Punta Gorda (/ˌpʌntə ˈɡɔːrdə/; English: Fat Point) is a city located in Southwest Florida and is the county seat of Charlotte County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 U.S. Census the city had a population of 19,471. Punta Gorda is part of the Sarasota-Bradenton-Punta Gorda Combined Statistical Area.
Punta Gorda was the scene of massive destruction after Charley, a Category 4 hurricane, came through the city on August 13, 2004. Charley was the strongest tropical system to hit Florida since Hurricane Andrew in 1992, and the first hurricane since Hurricane Donna in 1960 to make a direct hit on Florida’s southwest coast. In the years following the storm, buildings were restored or built to hurricane-resistant building codes. The new buildings, restorations and amenities concurrently preserved the city’s past while showcasing newer facilities. During this time, Laishley Park Municipal Marina was built and the Harborwalk, Linear Park and various trails were created throughout the city for bicycle and pedestrian traffic.
| Name: | Punta Gorda city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Florida |
| County: | Charlotte County |
| Elevation: | 6 ft (2 m) |
| Total Area: | 21.87 sq mi (56.64 km²) |
| Land Area: | 15.50 sq mi (40.13 km²) |
| Water Area: | 6.37 sq mi (16.51 km²) 28.52% |
| Total Population: | 19,471 |
| Population Density: | 1,256.52/sq mi (485.14/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 33950-33951, 33955 , 33980 |
| Area code: | 941 |
| FIPS code: | 1259200 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0289380 |
| Website: | www.ci.punta-gorda.fl.us |
Online Interactive Map
Punta Gorda location map. Where is Punta Gorda city?
History
Early history
Before the arrival of European explorers and settlers, the region centered on present-day Punta Gorda was home to the Calusa people. The name Punta Gorda (“Fat Point”) has been on maps at least since 1851, referring to a point of land that juts into Charlotte Harbor, an estuary off the Gulf of Mexico. In the late 1800s, white settlers began to arrive in the present-day Punta Gorda area.
Frederick and Jarvis Howard, Union Army veterans, homesteaded an area south of the Peace River near present-day Punta Gorda about a decade after the Civil War. In 1876, James and Josephine Lockhart bought land and built a house on property that is now at the center of the city. About two years later, Lockhart sold his claim to James Madison Lanier, a hunter and trapper, who lived there for two years.
In 1879, a charter for a railroad with termini at Charlotte Harbor and Lake City, Florida, was established under the name Gainesville, Ocala, and Charlotte Harbor Railroad. It was taken over by the Florida Southern Railroad, which reaffirmed Charlotte Harbor as a terminus in its own charter. In 1883, Lanier sold his land to Isaac Trabue, who purchased additional property along the harbor and directed the platting of a town (by Kelly B. Harvey) named Trabue. Harvey recorded the plat on February 24, 1885. At the time, Isaac was in Kentucky, and his cousin, John Trabue, was in charge of selling lots. To ensure his development’s success, Trabue convinced the Florida Southern Railway to bring its road to his town on the south side of Charlotte Harbor.
The railroad rolled into Trabue in August 1886, and with it came the first land developers and Southwest Florida’s first batch of tourists. Punta Gorda became the southernmost stop on the Florida Southern Railroad, until an extension was built to Fort Myers in 1904, attracting the industries that propelled its initial growth.
On December 3, 1887, dissatisfied with Trabue’s lack of infrastructure development, 34 townspeople met at Hector’s Billiard Parlor to discuss incorporation. The group voted to incorporate and rename the town after the Spanish name for the point on which it was located, Punta Gorda. Once Punta Gorda was officially incorporated, mayoral elections took place and a council was formed. The first mayor, W. H. Simmons, was elected.
Phosphate was discovered on the banks of the Peace River just above Punta Gorda in 1888. Phosphate mined in the Peace River Valley was barged down the Peace River to Punta Gorda and Port Boca Grande, where it was loaded onto vessels for worldwide shipment. In 1896, the Florida Times-Union reported that phosphate mining was Punta Gorda’s chief industry and that Punta Gorda was the world’s greatest phosphate shipping point. By 1907, a railroad was built direct to Port Boca Grande, ending the brief phosphate shipping boom from Punta Gorda.
In 1890, Isaac Trabue appointed the first postmaster, Robert Meacham, an African American, as a deliberate affront to Kelly B. Harvey and those who had voted to change the name of the town from Trabue to Punta Gorda.
The Punta Gorda Herald was founded by Robert Kirby Seward in 1893 and published weekly during its early years. The newspaper covered such events as rum-running, other smuggling activities, and lawlessness in general. It underwent many changes in both ownership and name, and today is known as The Charlotte Sun Herald.
Early Punta Gorda greatly resembled the modern social climate of various classes living together and working together. While the regal Punta Gorda Hotel, at one point partly owned by Cornelius Vanderbilt, reflected the upper class, Punta Gorda was a pretty rough town, like most frontier towns. Its location at the end of the railway line spiked the crime rate, resulting in approximately 40 murders between 1890 and 1904. This included City Marshal John H. Bowman, who was shot and killed in his front parlor on January 29, 1903, in view of his family.
20th century
In 1925, a bungalow was built by Joseph Blanchard, an African American sea captain and fisherman. The Blanchard House Museum still stands as a museum, providing education about the history of middle-class African American life in the area.
Punta Gorda maintained steady growth. Charlotte County was formed in 1921 after DeSoto County was split. Also in 1921, the first bridge was constructed connecting Punta Gorda and Charlotte Harbor along the brand-new Tamiami Trail. This small bridge was replaced by the original Barron Collier Bridge in 1931, and then by the current Barron Collier Bridge and Gilchrist Bridge crossing the Peace River.
During World War II, a U.S. Army airfield was built in Punta Gorda to train combat air pilots. After the war, the airfield was turned over to Charlotte County. Today the old airfield is the Punta Gorda Airport, serving both commercial and general aviation.
Punta Gorda’s next intense growth phase started in 1959 with the creation of a neighborhood of canal-front home sites, Punta Gorda Isles, by a trio of entrepreneurs, Al Johns, Bud Cole and Sam Burchers. They laid out 55 miles of canals 100 feet wide and 17 feet deep using dredged sand to raise the level of the canal front land. This gave dry home sites access to the Charlotte Harbor and the Gulf of Mexico. Johns went on to develop several other communities in Punta Gorda, among which were Burnt Store Isles, another waterfront community with golf course, and Seminole Lakes, a golf course community. These communities provided waterfront or golf course homes for retirees with access to a downtown with shopping, restaurants, and parks.
In the early 1980s at the site of the old Maud Street Fishing Docks, a new shopping, restaurant and marina complex, Fishermen’s Village, was constructed that continues to be one of Southwest Florida’s primary attractions.
21st century
In 2004, a major hurricane, Hurricane Charley, moved through Punta Gorda, damaging many buildings, but also creating an opportunity for revitalization of both the historic downtown and the waterfront. During the first part of the 21st century, Punta Gorda continued to grow and improve, adding a new Harborwalk that continues to expand, a linear park that winds through the city, and many new restaurants and neighborhoods.
A replica of the Vietnam Veterans Memorial was dedicated on November 5, 2016. The city also features the Whispering Giant statue, a public art sculpture of the face of a Native American man and a Native American woman.
On September 28, 2022, the Category 4 Hurricane Ian made landfall in Punta Gorda, resulting in severe damage throughout Florida. Coincidentally, the storm made landfall with the same wind speed (145 mph, 235 km/h) as Hurricane Charley, and its minimum barometric pressure was only one millibar less than Charley’s.
Historic sites
There are many historic places in Punta Gorda, including ten on the National Register of Historic Places:
- A. C. Freeman House
- Charlotte High School
- Clarence L. Babcock House
- H. W. Smith Building
- Old First National Bank of Punta Gorda (also known as Old Merchants Bank of Punta Gorda)
- Punta Gorda Atlantic Coast Line Depot
- Punta Gorda Ice Plant
- Punta Gorda Residential District
- Punta Gorda Woman’s Club
- Villa Bianca
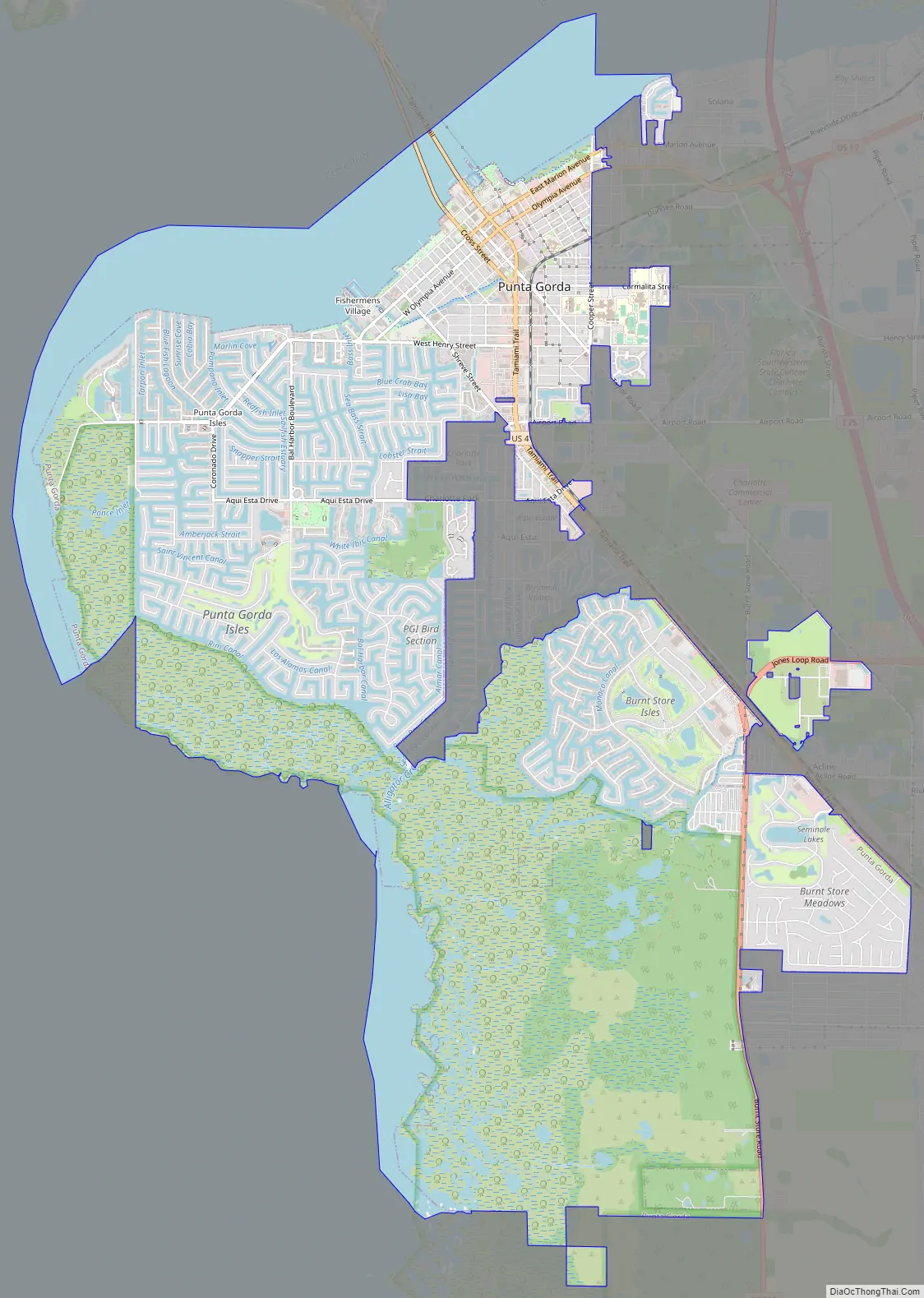
Punta Gorda Road Map
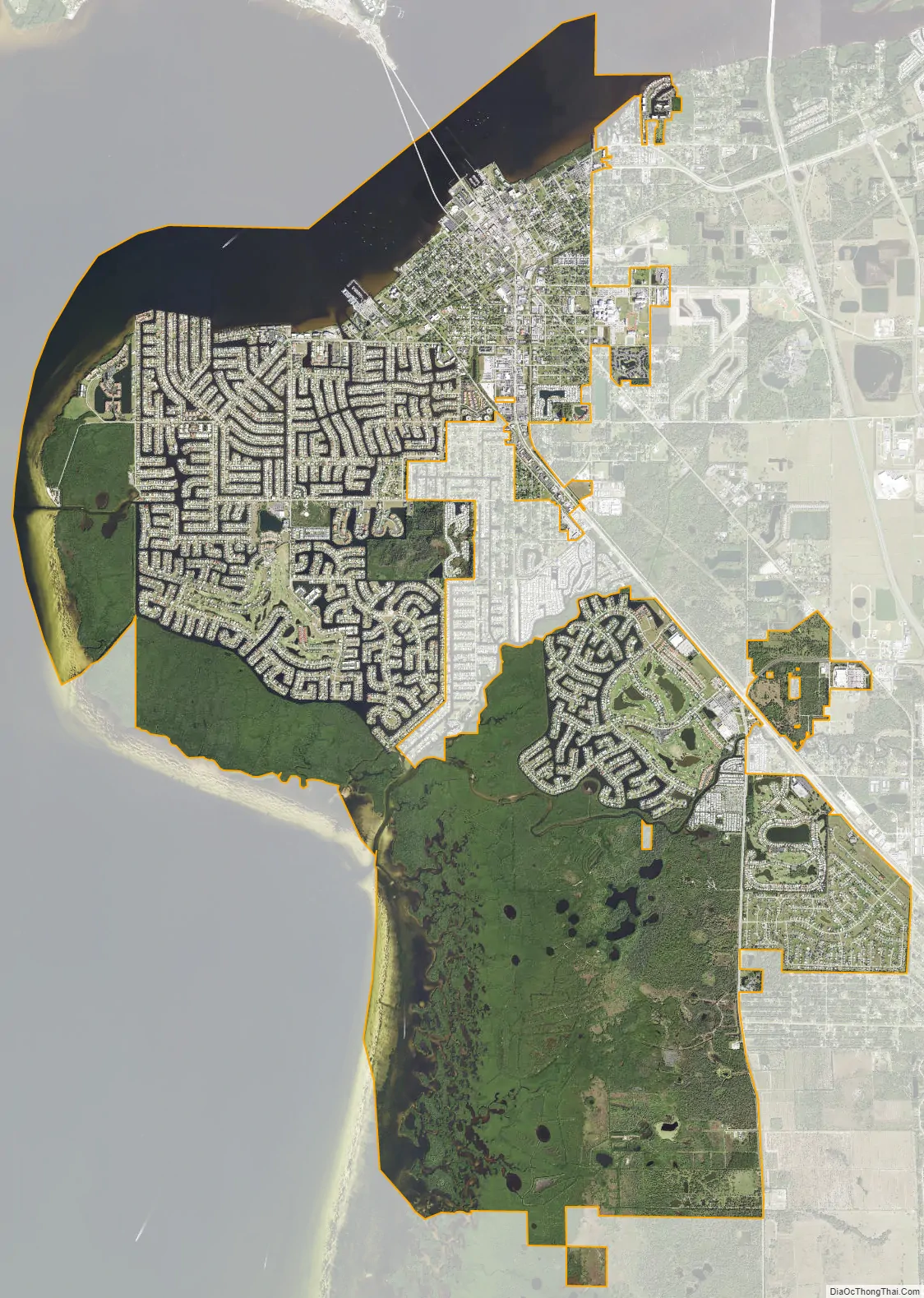
Punta Gorda city Satellite Map
Geography
Punta Gorda lies on the south bank of the tidal Peace River and the eastern shore of Charlotte Harbor, an arm of the Gulf of Mexico. Unincorporated communities bordering Punta Gorda include Charlotte Park (nearly surrounded by the city), Solana to the east, and Charlotte Harbor to the north, across the Peace River. Port Charlotte is west of Punta Gorda’s incorporated residential neighborhoods Deep Creek and Suncoast Lakes, north of the Peace River. Harbour Heights lies east of Punta Gorda’s Deep Creek residential neighborhood.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has an area of 21.0 square miles (54.4 km), of which 15.0 square miles (38.9 km) is land and 6.0 square miles (15.5 km) (28.52%) is water.
Climate
Zoning
As of October 5, 2017, Punta Gorda has 11 zoning districts, five overlay districts, and three planned development districts. Of the zoning districts, six are designated for residential use, two for commercial use, one for governmental use, and two districts allow mixed use.
See also
Map of Florida State and its subdivision:- Alachua
- Baker
- Bay
- Bradford
- Brevard
- Broward
- Calhoun
- Charlotte
- Citrus
- Clay
- Collier
- Columbia
- Desoto
- Dixie
- Duval
- Escambia
- Flagler
- Franklin
- Gadsden
- Gilchrist
- Glades
- Gulf
- Hamilton
- Hardee
- Hendry
- Hernando
- Highlands
- Hillsborough
- Holmes
- Indian River
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Lafayette
- Lake
- Lee
- Leon
- Levy
- Liberty
- Madison
- Manatee
- Marion
- Martin
- Miami-Dade
- Monroe
- Nassau
- Okaloosa
- Okeechobee
- Orange
- Osceola
- Palm Beach
- Pasco
- Pinellas
- Polk
- Putnam
- Saint Johns
- Saint Lucie
- Santa Rosa
- Sarasota
- Seminole
- Sumter
- Suwannee
- Taylor
- Union
- Volusia
- Wakulla
- Walton
- Washington
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming