Reading (/ˈrɛdɪŋ/ (listen) RED-ing) is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, 16 miles (26 km) north of central Boston. The population was 25,518 at the 2020 census.
| Name: | Reading CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | Massachusetts |
| County: | Middlesex County |
| Elevation: | 127 ft (39 m) |
| Total Area: | 9.9 sq mi (25.7 km²) |
| Land Area: | 9.9 sq mi (25.7 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.0 sq mi (0.0 km²) |
| Total Population: | 25,518 |
| Population Density: | 2,600/sq mi (990/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 01867 |
| Area code: | 339 / 781 |
| FIPS code: | 2556165 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0618232 |
| Website: | http://www.ci.reading.ma.us/ |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Reading location map. Where is Reading CDP?
History
Settlement and American independence
Many of the Massachusetts Bay Colony’s original settlers arrived from England in the 1630s through the ports of Lynn and Salem. In 1639 some citizens of Lynn petitioned the government of the colony for a “place for an inland plantation”. They were initially granted six square miles, followed by an additional four. The first settlement in this grant was at first called “Lynn Village” and was located on the south shore of the “Great Pond”, now known as Lake Quannapowitt. On June 10, 1644 the settlement was incorporated as the town of Reading, taking its name from the town of Reading in England.
The first church was organized soon after the settlement, and the first parish separated and became the town of “South Reading” in 1812, renaming itself as Wakefield in 1868. Thomas Parker was one of the founders of Reading. He also was a founder of the 12th Congregational Church (now the First Parish Congregational Church), and served as deacon there. He was a selectman of Reading and was appointed a judicial commissioner. There is evidence that Parker was “conspicuous in naming the town” and that he was related to the Parker family of Little Norton, England, who owned land by the name of Ryddinge.
A special grant in 1651 added land north of the Ipswich River to the town of Reading. In 1853 this area became the separate town of North Reading. The area which currently comprises the town of Reading was originally known as “Wood End”, or “Third Parish”.
The town of Reading was initially governed by an open town meeting and a board of selectmen, a situation that persisted until the 1940s. In 1693, the town meeting voted to fund public education in Reading, with grants of four pounds for three months school in the town, two pounds for the west end of the town, and one pound for those north of the Ipswich River. In 1769, the meeting house was constructed, in the area which is now the Common in Reading. A stone marker commemorates the site.
Reading played an active role in the American Revolutionary War. It was prominently involved in the engagements pursuing the retreating British Army after the battles of Lexington and Concord. John Brooks, later to become Governor of Massachusetts, was captain of the “Fourth Company of Minute” and subsequently served at the Battle of White Plains and at Valley Forge. Only one Reading soldier was killed in action during the Revolution; Joshua Eaton died in the Battle of Saratoga in 1777.
In 1791, sixty members started the Federal Library. This was a subscription Library with each member paying $1.00 to join, and annual dues of $.25. The town’s public library was created in 1868.
19th century
The Andover-Medford Turnpike was built by a private corporation in 1806-7. This road, now known as Massachusetts Route 28, provided the citizens of Reading with a better means of travel to the Boston area. In 1845, the Boston and Maine Railroad came to Reading and improved the access to Boston, and the southern markets. During the first half of the 19th century, Reading became a manufacturing town. Sylvester Harnden’s furniture factory, Daniel Pratt’s clock factory, and Samuel Pierce’s organ pipe factory were major businesses. By the mid-19th century, Reading had thirteen establishments that manufactured chairs and cabinets. The making of shoes began as a cottage industry and expanded to large factories. Neckties were manufactured here for about ninety years. During and after Civil War the southern markets for Reading’s products declined and several of its factories closed. For many years, Reading was an important casket manufacturing center.
During the Civil War, members of the Richardson Light Guard of South Reading fought at the First Battle of Bull Run. A second company was formed as part of the Army of the Potomac, and a third company joined General Bank’s expedition in Louisiana. A total of 411 men from Reading fought in the Civil War, of whom 15 died in action and 33 died of wounds and sickness. A memorial exists in the Laurel Hill Cemetery commemorating those who died in the Civil War.
20th century
In the 20th century, Reading became a small, residential community with commuter service to Boston on the Boston and Maine Railroad and the Eastern Massachusetts Street Railway. Both commuter services were later taken over by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority, and for many years, there was discussion of extending the MBTA Orange Line to Reading. Industrial expansion during that time included the Goodall-Sanford Co. off Ash Street, later sold to General Tire & Rubber Company, later known as GenCorp. Additional businesses created after World War I included the Boston Stove Foundry, Roger Reed Waxes, Ace Art, Addison-Wesley Publishing and several other companies. For many years, Wes Parker’s Fried Clams was a landmark off state Route 128.
Military installations also came to the town, with two Nike missile sites, one on Bear Hill and the other off Haverhill Street, and the opening of Camp Curtis Guild, a National Guard training facility. The business community currently consists of a number of retail and service businesses in the downtown area, a series of commercial businesses in and around the former town dump on Walker’s Brook Road (formerly John Street) as well as the Analytical Sciences Corporation (TASC).
In 1944, Reading adopted the representative town meeting model of local government in place of the open town meeting. This retained the representative town meeting and board of selectmen, but focused policy and decision making in a smaller number of elected boards and committees whilst providing for the employment of a town manager to be responsible for day-to-day operations of the local government.
Basketball player Bill Russell lived in Reading in the 1960s at 1361 Main Street, but later moved to 701 Haverhill Street. Vandals broke into the basketball player’s home and damaged his property, leaving racial epithets in their wake as well as defecating in Russell’s bed. Russell left Reading after retiring as coach of the Boston Celtics in 1969.
In recent years the town of Reading struggled with the decisions to build a new elementary school, to cope with the influx of new families to the community, and renovate Reading Memorial High School which was opened in 1954 with an addition added in 1971. Both of these projects were approved and in August 2007 the new $57 million renovation at the High School was completed.
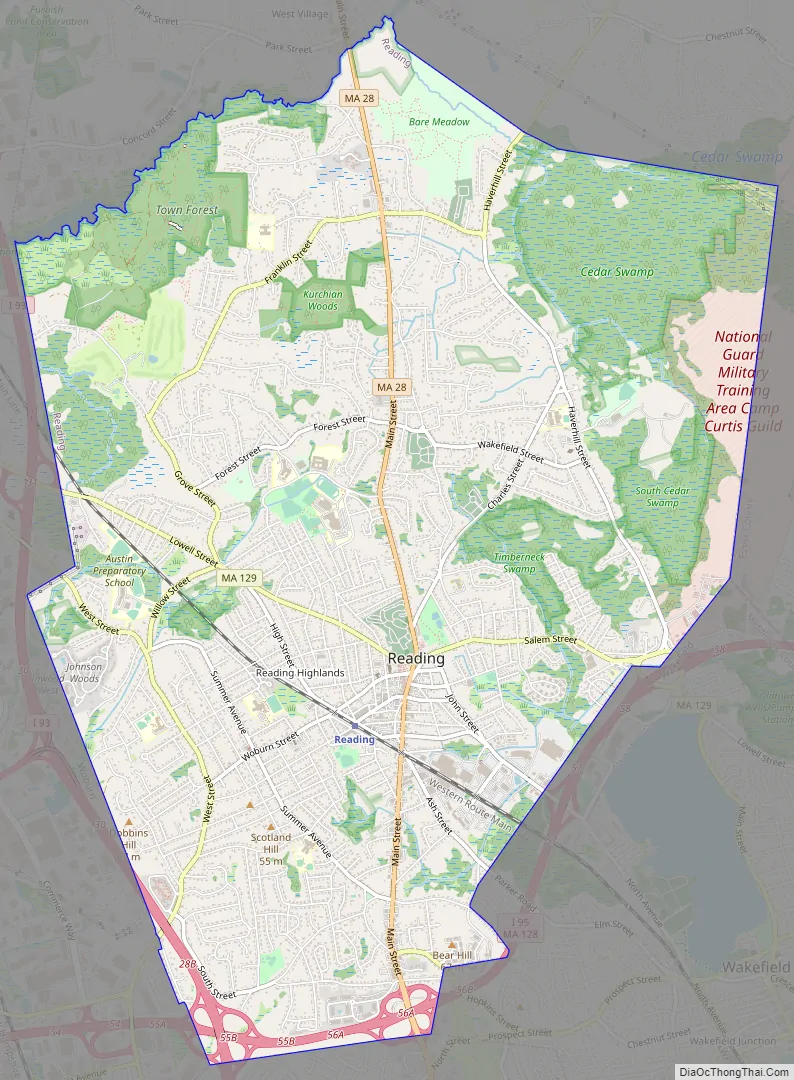
Reading Road Map
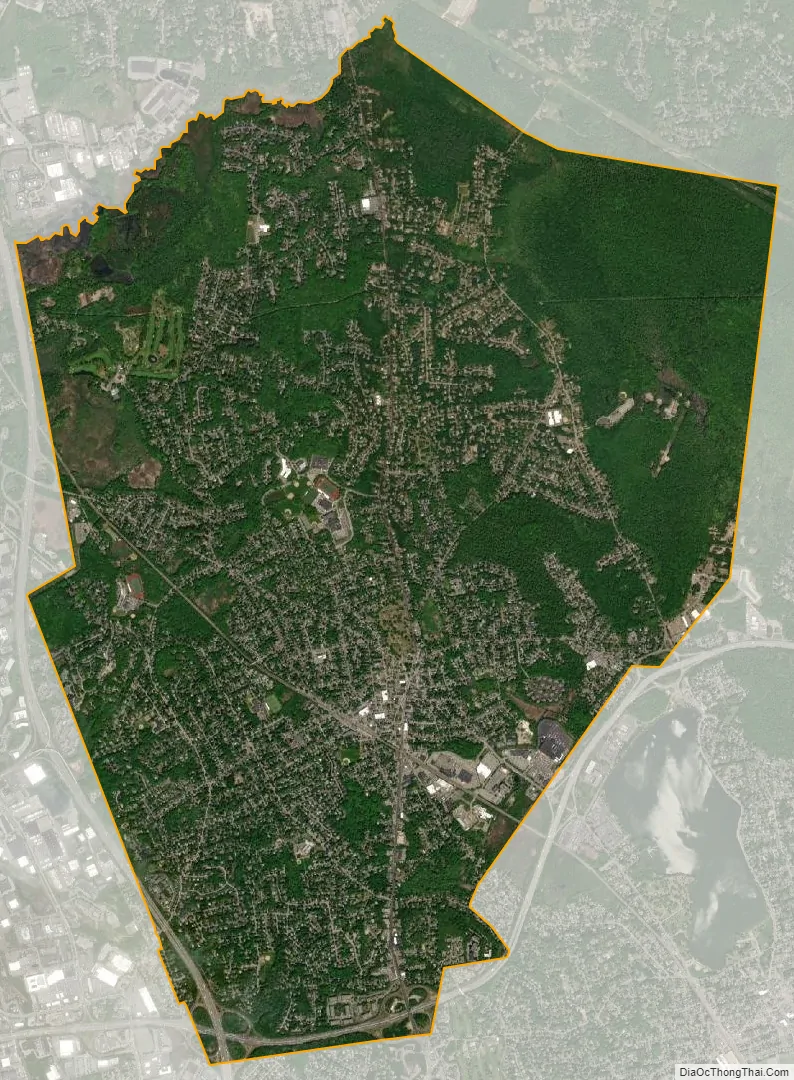
Reading city Satellite Map
Geography
Reading is located at 42°31′33″N 71°6′35″W / 42.52583°N 71.10972°W / 42.52583; -71.10972 (42.52585, −71.109939). According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 9.9 square miles (25.7 km). No significant amount of land is covered permanently by water, although there is a plethora of vernal pools in various areas of conservation land.
Reading borders the towns of Woburn, Stoneham, Wakefield, Lynnfield, North Reading, and Wilmington.
See also
Map of Massachusetts State and its subdivision: Map of other states:- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming