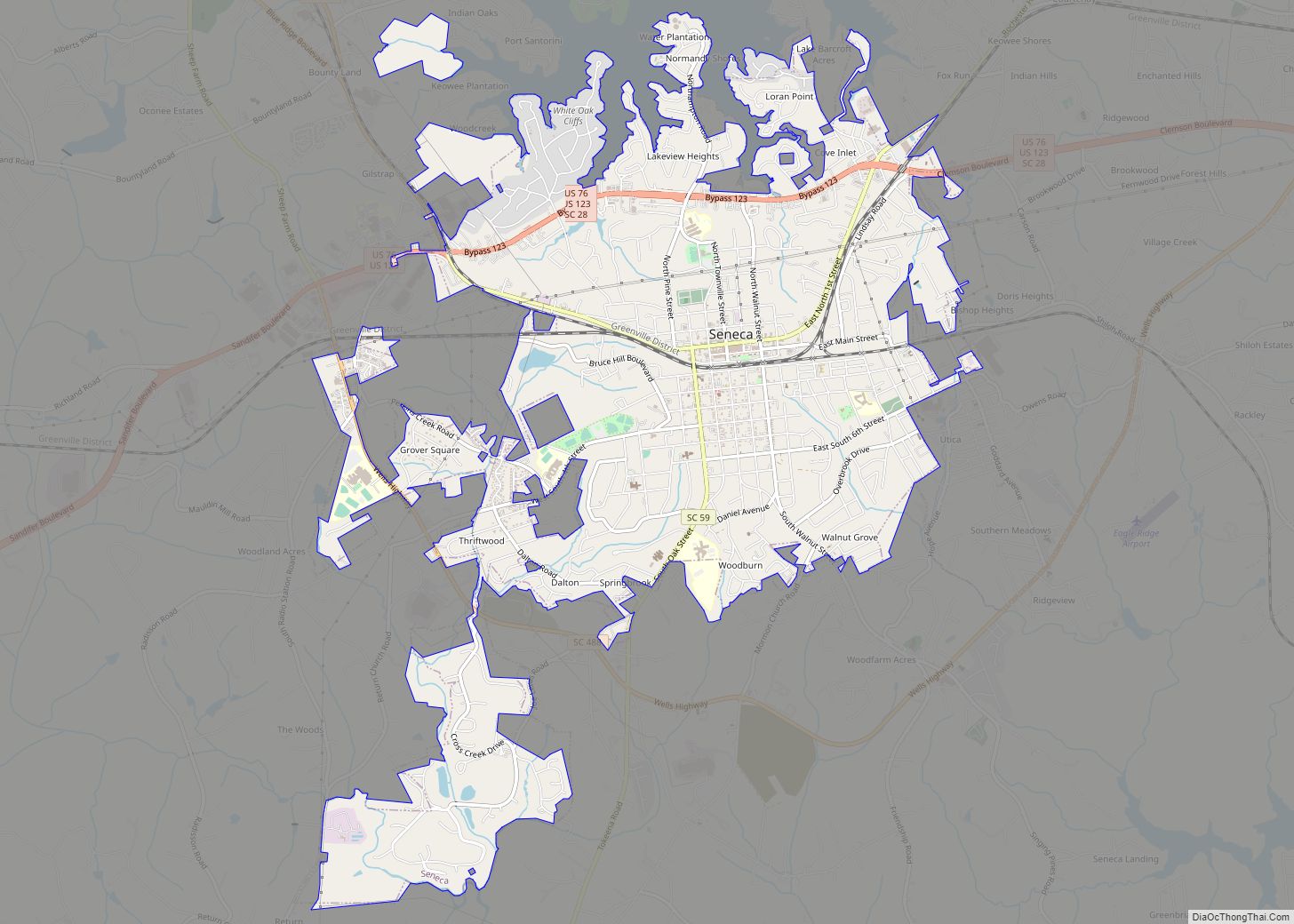
Seneca is a city in Oconee County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 8,102 at the 2010 census. It is the principal city of the Seneca Micropolitan Statistical Area (population 74,273 at the 2010 census), an (MSA) that includes all of Oconee County, and that is included within the greater Greenville–Spartanburg–Anderson, South Carolina Combined Statistical Area (population 1,266,995 at the 2010 census). Seneca was named for the nearby Cherokee town of Isunigu, which English colonists knew as “Seneca Town”.
| Name: | Seneca city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | South Carolina |
| County: | Oconee County |
| Elevation: | 951 ft (290 m) |
| Total Area: | 8.30 sq mi (21.49 km²) |
| Land Area: | 8.24 sq mi (21.35 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.05 sq mi (0.14 km²) |
| Total Population: | 8,850 |
| Population Density: | 1,073.64/sq mi (414.55/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 29672, 29678, 29679 |
| Area code: | 864 |
| FIPS code: | 4565095 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1250833 |
| Website: | http://www.seneca.sc.us/ |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
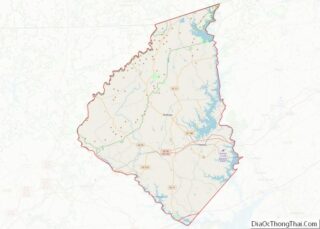
Seneca location map. Where is Seneca city?
History
In the antebellum period, this area was part of the Pickens District, South Carolina. The state had used jurisdictions such as parish, county, district, and county again in its history. Oconee County was not organized until 1868, after the American Civil War.
Seneca was founded in 1873, during the Reconstruction era, as the railroad town “Seneca City”, named for the Seneca River and a historic Cherokee town known as Isunigu. It was called Seneca in a kind of transliteration by British colonists.
Seneca City was developed at the intersection of the Blue Ridge Railroad and the newly built Atlanta and Charlotte Air Line Railroad. Both lines are now part of the Norfolk Southern Railway. A. W. Thompson and J. J. Norton, who were locating engineers for the Air Line Railroad, purchased the land from Col. Brown of Anderson, South Carolina, also in the large Pickens District. A stake marking the center of town was driven into the ground at the intersection of the railroad tracks and the current Townville Street. The land was divided into lots for a one-half mile from the stake. An auction was held on August 14, 1873. The town was given a charter by the state legislature on March 14, 1874. In 1908, the name was changed to the shorter Seneca.
Seneca developed as a marketing and shipping point for cotton, the major commodity crop in this uplands area. During the harvest, wagons bringing cotton would line up for blocks from the railroad station. A passenger terminal, several hotels, and a park were built near the railroad tracks. Recently, this park was named the Norton-Thompson Park in honor of the city’s founders.
The first school was built in 1874. The community also was home of the Seneca Institute – Seneca Junior College, established here in 1899 as an historically black college. It was reserved for African-American students until 1939.
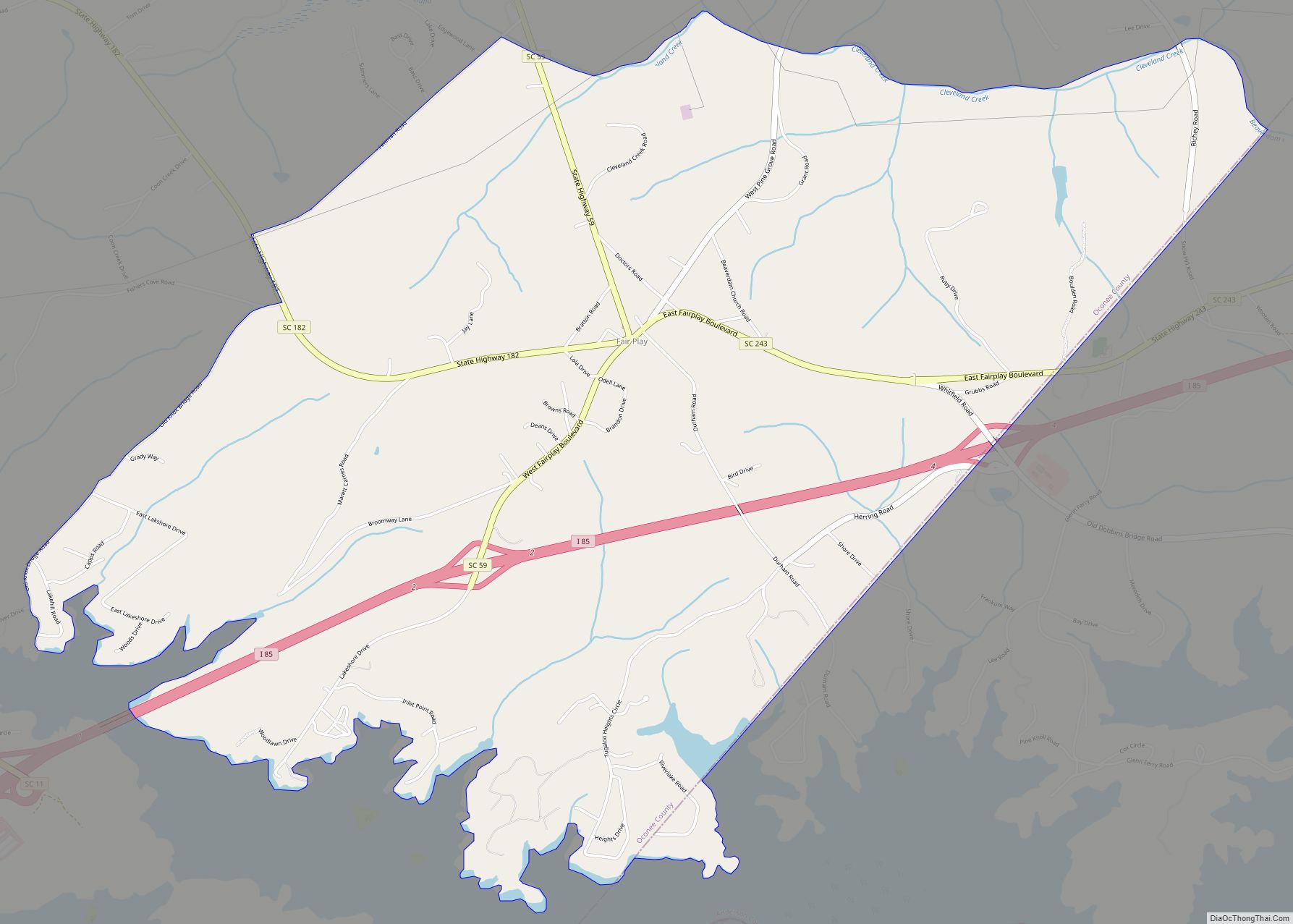
Textile mills were built in the area; a plant-and-mill village was built in 1893 by the Courtenay Manufacturing Company in Newry on the Little River, which supplied hydropower for the mill. W.L. Jordon built another textile plant and mill village east of Seneca. This village has been called Jordania, Londsdale, and Utica; these changes accompanied changes in ownership of the plant. The J. P. Stevens Plant, which was later called the Westpoint Stevens Plant, was a large textile mill built on Lake Hartwell. Its workforce was integrated, unlike most other plants that hired only whites. Many other textile mills were developed in this area. These plants were the main industry for Seneca for the first half of the twentieth century. With the shift of these jobs overseas, these textile mills are now closed.
In the late 20th century, major dam projects were constructed n the Keowee and other local rivers, to support recreation and public utilities. These projects created three major lakes: Lake Hartwell in 1963, Lake Keowee in 1971, and Lake Jocassee in 1974, stimulating development in Seneca and the region. Duke Power’s Oconee Nuclear Station was built on Lake Keowee, drawing cooling water for its operations from the lake.
The recreation provided by the lakes, and other attractions, such as nearby Clemson University attracted many retirees from other parts of the country. Retirement communities have been built in the area. Concerned about over-development, some residents formed the Friends of Lake Keowee Society (FOLKS) to advocate for balance.
Early on April 13, 2020, a high-end EF3 tornado struck residential areas south and east of Seneca. Many buildings were damaged or destroyed and one person was killed.
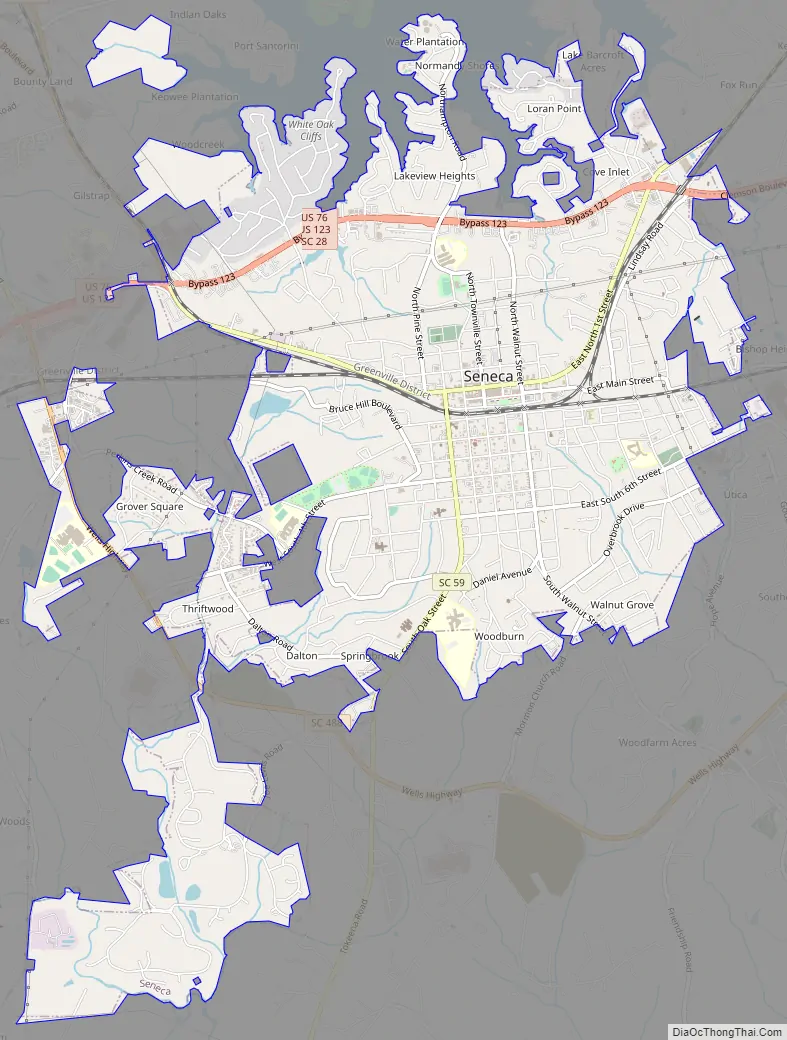
Seneca Road Map
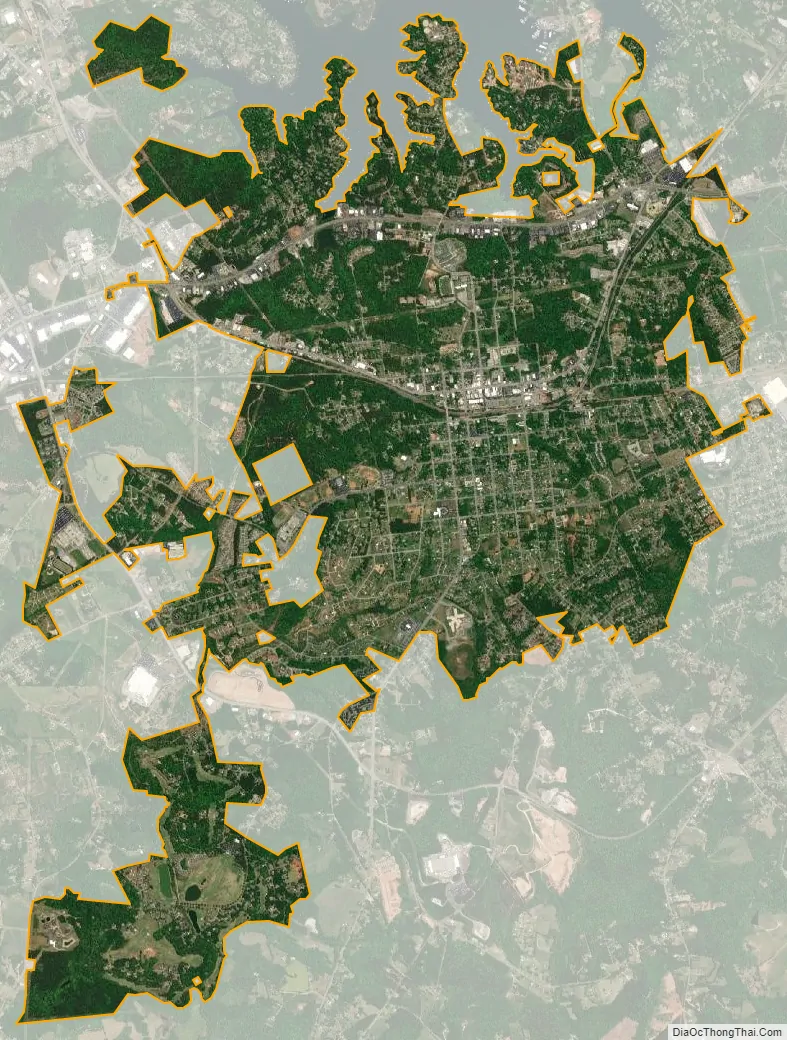
Seneca city Satellite Map
Geography
Seneca is located at 34°41′3″N 82°57′21″W / 34.68417°N 82.95583°W / 34.68417; -82.95583 (34.684145, -82.955778).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 7.1 square miles (18 km), of which 7.1 square miles (18 km) is land and 0.04 square miles (0.10 km) (0.56%) is water.
See also
Map of South Carolina State and its subdivision:- Abbeville
- Aiken
- Allendale
- Anderson
- Bamberg
- Barnwell
- Beaufort
- Berkeley
- Calhoun
- Charleston
- Cherokee
- Chester
- Chesterfield
- Clarendon
- Colleton
- Darlington
- Dillon
- Dorchester
- Edgefield
- Fairfield
- Florence
- Georgetown
- Greenville
- Greenwood
- Hampton
- Horry
- Jasper
- Kershaw
- Lancaster
- Laurens
- Lee
- Lexington
- Marion
- Marlboro
- McCormick
- Newberry
- Oconee
- Orangeburg
- Pickens
- Richland
- Saluda
- Spartanburg
- Sumter
- Union
- Williamsburg
- York
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming