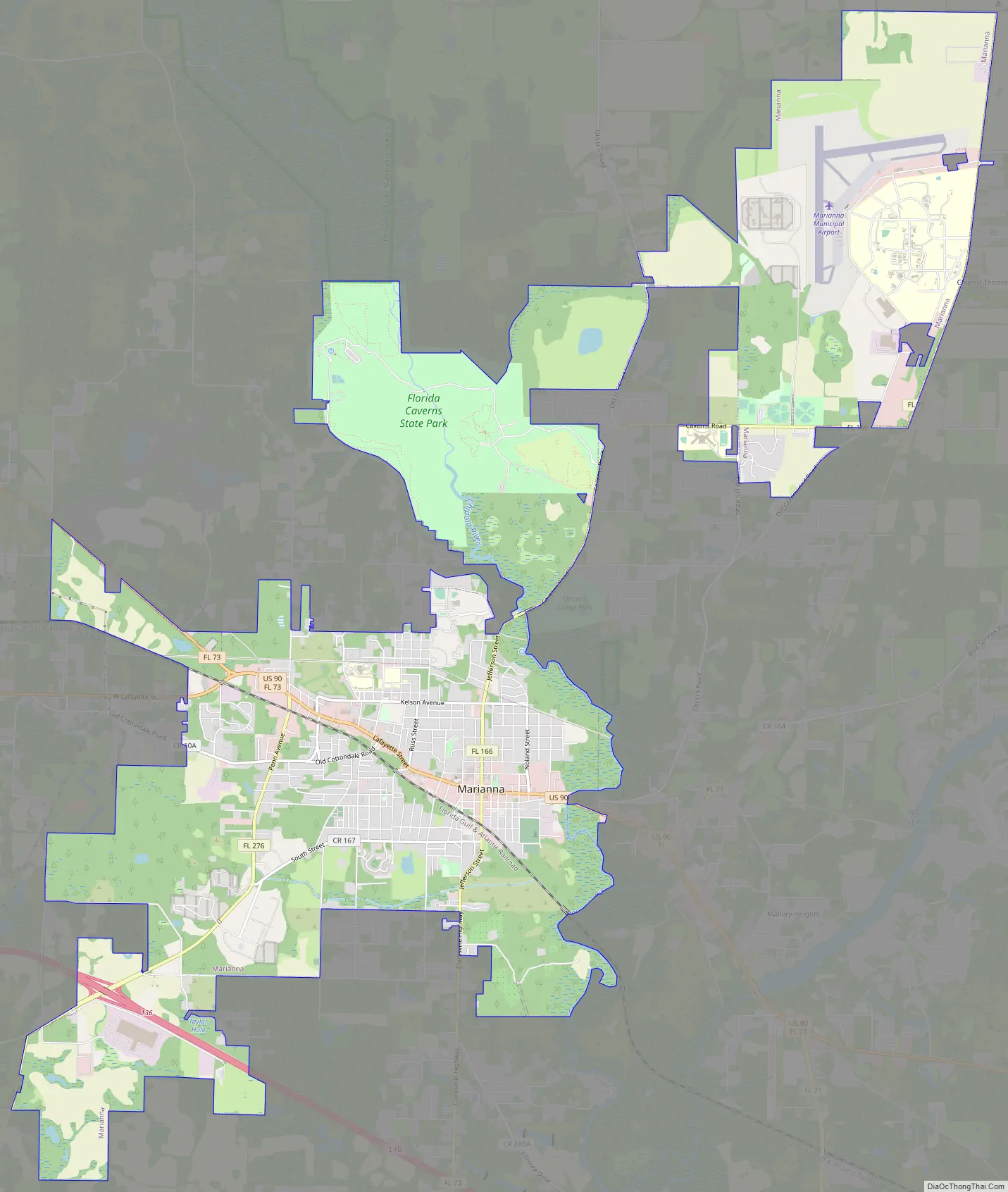
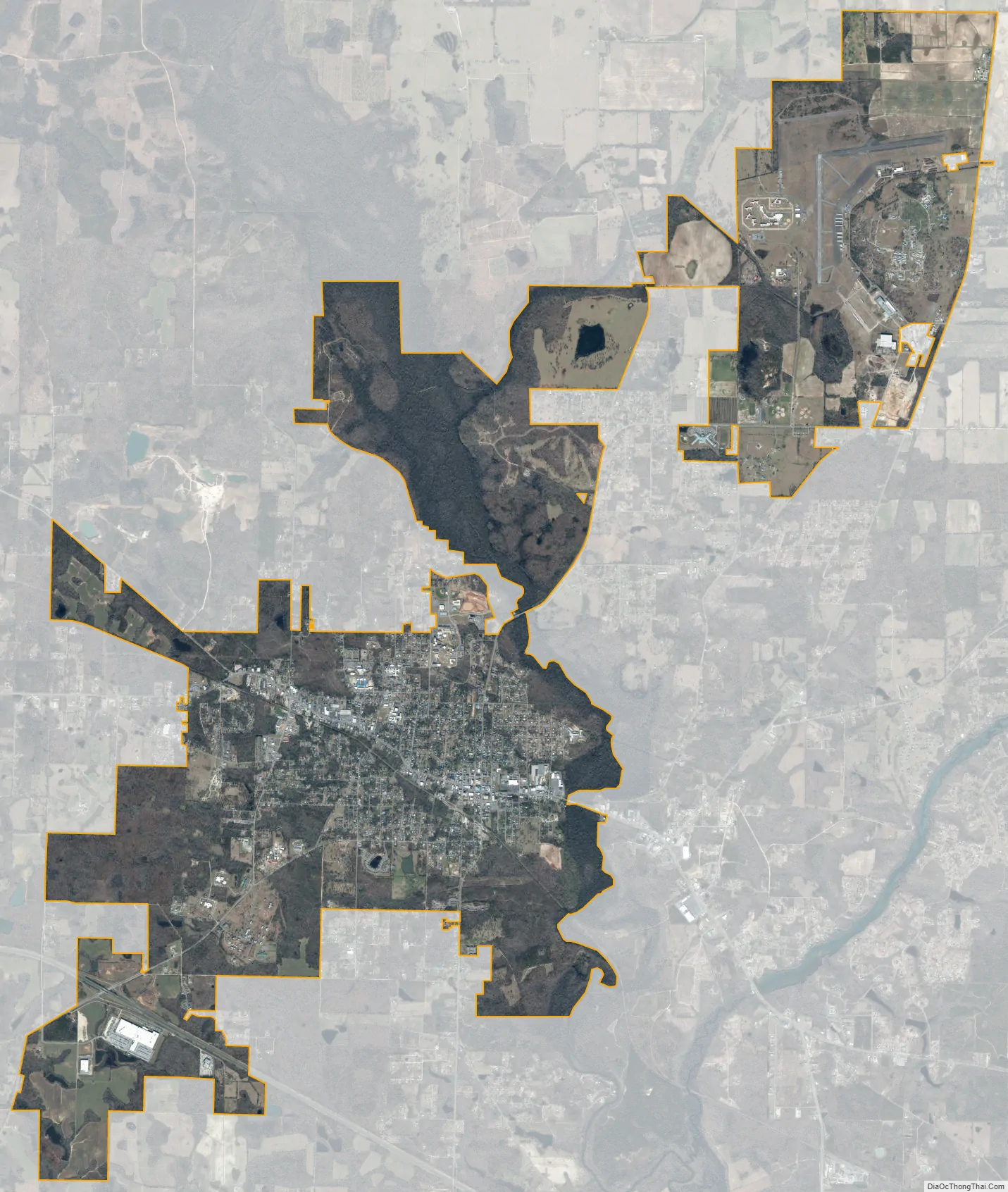
Marianna is a city in and the county seat of Jackson County, Florida, United States, and it is home to Chipola College. The population was 6,102 at the 2010 census. In 2018 the estimated population was 7,091. The official nickname of Marianna is “The City of Southern Charm”.
| Name: | Marianna city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Florida |
| County: | Jackson County |
| Elevation: | 167 ft (51 m) |
| Total Area: | 18.65 sq mi (48.29 km²) |
| Land Area: | 18.60 sq mi (48.17 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.05 sq mi (0.12 km²) |
| Total Population: | 6,245 |
| Population Density: | 335.75/sq mi (129.63/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 32446-32448 |
| Area code: | 850 |
| FIPS code: | 1243175 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0286422 |
| Website: | www.cityofmarianna.com |
Online Interactive Map
Marianna location map. Where is Marianna city?
History
Marianna was founded in 1828 by Scottish entrepreneur Scott Beverege, who named the town after his daughters Mary and Anna. The following year, it was designated as the county seat, superseding the earlier settlement of Webbville, which soon after dissolved and no longer exists. Marianna was platted along the Chipola River. Many planters from North Carolina relocated to Jackson County to develop new plantations to take advantage of the fertile soil. They relied on the labor of enslaved African Americans brought from the Upper South in the domestic slave trade.
Civil War era
Governor John Milton, a major planter who owned the Sylvania Plantation and hundreds of slaves, was a grandson of Revolutionary War hero John Millton, and a descendant of Sir Christopher Milton, the brother of the famous English poet, John Milton. However, Milton did not have to rely solely on a distinguished American founding family name. A Marianna resident, he was elected as governor of Florida, serving during the Civil War years. Governor Milton opposed the Confederate States of America rejoining the United States.
As federal troops were preparing to take control of Tallahassee, Governor Milton received word that the Civil War had ended and that Florida would again be part of the United States. On April 1, 1865, as the Southern cause was collapsing, Milton died of a gunshot wound from his gun at Sylvania. A New York Times article, written in polemic style, attributed Governor Milton’s sudden death to suicide, which conflicted with local reporting from Florida. The Governor’s words, likely political oratorical hyperbole, that he “would rather die” than suffer the humiliation of Federal invasion, were linked to his sudden death by the New York Times. The West Florida News reported the sudden death of Florida’s fifth Governor as a hunting accident. Governor Milton was buried in the St. Luke’s Episcopal churchyard at Marianna. The New York Times article’s account persisted in the difficult days of Reconstruction.
Marianna was the site of a Civil War battle in 1864 between a small home guard of about 150 boys, older men, and wounded soldiers, and a contingent of approximately 700 Federal troops.
Reconstruction period
During the early years after the Civil War, violence flared in Marianna and Jackson County, where 150 to 200 Republicans, some black, were assassinated in what was known as the Jackson County War by members of the Ku Klux Klan in an effort to secure white supremacy. Locals claimed this was the work of “ruffians” from border states and carpetbaggers. Bishop Charles H. Pearce of Massachusetts, an AME minister who became a state senator in Florida, had first-hand knowledge of the situation. He placed the blame on the planters of Jackson County, who supported action against black Republicans. Disputes over farm land caused much of the disorder, as poor whites objected to negro ownership of choice farms.
Post-Reconstruction to mid-20th century
Violence continued in the state after Reconstruction, reaching a peak in most areas at the turn of the 20th century. This was the period in which southern states also disenfranchised most blacks and thousands of poor whites by raising barriers to voter registration. From 1900 to 1930, Florida had the highest rate of lynchings per capita in the South and the nation. Refusing to accept the violence, thousands of African Americans left the state during the Great Migration of the early 20th century, going to northern and midwestern industrial cities for work and other opportunities.
In 1934 Claude Neal, a local African-American man, was accused of the rape and murder of a young white woman. He was moved between jails, but a lynch mob found him in Brewton, Alabama. The mob abducted him and brought him back to Florida, killing him near the Chattahoochee River and Greenwood. The men brought his body to the Cannady farm, where a larger mob of an estimated 2,000 persons was waiting; people shot and mutilated the body. Neal’s body was hanged from a tree at the Marianna courthouse square. The next day, whites rioted in town, attacking blacks and destroying some of their houses. The governor ordered more than 100 troops of the National Guard to Marianna to suppress the violence. About 200 blacks and two police were injured. The six white vigilantes who led the lynching remain unidentified.
In 1943 Cellos Harrison was taken from the county jail at Marianna by a white mob and hanged (lynched) near Greenwood. His case had been in the courts for two years in appeals after the African-American man was arrested and twice convicted by all-white juries and sentenced to death for the 1940 murder of a white man. He had confessed without benefit of counsel, and his convictions were overturned by the Florida Supreme Court as a result. But whites were tired of waiting for the case to be resolved, and lynched him. President Franklin D. Roosevelt directed the Department of Justice to investigate Harrison’s lynching; he felt it was unjust that blacks were getting lynched at home while the U.S. was ostensibly fighting for freedom in Europe. No one was ever prosecuted for Harrison’s death.
Florida School for Boys
The Florida School for Boys, a large state reform school, operated in Marianna from January 1, 1900, to June 30, 2011. For a time, it was the largest juvenile reform institution in the United States. Throughout its 111-year history, the school gained a reputation for abuse, beatings, rapes, and torture of students by staff. It was rumored that students had died there as a result of injuries. Despite periodic investigations, changes of leadership, and promises by the state to improve conditions, the allegations of cruelty and abuse continued.
Many of the allegations were confirmed by separate investigations by the Florida Department of Law Enforcement in 2010 and the Civil Rights Division of the United States Department of Justice in 2011. State authorities closed the school permanently in June 2011. In 2015, a multi-year investigation of the cemetery and grounds by the University of South Florida (USF), which was attempting to find undocumented burials on the grounds, revealed details of a secret “rape dungeon”, where boys younger than 12 were sexually abused. It positively identified five bodies from remains recovered on the grounds. By January 2016, the end of the USF’s studies of the grounds and exhumation of remains, it had identified 55 previously unknown burials, made a match for seven bodies through DNA, and presumptively identified another 14 sets of remains of 51 found. Twenty-seven more graves were discovered in 2019. The team created a website containing documentation of their investigation and will continue to work with state agencies and families of former students to identify more remains.
Hurricane Michael
The city was one of several Florida Panhandle communities devastated by Category 5 Hurricane Michael on October 10, 2018. The downtown area was heavily hit, with several historic buildings collapsing and blocking Lafayette Street, which is the main road. The city was without power for three weeks, which caused extensive school cancellations. More than 80% of homes and businesses in Marianna were heavily damaged or destroyed due to Michael’s extreme winds. Millions of dollars in insurance claims were filed and the area also suffered millions of dollars in economic losses. This hurricane is the worst natural disaster to ever strike Marianna, surpassing the damages caused by a F-3 tornado spawned by Hurricane Ivan in September 2004.
Marianna Road Map
Marianna city Satellite Map
Geography
Marianna is located in central Jackson County at 30°46′35″N 85°14′17″W / 30.77639°N 85.23806°W / 30.77639; -85.23806 (30.776370, –85.238149). U.S. Route 90 passes through the center of town as Lafayette Street, leading east 14 miles (23 km) to Grand Ridge and west 9 miles (14 km) to Cottondale. Interstate 10 passes through the southern end of the city, leading east 65 miles (105 km) to Tallahassee, the state capital, and west 130 miles (210 km) to Pensacola. Access to Marianna is at Exit 136, Florida State Road 276.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 16.8 square miles (43.6 km), of which 0.04 square miles (0.1 km), or 0.29%, are water. The Chipola River, which forms the eastern border of the city, is part of the Apalachicola River watershed.
Climate
See also
Map of Florida State and its subdivision:- Alachua
- Baker
- Bay
- Bradford
- Brevard
- Broward
- Calhoun
- Charlotte
- Citrus
- Clay
- Collier
- Columbia
- Desoto
- Dixie
- Duval
- Escambia
- Flagler
- Franklin
- Gadsden
- Gilchrist
- Glades
- Gulf
- Hamilton
- Hardee
- Hendry
- Hernando
- Highlands
- Hillsborough
- Holmes
- Indian River
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Lafayette
- Lake
- Lee
- Leon
- Levy
- Liberty
- Madison
- Manatee
- Marion
- Martin
- Miami-Dade
- Monroe
- Nassau
- Okaloosa
- Okeechobee
- Orange
- Osceola
- Palm Beach
- Pasco
- Pinellas
- Polk
- Putnam
- Saint Johns
- Saint Lucie
- Santa Rosa
- Sarasota
- Seminole
- Sumter
- Suwannee
- Taylor
- Union
- Volusia
- Wakulla
- Walton
- Washington
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming