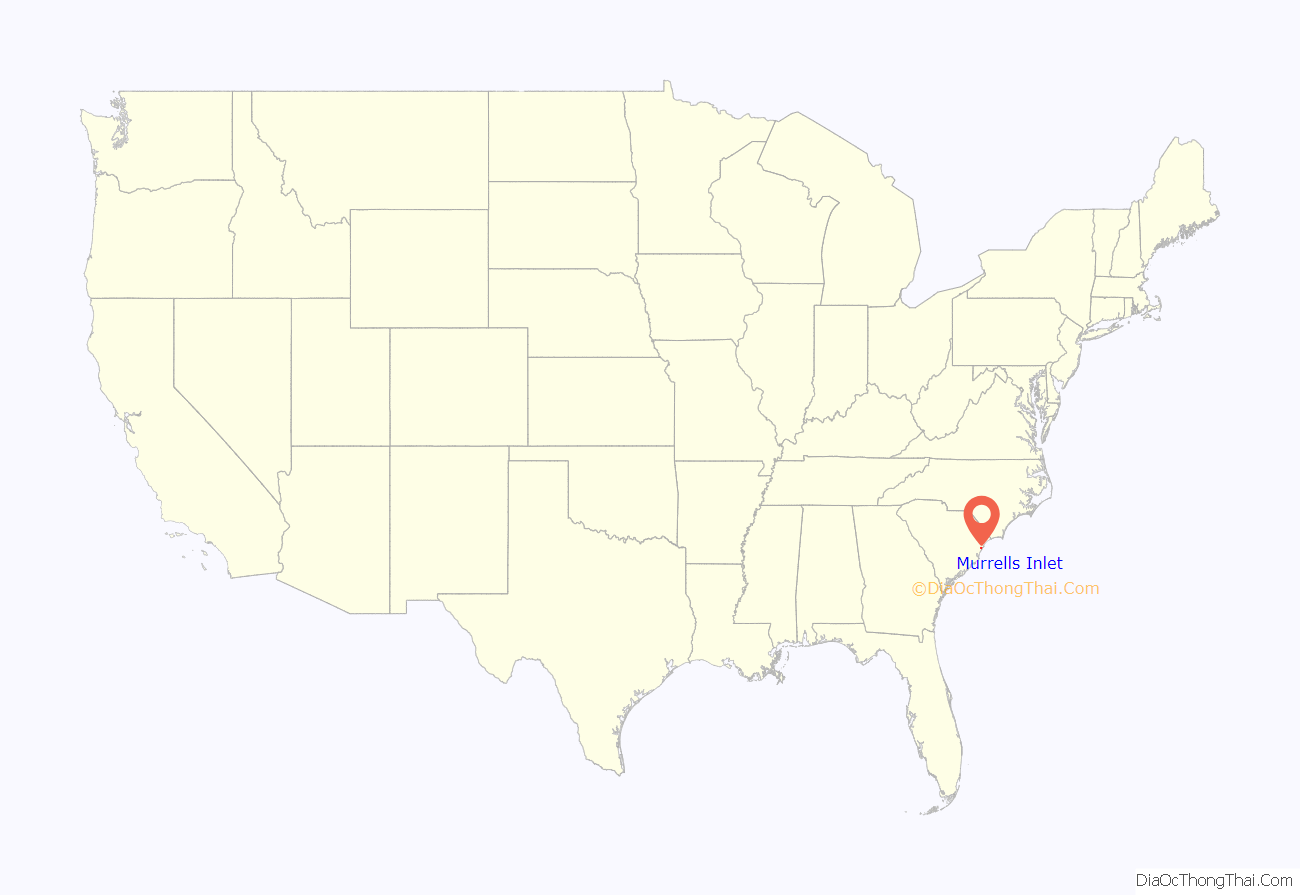
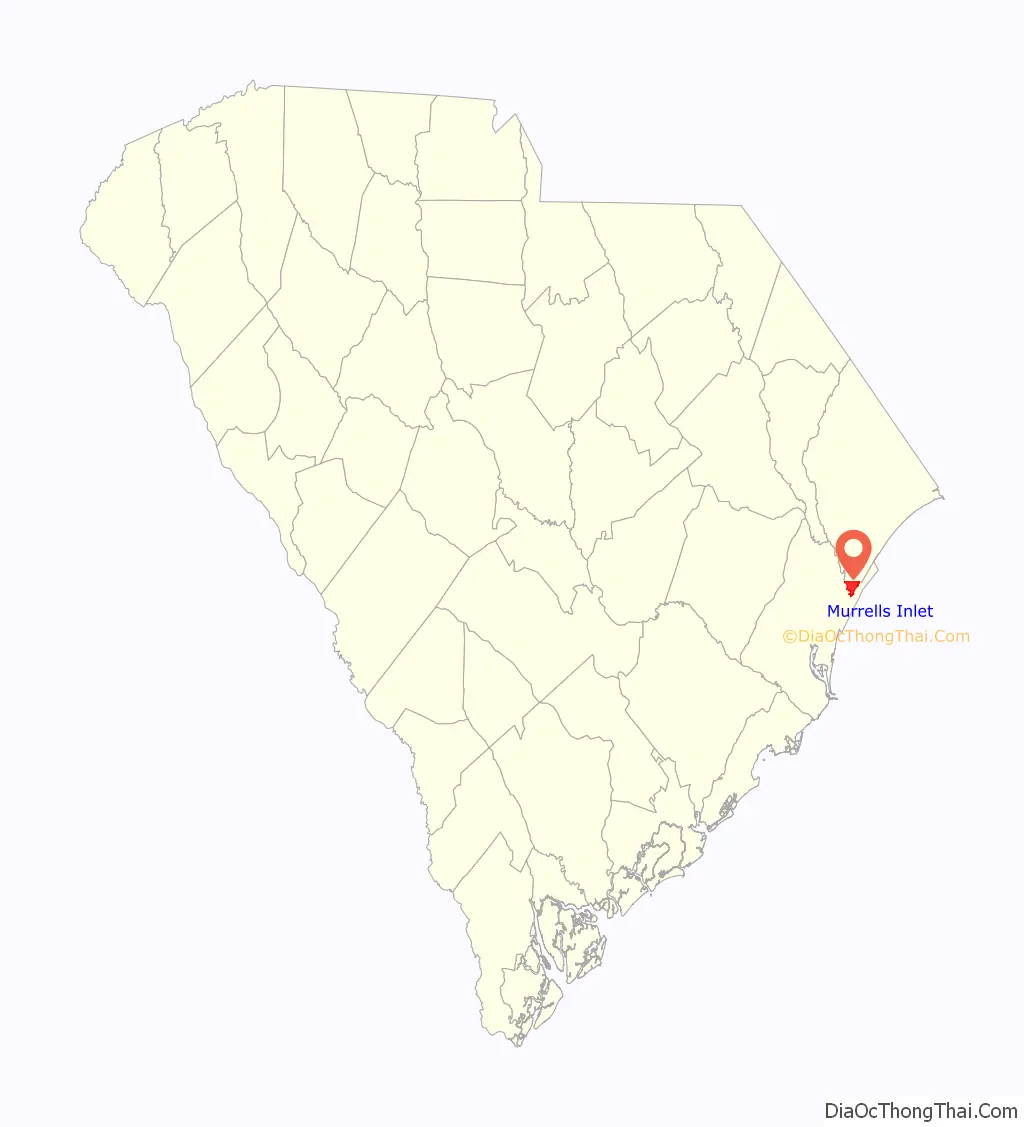
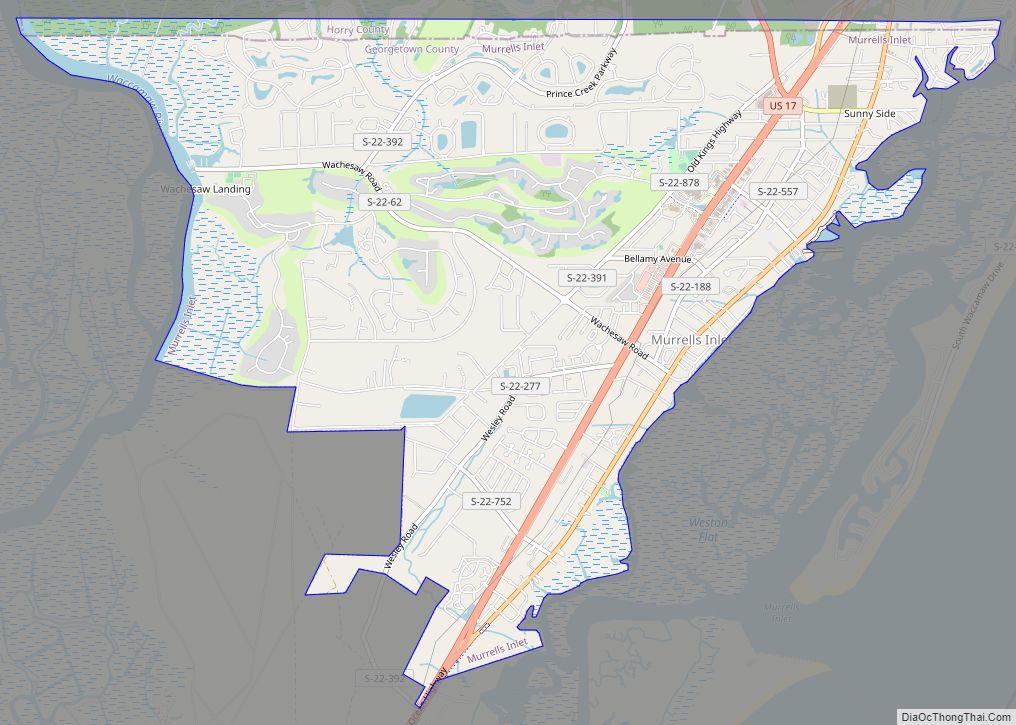
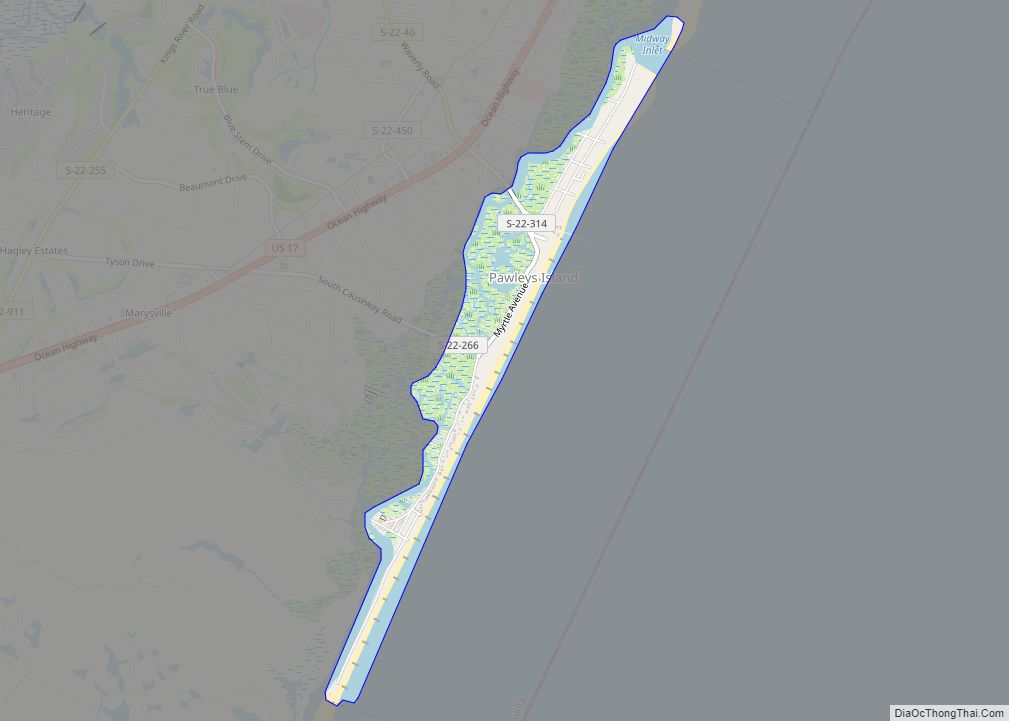
Murrells Inlet is an unincorporated area and census-designated place in Georgetown County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 7,547 at the 2010 census. It is about 13 miles south of Myrtle Beach, South Carolina and 21 miles north of Georgetown, the county seat.
The community was once primarily a fishing village. It has developed in modern times, along with the rest of the Grand Strand, as a tourist and retirement location. It is known for the Murrells Inlet Marshwalk, a 1⁄2-mile-long (0.8 km) boardwalk overlooking a salt marsh. Many restaurants have been developed along the boardwalk.
| Name: | Murrells Inlet CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | South Carolina |
| County: | Georgetown County |
| Elevation: | 3 ft (0.9 m) |
| Total Area: | 7.48 sq mi (19.36 km²) |
| Land Area: | 7.32 sq mi (18.95 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.16 sq mi (0.42 km²) |
| Total Population: | 9,740 |
| Population Density: | 1,331.51/sq mi (514.10/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 29576 |
| FIPS code: | 4548985 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1253479 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
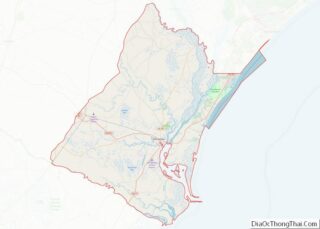
Murrells Inlet location map. Where is Murrells Inlet CDP?
History
The land around Murrells Inlet has a record of human settlement that goes back thousands of years, before written history. Shell mounds and archeological findings from the Atlantic Ocean to the Waccamaw River document the cultures of indigenous peoples who lived in this area. At the time of European encounter, the inhabitants included the historic Waccamaw people, who took advantage of the natural resources provided by the creeks and rivers. Wachesaw is loosely translated as “Place of Great Weeping”, in reference to the burial grounds. Indian burial mounds have been found along the high bluffs at Wachesaw that contained European beads, urns and other artifacts.
The recorded history of the area begins with English colonial settlements and the land grants made by the Lords Proprietors. To encourage development of the colony of South Carolina, they granted large portions of the Waccamaw Neck to men who were willing to transport workers here and settle the land. These estates stretched from the Atlantic Ocean to the Waccamaw River. The baronies were typically tens of thousands of acres that were subdivided into long narrow plantations that ranged from 500 to 1,500 acres (200 to 610 ha).
The plantations of Murrells Inlet included The Oaks, Brookgreen, Springfield, Laurel Hill, Richmond Hill, and Wachesaw (from south to north). The first land grants were given to Robert Daniell in 1711, who in turn sold to several other speculators. The first planters arrived in the 1730s, some from Virginia, to begin developing agriculture and settlements. Captain John Murrell bought 2,340 acres (950 ha), which were eventually developed as Wachesaw and Richmond Hill plantations. He had a house on a bluff built around 1733. He was a subsistence farmer, and raised indigo as the primary cash crop. He died in 1771, leaving his land to son Daniel and two daughters. It was divided into the two plantations named above. Wachesaw Plantation was purchased by Allard Belin around 1800. Richmond Hill was held by Murrell descendants until it was sold to an Allston (most likely John Hayes Allston, who pioneered rice planting techniques with clay). In the nineteenth century, rice replaced indigo as the commodity crop throughout the Lowcountry region.
Adjacent plantations were owned by such planters as Plowden Weston, his grandson Plowden C. J. Weston, William Allston, Benjamin Allston, Henry Flagg, Allard Flagg, Joshua Ward, Allard Belin and their descendants. These plantations prospered during the establishment of the rice culture of the late 1700s and 1800s. These planters generally supported the American cause during the Revolutionary War. William Allston served as a captain under his brother-in-law Francis Marion (who had family ties through marriage to the Allston family).
The Waccamaw Neck planters comprised the elite class: they were elected to the state Senate and House, as well as to the Governor’s and Lieutenant Governor’s offices during the 1800s. The wealthy rice planters also established social, educational, and religious organizations, including the Planters Club, the Winyah Indigo Society in Georgetown, the Hot and Hot Fish Club, the All Saints Academy, the Waccamaw Methodist Mission, and All Saints Waccamaw. Various historic maps dating to 1783 show these family names on plantations. “Murrells Inlet” was likely named after that early family. It has been alternately shown as “Morrall’s Inlet” and “Murrays Inlet” on later maps.
The rice plantation era came to an end after the Civil War with the emancipation of the slaves (rice cultivation was labor-intensive) and a series of hurricanes that climaxed with the 1893 Hurricane (also known as the Flagg flood, where the Atlantic Ocean was reported to meet the Waccamaw River). The loss of the slave labor resulted in the decline of the fields, dikes, and water control structures required for rice cultivation, since planters had to rely on freedmen to work the fields. Several powerful hurricanes following the Civil War and up to the 1893 hurricane resulted in uprooted trees and flood-damaged dikes in the rice fields and ultimately ended the production of rice on the Waccamaw Neck. The 1893 hurricane became known as the Flagg Flood, because the Flagg families that lived in houses on Magnolia Beach (Arthur, his wife Georgeanne, his son Arthur Jr., and his wife and six children) were swept away in the storm surge. Ward Flagg (one of three sons) survived the storm and retired to the miller’s cottage in Brookgreen and reportedly never visited the ocean again.
After Allard Flagg’s death in 1901, his daughter sold Wachesaw and the Hermitage to Samuel Sidney Fraser, a real estate speculator, who bought and sold interests in several old plantations after the Civil War. Fraser held onto the plantation briefly before selling to Robert Ernest Beaty in 1905. Clarke A. Willcox of Marion purchased Wachesaw and the Hermitage in 1910 for $10,000 to use as a summer retreat. The Willcox family retained the Hermitage, but sold Wachesaw in 1930 to William A. Kimbel, who also bought Richmond Hill with the purpose of developing a large hunting estate. With his purchase of both properties, Kimbel had restored the boundaries of John Murrell’s original plantation.
In 1920, Julius A. Mood of Sumter and a group of sportsmen bought Brookgreen, Springfield, Laurel Hill, and The Oaks to use as a hunting preserve. His daughter, Julia Mood Peterkin, made several visits to Brookgreen and used the area as the setting for some of her novels. She won the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction for Scarlet Sister Mary in 1928. Club members enjoyed their hunting paradise for ten years, as a succession of owners conserved the property before selling out to yet another wealthy outsider seeking a rural estate in the South where land was cheap. After numerous owners, railroad magnate Archer Milton Huntington purchased Brookgreen in 1930. At first, he and his wife, Anna Hyatt Huntington, intended Brookgreen as a winter resort. Eventually, they decided to use the plantation as an outdoor gallery for Mrs. Huntington’s award-winning sculptures. The Huntingtons constructed Atalaya, a Spanish-style fort, on the beach to use for her studio and living quarters at what is now Huntington Beach State Park, abandoning the plantation houses.
The years from Reconstruction until World War I saw an increase in the number of settlers who moved to Murrells Inlet to enjoy the natural resources provided. The family names listed in the 1900–1930 census records reflect the growth and are still found in Murrells Inlet today. The families that moved into this area were from communities like Marion, Conway, Southport, and other nearby counties.
The transportation corridors up to the 1900s were primarily the Waccamaw River and the Atlantic Ocean for boats, and the Kings Road (used during George Washington’s visit) and the River Road (along the Waccamaw River near the plantation houses) for horse and wagons. These dirt paths were crude rough paths that bore no resemblance to today’s modern highways. Highway 17 was paved around 1933 as part of a federal effort to provide paved roads across the United States. Early shipping routes relied on the deepwater access provided by the Waccamaw River to move vast quantities of materials and goods. The Comanche was an early steamship that called on Wachesaw Landing to deliver passengers and mail to Murrells Inlet.
Historic landmarks
Murrells Inlet landmarks that are registered and listed on the National Register of Historic Places:
- Atalaya
- Murrells Inlet Historic District
- Richmond Hill
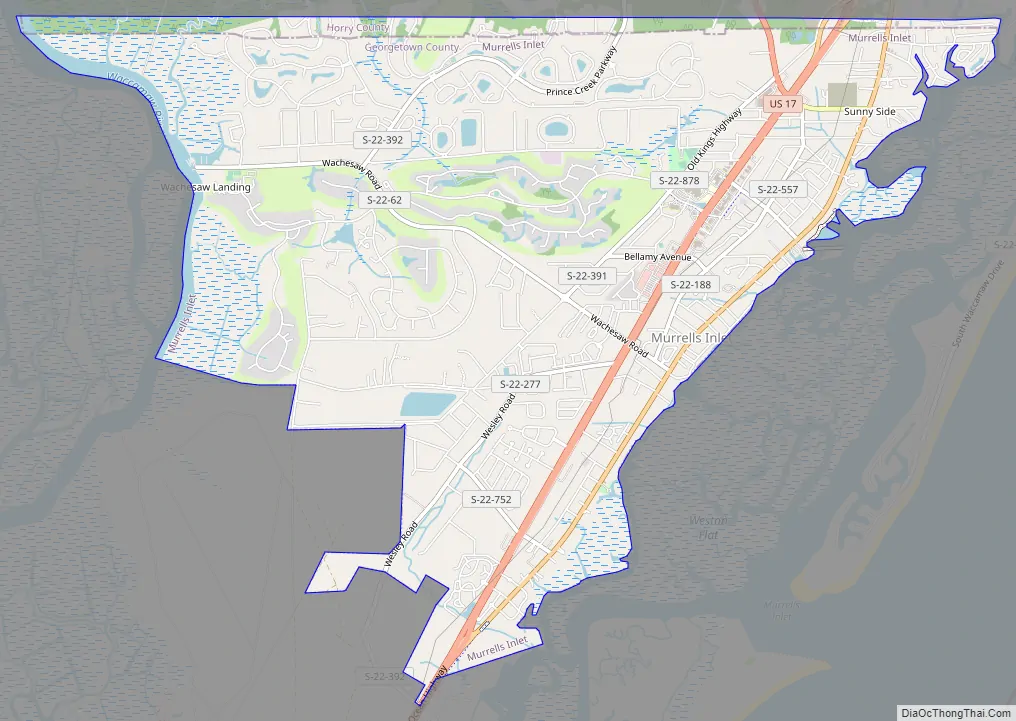
Murrells Inlet Road Map
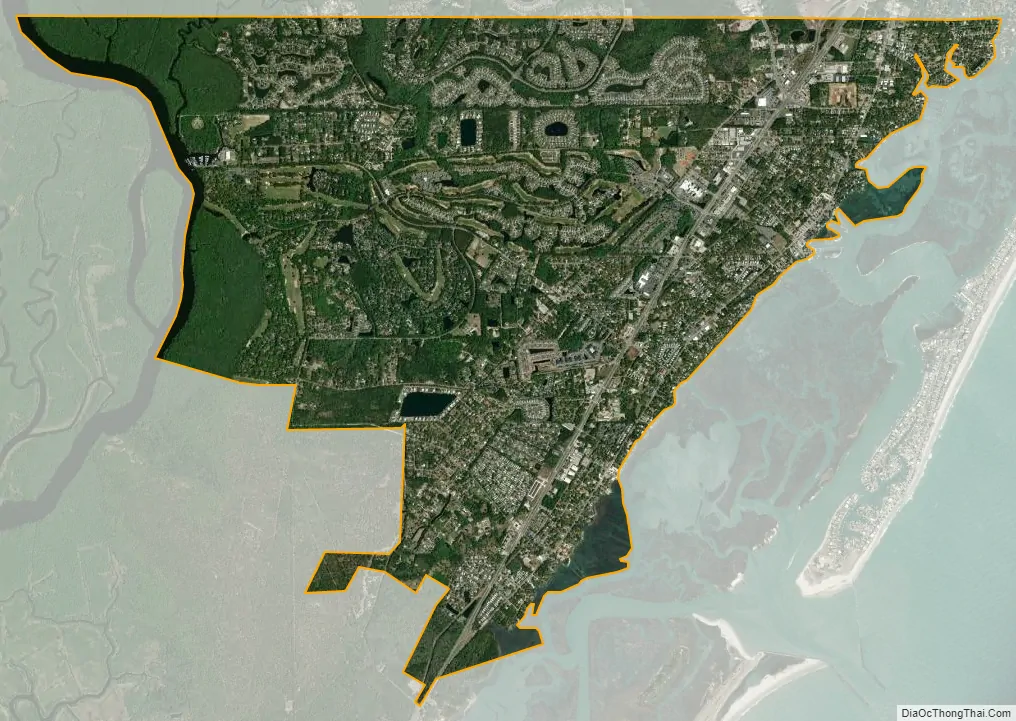
Murrells Inlet city Satellite Map
Geography
Murrells Inlet is located in northeastern Georgetown County at 33°33′6″N 79°2′56″W / 33.55167°N 79.04889°W / 33.55167; -79.04889 (33.551593, -79.048794). The northern edge of the CDP follows the Horry County line. U.S. Route 17 (Ocean Highway) runs through the center of the community, leading northeast 13 miles (21 km) to Myrtle Beach and southwest 21 miles (34 km) to Georgetown, the seat of Georgetown County.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the Murrells Inlet CDP has a total area of 7.5 square miles (19.5 km), of which 7.4 square miles (19.1 km) are land and 0.2 square miles (0.4 km), or 2.21%, are water. It has a humid subtropical climate (Cfa) and average monthly temperatures range from 46.5 °F in January to 80.5 °F in July. The local hardiness zone is 8b.
See also
Map of South Carolina State and its subdivision:- Abbeville
- Aiken
- Allendale
- Anderson
- Bamberg
- Barnwell
- Beaufort
- Berkeley
- Calhoun
- Charleston
- Cherokee
- Chester
- Chesterfield
- Clarendon
- Colleton
- Darlington
- Dillon
- Dorchester
- Edgefield
- Fairfield
- Florence
- Georgetown
- Greenville
- Greenwood
- Hampton
- Horry
- Jasper
- Kershaw
- Lancaster
- Laurens
- Lee
- Lexington
- Marion
- Marlboro
- McCormick
- Newberry
- Oconee
- Orangeburg
- Pickens
- Richland
- Saluda
- Spartanburg
- Sumter
- Union
- Williamsburg
- York
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming