Vancouver is a city on the north bank of the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, located in Clark County. Incorporated in 1857, Vancouver has a population of 190,915 as of the 2020 census, making it the fourth-largest city in Washington state. Vancouver is the county seat of Clark County and forms part of the Portland-Vancouver metropolitan area, the 25th-largest metropolitan area in the United States. Originally established in 1825 around Fort Vancouver, a fur-trading outpost, the city is located on the Washington–Oregon border along the Columbia River, directly north of Portland, and is considered a suburb of the city along with its surrounding areas.
| Name: | Vancouver city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
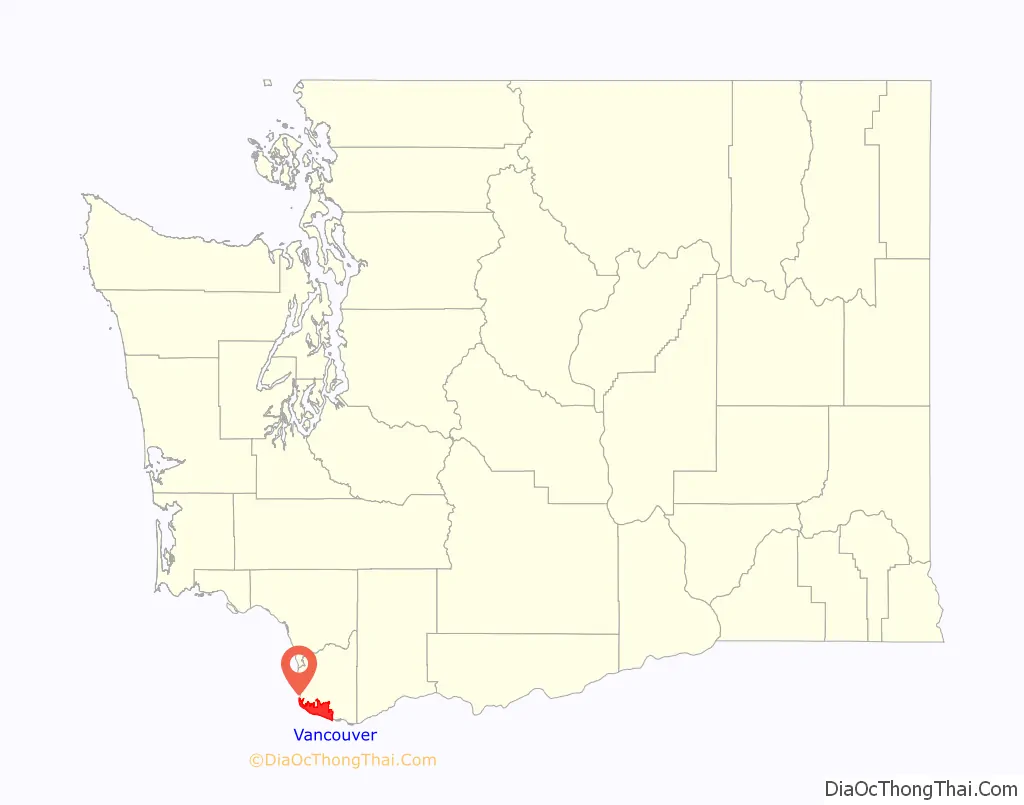
| State: | Washington |
| County: | Clark County |
| Founded: | 1825 |
| Incorporated: | 1857 |
| Elevation: | 171 ft (52 m) |
| Land Area: | 48.74 sq mi (126.25 km²) |
| Water Area: | 3.70 sq mi (9.59 km²) |
| Population Density: | 3,784.32/sq mi (1,461.14/km²) |
| Area code: | 360, 564 |
| FIPS code: | 5374060 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1531916 |
| Website: | cityofvancouver.us |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
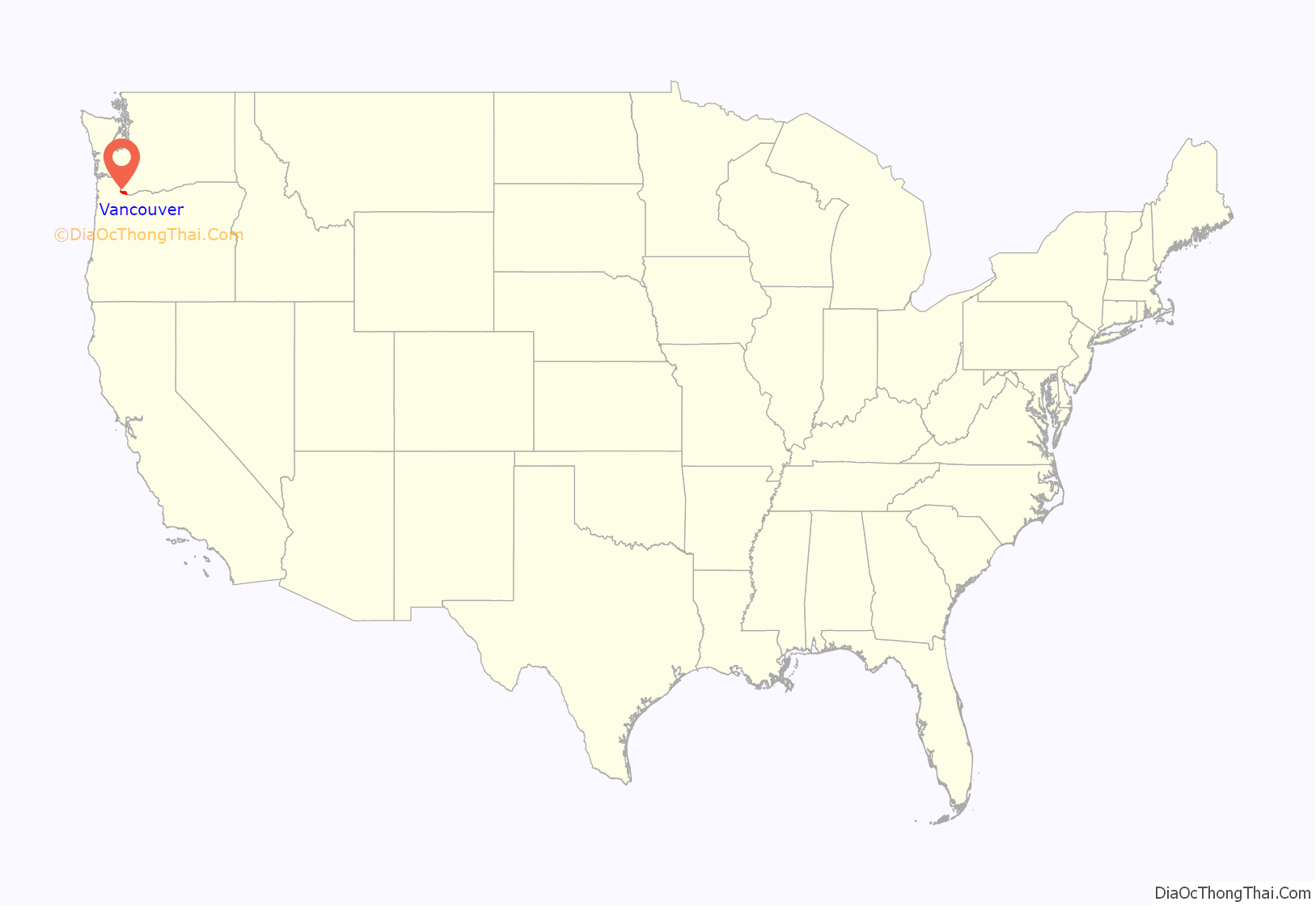
Vancouver location map. Where is Vancouver city?
History
The Vancouver area was inhabited by several Native American tribes, most recently the Chinook and Klickitat nations, with permanent settlements of timber longhouses. The Chinookan and Klickitat names for the area were reportedly Skit-so-to-ho and Ala-si-kas, respectively, meaning “land of the mud-turtles”. First known European contact was made by William Robert Broughton in 1792, with approximately half of the indigenous population killed by smallpox before the Lewis and Clark Expedition arrived in the area in 1806. Within another fifty years, other diseases such as measles, malaria and influenza had reduced the Chinookan population from an estimated 80,000 “to a few dozen refugees, landless, slaveless and swindled out of a treaty”.
Meriwether Lewis wrote that the Vancouver area was “the only desired situation for settlement west of the Rocky Mountains.” The first permanent European settlement did not occur until 1824, when Fort Vancouver was established as a fur trading post of the Hudson’s Bay Company. From that time on, the area was settled by both the US and Britain under a “joint occupation” agreement. Joint occupation led to the Oregon boundary dispute and ended on June 15, 1846, with the signing of the Oregon Treaty, which gave the United States full control of the area. Before 1845, American Henry Williamson laid out a large claim west of the Hudson’s Bay Company (including part of the present-day Port of Vancouver), called Vancouver City and properly registered his claim at the U.S. courthouse in Oregon City, before leaving for California. In 1848, Williamson had it surveyed and platted by Peter Crawford. In 1850, Amos Short traced over the claim of Williamson and named the town Columbia City. It changed to Vancouver in 1855. The City of Vancouver was incorporated on January 23, 1857.
Based on an act in the 1859–60 legislature, Vancouver was briefly the capital of Washington Territory, before capital status was returned to Olympia, Washington by a 2–1 ruling of the territory’s supreme court, in accordance with Isaac Stevens’ preference and concern that proximity to the border with Oregon might give some of the state’s influence away to Oregon.
During 1852–54, future United States President Ulysses S. Grant, then a captain in the U.S. Army, was quartermaster at what was then known as Columbia Barracks. Soon after leaving Vancouver, Grant resigned from the army and did not serve again until the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861. Other notable generals to have served in Vancouver include George B. McClellan, Philip Sheridan, Oliver O. Howard and 1953 Nobel Peace Prize recipient George C. Marshall.
Army presence in Vancouver was very strong, as the Department of the Columbia built and moved to Vancouver Barracks, the military reservation for which stretched from the river to what is currently Fourth Plain Boulevard and was the largest Army base in the region until surpassed by Fort Lewis, 120 miles (190 km) to the north. Built on the old company gardens and skirmish range, Pearson Army Field (later Pearson Field) was a key facility, and at one point the US Army Signal Corps operated the largest spruce cut-up plant in the world to provide much-needed wood for airplanes. Vancouver became the end point for two ultra-long flights from Moscow, USSR, over the North Pole. The first of these flights was performed by Valery Chkalov in 1937 on a Tupolev ANT-25RD airplane. Chkalov was originally scheduled to land at an airstrip on Swan Island in nearby Portland, Oregon, but was redirected at the last minute to Vancouver’s Pearson Airfield. In June 1975, a monument was dedicated commemorating the event near State Highway 14, then moved to the north side of Pearson Field in 1987. Chkalov Drive, in east Vancouver, was named in his honor.
The neighborhood of Sifton was the terminus of an early electric trolley operated by the Northcoast Power Company that also served nearby Orchards from 1910 until 1926. The trolleys made ten stops and ran once per hour, charging 15 cents each way. A mural in the heart of Orchards depicts the trolley and the rural character of the area at the time it was operating. The community was named after Doctor Sifton, a promoter of the trolley service.
According to the archives of the Vancouver Columbian newspaper, the Orchards-Sifton route ran along Vancouver’s Main Street to 26th street (renamed Fourth Plain Blvd), then from 26th to K Street and thence north to 33rd street. From there, it ran on 33rd over Burnt Bridge Creek and past the city limits. At that point the trolley became more like a regular train as it followed a cut through the wilderness. Few houses were seen between Vancouver and Orchards. The public’s growing preference for motor cars in the 1920s heralded the end of the trolley.
Separated from Oregon until 1917, when the new Interstate Bridge began to replace ferries, Vancouver had three shipyards just downstream which produced ships for World War I before World War II brought an enormous economic boom. An Alcoa aluminum plant opened on September 2, 1940, using inexpensive power from the nearby New Deal hydropower turbines at Bonneville Dam. After the bombing of Pearl Harbor, Henry Kaiser opened a shipyard next to the U.S. Army base, which by 1944 employed as many as 36,000 people in a twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week production of Liberty ships, landing ship tanks, and escort carriers. This influx of shipyard workers boosted the population from 18,000 to over 80,000 in just a few months, leading to the creation of the Vancouver Housing Authority and six new residential developments: Fruit Valley, Fourth Plain Village, Bagley Downs, Ogden Meadows, Burton Homes and McLoughlin Heights. Each of these was later incorporated into the city, and are well-known neighborhoods, while the neighboring “shipyard city” of Vanport, Oregon, would be destroyed by the Memorial Day flood of 1948.
Vancouver has recently experienced conflicts with other Clark County communities because of rapid growth in the area. The city’s first annexation more than doubled its size in 1909, with the largest annexation of 1997 adding 11,258 acres (45.56 km) and 58,171 residents. As a result of urban growth and the 1997 annexation, Vancouver is often thought of as split between two areas, East and West Vancouver, divided by NE Andresen Road. West Vancouver is home to downtown Vancouver and most of the more historical parts of the city, as well as recent high-density mixed-use development. East Vancouver includes the communities of Cascade Park East and West, which had populations of 6,996 and 6,956 in 1990, before annexation.
More than one-third of the Vancouver urban area’s population lives in unincorporated urban areas north of the city limits, including the communities of Hazel Dell, Felida, Orchards and Salmon Creek. If county leaders had approved another major annexation plan in 2006, Vancouver would have passed Tacoma and Spokane to become the state’s second-largest city.
Etymology
Vancouver shares its name with the larger city of Vancouver in southern British Columbia, Canada, approximately 300 miles (480 km) to the north. Both cities were named after British sea captain George Vancouver, but the US city is older. Vancouver, British Columbia, was incorporated 29 years after the incorporation of Vancouver, Washington, and more than 60 years after the name Vancouver was first used in reference to the historic Fort Vancouver trading post on the Columbia River. City officials have periodically suggested changing the U.S. city’s name to Fort Vancouver to reduce confusion with its larger and better-known northern neighbor. Many Pacific Northwest residents distinguish between the two cities by referring to the Canadian city as “Vancouver, B.C.” and the United States city as “Vancouver, Washington,” or “Vancouver, USA.” Local nicknames include “Vantucky” (though this is often used as a derogatory term) and “The ‘Couv(e)”.
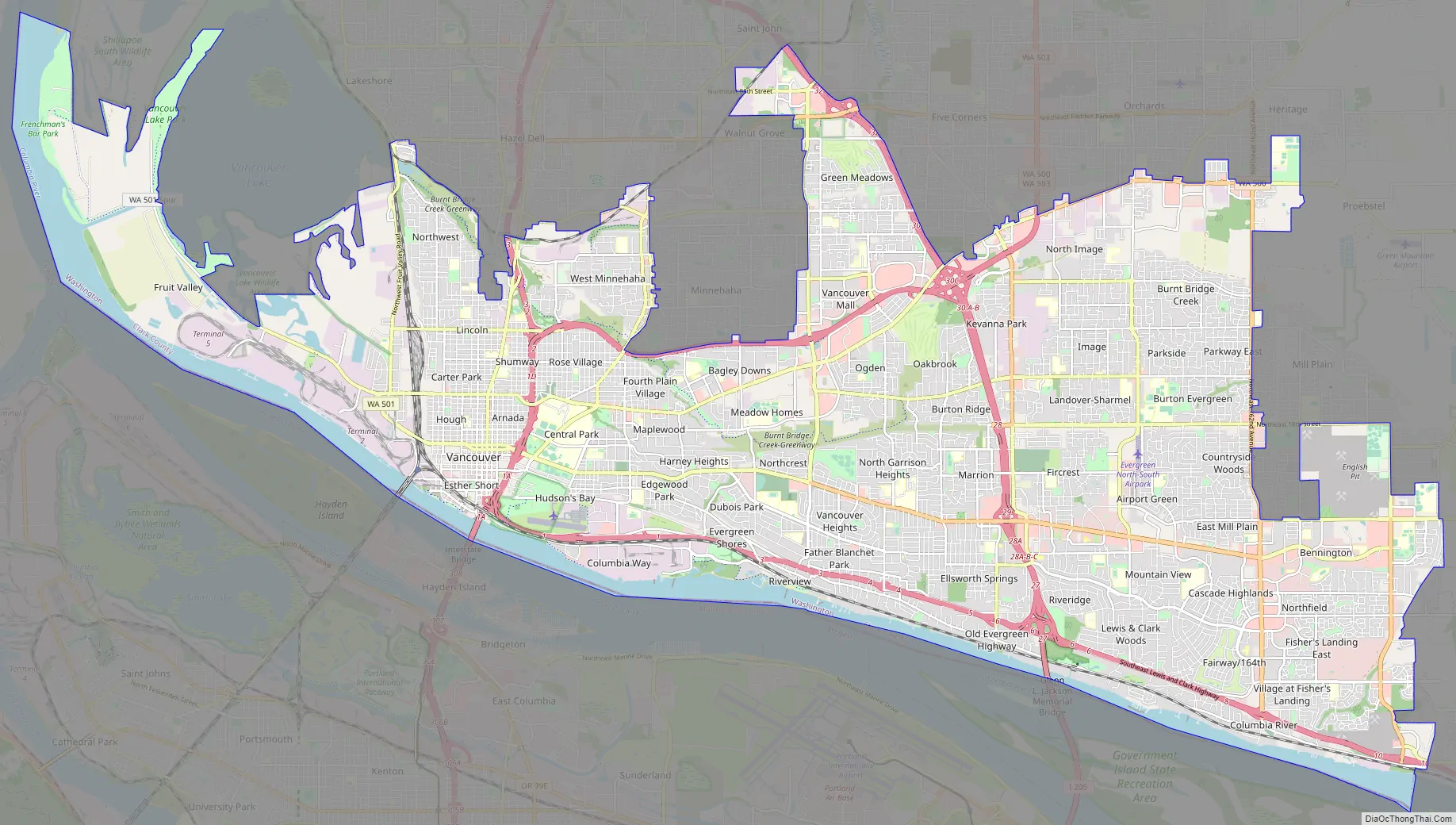
Vancouver Road Map
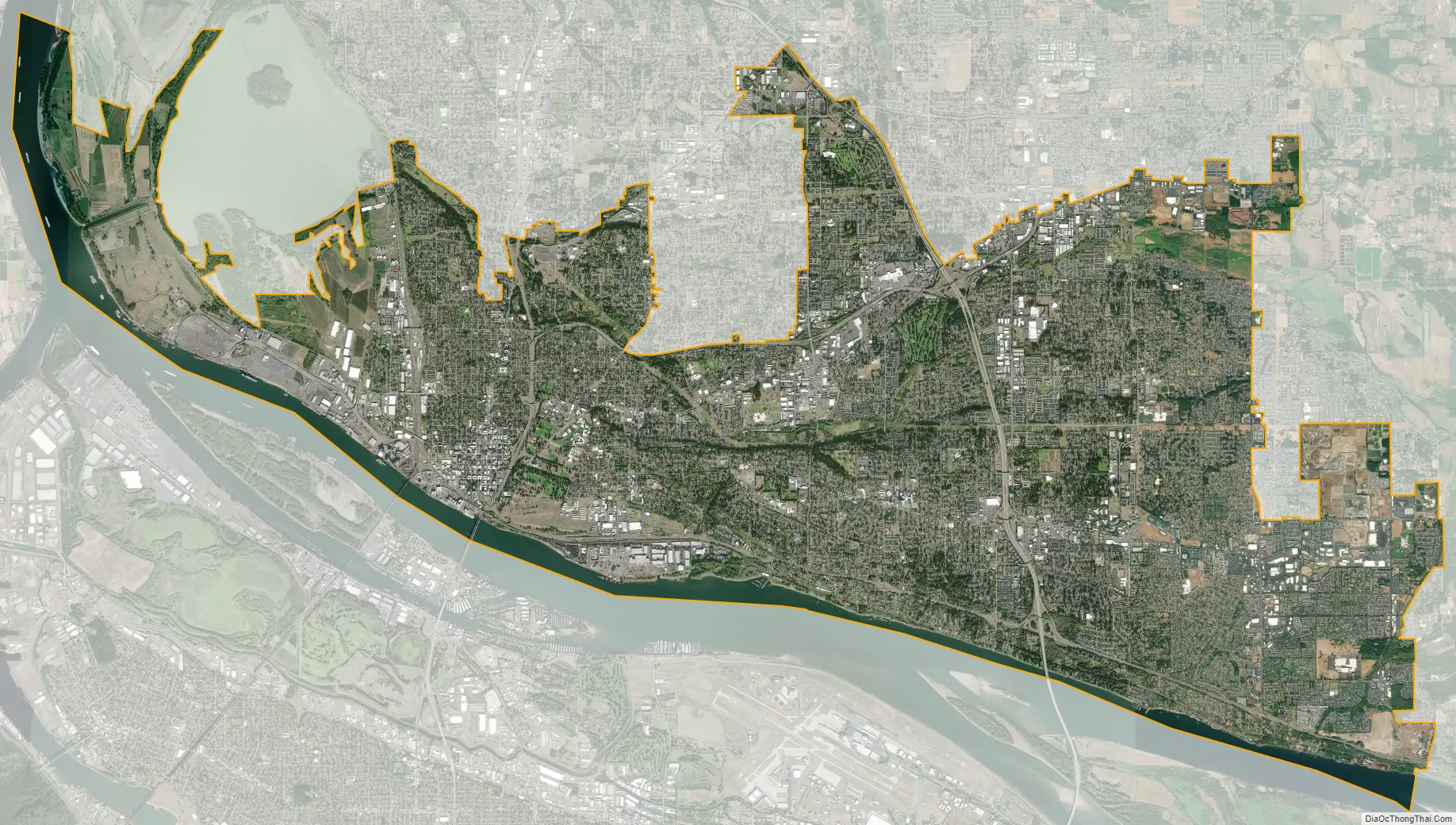
Vancouver city Satellite Map
Geography
Vancouver is located just north of the Columbia River and the Oregon border, just west of where the Columbia River Gorge bisects the volcanic Cascade Range and just east of where the Willamette River enters the Columbia. The city of Vancouver is in the Western Lowlands region of Washington. When clouds do not blanket the Puget–Willamette trough formed by the Cascade and Coast Range, Mount Hood, Mount St. Helens, Mount Rainier, Mount Jefferson and Mount Adams are all visible from Vancouver.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 49.86 sq mi (129.14 km), of which 46.46 sq mi (120.33 km) is land and 3.4 sq mi (8.81 km) is water.
Climate
Vancouver lies just north of Portland, Oregon, with which it shares a similar climate. Both are classified as warm-summer Mediterranean (Csb) on the Köppen climate classification, with certain key exceptions. High pressures east of the Cascade Range create something of a venturi effect, leading to cold east winds down the Columbia River Gorge. Unsheltered by the Willamette Valley, Vancouver has historically seen colder temperatures, including “silver thaw” storms where freezing rain cakes limbs and power lines. Such storms can paralyze Vancouver. This occasionally freezes the river, and in 1916 cut electric power in the city for almost two weeks. Rainfall occurs frequently throughout the fall, winter, and spring, but ceases around the middle of June, with dry and warm weather lasting through September. Average annual precipitation is 42 in (1,100 mm). Heavy snowfalls are infrequent and snow often falls and doesn’t stick, with major snowstorms only occurring every 2–4 years. Close proximity to the river was also a concern for flooding, before dams constricted the river, destroying features such as Celilo Falls. Periodic floods have been a nuisance, with two of the most destructive occurring in June 1894 and May 1948. The 1948 Columbia River flood almost topped the Interstate Bridge’s support piers and completely destroyed nearby Vanport, Oregon. Other unusual storms include the Columbus Day Storm of 1962 and an April 5, 1972, tornado which rated F3 on the Fujita scale, striking a local school. An EF1 tornado struck on January 10, 2008, just after noon, causing moderate damage along a two-mile (3.2 km) path from Vancouver Lake to the unincorporated Hazel Dell area.
Because many Vancouver residents work in Portland, there is typically significant rush-hour traffic congestion on two bridges that cross the Columbia River – the Interstate Bridge and the Glenn Jackson Bridge. In 2017 there were 297,932 weekday vehicle crossings on the two bridges.
See also
Map of Washington State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Asotin
- Benton
- Chelan
- Clallam
- Clark
- Columbia
- Cowlitz
- Douglas
- Ferry
- Franklin
- Garfield
- Grant
- Grays Harbor
- Island
- Jefferson
- King
- Kitsap
- Kittitas
- Klickitat
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Mason
- Okanogan
- Pacific
- Pend Oreille
- Pierce
- San Juan
- Skagit
- Skamania
- Snohomish
- Spokane
- Stevens
- Thurston
- Wahkiakum
- Walla Walla
- Whatcom
- Whitman
- Yakima
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming