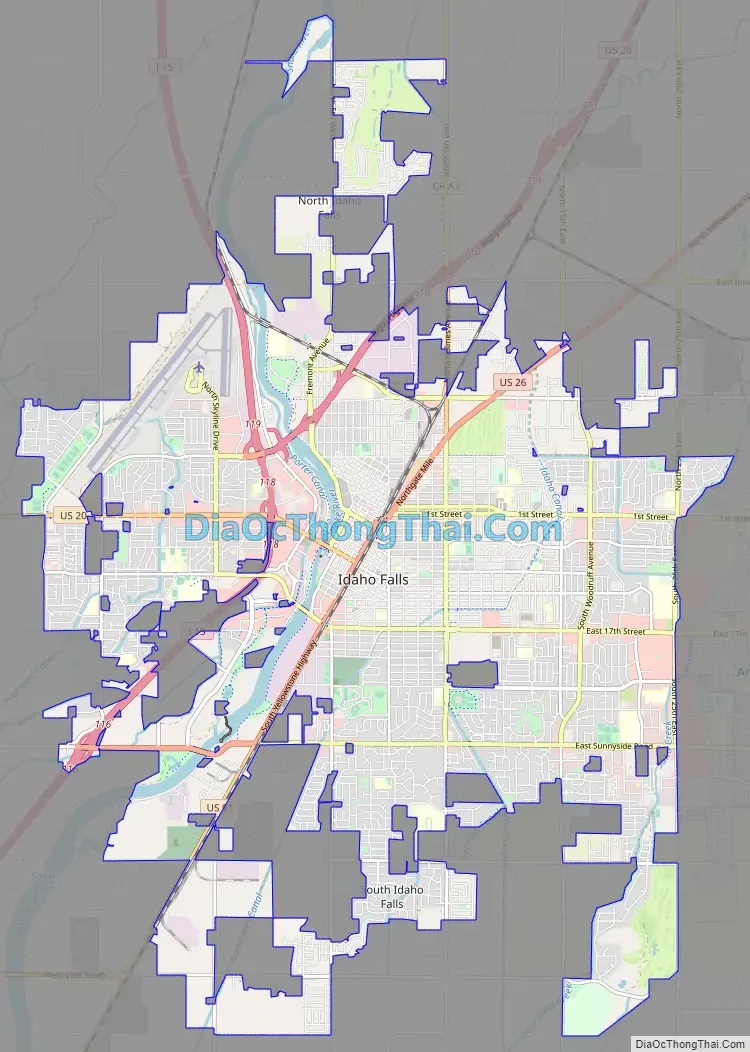
Idaho Falls Road Map
Idaho Falls city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 22.80 square miles (59.05 km), of which 22.35 square miles (57.89 km), 98% is land and 0.45 square miles (1.17 km, 2%) is water.
Natural disasters are rare in the area, although an F2 tornado hit the Idaho Falls area on April 7, 1978, causing up to $5 million in damage.
River Walk
Idaho Falls has an extensive river walk trail featuring running and bike trails, art installations, and points of interest along several miles of the Snake River. It is maintained by the city and periodically receives donations and grants that allow for expansion.
Neighborhoods
Notable Idaho Falls neighborhoods include:
- Downtown – Historic downtown Idaho Falls sits on several blocks of the original townsite along the east side of the river. It features restaurants, plazas, shops, and cultural amenities including the Museum of Idaho, Colonial Theatre, Art Museum of Eastern Idaho, Idaho Falls Public Library, and Japanese Friendship Garden. It is home to the Idaho Falls Farmers’ Market and many other community events.
- The Numbered Streets – The numbered streets area was the first planned neighborhood in Idaho Falls. The streets run west and east between South Boulevard and Holmes Avenue. Traffic on the odd-numbered streets travels east, and west on the even-numbered streets. Kate Curley Park is located in the neighborhood, as is the Wesley W. Deist Aquatic Center and the Eleventh Street Historic District.
- West Side – The West Side houses Idaho Falls Regional Airport and I-15. It has retained more of a small-town feel than the east side, which has grown and developed much more rapidly since the 1980s.
- Snake River Landing – SRL is a large, mixed-use development on the west side of the river near I-15, which includes residential, restaurant, park, and community event space, including a planned mid-sized indoor arena. It now hosts the Melaleuca Freedom Celebration, a large Independence Day event.
Climate
Idaho Falls experiences a humid continental climate with warm summers and cold winters (Köppen Dfb). Precipitation is relatively sparse, but not low enough to classify the climate as semi-arid.
See also
Map of Idaho State and its subdivision:- Ada
- Adams
- Bannock
- Bear Lake
- Benewah
- Bingham
- Blaine
- Boise
- Bonner
- Bonneville
- Boundary
- Butte
- Camas
- Canyon
- Caribou
- Cassia
- Clark
- Clearwater
- Custer
- Elmore
- Franklin
- Fremont
- Gem
- Gooding
- Idaho
- Jefferson
- Jerome
- Kootenai
- Latah
- Lemhi
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Madison
- Minidoka
- Nez Perce
- Oneida
- Owyhee
- Payette
- Power
- Shoshone
- Teton
- Twin Falls
- Valley
- Washington
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming