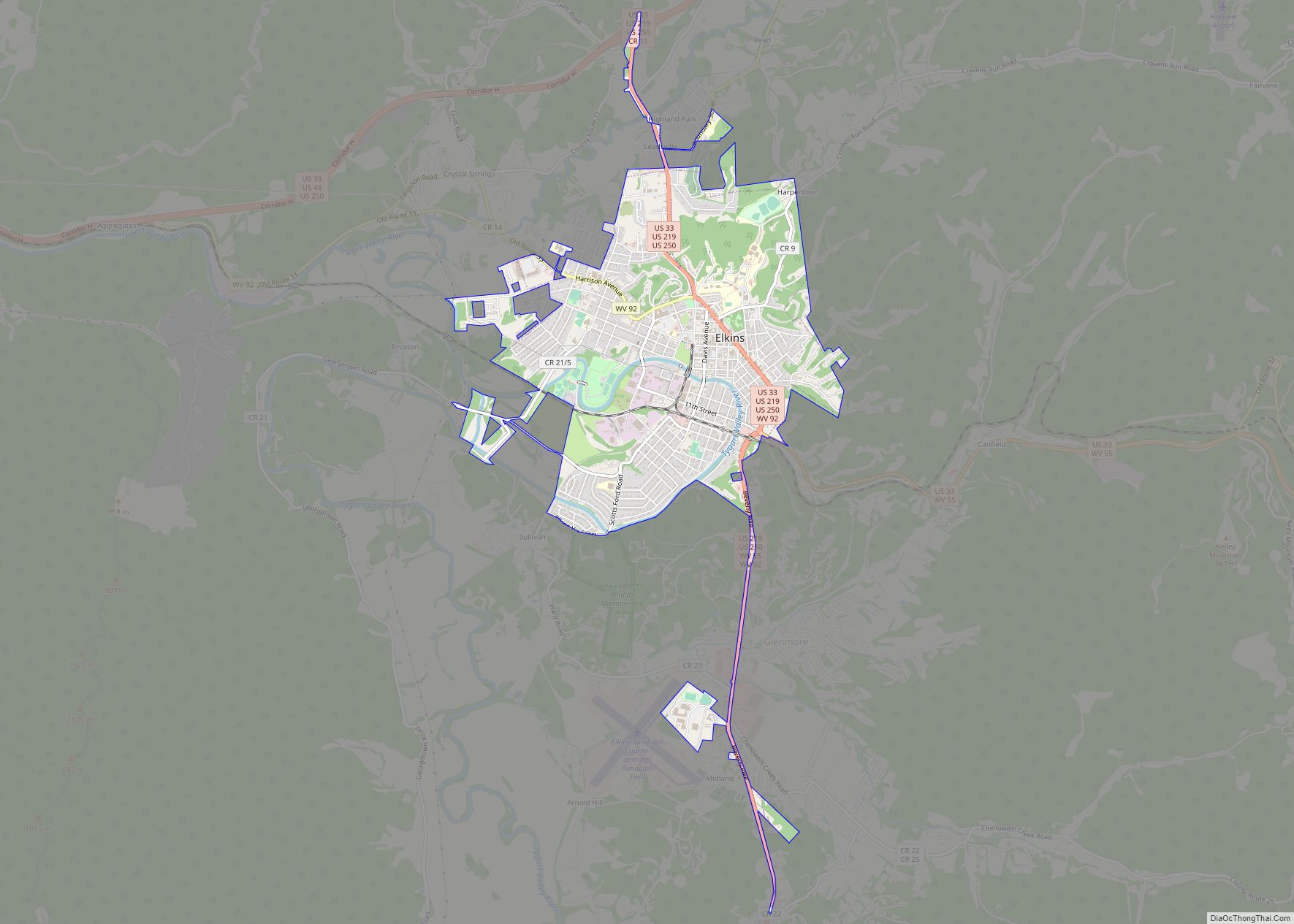
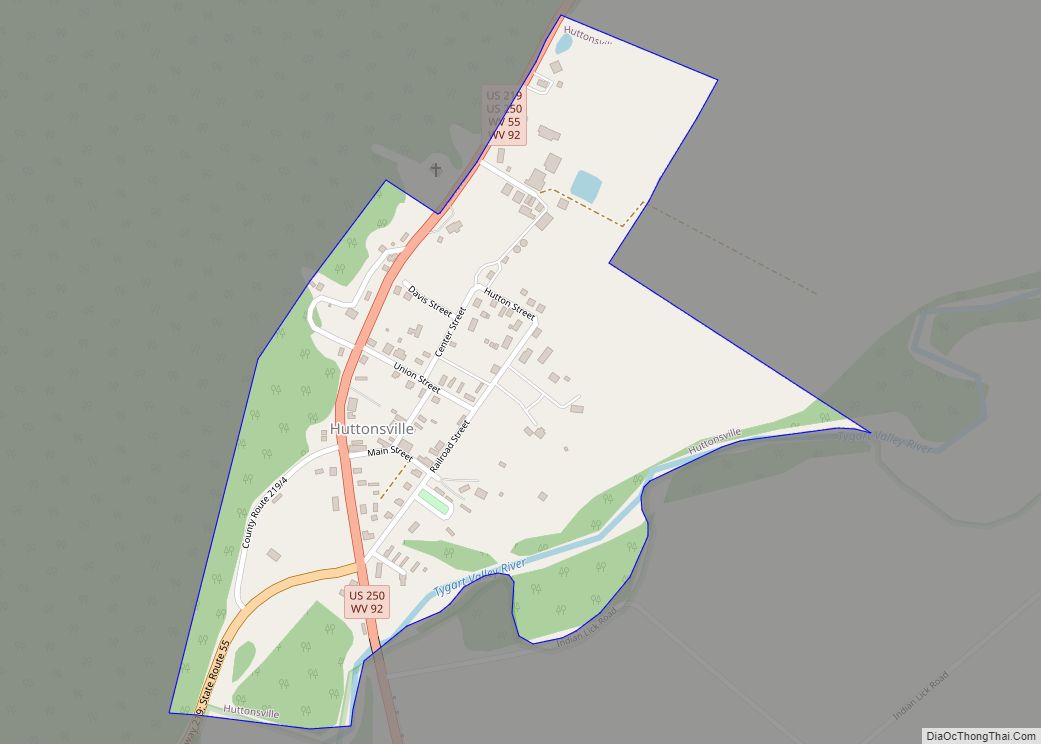
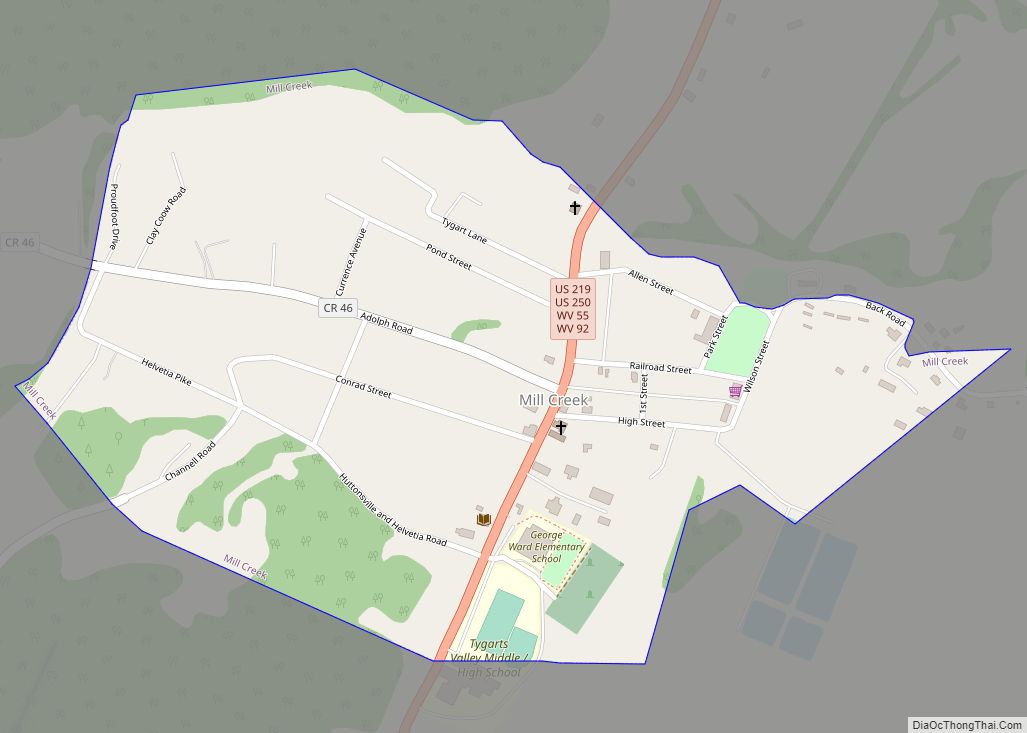
Elkins is a city in and the county seat of Randolph County, West Virginia, United States, along the Tygart Valley River. The community was incorporated in 1890 and named in honor of Stephen Benton Elkins, a U.S. Senator from West Virginia. The population was 6,950 at the 2020 census and estimated at 6,895 in 2021. Elkins is home to Davis and Elkins College and to the Mountain State Forest Festival, held in early October every year.
| Name: | Elkins city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | West Virginia |
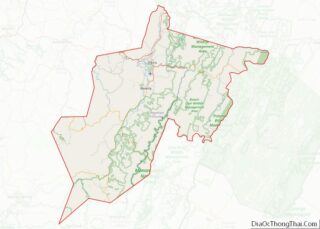
| County: | Randolph County |
| Elevation: | 1,926 ft (587 m) |
| Total Area: | 3.63 sq mi (9.41 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3.63 sq mi (9.41 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 6,950 |
| Population Density: | 1,923.50/sq mi (742.65/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 26241 |
| Area code: | Area codes 304 and 681 |
| FIPS code: | 5424580 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1551037 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Elkins location map. Where is Elkins city?
History
Thomas Skidmore (ca. 1733-1807), born in Maryland, obtained a title to 400 acres of land (“by virtue of a settlement”) in the future Elkins area before 1778. This land, on the east side of the Tygart Valley River, was surveyed by John Poage in 1780 and included the land that is now most of downtown Elkins. Thus, Skidmore was probably the first white settler in what became Elkins.
Before its major development, the area that would become Elkins was known as Leadsville, and was the site of a few scattered homesteads – a place where the local farmers’ corn crop was loaded onto boats and floated down the Tygart Valley River. The City of Elkins was developed by U.S. Senators Henry Gassaway Davis (1823–1916) and Stephen Benton Elkins (1841–1911) – and named for the latter – in 1890. (Elkins was Davis’ son-in-law.) The two founders developed railroad lines, coal mines, and timbering businesses. Together, they built the West Virginia Central and Pittsburgh Railway into Elkins in 1889, opening a vast territory to industrial development by the late 1890s. After an intense county seat war with nearby Beverly, where the new county courthouse building was burned down in 1897 under suspicious circumstances, Elkins became the county seat in 1899. This was resolved, however, only after multiple referendums, court judgments, and the mobilization of armed bands in both towns. In the end, bloodshed was averted.
In 1904 the new Randolph County Courthouse – designed in the Richardsonian Romanesque style – was completed in Elkins. As the railroad (merged into the Western Maryland Railway in 1905) expanded, Elkins experienced the luxury of passenger train service. In 1930, 18 passenger trains were arriving and leaving Elkins daily. All passenger service was discontinued in 1958.
Where the view of the new town was most delightful and picturesque, Davis and Elkins each built permanent places of residence, known as Graceland (1893) and Halliehurst (1890), respectively.
Today, Elkins has an active economic development authority, chamber of commerce, downtown business organization and numerous social, fraternal and service organizations that sponsor annual events like the Mountain State Forest Festival, which brings thousands of people into the city every year.
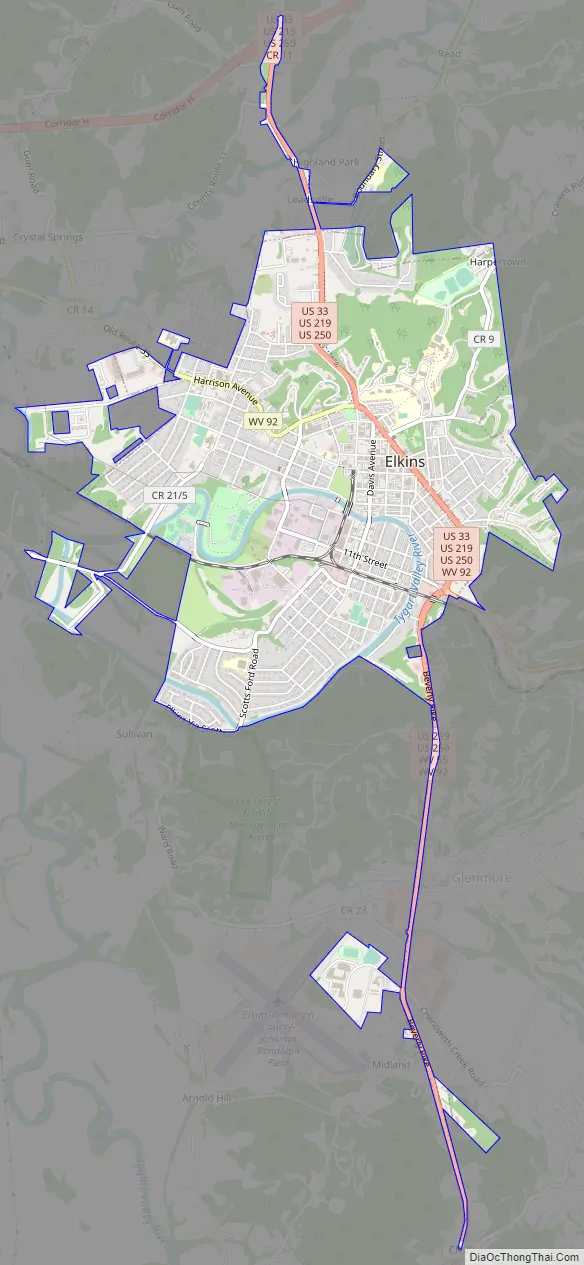
Elkins Road Map
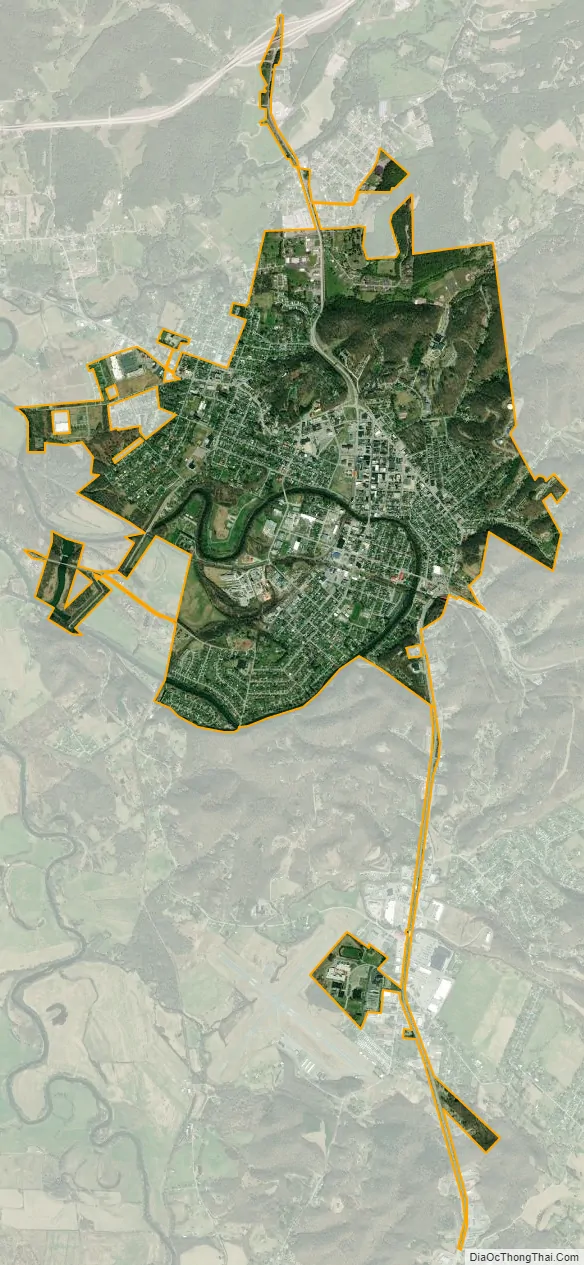
Elkins city Satellite Map
Geography
Elkins is located at the confluence of the Tygart Valley River and Leading Creek. The average elevation is 2,000 feet (610 m) above sea level. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 3.43 square miles (8.88 km), all land. Elkins is headquarters for the Monongahela National Forest, a 910,155-acre (368,327 ha) federal reserve encompassing the “High Alleghenies” area to the east of the city.
In 1995, a second edition of The 100 Best Small Towns in America, written by Norman Crampton, featured Elkins among the special places in the United States. Crampton quoted then Editor Emerita of The Inter-Mountain, Eldora Marie Bolyard Nuzum, “You can stand on any street in Elkins and turn in all directions and see forest covered mountains rimming the city. It is unbelievable.”
Climate
Record weather events include:
- High temperature: 99 °F (37 °C) on July 16, 1988 and on August 6, 1918
- Highest daily minimum: 78 °F (26 °C) on July 21, 1930
- Lowest daily maximum: −6 °F (−21 °C) on December 25, 1983
- Low temperature: −28 °F (−33 °C) on December 30, 1917
- Highest one-day snowfall: 19.9 inches (51 cm), on December 19, 2009.
- Highest one-day precipitation: 5.02 inches (12.8 cm), on November 4, 1985.
See also
Map of West Virginia State and its subdivision:- Barbour
- Berkeley
- Boone
- Braxton
- Brooke
- Cabell
- Calhoun
- Clay
- Doddridge
- Fayette
- Gilmer
- Grant
- Greenbrier
- Hampshire
- Hancock
- Hardy
- Harrison
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Kanawha
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Marion
- Marshall
- Mason
- McDowell
- Mercer
- Mineral
- Mingo
- Monongalia
- Monroe
- Morgan
- Nicholas
- Ohio
- Pendleton
- Pleasants
- Pocahontas
- Preston
- Putnam
- Raleigh
- Randolph
- Ritchie
- Roane
- Summers
- Taylor
- Tucker
- Tyler
- Upshur
- Wayne
- Webster
- Wetzel
- Wirt
- Wood
- Wyoming
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming