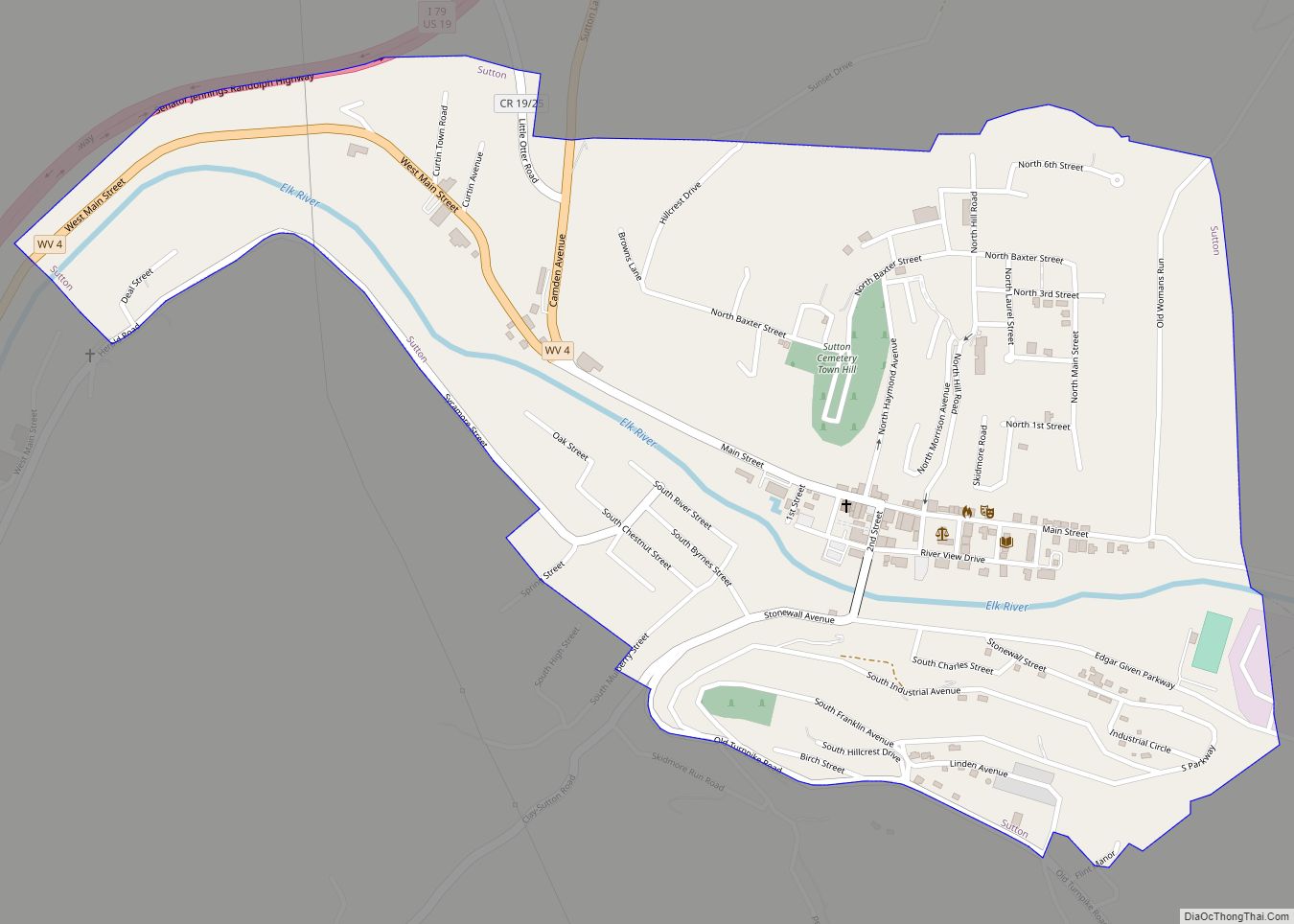
Sutton is a town in Braxton County, West Virginia, United States. The population was 876 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Braxton County. Sutton is situated at a center of transportation in West Virginia. Interstate 79, a major north–south route, connects with Appalachian Corridor L (U.S. Route 19), another significant north–south route, passes several miles south of town.
| Name: | Sutton town |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 43 |
| LSAD Description: | town (suffix) |
| State: | West Virginia |
| County: | Braxton County |
| Elevation: | 840 ft (256 m) |
| Total Area: | 0.82 sq mi (2.13 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.78 sq mi (2.01 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.04 sq mi (0.12 km²) |
| Total Population: | 876 |
| Population Density: | 1,271.56/sq mi (491.23/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 26601 |
| Area code: | 304 |
| FIPS code: | 5478580 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1555762 |
| Website: | suttonwv.com/home.aspx |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Sutton location map. Where is Sutton town?
History
Sutton was settled in 1792 by Adam O’Brien, from Bath County, Virginia. In 1809, John D. Sutton settled at the confluence of Granny’s Creek and the Elk River, at the edge of the present town. The village of Suttonville, formerly known as Newville, was laid out in 1835. When Braxton County was formed in 1836, the first court was held in the home of John D. Sutton.
Sutton was a transportation hub. In addition to the navigable Elk River, the Weston and Gauley Bridge Turnpike connected the Staunton and Parkersburg Turnpike to the James River and Kanawha Turnpike, via Sutton. A suspension bridge was constructed on the Weston and Gauley Bridge Turnpike across the Elk River at Sutton in 1853. Railroads also served the town of Sutton, with the Sutton Branch connecting to the West Virginia and Pittsburgh Railroad at Flatwoods, West Virginia via McNutt (near the area now called Laurel Court), a path that would later be used by West Virginia State Route 4. Another branch that ran along the southeastern bank of the Elk River joined the Coal and Coke Railway six miles to the east at Gassaway.
Due to its location, Sutton was embroiled in the American Civil War. On September 5, 1861, the town was occupied by 5,000 Union troops. Later in 1861, General William Rosecrans bivouacked 10,000 Union troops there, including future President William McKinley. On December 29, 1861, Confederate soldiers burned most of the downtown.
Sutton slowly rebuilt but remained small until the local timber industry boomed. The town then became a commercial center, and many of the banks, hotels, shops, and other historic buildings in the Sutton Downtown Historic District date from this 1890–1920 period. After this, Sutton once again slowed in development. Sutton Dam was built on the Elk River upstream from the town in 1961, adding a tourism component to the local economy.
The William Edgar Haymond House and Old Sutton High School are listed on the National Register of Historic Places, along with the historic district.
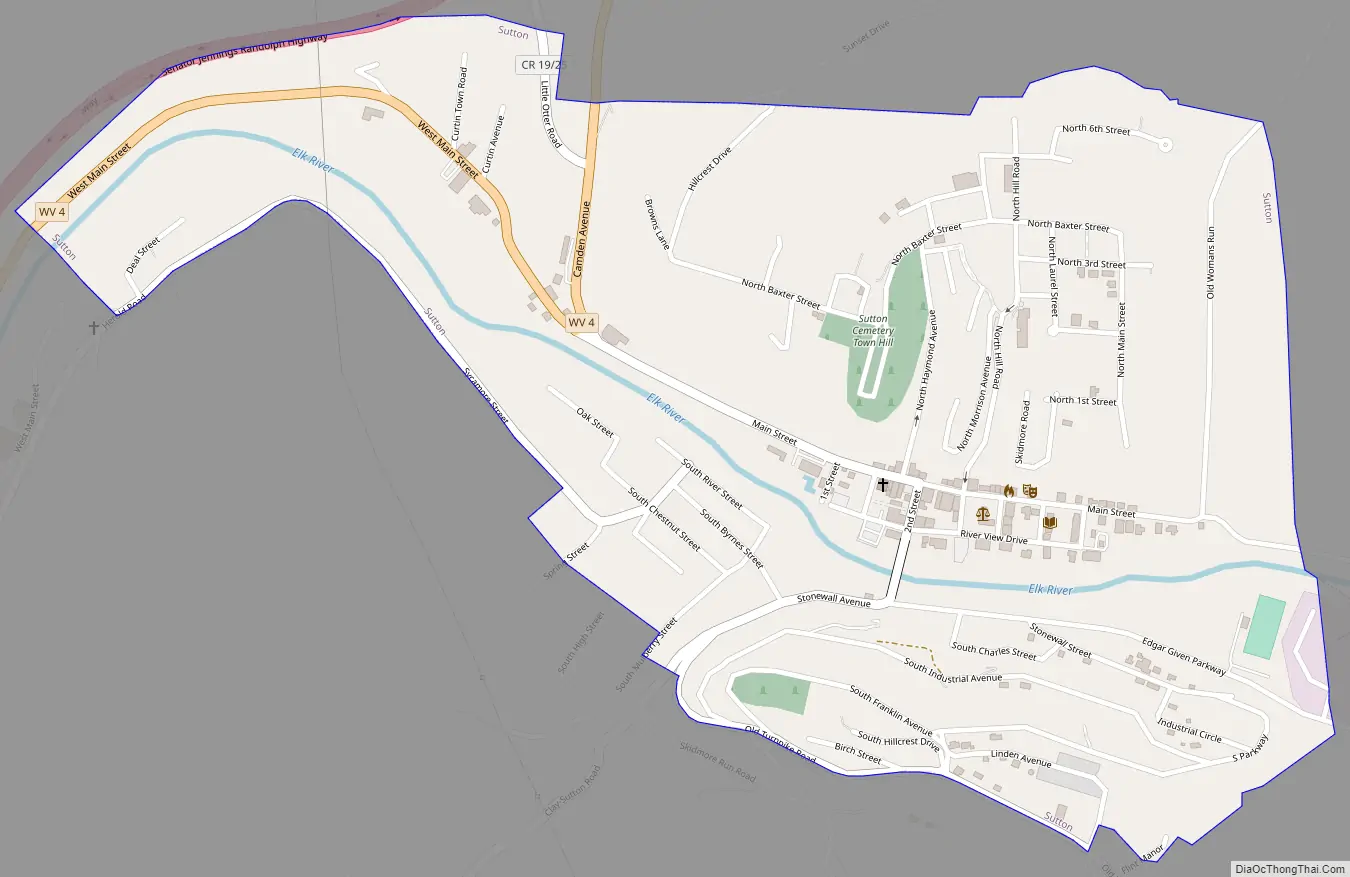
Sutton Road Map
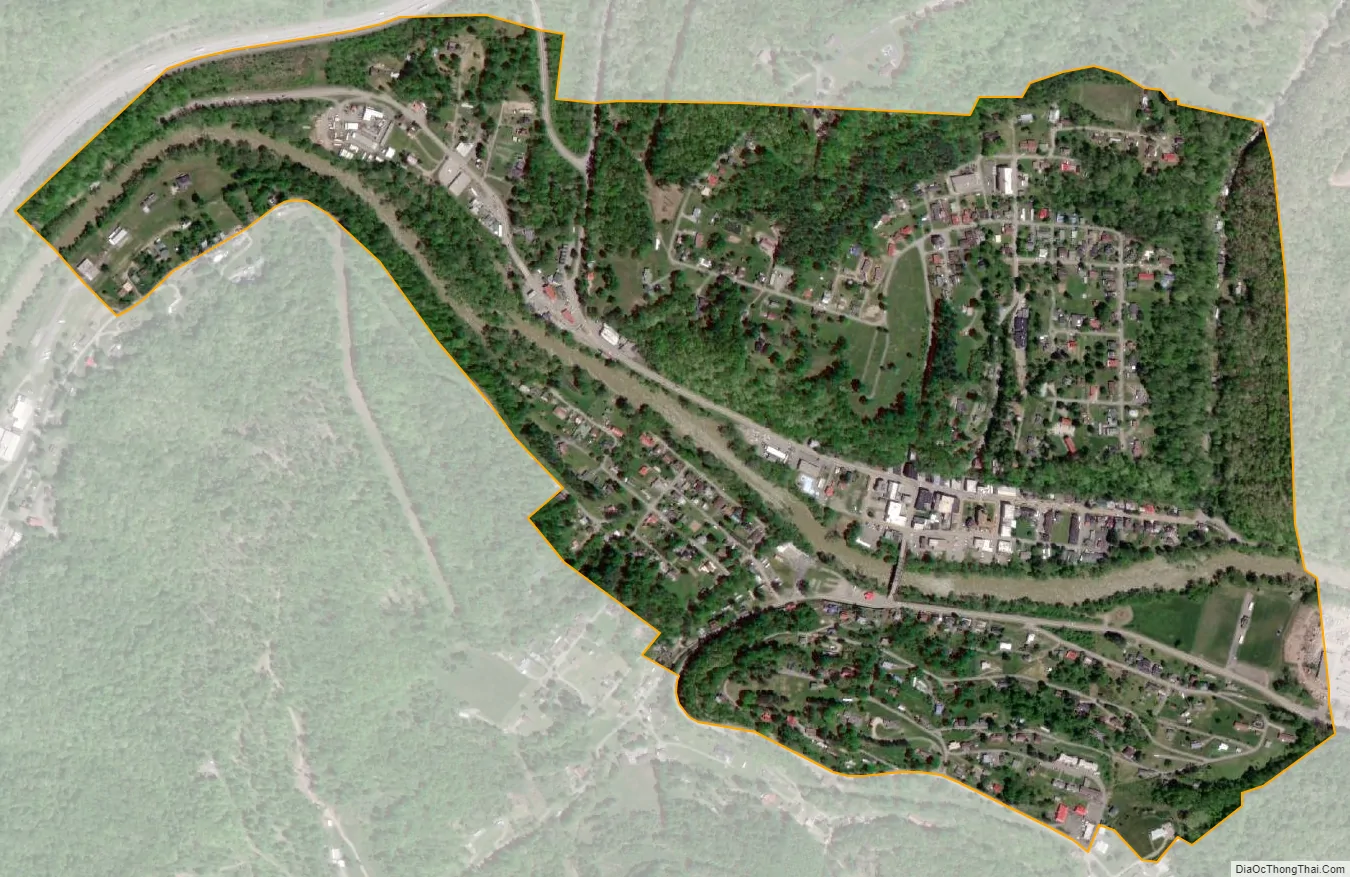
Sutton city Satellite Map
Geography
Sutton is located at 38°39′52″N 80°42′37″W / 38.66444°N 80.71028°W / 38.66444; -80.71028 (38.664437, -80.710172), along the Elk River.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 0.83 square miles (2.15 km), of which 0.78 square miles (2.02 km) is land and 0.05 square miles (0.13 km) is water.
The Sutton Lake project was authorized by Congress in the Flood Control Act of 1938. Construction began in October 1949, but was interrupted by the Korean War. Work resumed in 1956 and in the dam was finally completed in 1961. The Dam and lake provide opportunities for boating, picnicking, playgrounds, camping and pavilions available for rent. A handicap-access fishing area was also recently constructed at the Sutton Dam.
The geographic center of West Virginia is located just four miles east of Sutton.
See also
Map of West Virginia State and its subdivision:- Barbour
- Berkeley
- Boone
- Braxton
- Brooke
- Cabell
- Calhoun
- Clay
- Doddridge
- Fayette
- Gilmer
- Grant
- Greenbrier
- Hampshire
- Hancock
- Hardy
- Harrison
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Kanawha
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Marion
- Marshall
- Mason
- McDowell
- Mercer
- Mineral
- Mingo
- Monongalia
- Monroe
- Morgan
- Nicholas
- Ohio
- Pendleton
- Pleasants
- Pocahontas
- Preston
- Putnam
- Raleigh
- Randolph
- Ritchie
- Roane
- Summers
- Taylor
- Tucker
- Tyler
- Upshur
- Wayne
- Webster
- Wetzel
- Wirt
- Wood
- Wyoming
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming