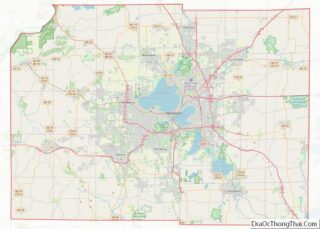
Mount Horeb is a village in Dane County, Wisconsin,. The population was 7,754 at the time of the 2020 census. It is part of the Madison Metropolitan Statistical Area.
| Name: | Mount Horeb village |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 47 |
| LSAD Description: | village (suffix) |
| State: | Wisconsin |
| County: | Dane County |
| Elevation: | 1,243 ft (379 m) |
| Total Area: | 3.23 sq mi (8.35 km²) |
| Land Area: | 3.23 sq mi (8.35 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 7,754 |
| Population Density: | 2,336.12/sq mi (901.86/km²) |
| Area code: | 608 |
| FIPS code: | 5554725 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1569817 |
| Website: | mounthorebwi.info |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
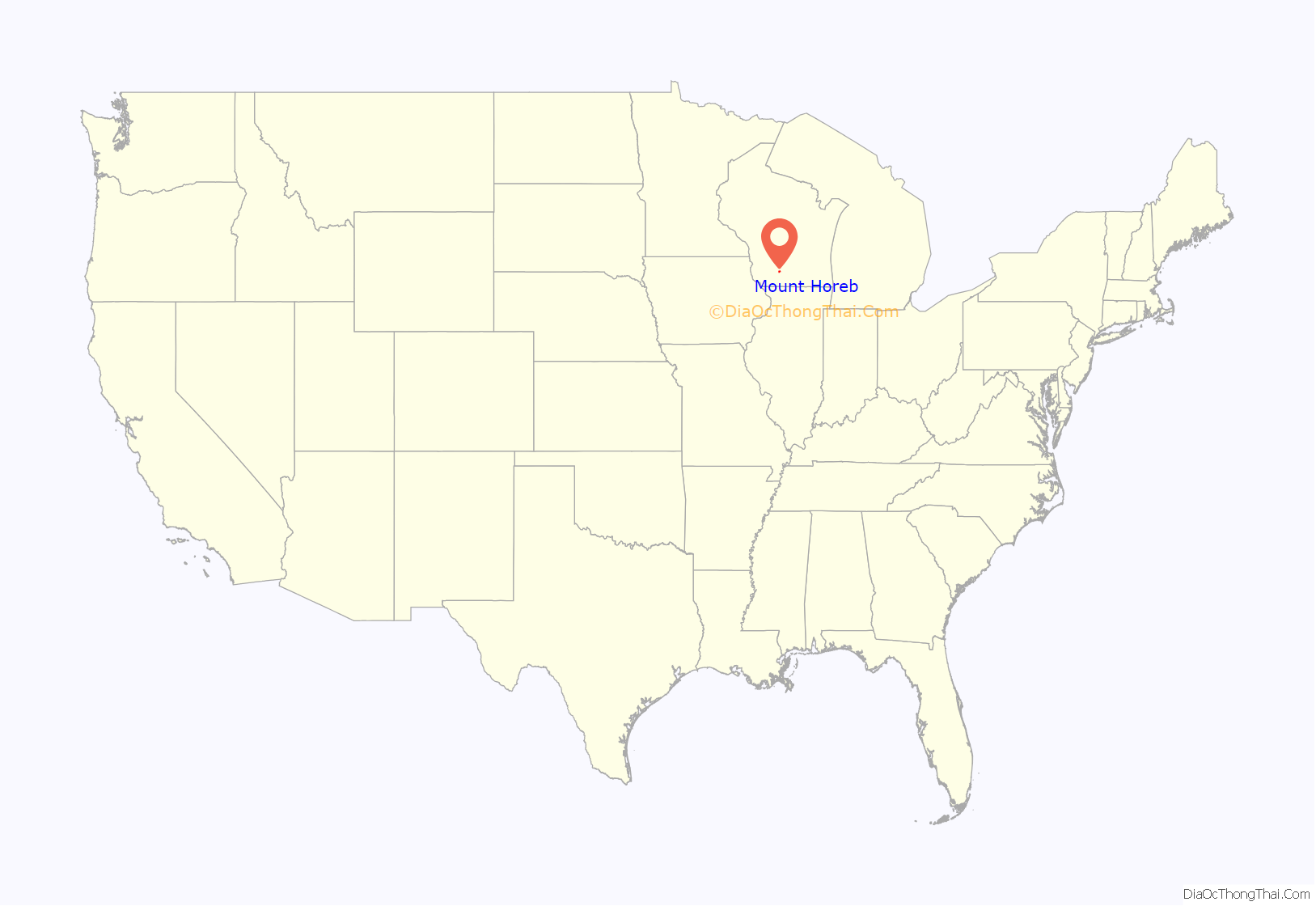
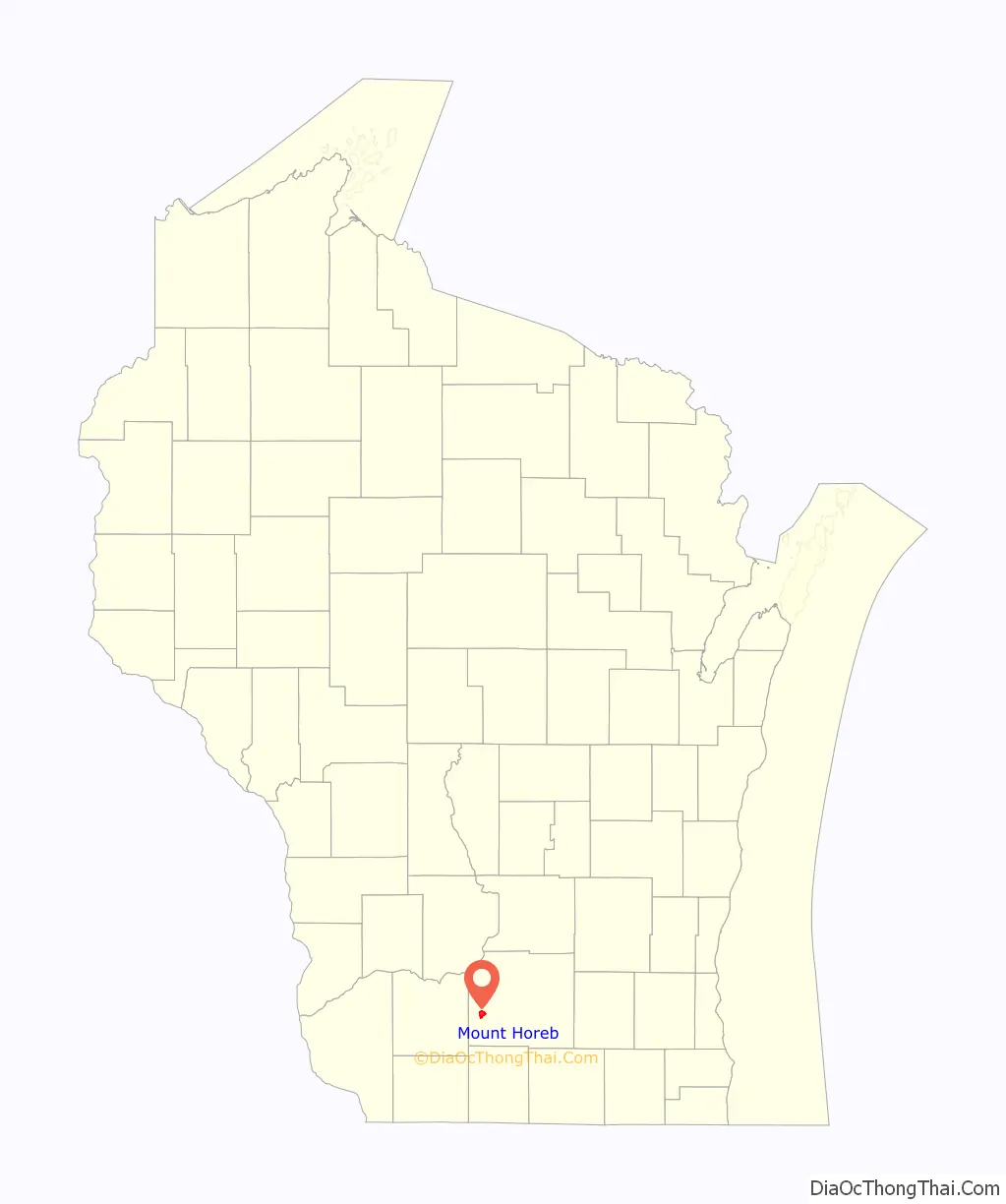
Mount Horeb location map. Where is Mount Horeb village?
History
The Ho-Chunk nation
The Village of Mount Horeb is part of the ancestral territory of the Ho-Chunk nation. Ho-Chunk translates into “People of the Sacred Language,” or “People of the Big Voice,” and belong to the Siouan linguistic family. Beginning in 1829, the Ho-Chunk, sometimes referred to by the exonym, Winnebago (which is derived from the French “Ouinipegouek,” or “People of the Stinking Water”) experienced massive amounts of pressure from European and American settlers as their land was opened for agriculture and lead mining. Their territory was ceded to the United States’ Government through three treaties: 1829, 1832, and 1837. The treaty signed in 1829, encompassed territory that would be the future site of Mount Horeb. These treaties, accompanied by colonizing pressure and xenophobic fears rising from the Dakota War of 1862, forced the tribe West from their land across the Mississippi River. Currently, the tribe has no reservation, rather, 8,800 acres, located throughout twenty counties in western Wisconsin, are held by the 7,100 members of the Ho-Chunk.
Early settlement
Settlement in Dane County began in 1828 when Ebenezer Brigham discovered a load of lead in the Blue Mounds area, and established a tavern and inn. In 1849, the tract of land that would become Mount Horeb was purchased by James Morrison, and a year later sold a portion to Granville Neal. This initial settlement largely drew individuals of English, Irish, German, and Scottish ethnic backgrounds, as well as Yankees and settlers from Southern states. As the population of the Blue Mounds Township grew, so too did the need for a new post office. In 1861, the first post office in Mount Horeb was established in the home of English immigrant and Methodist Episcopal lay minister George Wright. As the new postmaster, Wright selected the name Mount Horeb for the settlement. The “Mount” portion of the name is said to be inspired by the surrounding geography, while “Horeb” is derived from the Biblical location wherein the prophet Moses received the Ten Commandments from the Judeo-Christian God while leading the Jewish people through the Sinai Peninsula on their exodus out of Egypt. References to this site can be found in the books of Exodus, Deuteronomy, 1 Kings, Psalms, and Malachi. When Wright moved to Norwalk, Iowa, the post office moved to a space closer to the settlement referred to as “The Corners.” The name changed to “Horeb’s Corner,” before officially being designated as Mount Horeb.
Norwegian immigration
The presence of Norwegian immigrants has played a significant factor in the historic and contemporary identity of not only Mount Horeb, but the State of Wisconsin. The first Norwegian immigrant to arrive in the Wisconsin Territory was Ole Nattestad, from the Numedal valley east of Telemark in 1838, establishing Jefferson Prairie near Beloit. By 1850, 9,467 Norwegians were identified by the federal census, and by the 1870 census, the population had exploded to 59,619. Norwegian-immigration historian Odd S. Lovoll observes that by the 1870s, Norwegian immigrants had created significant settlements throughout Wisconsin, particularly in Dane County. In 1871, Andrew Levordson became the first Norwegian immigrant to arrive in Mount Horeb, marking the beginning of this ethnic-group’s presence in the village.
Although Mount Horeb had large Norwegian and Norwegian-American ethnic populations, the community also chose to display its identity through multiple forms of museums, performances, and tourist oriented ideas. The first of which was Little Norway, Wisconsin, near Blue Mounds. In 1856, Osten Olson Haugen and his family, who emigrated from Tinn, Telemark, Norway, established a forty-acre farmstead. In 1926, Isak J Dahle, an insurance agent from Chicago, Illinois, but who was raised in Mount Horeb, purchased the site and renamed the farmstead Nissedahle. The name is a play on words. Nisse (see Tomte), in Norwegian folklore traditions, are playful elves that provide assistance to humans when kept in good spirit. While the Norwegian word “Nissedal” translates into “Valley of the Elves,” Dahle chose to incorporate his last name into valley, therefore, “Nissedahle.” Over the years, Dahle converted the site into a living history museum, creating an idealized folk version of Norway. The site was opened to the public in 1934. One of the most striking features of Little Norway was the replica of the 12th century “Stavkirke,” a Christian Norwegian stave church. This structure was built in Trondheim, Norway for the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago, Illinois. Eventually, it would be purchased by the Wrigley family, and later gifted to Dahle in 1935. The stave church housed over 7,000 individual artifacts. Little Norway became a major attraction in the area, and guests were invited to participate in educational activities as they explored the open air museum as it told the story of immigrant Norwegian and Norwegian rural life. After eighty-five years, Little Norway closed its doors due to financial reasons. Many of the objects in the museum were auctioned to historical preservation and interpretation organizations, and the stave church returned to Norway. Today, visitors to the Driftless Historium in Mount Horeb can take virtual, 3-D tours of the stave church.
After returning from a trip abroad to Scandinavia, Mount Horeb resident and artist, Oljanna Cunneen, suggested to that hosting a festival centered on a performance of ethnic identity may be a “fun” endeavor for the community to engage. In 1966, Mount Horeb premiered “Song of Norway” (1944), an operetta by Robert Wright (writer) and George Forrest (author) (1944). “Song of Norway” tells the fictionalized account of Norwegian composer, Edvard Grieg. The first performance was held at the Tyrol Ski Basin. In 1979, the play moved to the Cave of the Mounds, where a permanent stage was constructed. The play featured local and professional actors who performed on an outdoor stage. The Norwegian folk costumes, such as the bunad, were made by local artists dedicated to the success of this play and its performance of the community’s Norwegian heritage. The play ran currently each summer until the early 2000s when it eventually ceased annual production.
During the 1980s, as part of an effort to continue celebrating their Norwegian and Norwegian-American heritage, as well as a reaction to the construction of the Business Highway 18/151 bypass, Mount Horeb has transformed itself into the “Troll Capital of the World.” In Norwegian folklore, trolls are said to be about the size of, if not smaller than, humans. They have ugly faces, stout bodies, and tails. These trolls featured in Mount Horeb hearken to this tradition, and residents have incorporated these playful, often numbskull, characters throughout the village. The majority of them, whether painted, sculpted, or carved from logs with a chainsaw, are located along Main Street, “The Trollway.” Each of the 40 trolls in Mount Horeb have their own distinct identity, such as “The Chicken Thief,” “The Accordion Player,” and “Sweet Swill.”
The “Trollway” originated from the Chamber of Commerce’s attempts to draw traffic away from the bypass and back into the center of town to promote local businesses.
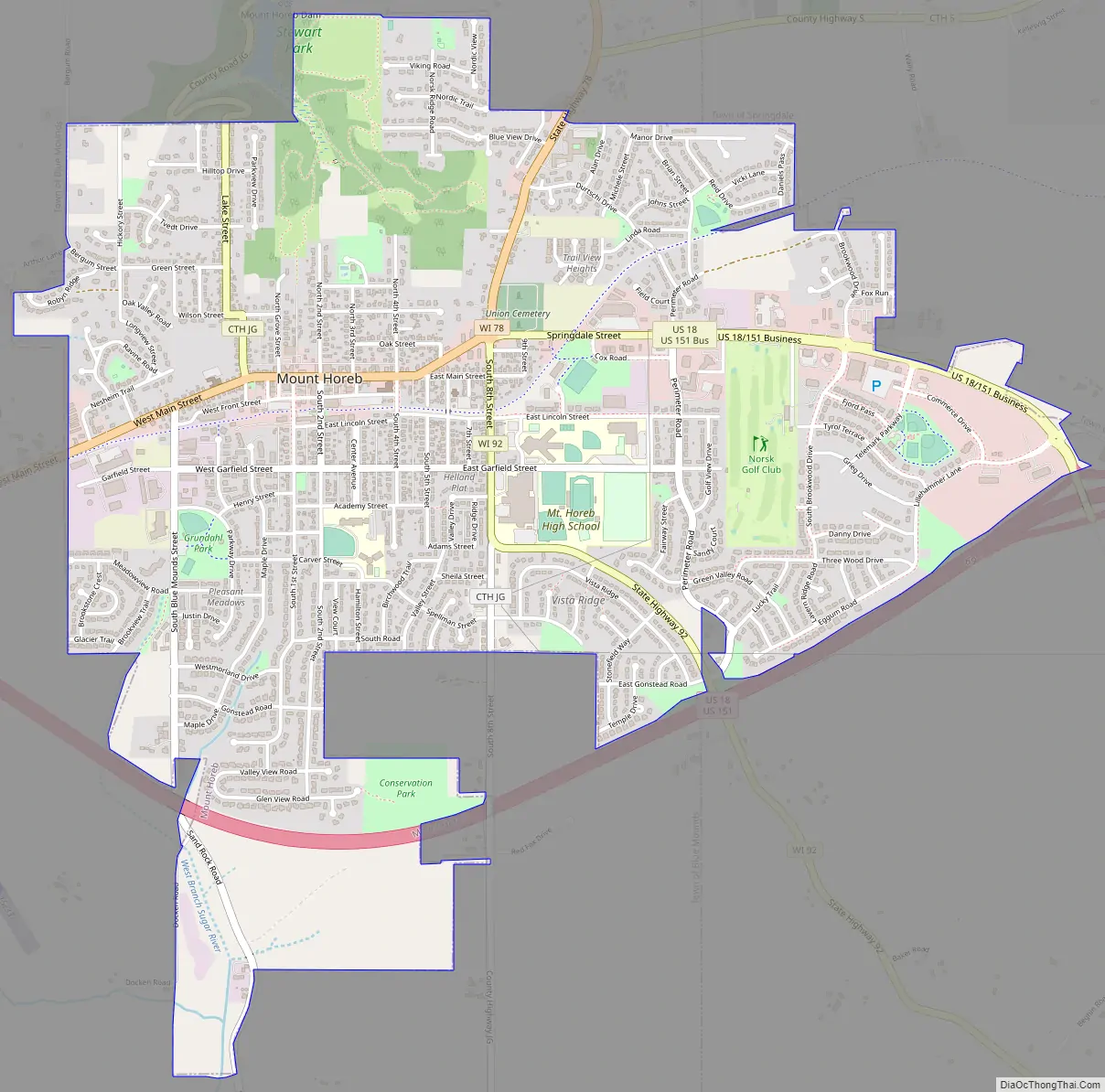
Mount Horeb Road Map
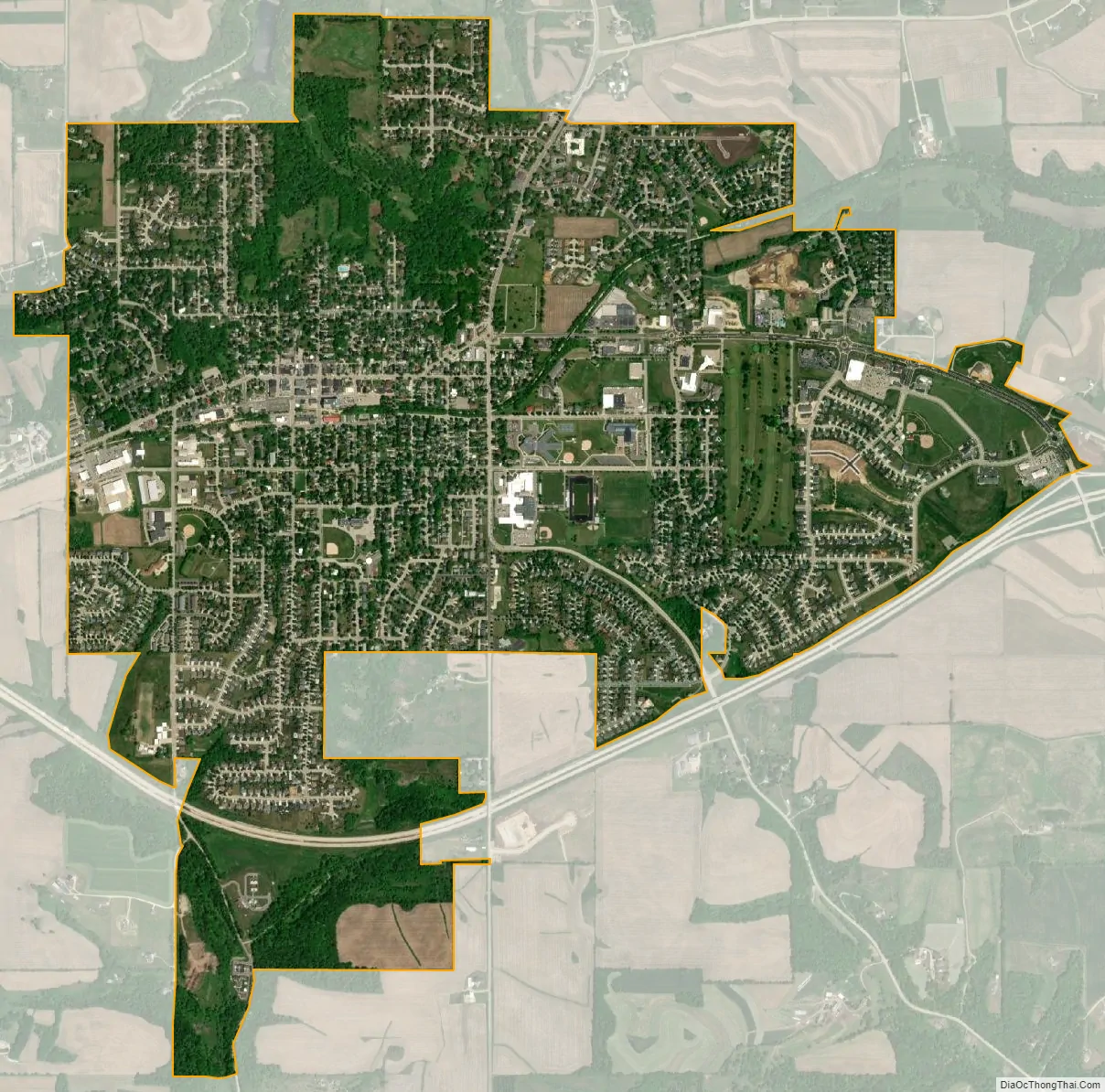
Mount Horeb city Satellite Map
Geography
Located in southwestern Wisconsin, Mount Horeb is situated in a region referred to as the Driftless Area. While including parts of southeast Minnesota, northeast Iowa, and northwest Illinois, the Driftless Area is a distinct feature to the Wisconsin landscape, stretching across eighteen different counties. In her analysis of place name in the Driftless Area, folklorist Janet Gilmore observes that, “travelers who cross in and out of the territory today will note how its distinctive contours and impressive views emerge from wider, flatter expanses to the east, south, west, and north.” These “contours” are the result of glaciers going around this space, smoothing out the surrounding prairie while leaving behind rolling hills. The Village of Mount Horeb is located in southwest Dane County. The geographic boundary of the Driftless Area runs down the center of the county, creating an east/west topographical division. Mount Horeb is also located near Blue Mound State Park, which also has access to the Military Ridge State Trail. Mount Horeb is located approximately twenty miles southwest of State Capital, Madison, Wisconsin, which is also home to the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
Located along the major thoroughfare of U.S. Highway 151, Mount Horeb encompasses a total area of 3.25 square miles.
See also
Map of Wisconsin State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Ashland
- Barron
- Bayfield
- Brown
- Buffalo
- Burnett
- Calumet
- Chippewa
- Clark
- Columbia
- Crawford
- Dane
- Dodge
- Door
- Douglas
- Dunn
- Eau Claire
- Florence
- Fond du Lac
- Forest
- Grant
- Green
- Green Lake
- Iowa
- Iron
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Juneau
- Kenosha
- Kewaunee
- La Crosse
- Lafayette
- Lake Michigan
- Lake Superior
- Langlade
- Lincoln
- Manitowoc
- Marathon
- Marinette
- Marquette
- Menominee
- Milwaukee
- Monroe
- Oconto
- Oneida
- Outagamie
- Ozaukee
- Pepin
- Pierce
- Polk
- Portage
- Price
- Racine
- Richland
- Rock
- Rusk
- Saint Croix
- Sauk
- Sawyer
- Shawano
- Sheboygan
- Taylor
- Trempealeau
- Vernon
- Vilas
- Walworth
- Washburn
- Washington
- Waukesha
- Waupaca
- Waushara
- Winnebago
- Wood
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming