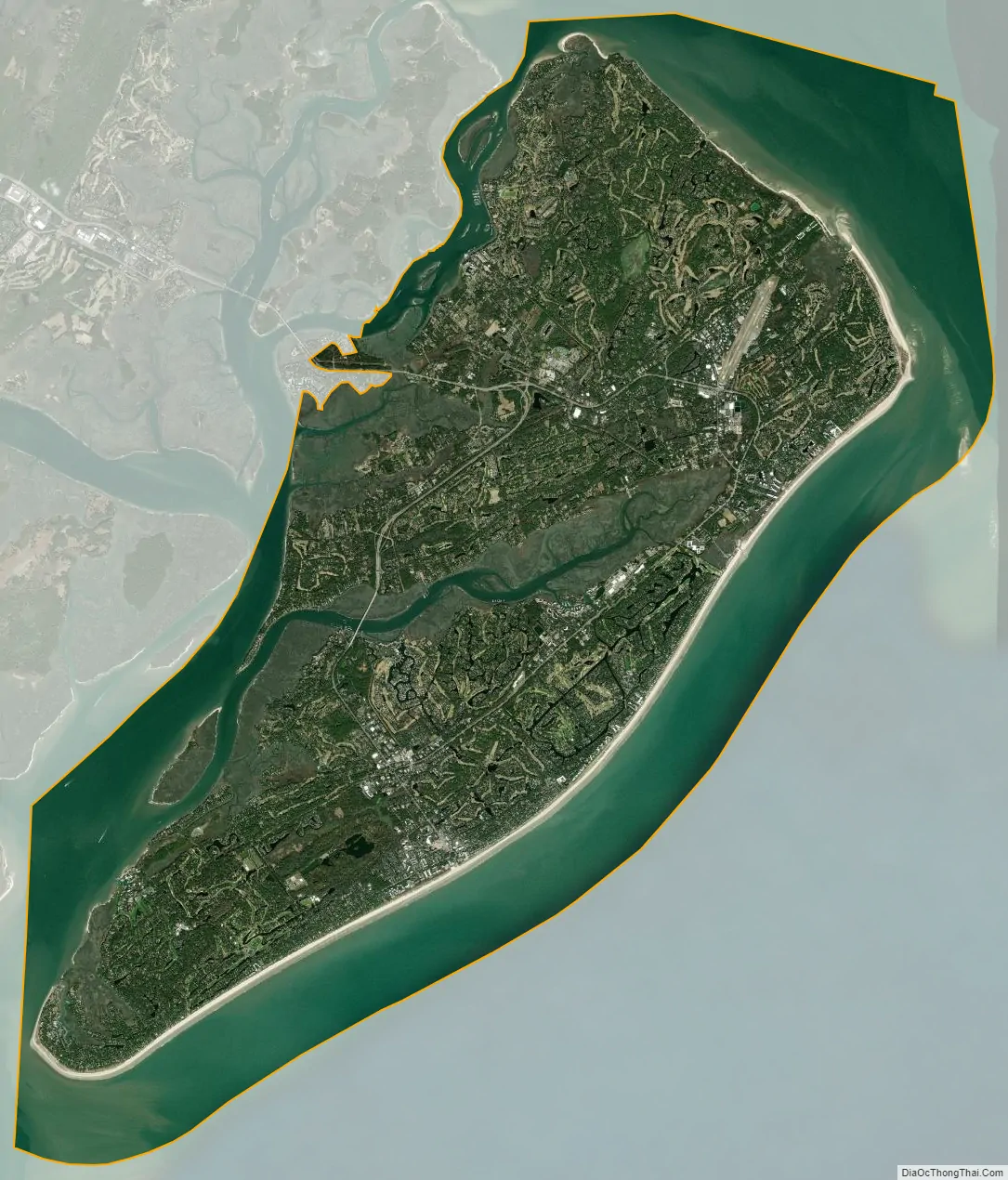
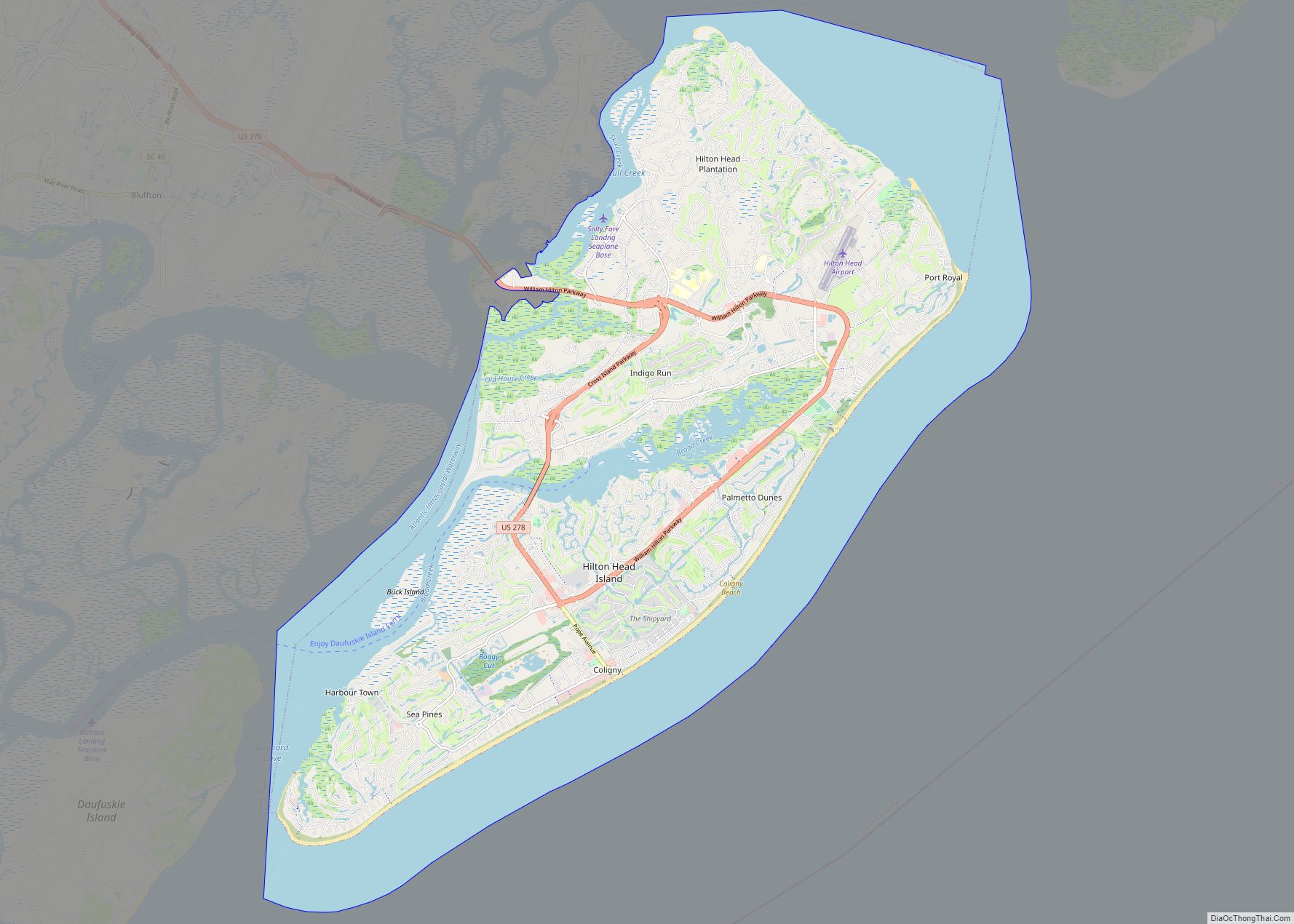
Hilton Head Island, sometimes referred to as simply Hilton Head, is a Lowcountry resort town and barrier island in Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States. It is 20 miles (32 km) northeast of Savannah, Georgia, and 95 miles (153 km) southwest of Charleston. The island is named after Captain William Hilton, who in 1663 identified a headland near the entrance to Port Royal Sound, which mapmakers named “Hilton’s Headland.” The island features 12 miles (19 km) of beachfront on the Atlantic Ocean and is a popular vacation destination. In 2004, an estimated 2.25 million visitors infused more than $1.5 billion into the local economy. The year-round population was 37,661 at the 2020 census, although during the peak of summer vacation season the population can swell to 150,000. Hilton Head Island is the largest city within the Hilton Head Island–Bluffton metropolitan area, which had an estimated population of 215,908 in 2020.
The island has a rich history that started with seasonal occupation by Native Americans thousands of years ago and continued with European exploration and the Sea Island Cotton trade. It became an important base of operations for the Union blockade of the Southern ports during the Civil War. Once the island fell to Union troops, hundreds of ex-slaves flocked to Hilton Head, which is still home to many of their descendants, who are known as the Gullah (or Geechee). They have managed to hold on to much of their ethnic and cultural identity.
The Town of Hilton Head Island incorporated as a municipality in 1983 and is well known for its eco-friendly development. The town’s Natural Resources Division enforces the Land Management Ordinance which minimizes the impact of development and governs the style of buildings and how they are situated amongst existing trees. As a result, Hilton Head Island enjoys an unusual amount of tree cover relative to the amount of development. Approximately 70% of the island, including most of the tourist areas, is located inside gated communities. However, the town maintains several public beach access points, including one for the exclusive use of town residents, who have approved several multimillion-dollar land-buying bond referendums to control commercial growth.
Hilton Head Island offers an unusual number of cultural opportunities for a community its size, including plays at the Arts Center of Coastal Carolina, the 120-member full chorus of the Hilton Head Choral Society, the Hilton Head Symphony Orchestra, an annual outdoor, tented wine tasting event on the east coast, and several other annual community festivals. It also hosts the RBC Heritage, a PGA Tour tournament played on the Harbour Town Golf Links in Sea Pines Resort.
| Name: | Hilton Head Island town |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 43 |
| LSAD Description: | town (suffix) |
| State: | South Carolina |
| County: | Beaufort County |
| Elevation: | 10 ft (3 m) |
| Land Area: | 41.35 sq mi (107.10 km²) |
| Water Area: | 27.78 sq mi (71.95 km²) 40.17% |
| Population Density: | 910.72/sq mi (351.63/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 29925, 29926, 29928 |
| Area code: | 843 |
| FIPS code: | 4534045 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1246002 |
| Website: | www.hiltonheadislandsc.gov |
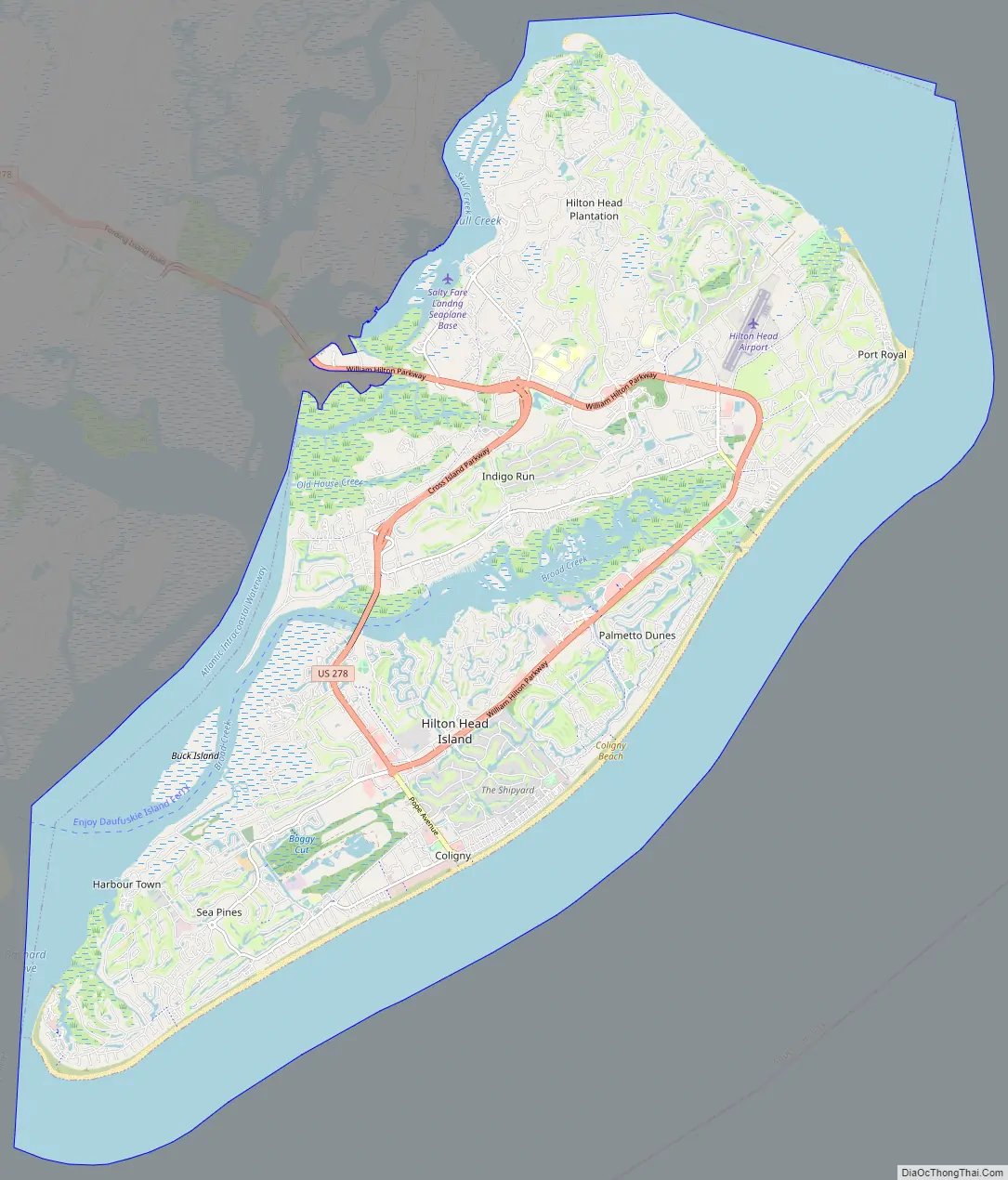
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Hilton Head Island location map. Where is Hilton Head Island town?
History
New World discovery
The Sea Pines shell ring can be seen near the east entrance to the Sea Pines Forest Preserve. The ring, one of at least 50 known to exist, is 150 feet (46 m) in diameter and is believed to be over 4,000 years old. Archeologists believe that the ring was a refuse heap, created by Indians who lived in the interior of the ring, which was kept clear and used as a common area. Two other shell rings on Hilton Head were destroyed when the shells were removed and used to make tabby for roads and buildings. The Green’s Shell Enclosure, Sea Pines, and Skull Creek shell rings are listed in the National Register of Historic Places and are protected by law.
Since the beginning of recorded history in the New World, the waters around Hilton Head Island have been known, occupied and fought for in turn by the English, Spanish, French, and Scots.
A Spanish expedition led by Francisco Cordillo explored the area in 1521, initiating European contact with local tribes. In 1663, Captain William Hilton sailed on the Adventure from Barbados to explore lands granted by King Charles II of England to the eight Lords Proprietor. In his travels, he identified a headland near the entrance to Port Royal Sound. He named it “Hilton’s Head” after himself. He stayed for several days, making note of the trees, crops, “sweet water”, and “clear sweet air”.
17th to 19th centuries
In 1698, Hilton Head Island was granted as part of a barony to John Bayley of Ballingclough, County of Tipperary, Kingdom of Ireland. Another John Bayley, son of the first, appointed Alexander Trench as the island’s first retail agent. For a time, Hilton Head was known as Trench’s Island. In 1729, Trench sold some land to John Gascoine which Gascoine named “John’s Island” after himself. The land later came to be known as Jenkin’s Island after another owner.
In the mid-1740s, the South Carolina provincial half-galley Beaufort was stationed in a cove at the southern tip of Hilton Head to guard against intrusions by the Spanish of St. Augustine. The point and cove are named after Captain David Cutler Braddock, commander of the Beaufort. Captain Braddock was a mariner and privateer of note in Colonial times. Earlier, he had been placed in command of the Georgia schooner Norfolk by James Oglethorpe, founder of Georgia, and helped chase the Spanish back to St. Augustine after their failed 1742 invasion of St. Simons Island. After relocating to Savannah in 1746, he served two terms in the Georgia Commons House of Assembly while earning a living as a highly active privateer. He drew a well-known chart of the Florida Keys while on a privateering venture in 1756. The chart is in the Library of Congress.
During the revolution there was only a very small population of farmers living on Hilton Head Island. This population was exclusively Loyalist, remaining allied to Parliament and the King throughout the entirety of the revolution. However, after the revolution they chose to simply “stay on” in South Carolina and make the best of living under the new republican form of government. In 1788, a small Episcopal church called the Zion Chapel of Ease was constructed for plantation owners. The chapel’s old cemetery, located near the corner of William Hilton Parkway and Mathews Drive (Folly Field), is all that remains. Charles Davant, a prominent island planter during the Revolutionary War, is memorialized there. Davant was shot by Captain Martinangel of Daufuskie Island in 1781. This location is also home to the oldest intact structure on Hilton Head Island, the Baynard Mausoleum, which was built in 1846.
William Elliott II of Myrtle Bank Plantation grew the first crop of Sea Island Cotton in South Carolina on Hilton Head Island in 1790.
During the Civil War, Fort Walker was a Confederate fort in what is now Port Royal Plantation. The fort was a station for Confederate troops, and its guns helped protect the 2-mile wide (3 km) entrance to Port Royal Sound, which is fed by two slow-moving and navigable rivers, the Broad River and the Beaufort River. It was vital to the Sea Island Cotton trade and the southern economy. On October 29, 1861, the largest fleet ever assembled in North America moved south to seize it. In the Battle of Port Royal, the fort came under attack by the U.S. Navy, and on November 7, 1861, it fell to over 12,000 Union troops. The fort was renamed Fort Welles, in honor of Gideon Welles, the Secretary of the Navy.
Hilton Head Island had tremendous significance in the Civil War and became an important base of operations for the Union blockade of the Southern ports, particularly Savannah and Charleston. The Union also built a military hospital on Hilton Head Island with a 1,200-foot (370 m) frontage and a floor area of 60,000 square feet (6,000 m).
Hundreds of ex-slaves flocked to Hilton Head Island, where they could buy land, go to school, live in government housing, and serve in what was called the First Regiment of South Carolina Volunteers (although in the beginning, many were “recruited” at the point of a bayonet). A community called Mitchelville (in honor of General Ormsby M. Mitchel) was constructed on the north end of the island to house them.
In an order from May 15 of 1865, Major General Quincy Adams Gillmore, who was commanding the Department of the South with headquarters at Hilton Head declared that “the people of the black race are free citizens of the United States,” whose rights must be respected accorindlgy. He issued an additional order while based in Hilton Head saying that any plantation owners who were found to have not informed African-Americans of their new status as free people would be “made liable to the pains and penalties of disloyalty, and their lands subject to confiscation” under the act establishing the Freedmen’s Bureau. Martin Delany, the only black officer to reach the rank of major in the United States military during the Civil War, was also stationed at Hilton Head during this time.
The Leamington Lighthouse, also known as the Hilton Head Rear Range Lighthouse, was built in the 1870s on the southern edge of what is now Palmetto Dunes Oceanfront Resort.
In 1890, the wealthy shipping magnate William P. Clyde purchased 9,000 acres on Hilton Head Island for use as a private hunting preserve.
On August 27, 1893, the Sea Islands Hurricane made landfall near Savannah, with a storm surge of 16 feet (5 m), and swept north across South Carolina, killing over 1,000 people and leaving tens of thousands homeless.
20th and 21st centuries
An experimental steam cannon guarding Port Royal Sound was built around 1900, in what is now Port Royal Plantation. The cannon was fixed but its propulsion system allowed for long-range shots for the time.
In 1931, Wall Street tycoon, physicist, and patron of scientific research Alfred Lee Loomis, along with his brother-in-law and partner Landon K. Thorne, purchased 17,000 acres (69 km) on the island (over 63% of the total landmass) for about $120,000 to be used as a private game reserve. On the Atlantic coast of the island, large concrete gun platforms were built to defend against a possible invasion by the Axis powers of World War II. Platforms like these can be found all along the Eastern Seaboard. The Mounted Beach Patrol and Dog Training Center on Hilton Head Island trained U.S. Coast Guard Beach Patrol personnel to use horses and dogs to protect the southeastern coastline of the U.S.
In the early 1950s, three lumber mills contributed to the logging of 19,000 acres (77 km) of the island. The island population was only 300 residents. Before 1956, access to Hilton Head was limited to private boats and a state-operated ferry. The island’s economy centered on shipbuilding, cotton, lumbering, and fishing.
The James F. Byrnes Bridge was built in 1956. It was a two-lane toll swing bridge constructed at a cost of $1.5 million that opened the island to automobile traffic from the mainland. The swing bridge was hit by a barge in 1974, which shut down all vehicle traffic to the island until the Army Corps of Engineers built and manned a pontoon bridge while the bridge was being repaired. The swing bridge was replaced by the current four-lane bridge in 1982.
The beginning of Hilton Head as a resort started in 1956 with Charles E. Fraser developing Sea Pines Resort. Soon, other developments followed, such as Hilton Head Plantation, Palmetto Dunes Plantation, Shipyard Plantation, and Port Royal Plantation, imitating Sea Pines’ architecture and landscaping. Sea Pines, however, continued to stand out by creating a unique locality within the plantation, called Harbour Town, anchored by a recognizable lighthouse. Fraser was a committed environmentalist who changed the whole configuration of the marina at Harbour Town to save an ancient live oak. It came to be known as the Liberty Oak, known to generations of children who watched singer and songwriter Gregg Russell perform under the tree for over 25 years. Fraser was buried next to the tree when he died in 2002.
The Heritage Golf Classic was first played in Sea Pines Resort in 1969 and has been a regular stop on the PGA Tour ever since. Also in 1969, the Hilton Head Island Community Association successfully fought off the development of a BASF chemical complex on the shores of Victoria Bluff (now Colleton River Plantation). Soon after, the association and other concerned citizens “south of the Broad” fought the development of off-shore oil platforms by Brown & Root (a division of Halliburton) and ten-story tall liquefied natural gas shipping spheres by Chicago Bridge & Iron. These events helped to energize the community, and the Chamber of Commerce started drumming up support for the town to incorporate as a municipality. After the Four Seasons Resort (now Hilton Head Resort) was built along William Hilton Parkway, a referendum of incorporation was passed in May 1983, where Hilton Head Island became a town.
The Land Management Ordinance was passed by the Town Council in 1987. Disney’s Hilton Head Island Resort opened in 1996, and the Cross Island Parkway opened in January 1997. An indoor smoking ban in bars, restaurants, and public places took effect on May 1, 2007. Shelter Cove Towne Centre opened in 2014.
Fort Howell, Fort Mitchel, the Zion Cemetery and Baynard Mausoleum, Cherry Hill School, Daufuskie Island Historic District, Fish Haul Archaeological Site (38BU805), Green’s Shell Enclosure, Hilton Head Range Rear Light, Sea Pines, Skull Creek, SS William Lawrence Shipwreck Site, and Stoney-Baynard Plantation are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Hilton Head Island Road Map
Hilton Head Island city Satellite Map
Geography
Topography
Hilton Head Island is a shoe-shaped island that lies 20 miles (32 km) by air northeast of Savannah, Georgia, and 90 miles (140 km) south of Charleston.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 69.2 square miles (179.1 km), of which 41.4 square miles (107.1 km) is land, and 27.8 square miles (71.9 km), or 40.17%, is water.
Barrier island
Hilton Head Island is sometimes referred to as the second largest barrier island on the Eastern Seaboard after Long Island (which is not a barrier island but two glacial moraines). Technically, however, Hilton Head Island is only a half barrier island. The north end of the island is a sea island dating to the Pleistocene epoch, and the south end is a barrier island that appeared as recently as the Holocene epoch. Broad Creek, which is a land-locked tidal marsh, separates the two halves of the island.
The terrain of a barrier island is determined by a dynamic beach system with offshore bars, pounding surf, and shifting beaches; as well as grassy dunes behind the beach, maritime forests with wetlands in the interiors, and salt or tidal marshes on the lee side, facing the mainland. A typical barrier island has a headland, a beach and surf zone, and a sand spit.
Wildlife
The Hilton Head Island area is home to a vast array of wildlife, including alligators, deer, loggerhead sea turtles, manatees, hundreds of species of birds, and dolphins.
The Coastal Discovery Museum, in conjunction with the South Carolina Department of Natural Resources, patrols the beaches from May through October as part of the Sea Turtle Protection Project. The purpose of the project is to inventory and monitor nesting locations, and if necessary, move them to more suitable locations. During the summer months, the museum sponsors the Turtle Talk & Walk, which is a special tour designed to educate the public about this endangered species. To protect loggerhead sea turtles, a town ordinance stipulates that artificial lighting must be shielded so that it cannot be seen from the beach, or it must be turned off by 10:00 p.m. from May 1 to October 31 each year. The waters around Hilton Head Island are one of the few places on Earth where dolphins routinely use a technique called “strand feeding”, whereby schools of fish are herded up onto mud banks, and the dolphins lie on their side while they feed before sliding back down into the water.
Particularly prominent in the ocean waters surrounding Hilton Head Island, the stingray serves as a fascination and painful natural encounter for many beachgoers. Small stingrays inhabit the quieter, shallow region of ocean floor just beyond the break of the surf, typically buried beneath a thin layer of sand. Stingrays are a type of demersal, cartilaginous fish common to the South Carolina coast as well as other areas on the Atlantic shoreline. Typically, stingrays avoid contact with humans unless they are accidentally stepped upon, a situation often ending in a stingray injury, where the stingray punctures the human with its poisonous barb. While these injuries are extremely painful, they are not usually life-threatening as long as they are properly attended to by a medical professional.
The saltmarsh estuaries of Hilton Head Island are the feeding grounds, breeding grounds, and nurseries for many saltwater species of game fish, sport fish, and marine mammals. The dense plankton population gives the coastal water its murky brown-green coloration.
Plankton support marine life including oysters, shrimp and other invertebrates, and bait-fish species including menhaden and mullet, which in turn support larger fish and mammal species that populate the local waterways. Popular sport fish in the Hilton Head Island area include the red drum (or spot tail bass), spotted sea trout, sheepshead, cobia, tarpon, and various shark species.
Climate
Hilton Head Island has a humid subtropical climate – Köppen climate classification Cfa, represented with humid, warm summers and mild winters.
See also
Map of South Carolina State and its subdivision:- Abbeville
- Aiken
- Allendale
- Anderson
- Bamberg
- Barnwell
- Beaufort
- Berkeley
- Calhoun
- Charleston
- Cherokee
- Chester
- Chesterfield
- Clarendon
- Colleton
- Darlington
- Dillon
- Dorchester
- Edgefield
- Fairfield
- Florence
- Georgetown
- Greenville
- Greenwood
- Hampton
- Horry
- Jasper
- Kershaw
- Lancaster
- Laurens
- Lee
- Lexington
- Marion
- Marlboro
- McCormick
- Newberry
- Oconee
- Orangeburg
- Pickens
- Richland
- Saluda
- Spartanburg
- Sumter
- Union
- Williamsburg
- York
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming