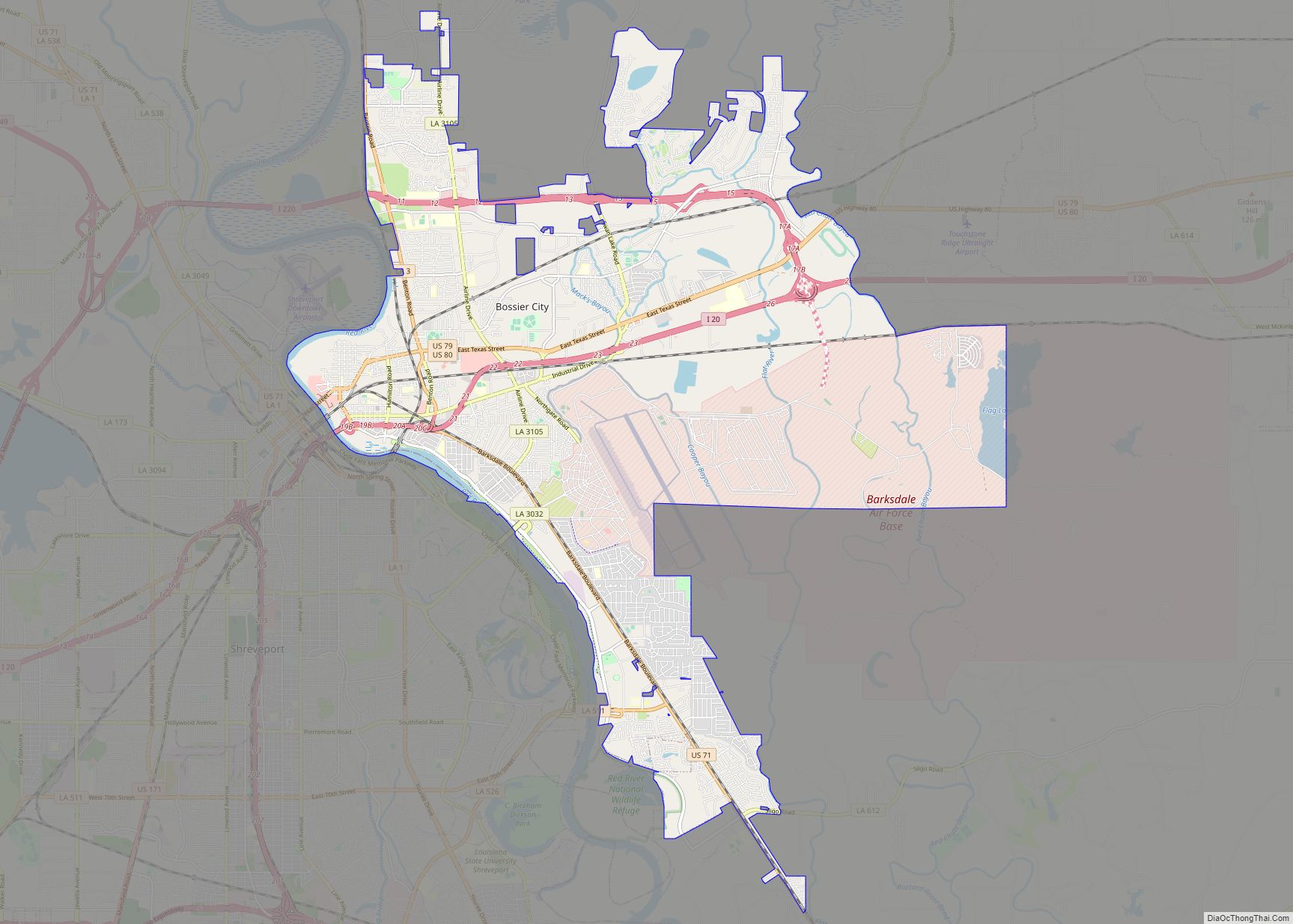
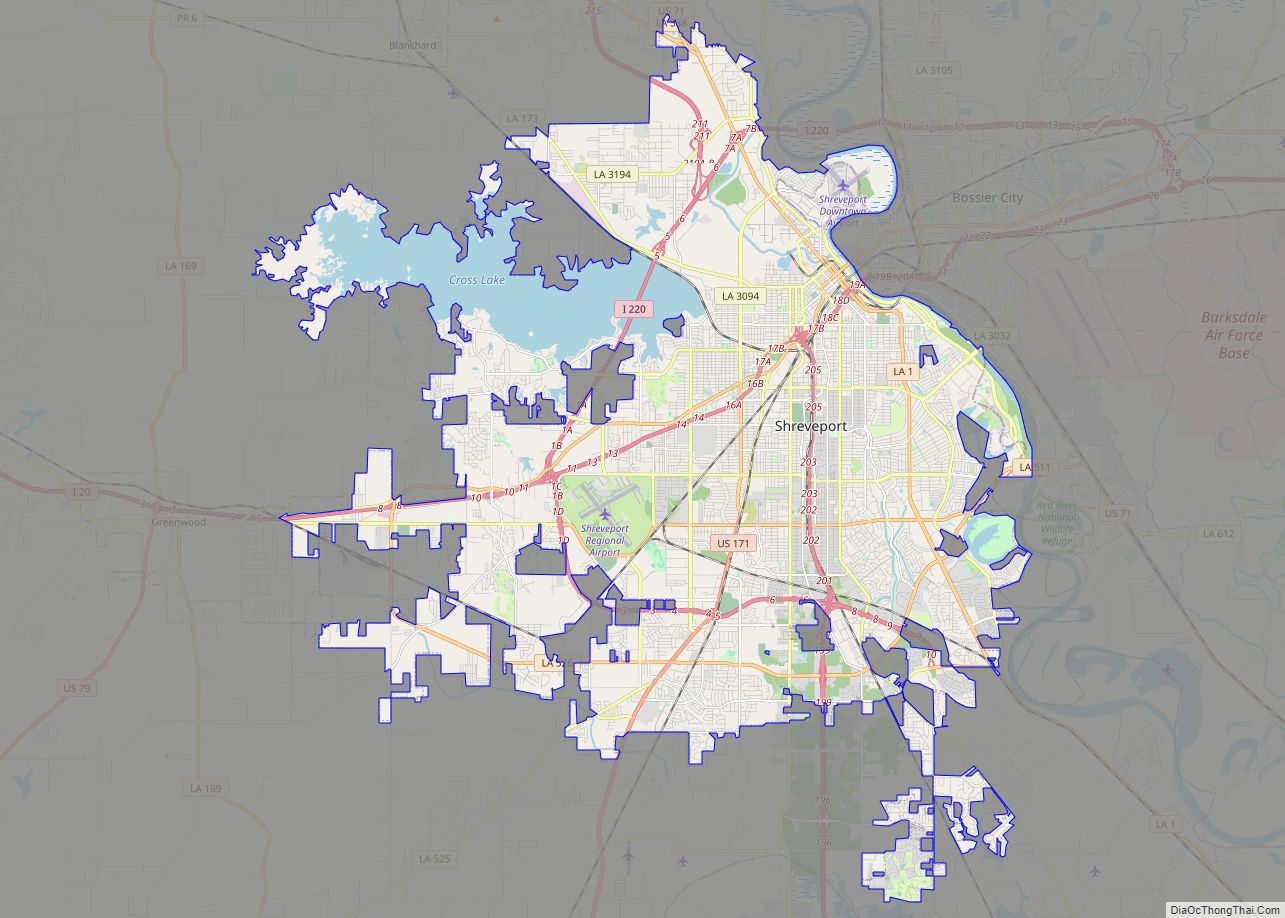
Bossier City (/ˈboʊʒər/ BOH-zhər) is a city in Bossier Parish in the northwestern region of the U.S. state of Louisiana in the United States. It is the second-most populous city in the Shreveport–Bossier City metropolitan statistical area. In 2020, it had a total population of 62,701, up from 61,315 in 2010.
Located on the eastern bank of the Red River, Bossier City is closely tied economically and socially to its larger sister city Shreveport on the opposite bank, though the city maintains its own community college (Bossier Parish Community College).
| Name: | Bossier City city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Louisiana |
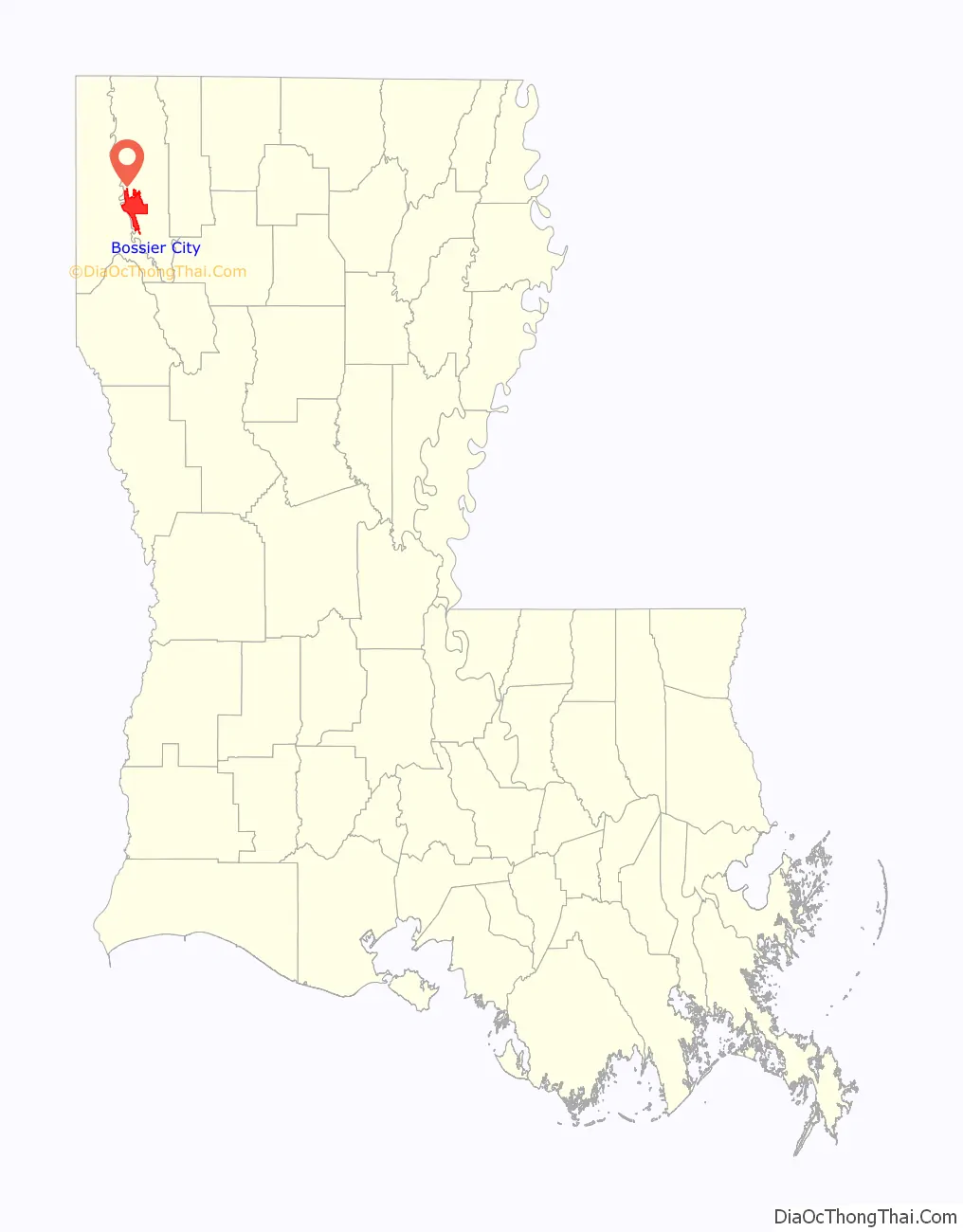
| County: | Bossier Parish |
| Founded: | 1907 |
| Elevation: | 174 ft (53 m) |
| Land Area: | 43.85 sq mi (113.57 km²) |
| Water Area: | 1.17 sq mi (3.03 km²) 1.89% |
| Population Density: | 1,429.90/sq mi (552.08/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 71111-71113, 71171-71172 |
| Area code: | 318 |
| FIPS code: | 2208920 |
| Website: | BossierCity.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
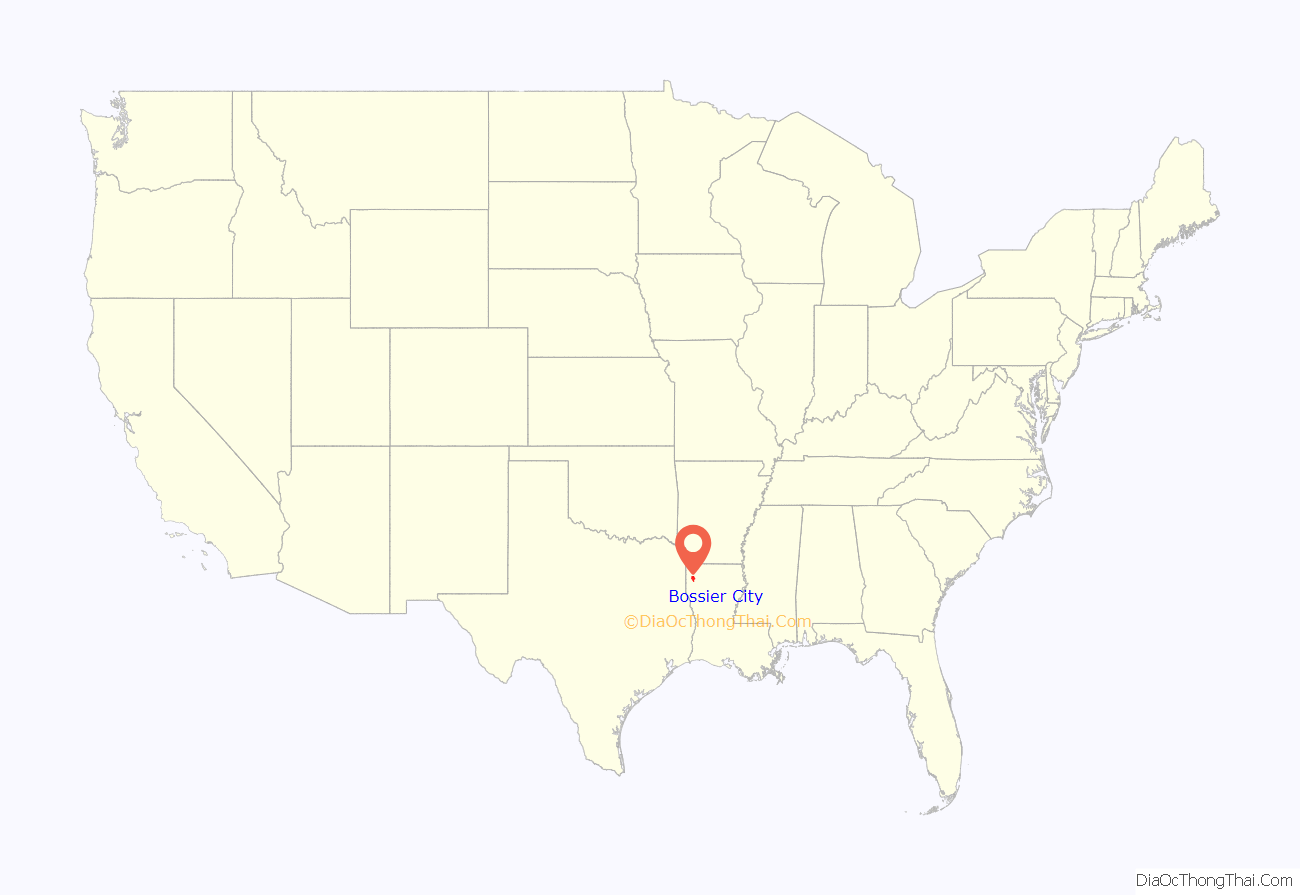
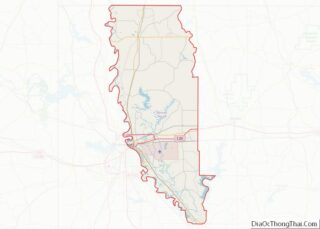
Bossier City location map. Where is Bossier City city?
History
19th century
In the 1830s, the area of Bossier City was the plantation Elysian Grove, which was purchased by James Cane and his second wife Mary Doal Cilley Bennett Cane. James had come to the area with his first wife Rebecca Bennett, and her brother, William Bennett, and his wife Mary Doal Cilley Bennett. They ran a trading post across the river on what was then Caddo Indian territory, a portion called “Bennett’s Bluff”. The trading post partners became a one-seventh partner in the new Shreve Town, which eventually developed as Shreveport.
Elysian Grove plantation was located along the Red River for access to transportation, where the Texas Trail crossed the Red River. The trading post on the west side operated a ferry between what would become Shreveport and Bossier City. The plantation loading and unloading dock was later recorded as Cane’s Landing in the old ferry log books. For a very short time, Cane’s Landing was known as Cane City. The Canes and Bennetts were among the earliest settlers in the area. Mary D. C. Bennett gave birth to the first white baby of the area, William Smith Bennett Jr., who died at an early age.
In 1843, a section of land east of the Red River was divided from the Great Natchitoches District and Claiborne Parish areas and was called Bossier Parish. It was named in honor of Pierre Evariste John Baptiste Bossier, a former Creole general, who became a cotton planter in Bossier Parish. He was one of the first European settlers in the area.
In the 1840s, the Great Western Migration of Americans and immigrants began, and the parish grew in population. Many early settlers passed through the region on their way to the Western U.S. By 1850, more than 200 wagons a week passed through Bossier City, many intending to settle in Texas. Some of these settlers stayed in Louisiana, attracted by the fertile soil and river valley. In 1850, the U.S. census listed the population at 6,962.
American Civil War
During the American Civil War, companies of Confederate soldiers shipped out of Cane’s Landing aboard steamboats for distant battlefields. Mrs. Cane hosted hundreds of Confederate officers and troops who were heading off to war. Mrs. Cane’s plantation was fortified to protect Shreveport by three batteries, with Fort Kirby Smith in the center. The others were Batteries Price, and Walker and Ewell.
Fort Smith protected the area from an eastern invasion. The American Civil War reached Bossier Parish in 1861, and ended in Shreveport four years later, when the Trans-Mississippi Department surrendered. In the 20th century, Bossier High School was constructed near the former site of the fort.
Shed Road
Shed Road, the first all-weather turnpike in the American South, was constructed in the 1870s and operated from 1874 to 1886. It extended for 9 miles (14 km) from Red Chute to the Red River. A plantation was at the end of the elevated and covered roadway, which was accessible by a ferry boat. The covered road made the transportation of goods easier before the arrival of the railroads.
Classification as a city
Anna B., granddaughter of James and Mary Cane, felt the area would prosper and began promoting the idea of a riverfront city. Anna B. and J. J. Stockwell sold lots in 1883. The area grew quickly, as did transportation through it. At the time, the unincorporated settlement was often called Cane City. Around 1907, Cane City was incorporated by former Louisiana Governor Newton C. Blanchard and renamed the village of Bossier City. Blanchard named a Shreveport businessman, Ewald Max Hoyer, as the first Bossier City mayor. By that time, Bossier City had grown from an area around a square mile to a city containing more than 35 sq mi (91 km). Continued growth led to Bossier City’s being redesignated from village to town by Governor John M. Parker. Later, Governor Earl Kemp Long issued a proclamation classifying Bossier City as a city.
The “golden spike” commemorated the completion of the east–west Vicksburg, Shreveport and Pacific Railroad. It was driven at Bossier City on July 12, 1884, by Julia “Pansy” Rule. It was the first such spike to be driven by a woman. The north–south Shreveport and Arkansas Railroad was completed on April 6, 1888. The Louisiana–Arkansas Railroad was completed on November 2, 1909. The Dixie Overland Highway from the East to the West Coast was built in 1918. These railroads and highways combined to make Bossier City a hub for future activity.
The discovery of crude oil, to the south, in 1908, thrust Bossier City into the nationwide oil boom. Bossier’s central location to the rural oil fields made it a major player in the oil patch. Several international oil companies were located in the area. The advantages brought by black gold fueled many civic, social and economic improvements.
A fire on June 23, 1925, consumed one-half of downtown Bossier City. Local citizens were unable to battle the blaze. The loss spurred civic improvements, including a modern water system capable of fighting such fires, a new city hall, a modern fire alarm system, modern sidewalks, and the first city park.
In the 1930s, construction began on Barksdale Airfield (now Barksdale Air Force Base). The land on which the base is built was unincorporated property south of Bossier City in 1929. This land was annexed by the city of Shreveport and donated to the federal government. Through the years, Bossier City expanded, eventually encompassing the area surrounding the base. The first unit assigned to Barksdale was the 20th Pursuit Group. Before World War II, Barksdale was a training school for the Army Air Corps. During World War II, Barksdale trained pilots, navigators, and bombardiers. Later, the base became one of the key bases of the Strategic Air Command in the new Air Force. Barksdale is the headquarters for the 8th Air Force.
In the 1890s, Cane City had a population of about 600. Bossier City in 2012 had an estimated population of over 64,000. First a cotton-exporting river landing, next a railroad town, then an airbase and oil-boom town, Bossier City has become known for its tourism and casino gambling.
Three casinos in the city have financed a number of municipal projects, many completed during the administration of the late Mayor George Dement. Recent improvements include the CenturyLink Center, Louisiana Boardwalk, Benton Road Overpass, and the Arthur Ray Teague Parkway, located along the eastern side of the Red River. Dement also procured Amtrak service between Bossier City and Dallas, Texas. Dement was succeeded as mayor in 2005 by his administrative assistant and former mayoral opponent from 1989, Lo Walker, the first Republican to hold the city’s top executive position.
Growth and redevelopment
On April 20, 2017, in their joint “State of Bossier” address, hosted by the Bossier Chamber of Commerce, Mayor Lo Walker, and Bossier Parish Police Jury President Bob Brotherton described the growth of the city and parish as “outstanding.” With a population of 69,000 in a 2015 study by Louisiana State University, Bossier City had become the sixth-largest city in the state and the fastest-growing one.
Walker said that the city and the parish “work extremely close together, and our business and civic leaders and military make us an outstanding parish.” The parish grew at 19%; the city grew at 10%. According to the Bossier Economic Development Foundation, the city could have reached 80,000 by 2019. Ongoing projects contributing to growth include the Walter O. Bigby Carriageway (the north parkway extension named for former state representative and judge Walter O. Bigby), Shed Road construction, and the South Bossier redevelopment districts.
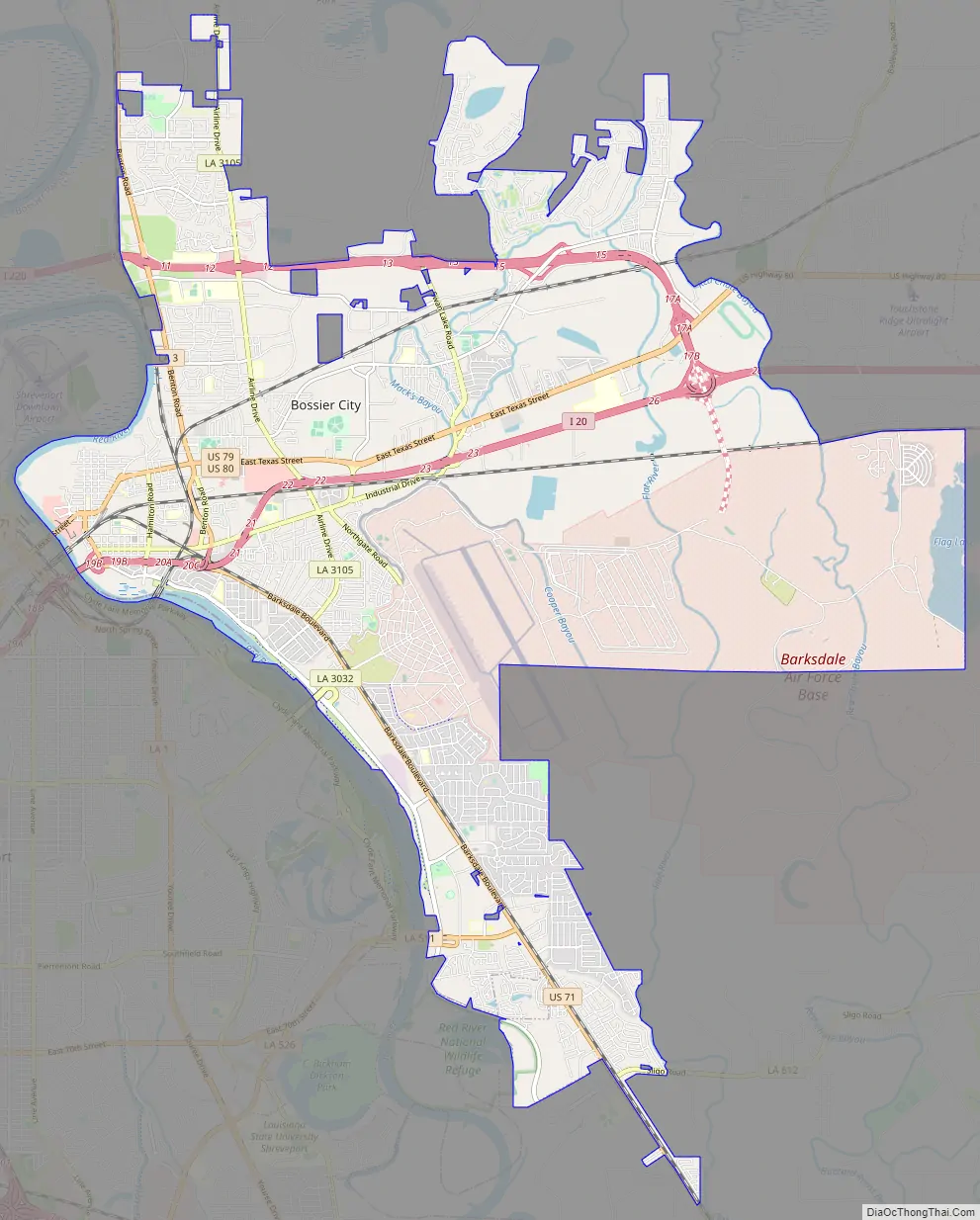
Bossier City Road Map
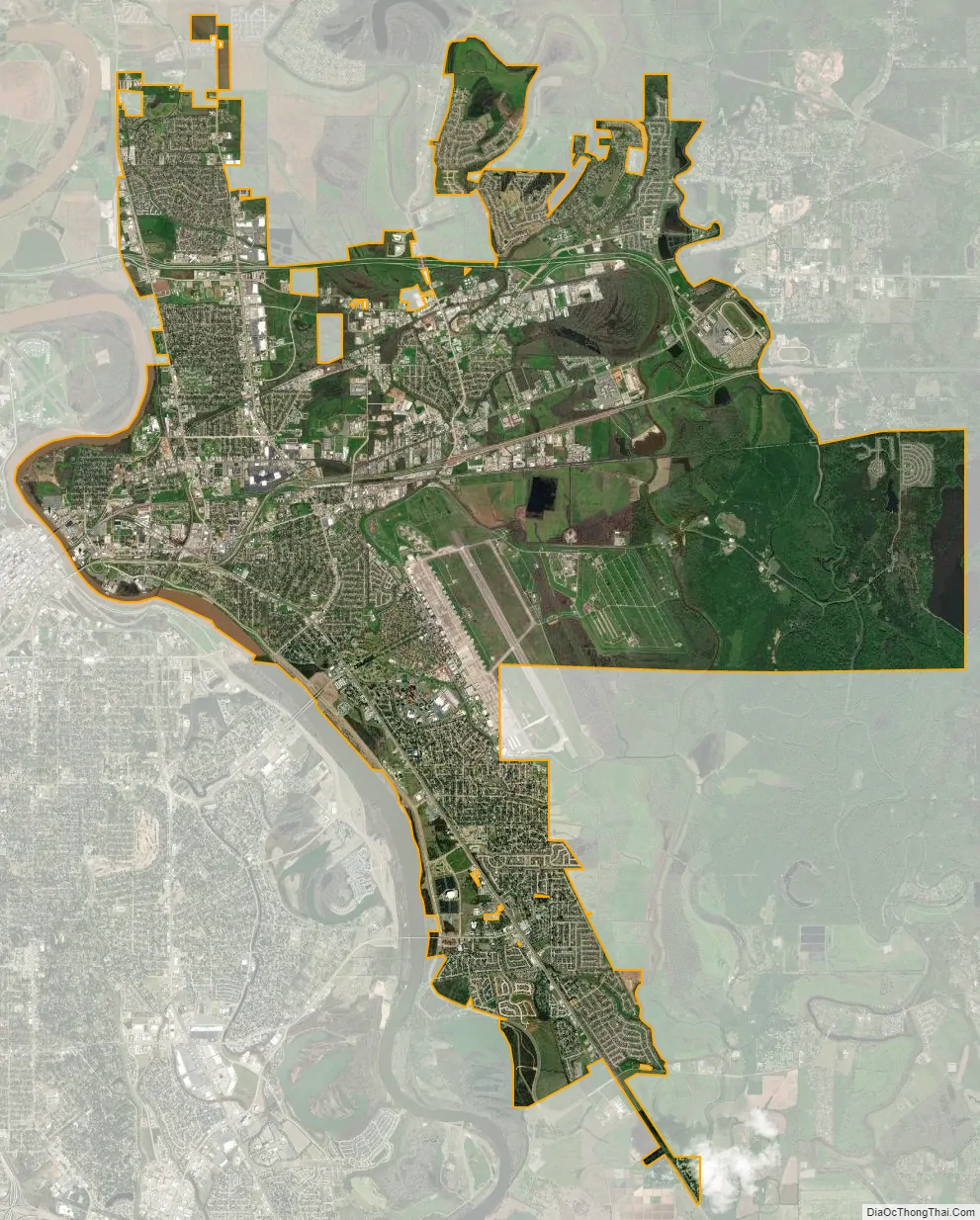
Bossier City city Satellite Map
Geography
Bossier City is located at 32°31′4″N 93°41′29″W / 32.51778°N 93.69139°W / 32.51778; -93.69139 (32.517651, −93.691397) within the Ark-La-Tex and has an elevation of 174 feet (53.0 m) above sea level. The city lies primarily on the banks of the Red River, and has a largely flat topography in contrast with Shreveport’s terrain. The northern city limits are noticeably more hilly than the rest of the city. Many small waterways flow through the city, such as Flat River and Red Chute Bayou, which provide drainage for many areas of the city.
The city has a total area of 43.90 square miles (113.69 km), of which 0.99 square miles (2.56 km) are covered by water.
Climate
Bossier shares most aspects of its climate with its sister city of Shreveport. The city has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) with hot, humid summers and mild winters.
During the warmer months, the city is prone to severe thunderstorms that feature heavy rain, high winds, hail, and occasional tornadoes. The city has a slightly above-average rate of tornadoes when compared to the U.S. average. Due to the flat topography of the city and the prominence of smaller waterways that are prone to backwater flooding from the Red River, the city occasionally experiences severe flooding events. A notable occurrence of severe flooding occurred in March 2016 after torrential rains caused a rapid rise of many local waterways, displacing upwards of 3,500 people from their homes across the area. Freezes and ice storms regularly occur during the winters.
See also
Map of Louisiana State and its subdivision:- Acadia
- Allen
- Ascension
- Assumption
- Avoyelles
- Beauregard
- Bienville
- Bossier
- Caddo
- Calcasieu
- Caldwell
- Cameron
- Catahoula
- Claiborne
- Concordia
- De Soto
- East Baton Rouge
- East Carroll
- East Feliciana
- Evangeline
- Franklin
- Grant
- Iberia
- Iberville
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Jefferson Davis
- La Salle
- Lafayette
- Lafourche
- Lincoln
- Livingston
- Madison
- Morehouse
- Natchitoches
- Orleans
- Ouachita
- Plaquemines
- Pointe Coupee
- Rapides
- Red River
- Richland
- Sabine
- Saint Bernard
- Saint Charles
- Saint Helena
- Saint James
- Saint John the Baptist
- Saint Landry
- Saint Martin
- Saint Mary
- Saint Tammany
- Tangipahoa
- Tensas
- Terrebonne
- Union
- Vermilion
- Vernon
- Washington
- Webster
- West Baton Rouge
- West Carroll
- West Feliciana
- Winn
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming