Glasgow is a city in and the county seat of Valley County, Montana, United States. The population was 3,202 at the 2020 census.
Despite being just the 23rd most populous city in Montana, Glasgow is the most populous city for over 110 mi (177 km), thus making it an important economic hub for a large region in Eastern Montana. Both Amtrak and the National Weather Service operate facilities in Glasgow that link the city to the surrounding region.
| Name: | Glasgow city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Montana |
| County: | Valley County |
| Founded: | 1887 |
| Elevation: | 2,090 ft (638 m) |
| Total Area: | 1.40 sq mi (3.63 km²) |
| Land Area: | 1.40 sq mi (3.63 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 3,202 |
| Population Density: | 2,282.25/sq mi (880.89/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 59230–59231 |
| Area code: | 406 |
| FIPS code: | 3031075 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0771793 |
| Website: | cityofglasgowmt.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Glasgow location map. Where is Glasgow city?
History
Native Americans inhabited the region for centuries, and extensive buffalo and pronghorn antelope herds provided ample food for the nomadic tribes. The Nakoda, Lakota, and Dakota peoples alternately inhabited and claimed the region from the 16th to the late 19th centuries. In 1804 the Lewis and Clark Expedition came within 15 miles (24 km) of the future site of Glasgow and noted the extensive herds of buffalo and various game. In 1851, the US government formed the first treaty with the Native American tribes, in 1885 the tribes engaged in the last known buffalo hunt in the region, and in 1887, a treaty was signed where the tribes surrendered 17.5 million acres (71,000 km), which led from 1888 to the formation of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation and the removal of the tribes from the Glasgow area.
Glasgow was founded in 1887 as a railroad town by James Hill, who was responsible for creating many communities along the Hi-Line. He and a local railroader named the town when they spun a globe and their finger landed on Glasgow, Scotland. Glasgow grew during the 1930s when President Franklin D. Roosevelt authorized the construction of the Fort Peck Dam, which became a major source of employment for the Glasgow area.
During World War II, the Glasgow Army Airfield housed the 96th Bombardment Squadron and 614th Bombardment Squadron, flying B-17 Flying Fortresses, at different times during the war. Starting in December 1944, a German POW camp was established at the facility, lasting until the end of the war. After the war ended the base was closed, and part of the facility eventually became the present day Glasgow Airport. Glasgow was the death place of Lieutenant Colonel Ronald Speirs, famed member of Easy Company, 101st Airborne.
In the 1960s, the population rose to about 6,400 due to the nearby presence of the Glasgow Air Force Base, (SAC air command and housing B-52 bombers) used during the Vietnam War and the earlier part of the Cold War. A significant amount of mid-century modern and Googie-style architecture was built then. After the de-activation and closure of the base in 1969, Glasgow’s population declined to about half its one-time size by 1990, when the loss rate stabilized. Glasgow currently functions as the major regional administrative, shopping and services hub for Valley County and some of the areas beyond.
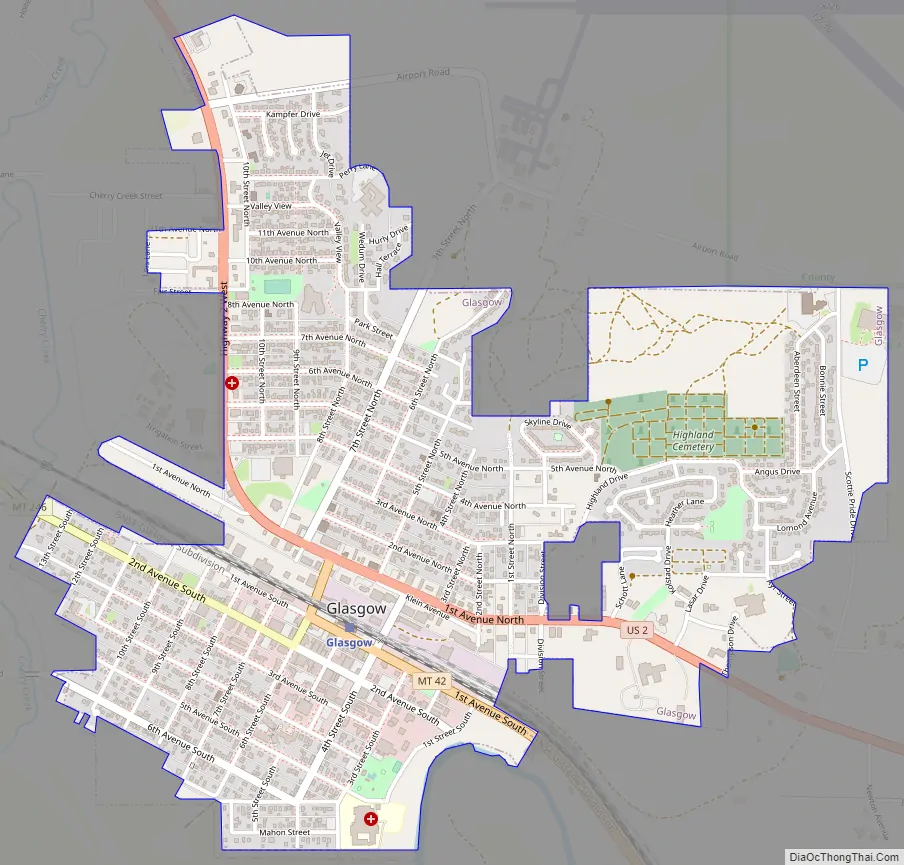
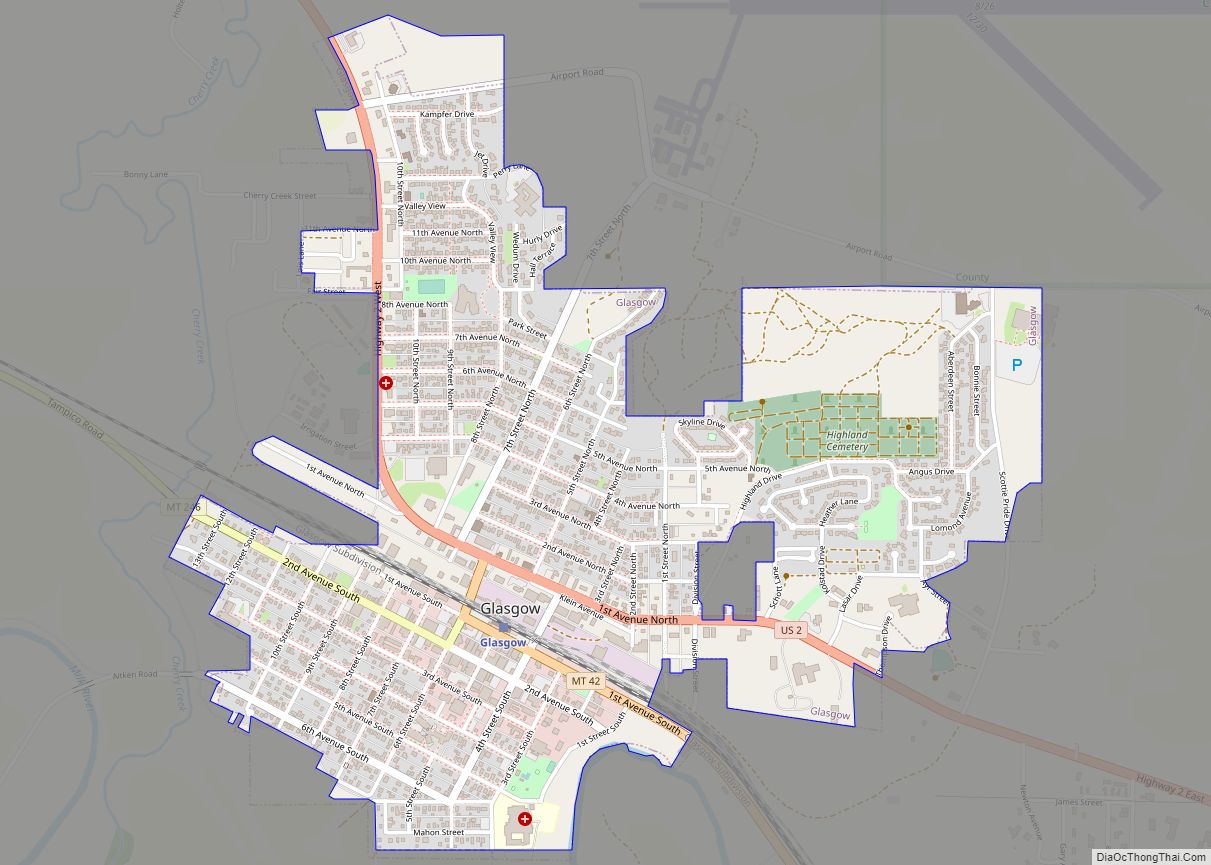
Glasgow Road Map
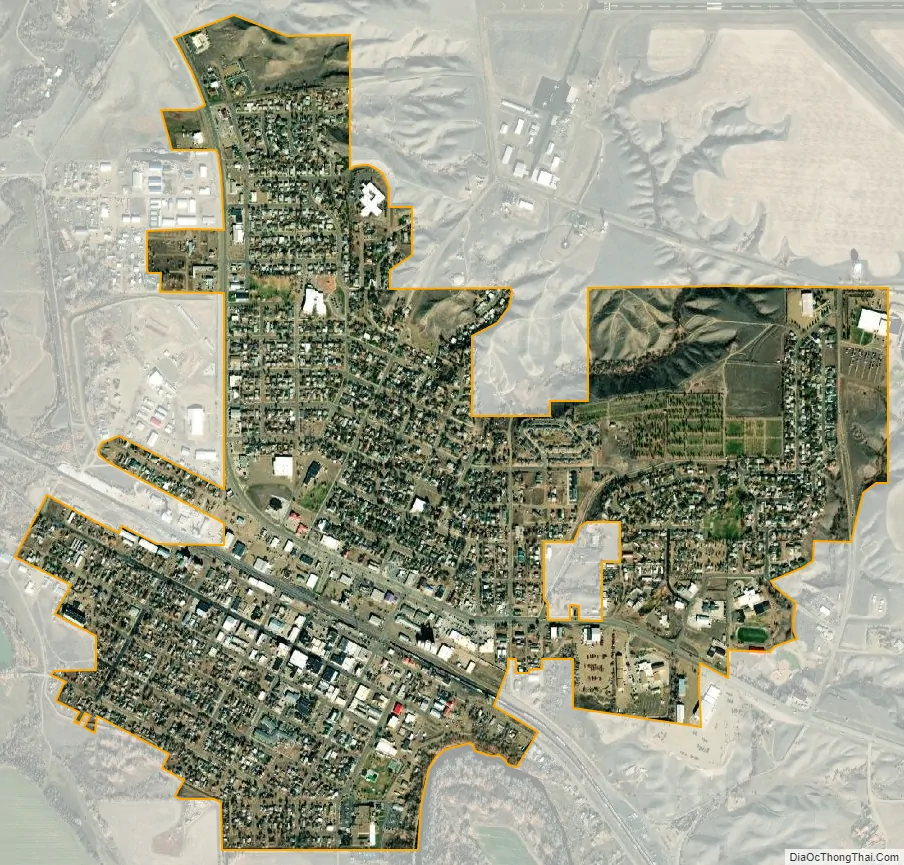
Glasgow city Satellite Map
Geography
Glasgow is located at 48°11′54″N 106°38′7″W / 48.19833°N 106.63528°W / 48.19833; -106.63528 (48.198252, −106.635402).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 1.43 square miles (3.7 km), all land. The town has an elevation of 2,093 feet (638 m) and is nestled in the Milk River Valley.
Using data from Oxford University’s Big Data Institute, The Washington Post, in 2018, identified Glasgow as “the middle of nowhere” for the contiguous United States. The article stated “Of all towns with more than 1,000 residents, Glasgow … is farthest – about 4.5 hours in any direction – from any metropolitan area of more than 75,000 people”.
Glasgow experiences a continental semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification BSk) with long, dry winters with typically freezing but exceedingly variable temperatures and hot, dry summers. The extreme variability of winter temperatures is due to the large warming produced by chinook winds as air descending from the Rockies is warmed, contrasting with very cold continental air masses typical of inland locations at this latitude. As an illustration, the record cold month of February 1936 averaged −15.8 °F (−26.6 °C), but the two warmest Februaries of 1931 and 1984 averaged above 32 °F or 0 °C and had mean maxima above 43.5 °F or 6.4 °C. Snowfall averages 34.8 inches or 0.88 metres per year. Tornadoes are a rare occurrence. Two F2 tornadoes did, however, hit the Glasgow area on June 25, 1975.
See also
Map of Montana State and its subdivision:- Beaverhead
- Big Horn
- Blaine
- Broadwater
- Carbon
- Carter
- Cascade
- Chouteau
- Custer
- Daniels
- Dawson
- Deer Lodge
- Fallon
- Fergus
- Flathead
- Gallatin
- Garfield
- Glacier
- Golden Valley
- Granite
- Hill
- Jefferson
- Judith Basin
- Lake
- Lewis and Clark
- Liberty
- Lincoln
- Madison
- McCone
- Meagher
- Mineral
- Missoula
- Musselshell
- Park
- Petroleum
- Phillips
- Pondera
- Powder River
- Powell
- Prairie
- Ravalli
- Richland
- Roosevelt
- Rosebud
- Sanders
- Sheridan
- Silver Bow
- Stillwater
- Sweet Grass
- Teton
- Toole
- Treasure
- Valley
- Wheatland
- Wibaux
- Yellowstone
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming