Coronado (Spanish for “Crowned”) is a resort city located in San Diego County, California, United States, across the San Diego Bay from downtown San Diego. It was founded in the 1880s and incorporated in 1890. Its population was 20,192 in 2020, down from 24,697 in 2010.
Coronado is a tied island which is connected to the mainland by a tombolo (a sandy isthmus) called the Silver Strand. The explorer Sebastian Vizcaino gave Coronado its name and drew its first map in 1602. Coronado is Spanish term for “crowned” and thus it is nicknamed The Crown City. Its name is derived from the Coronado Islands, an offshore Mexican archipelago. Three ships of the United States Navy have been named after the city, including USS Coronado.
| Name: | Coronado city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
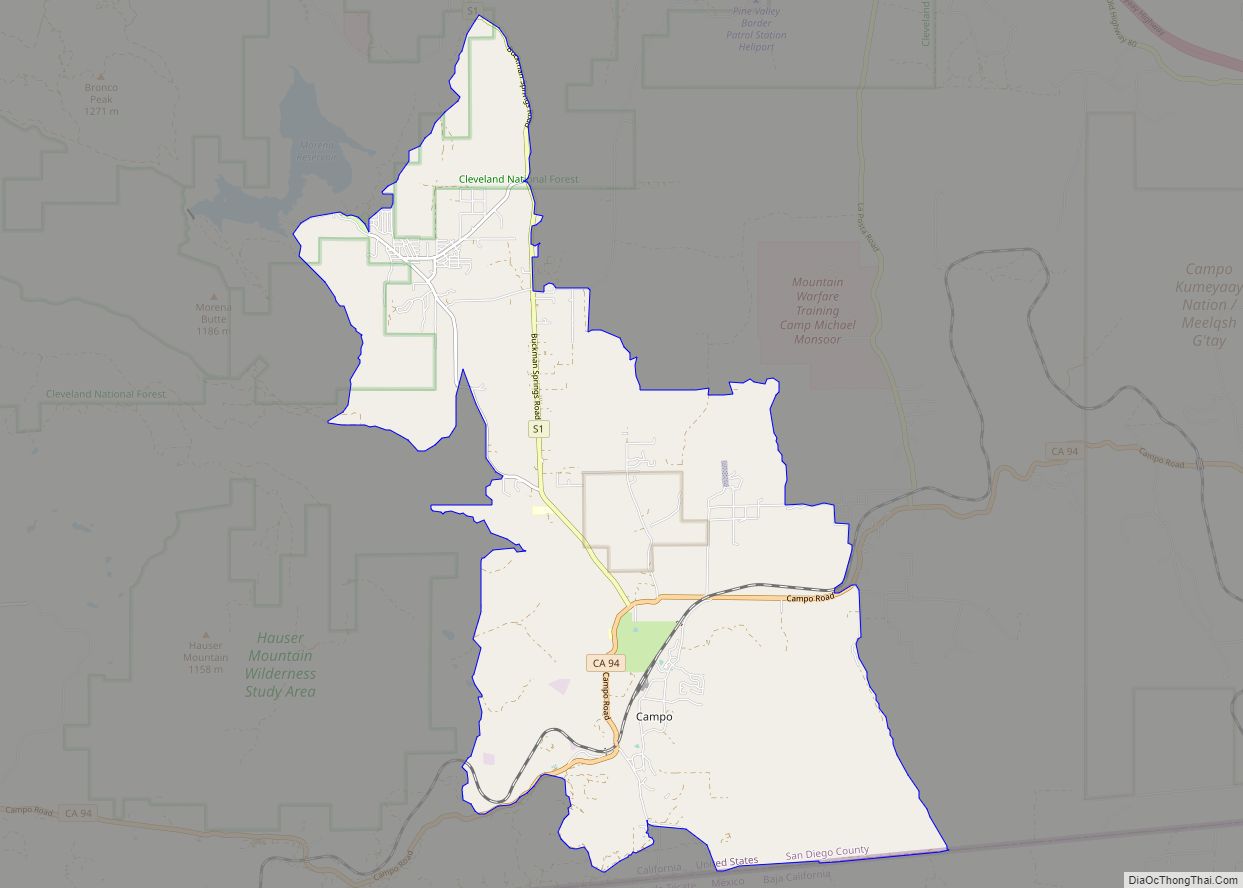
| County: | San Diego County |
| Incorporated: | December 11, 1890 |
| Elevation: | 16 ft (5 m) |
| Total Area: | 32.50 sq mi (84.17 km²) |
| Land Area: | 7.80 sq mi (20.22 km²) |
| Water Area: | 24.69 sq mi (63.96 km²) 75.72% |
| Total Population: | 20,192 |
| Population Density: | 2,587.06/sq mi (998.82/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 92118, 92178 |
| Area code: | 619 |
| FIPS code: | 0616378 |
| Website: | www.coronado.ca.us |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Coronado location map. Where is Coronado city?
History
Prior to European settlement, Coronado was inhabited by the Kumeyaay, who sustained fishing villages on the peninsula in North Island and on the Coronado Cays. As American settlers moved into the area, the Kumeyaay were pushed out of Coronado, with the last six Kumeyaay families deported to Mesa Grande Reservation in 1902.
Coronado was incorporated as a town on December 11, 1890. The community’s first post office predates Coronado’s incorporation, established on February 8, 1887, with Norbert Moser assigned as the first postmaster. The land was purchased by Elisha Spurr Babcock, along with Hampton L. Story, and Jacob Gruendike. Their intention was to create a resort community, and in 1886, the Coronado Beach Company was organized. By 1888, they had built the Hotel del Coronado, and the city became a major resort destination. They also built a schoolhouse and formed athletic, boating, and baseball clubs.
In 1900, a tourist/vacation area just south of the Hotel del Coronado was established by John D. Spreckels and named Tent City. Spreckels also became the hotel’s owner. Over the years, the tents gave way to cottages, the last of which was torn down in late 1940 or early 1941.
In the 1910s, Coronado had streetcars running on Orange Avenue. These streetcars became a fixture of the city until their retirement in 1939.
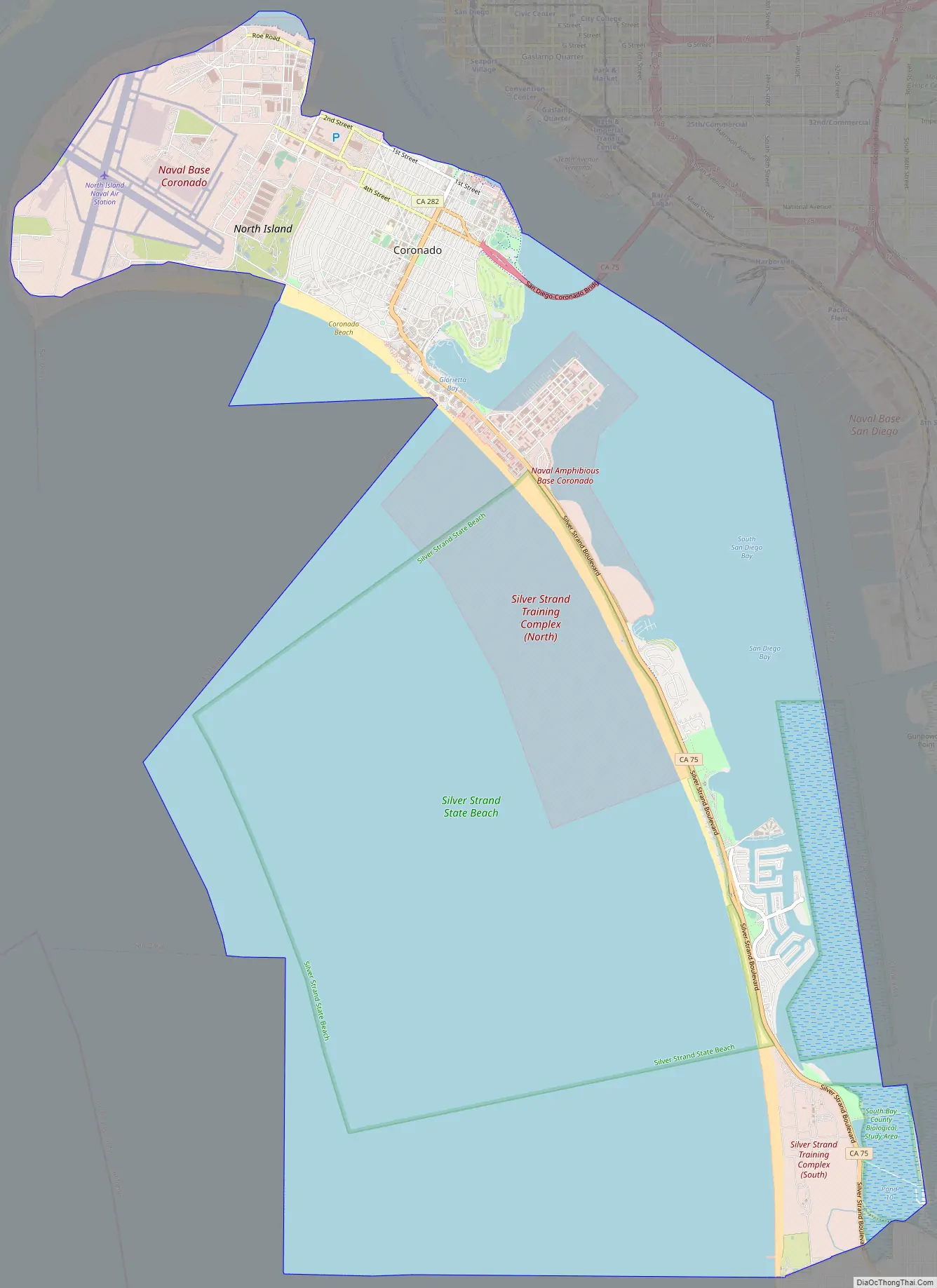
Coronado Road Map
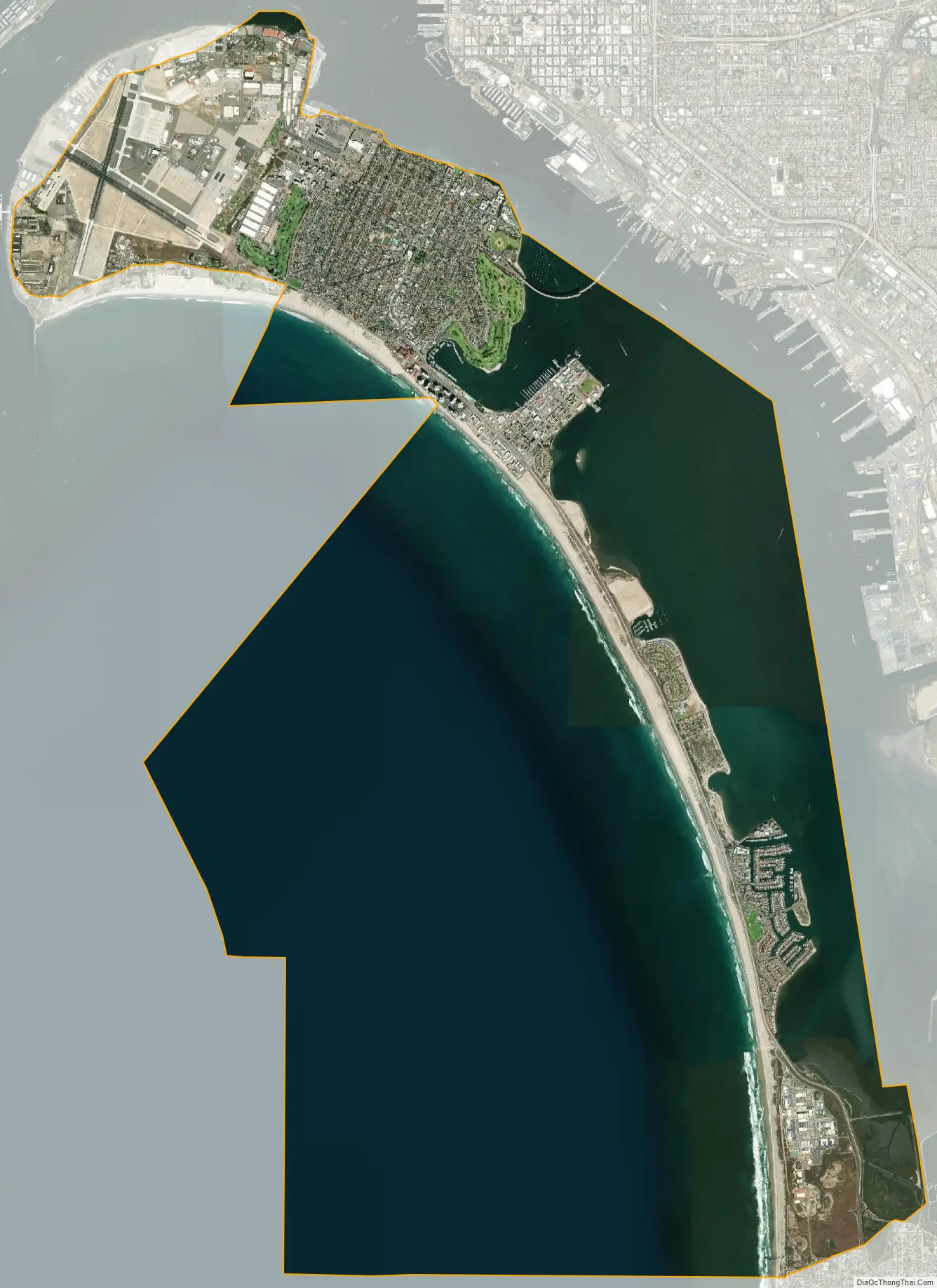
Coronado city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 32.7 square miles (85 km); 7.9 square miles (20.5 km) of the city is land and 24.7 square miles (64 km) of it (75.72%) is water.
Geographically, Coronado is a tied island connected to the mainland by a tombolo known as the Silver Strand. The Silver Strand, Coronado and North Island, form San Diego Bay. Since recorded history, Coronado was mostly separated from North Island by a shallow inlet of water called the Spanish Bight. The development of North Island by the United States Navy prior to and during World War II led to the filling of the bight by July 1944, combining the land areas into a single body. The Navy still operates Naval Air Station North Island (NASNI or “North Island”) on Coronado. On the southern side of the town is Naval Amphibious Base Coronado, a training center for Navy SEALs and Special warfare combatant-craft crewmen (SWCC). Both facilities are part of the larger Naval Base Coronado complex. Coronado has increased in size due to dredge material being dumped on its shoreline and through the natural accumulation of sand. The “Country Club” area on the northwest side of Coronado, the “Glorietta” area and golf course on the southeast side of Coronado, most of the Naval Amphibious Base Coronado, most of the Strand Naval Housing, and most of the Coronado Cays (all on the south side of Coronado) were built on dirt dredged from San Diego Bay.
On New Year’s Day 1937, during the Great Depression, the gambling ship SS Monte Carlo, known for “drinks, dice, and dolls,” was shipwrecked on the beach about a quarter mile (400 m) south of the Hotel del Coronado.
In 1969, the San Diego–Coronado Bridge was opened, allowing much faster transit between the cities than bay ferries or driving via State Route 75 along the Silver Strand. The bridge is made up of five lanes, one of which is controlled by a moveable barrier that allows for better traffic flow during rush hours. In the morning, the lane is moved to create three lanes going southbound towards Coronado, and in the evening it is moved again to create three lanes going northbound towards downtown San Diego.
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification system, Coronado has a semi-arid climate, abbreviated “BSk” on climate maps.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming