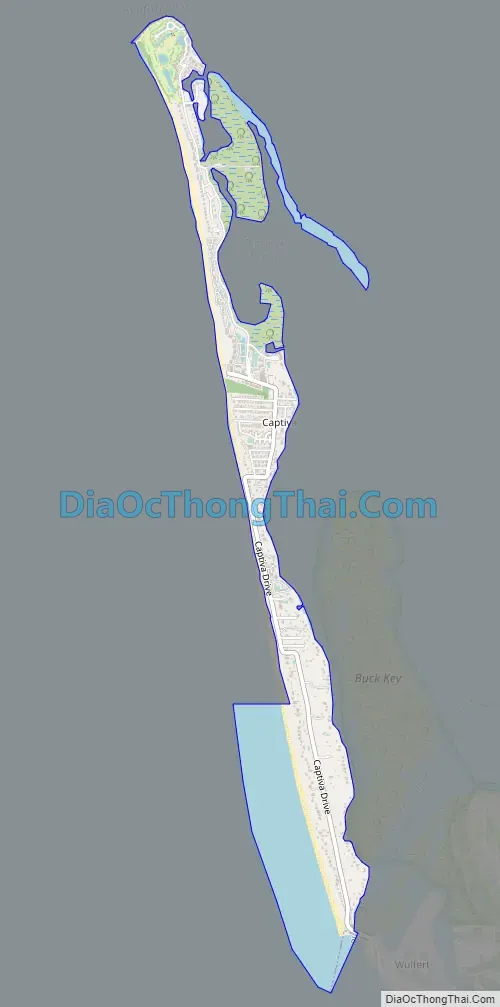
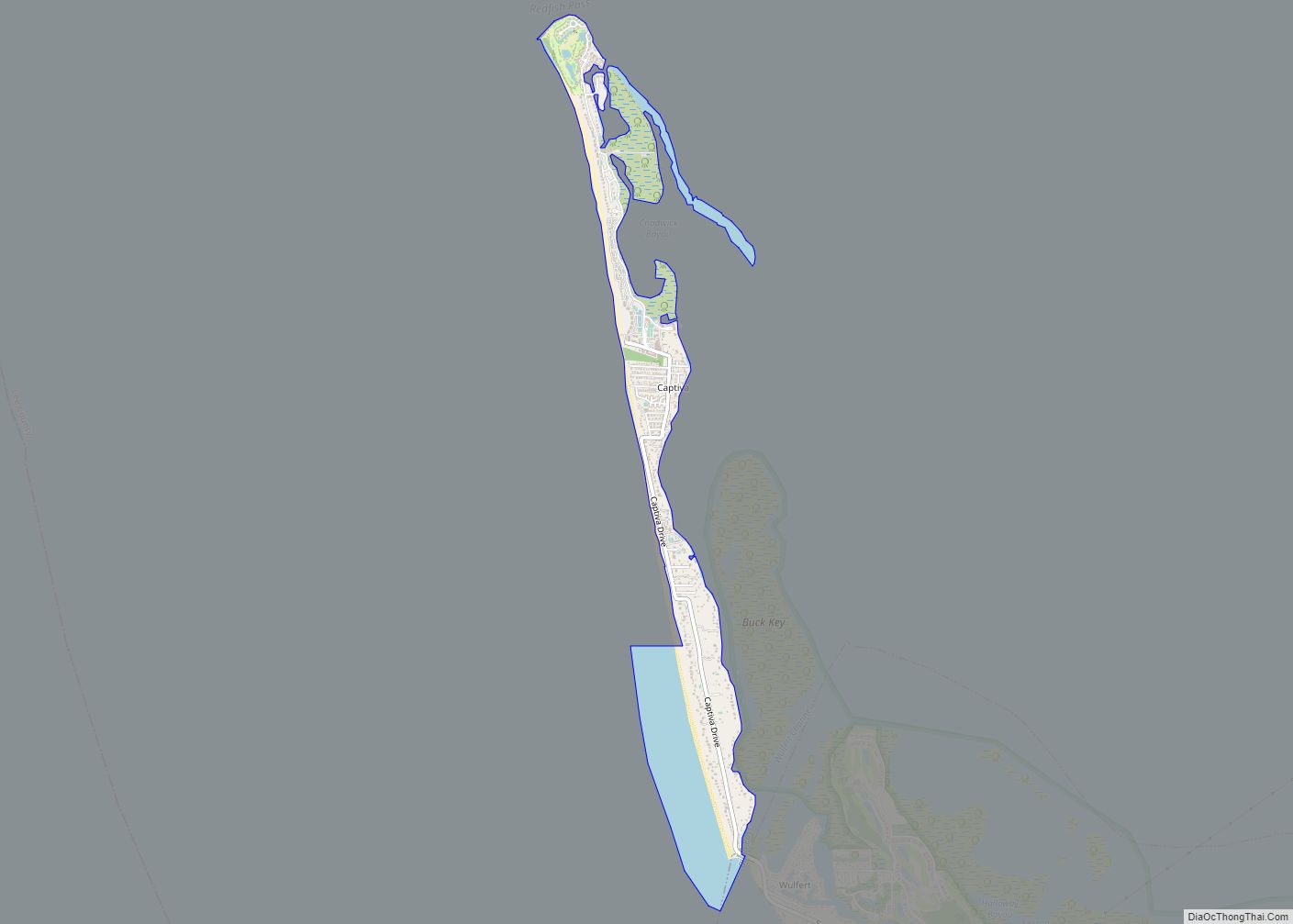
Captiva is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Lee County, Florida, United States. It is located on Captiva Island. As of the 2020 census the population was 318, down from 583 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Cape Coral-Fort Myers, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Located just offshore in the Gulf of Mexico, the island is just north of Sanibel Island. Captiva is accessed by a small bridge that crosses Blind Pass from Sanibel Island. There is a toll to use the causeway that goes from the mainland to Sanibel Island.
Many of Captiva’s homes, condominiums, and businesses were destroyed during Hurricane Charley in 2004, but the island recovered shortly thereafter. In September 2022, Hurricane Ian caused significant damage to the causeway and to the infrastructure of the island.
| Name: | Captiva CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | Florida |
| County: | Lee County |
| Elevation: | 7 ft (2 m) |
| Total Area: | 1.64 sq mi (4.26 km²) |
| Land Area: | 1.18 sq mi (3.06 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.46 sq mi (1.20 km²) |
| Total Population: | 318 |
| Population Density: | 269.26/sq mi (103.93/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 33924 |
| Area code: | 239 |
| FIPS code: | 1210425 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0280017 |
| Website: | sanibel-captiva.org |
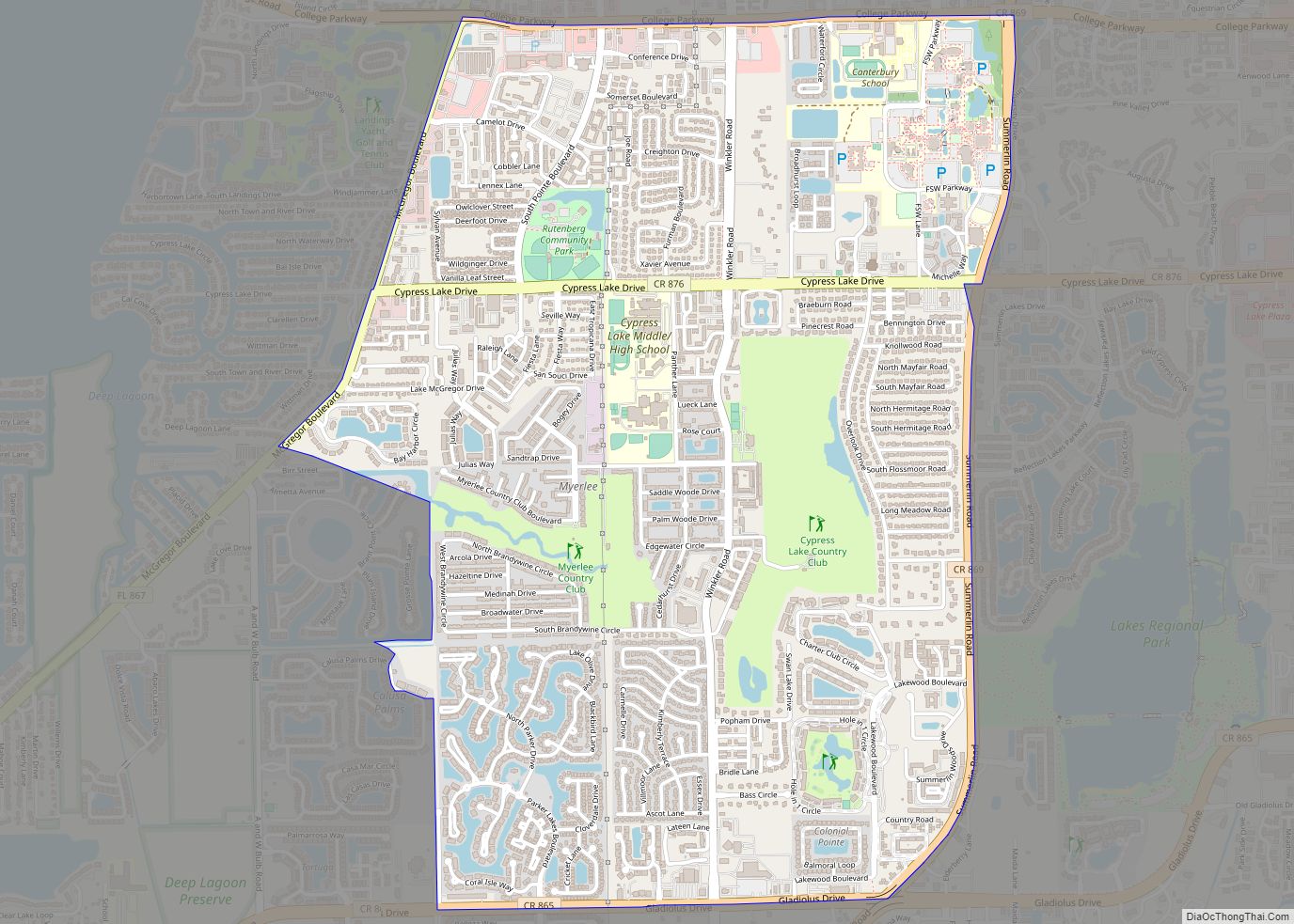
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Captiva location map. Where is Captiva CDP?
History
According to local folklore, Captiva got its name because the pirate captain José Gaspar (Gasparilla) held his female prisoners on the island for ransom. However, the supposed existence of José Gaspar is sourced from an advertising brochure of an early 20th-century developer, and may be a fabrication.
Around 3000 B.C., the sands of Captiva started to erode, resulting in the eventual formation of Sanibel Island. The Gulf of Mexico waters were eight feet lower than they are today. It is said that the first inhabitants of Captiva were the Calusa Indians. The population of the Calusa is believed to have reached as many as 50,000 people. “Calusa” means “fierce people”, and they were described as a war-like people. The Calusa Indians were resistant to colonization and attacked any explorers who came into their territory. Calusa Indians built their houses on stilts without walls. They wove palmetto leaves together to build roves (twisted strands of fibers). The Calusa Indians fished for food on the coast, bays, rivers, and waterways. They did not farm. “The Calusa Indians did not farm like the other Indian tribes in Florida. Instead, they fished for food on the coast, bays, rivers, and waterways. The men and boys of the tribe made nets from palm tree webbing to catch mullet, pinfish, pigfish, and catfish. They used spears to catch eels and turtles. They made fish bone arrowheads to hunt for animals such as deer. The women and children learned to catch shellfish like conchs, crabs, clams, lobsters, and oysters.” The Calusa Indians used the shells on the island for utensils, jewelry, tools, weapons, and ornaments.
By the late 1700s most of the Calusa Indians had died out. Many were captured and sold as slaves while others died from diseases such as smallpox and measles.
An Austrian named Binder (b. 1850) was on a German freighter headed to New Orleans when the ship crashed and he was shipwrecked off Boca Grande. He then washed up to shore on what has been since 1921, Upper Captiva. “He lived for several weeks on what the unoccupied island had to offer, built a makeshift raft, and got himself to Pine Island, where he was helped to return to his home. By 1888, due to his having fought with the U.S. Army, he became naturalized, and was allowed to homestead on Captiva in 1888, when he was 38 years old. For 10 years he was Captiva’s first and only inhabitant. He died in 1932.”
Captiva Road Map
Captiva city Satellite Map
Geography
Captiva is located in western Lee County at 26°31′5″N 82°11′28″W / 26.51806°N 82.19111°W / 26.51806; -82.19111 (26.518028, -82.191057). The CDP comprises the entire island, bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico and to the east by Pine Island Sound. Captiva Drive is the main road on the island, running from the town center south to the Blind Pass bridge to Sanibel. It is a 13-mile (21 km) drive from Captiva to the Sanibel Causeway and a total of 31 miles (50 km) by road from Captiva to the center of Fort Myers.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the Captiva CDP has a total area of 1.7 square miles (4.3 km), of which 1.2 square miles (3.1 km) are land and 0.46 square miles (1.2 km), or 28.15%, are water.
Originally part of neighboring Sanibel Island to the southeast, it was severed in 1926 when a hurricane’s storm surge created a new channel, Blind Pass. The channel filled in over subsequent years, but was reopened by dredging in the summer of 2009. Like Sanibel, Captiva is a barrier island to Pine Island (to the east of Captiva and north of Sanibel), however it is much narrower. The only automobile access to Captiva is via the Sanibel Causeway and Sanibel-Captiva Road, which ends in the CDP of Captiva, the island’s only CDP. Captiva was homesteaded in 1888 and a tiny cemetery next to The Chapel by the Sea has the grave of the original resident, William Herbert Binder (1850–1932), an Austrian. Half the island is in private ownership, with “Millionaire’s Row”, luxury homes on the gulf and bay sides of Captiva Drive. The South Seas Island Resort entry gate is at the end of this road. Roosevelt Channel on the east side of the island, is named for Theodore Roosevelt who fished there.
North Captiva Island or Upper Captiva is another island, in turn severed from Captiva in a 1921 hurricane, creating Redfish Pass. North Captiva has power from lines that originate on the north end of Captiva, and is privately owned. The island can only be accessed via boat or small plane.
Captiva was seriously damaged in August 2004 when the eastern eyewall of Hurricane Charley struck North Captiva, immediately before hitting Charlotte Harbor to the north-northeast. Initial reports indicated that 160 buildings were destroyed and another 160 seriously damaged. Reports indicate that the storm surge cut a path 491 yards (449 m) wide across the narrowest part of North Captiva, separating the island. The separation of the two halves of the island began three years earlier during a series of tornadoes caused by Tropical Storm Gabrielle that passed through the area in September 2001. The new pass filled in within a few years and is now back to its pre-Charley state. Most of the invasive Australian pines on the island blew over in the hurricane, making room for native mangroves and sabal palms.
In September 2022, Category 4 Hurricane Ian made landfall in Upper Captiva with sustained winds of 150 mph. The Sanibel Causeway was heavily damaged by the hurricane.
See also
Map of Florida State and its subdivision:- Alachua
- Baker
- Bay
- Bradford
- Brevard
- Broward
- Calhoun
- Charlotte
- Citrus
- Clay
- Collier
- Columbia
- Desoto
- Dixie
- Duval
- Escambia
- Flagler
- Franklin
- Gadsden
- Gilchrist
- Glades
- Gulf
- Hamilton
- Hardee
- Hendry
- Hernando
- Highlands
- Hillsborough
- Holmes
- Indian River
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Lafayette
- Lake
- Lee
- Leon
- Levy
- Liberty
- Madison
- Manatee
- Marion
- Martin
- Miami-Dade
- Monroe
- Nassau
- Okaloosa
- Okeechobee
- Orange
- Osceola
- Palm Beach
- Pasco
- Pinellas
- Polk
- Putnam
- Saint Johns
- Saint Lucie
- Santa Rosa
- Sarasota
- Seminole
- Sumter
- Suwannee
- Taylor
- Union
- Volusia
- Wakulla
- Walton
- Washington
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming