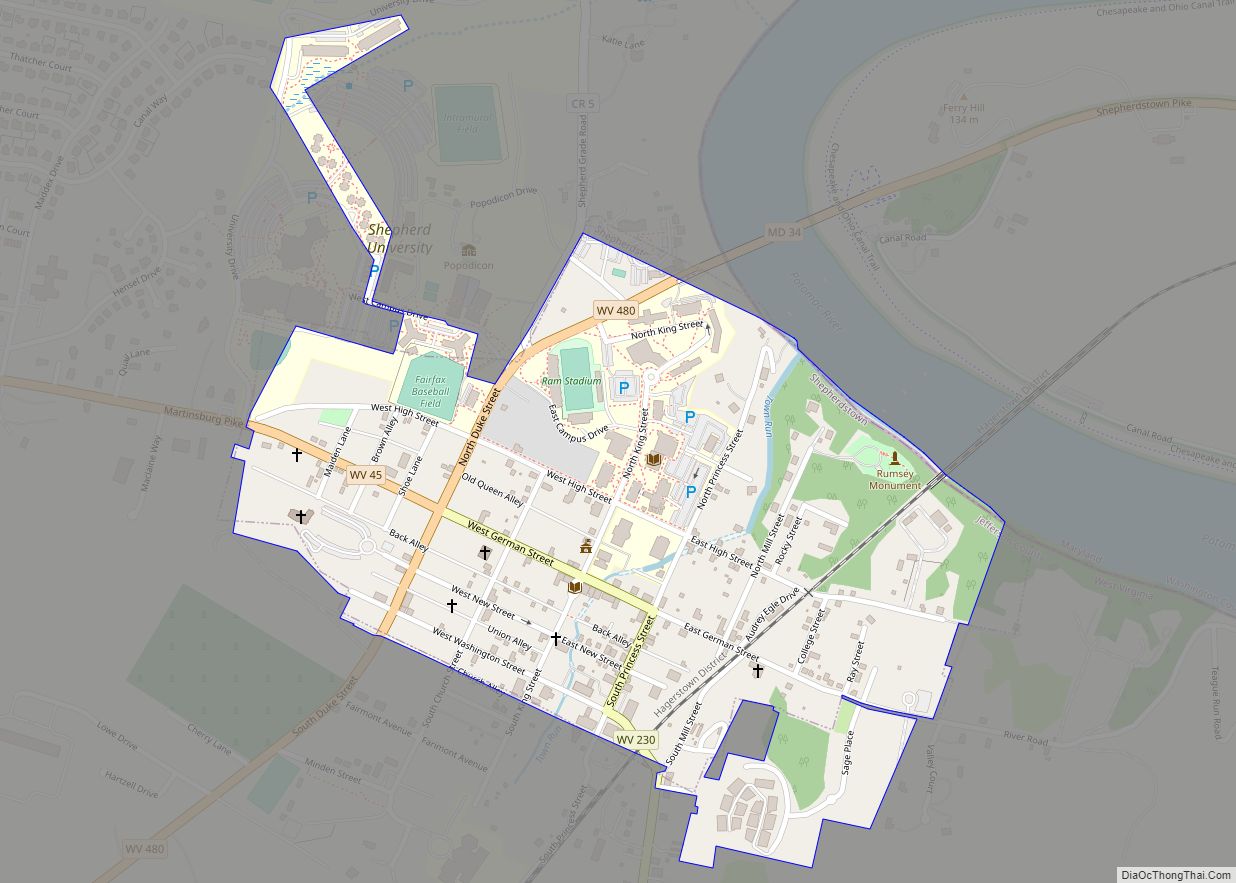
Shepherdstown is a town in Jefferson County, West Virginia, United States, located in the lower Shenandoah Valley along the Potomac River. Home to Shepherd University, the town’s population was 1,531 at the time of the 2020 census. The town was established in 1762 along with Romney; they are the oldest towns in West Virginia.
| Name: | Shepherdstown town |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 43 |
| LSAD Description: | town (suffix) |
| State: | West Virginia |
| County: | Jefferson County |
| Elevation: | 400 ft (122 m) |
| Total Area: | 0.401 sq mi (1.039 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.401 sq mi (1.039 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.000 sq mi (0.000 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,531 |
| Population Density: | 4,765.59/sq mi (1,838.73/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 25443 |
| Area code: | 304 |
| FIPS code: | 5473468 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1546673 |
| Website: | shepherdstown.info |
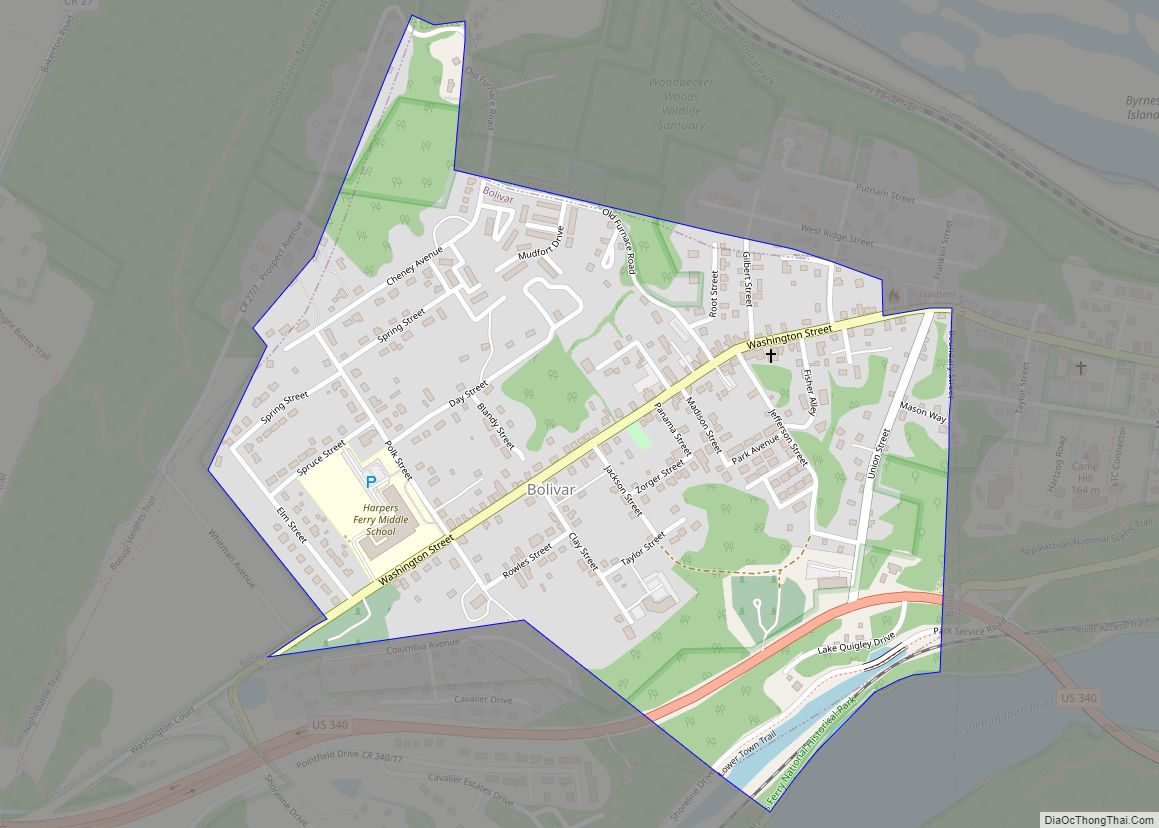
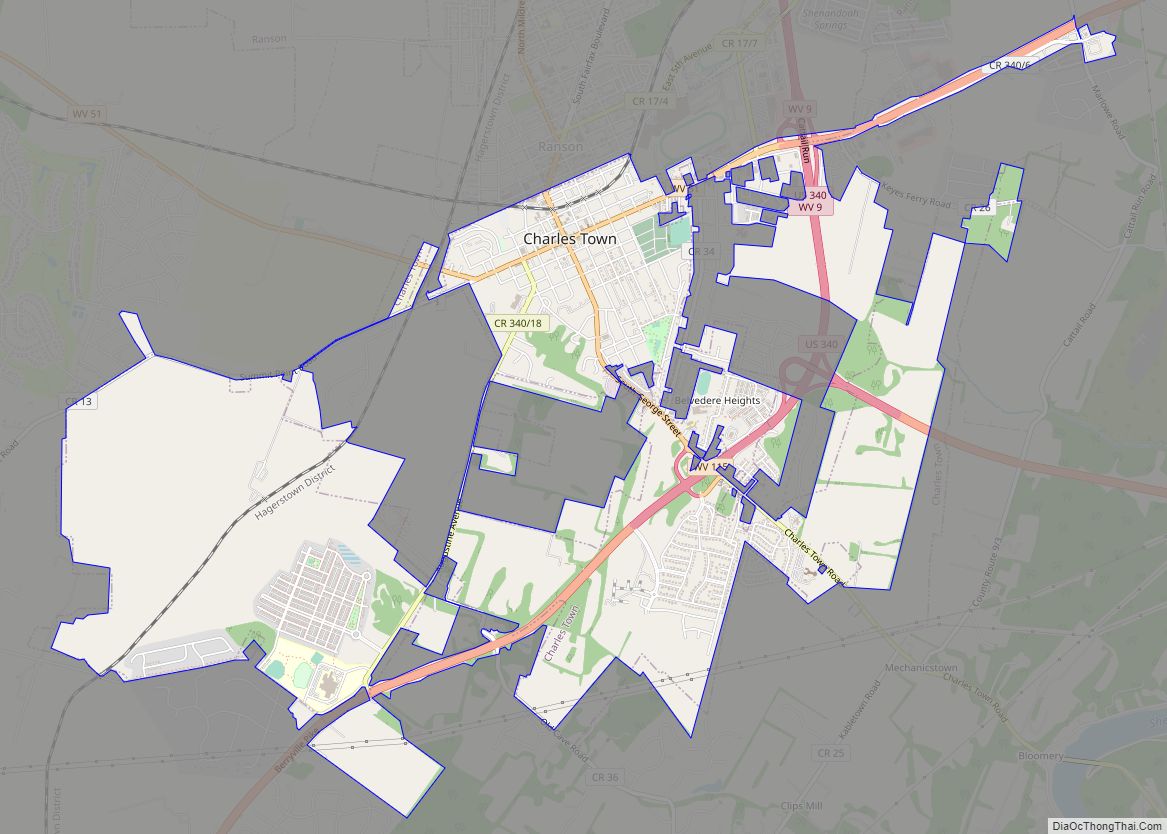
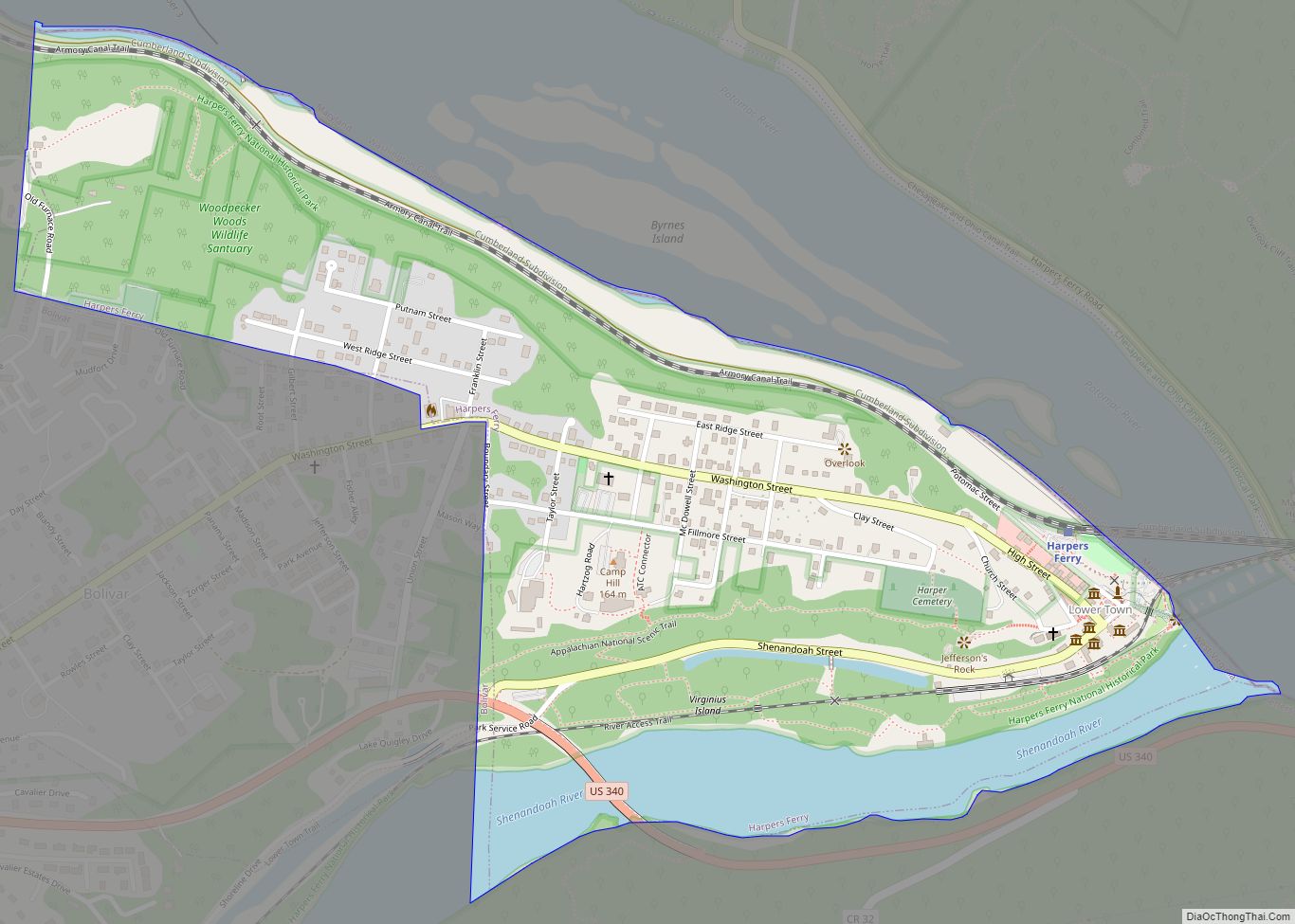
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
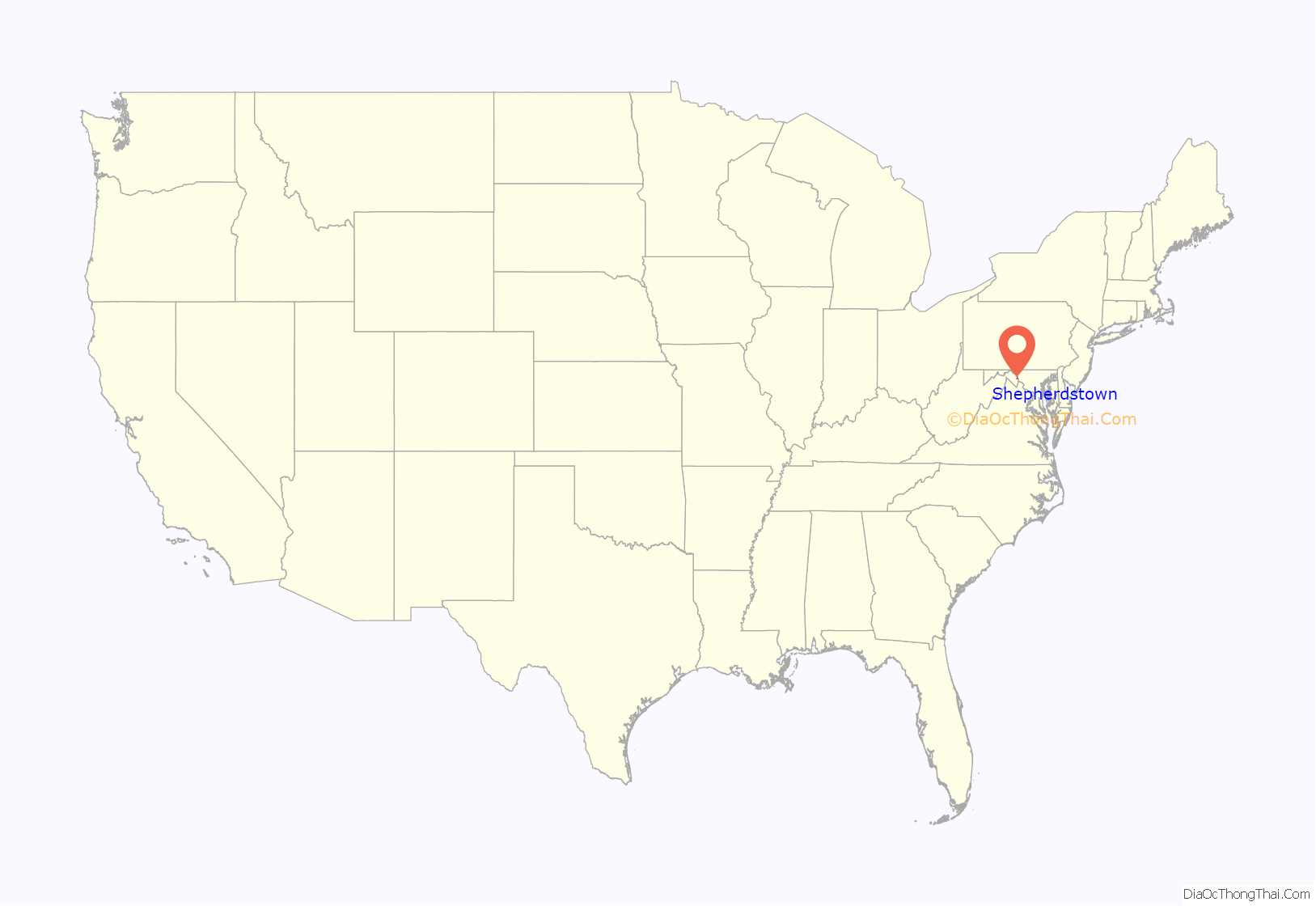
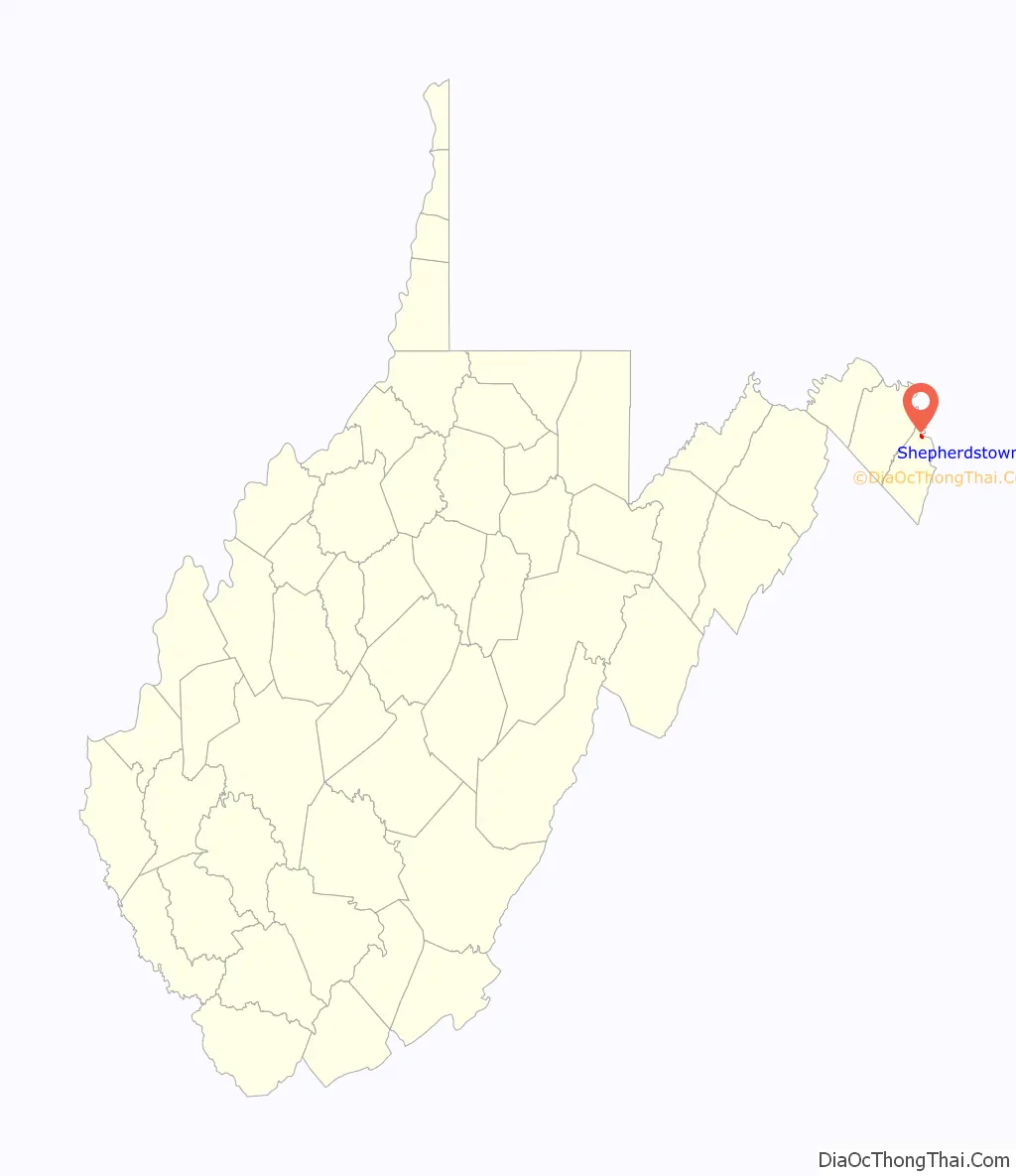
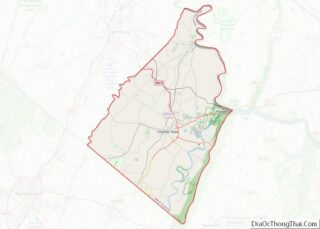
Shepherdstown location map. Where is Shepherdstown town?
History
18th century
Established on December 23, 1762, by consecutive acts passed by the Virginia House of Burgesses and approved by the governor, Mecklenburg (later renamed Shepherdstown), and Romney in Hampshire County are the oldest towns in West Virginia. On a list of more than 30 approved “publick and private bills” of that date, the bill containing An Act for establishing the town of Mecklenburg, in the county of Frederick immediately follows An act for establishing the town of Romney, in the county of Hampshire, and for other purposes therein-mentioned.
The first British colonial settlers began their migration into the northern end of the Shenandoah Valley in the early 18th century. Many crossed the Potowmack (now Potomac) River at Pack Horse Ford, about one mile (1.6 km) down river from the future site of Shepherdstown. The Colony of Virginia began issuing Valley land grants in the 1730s. In 1734, Thomas Shepherd (1705–1776) was granted 222 acres (90 ha) on the south side of the Potomac, along the Falling Spring Branch (now known as the Town Run). From that tract he selected 50 acres (20 ha) and laid out a town. Naming his town Mecklenburg, he petitioned the Virginia General Assembly for a charter, which was granted in 1762.
Shepherd was the sole trustee, owning the town and being responsible for its government. More than six natural springs feed Town Run before it enters the south end of town. It never floods, nor runs dry; it meanders through backyards, under houses, across alleys and beneath five streets. This setting was conducive to millers, tanners, potters, smiths and other artisans. As a result, by 1775, the town boasted 1,000 inhabitants. In 1775, General George Washington issued a call for “Virginia Volunteer Riflemen.” Captain Hugh Stephenson filled the ranks of his company here. The troops departed from “Morgan’s Spring,” about one-half mile (0.80 km) south of the town limits, on July 16, 1775. This famous “Beeline March to Cambridge” covered 600 mi (970 km) in 24 days. Thirty-eight Revolutionary veterans are buried in the surrounding area.
On December 3, 1787, James Rumsey conducted a successful trial of his new invention, the steamboat, in the Potomac at the north end of Princess Street. The first newspaper—The Potomac Guardian and Berkley Advertiser—and book (The Christian Panoply) in what is now West Virginia were published here (1790s). (The Shepherdstown Public Library has a copy of the book.) Shepherdstown was the birthplace of Robert Lucas (1781), the future governor of Ohio and territorial governor of Iowa.
A second charter, which allowed for self-government, was granted by the Commonwealth of Virginia in 1794. In 1798, the corporate limits were extended and the name was changed to Shepherd’s Town. After the American Civil War, the town’s name was officially contracted to Shepherdstown. The clay soil in the area was conducive to brick making. By the late 1790s, there were several commercial brickyards, and kilns could be built with little difficulty. In many instances, bricks were “burnt” at the construction sites. They were plentiful and cheaper than nails. Roofing material affected the market value and the insurance premiums of the brick structures. Those covered with tile were much more valuable than those topped with wooden shingles. Fires starting in the shingles destroyed many brick homes, mills, stores and outbuildings.
19th century
Running along the Maryland side of the Potomac River, the Chesapeake and Ohio (C&O) Canal reached Shepherdstown in the early 1830s. Lock no. 38—named “Shepherdstown River Lock”—was built across from Shepherdstown at mile 72.7 of the canal. One of only three of its kind on the canal, it allowed canal boats to transfer between the canal and the river to serve industries in Shepherdstown with shipments of cement, coal, flour, and grain. Shepherdstown is the only town in West Virginia that has a canal lock named for it.
Two free schools were built in the town in 1848. One still stands on the southeast corner of Princess and New Streets. When West Virginia became the 35th state (in 1863), these became the oldest free schoolhouses in the state.
The Hamtramck Guard (The Shepherdstown Light Infantry) was dispatched to nearby Harpers Ferry to subdue John Brown’s raid on the federal armory (October 1859). At the outbreak of the Civil War, this group became Company B, 2nd Virginia Infantry, Army of Northern Virginia. They became part of the famous “Stonewall Brigade.”
After the nearby Battle of Antietam in Maryland, September 17, 1862, General Robert E. Lee’s infantry crossed the Potomac at Pack Horse Ford. The town was overwhelmed with 5,000–8,000 casualties from the battle. Every house, building, church, alley, and street was filled with the wounded and dying. The Battle of Shepherdstown (also known as the Battle of Boteler’s Ford or Cement Mill) occurred on September 20, 1862, during Lee’s retreat. More than 100 Confederate soldiers died here and were buried in Elmwood Cemetery. Elmwood contains the graves of 285 Confederate veterans.
From 1865 to 1871, Shepherdstown served as the county seat of Jefferson County due to war damage to the courthouse in Charles Town. The Town Hall (northeast corner of German and King streets) housed the courthouse until it was moved back to Charles Town.
In 1872, the Town Hall Building was chartered as a “Classical and Scientific Institute.” The building was then leased to the state and Shepherd College was born. In 2004, the Shepherd College became Shepherd University. The East Campus occupies about one-third of the town proper, and the West Campus occupies a large area just northwest of the corporate limits.
20th century to present
The Shepherdstown Historic District was established and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1973, with a boundary expansion to include the entire town in 1987. Potomac Mills located nearby in Washington County, Maryland, was added in 2014.
On January 3, 2000, Shepherdstown was the site of the Peace Talks between Israel and Syria.
In 2012, the town celebrated its 250th anniversary. Billed as the most haunted town in America, Shepherdstown is known as much for its ghostly residents as it is for the local arts scene, university, and historic attractions. On June 12, 2016, Destination America’s premiered the paranormal show Ghosts of Shepherdstown, starring Nick Groff, Elizabeth Saint, and Bill Hartley.
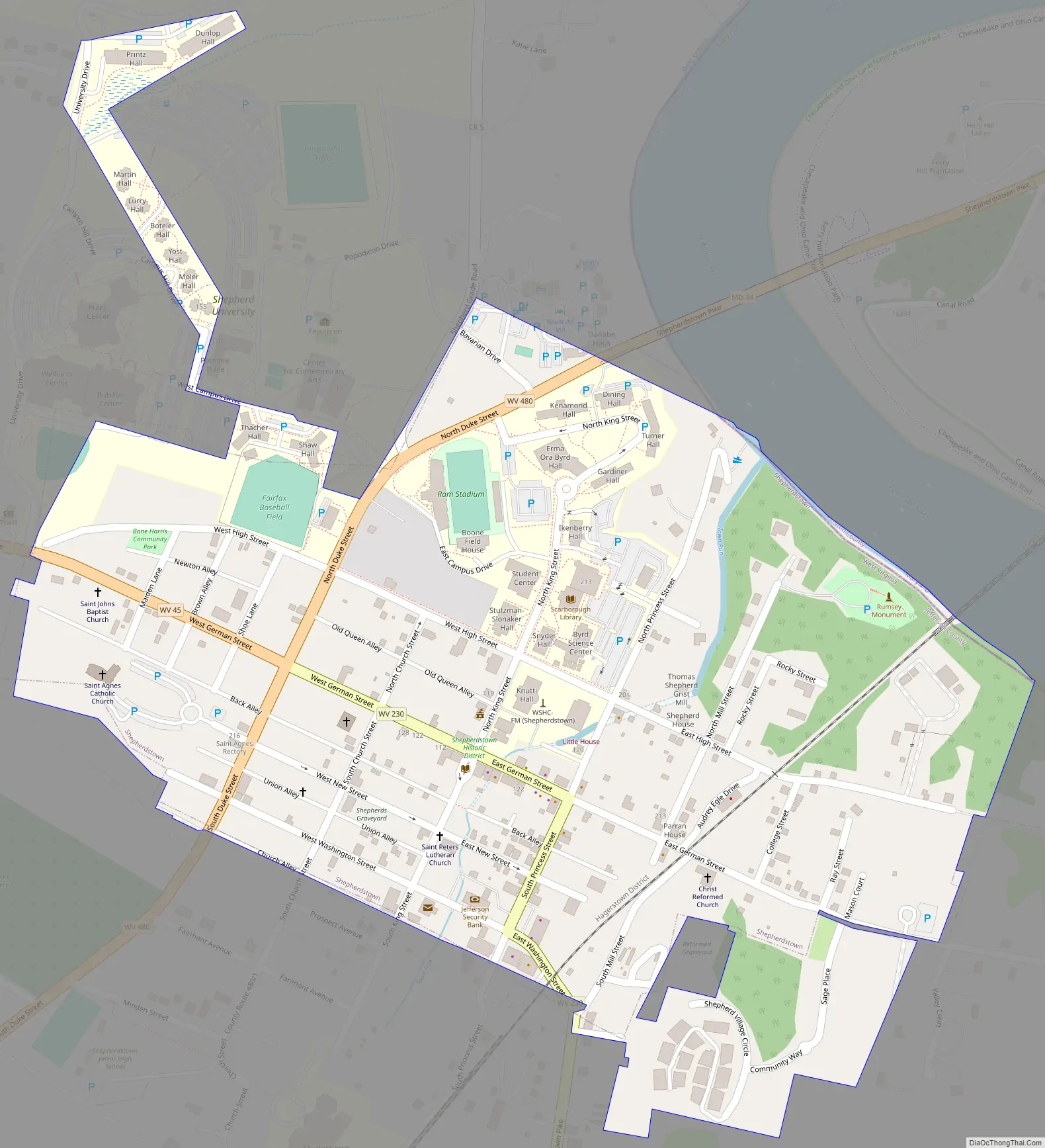
Shepherdstown Road Map
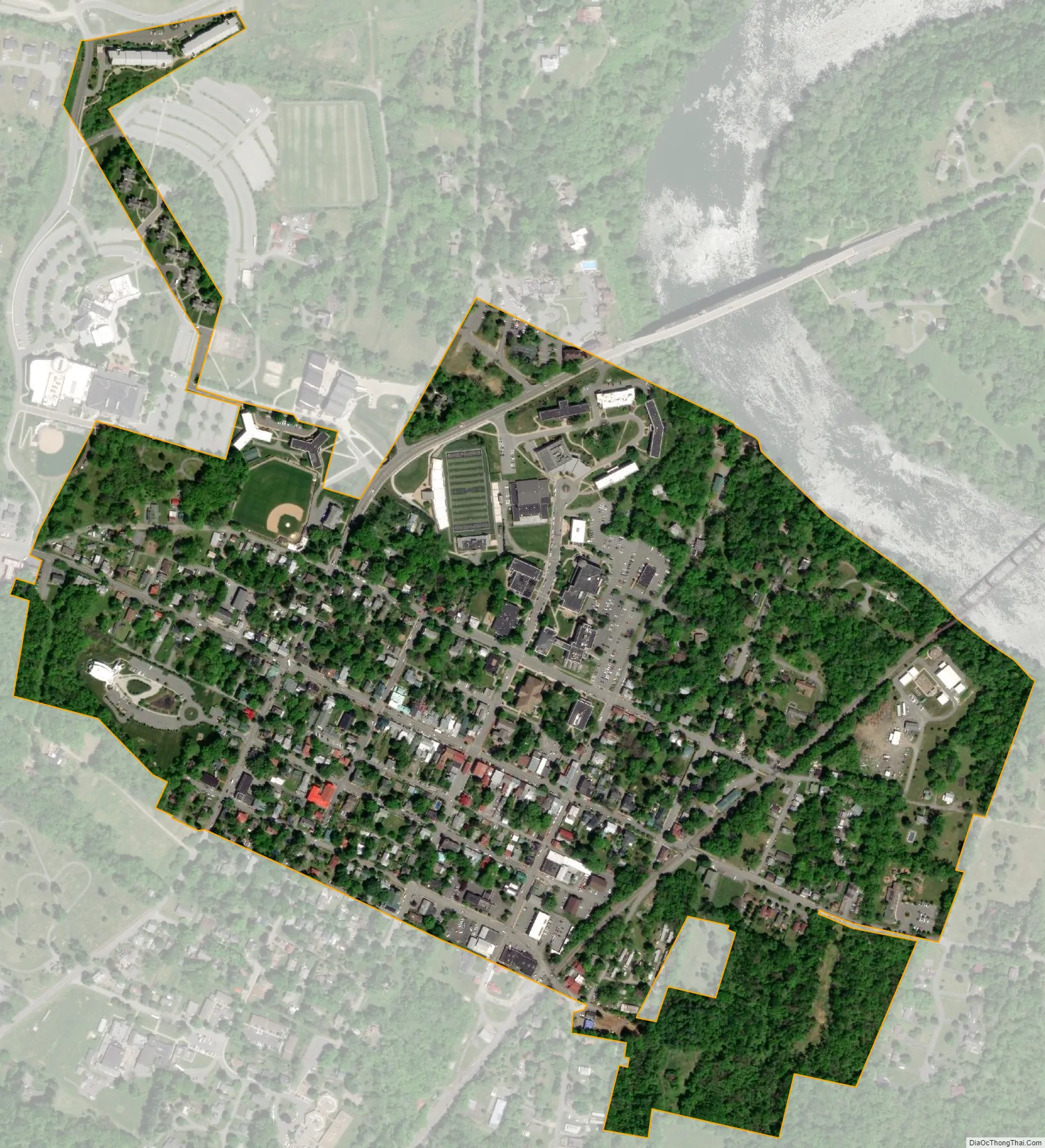
Shepherdstown city Satellite Map
Geography
Shepherdstown is located at 39°25′55″N 77°48′22″W / 39.43194°N 77.80611°W / 39.43194; -77.80611 (39.432005, −77.806108), in the upper Shenandoah Valley along the Potomac River in the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 0.37 square miles (0.96 km), all land.
Bedrock exposures of Cambrian-aged Conococheague limestone and dolomite are frequent in the town, and form cliffs between the settled area and the Potomac River.
See also
Map of West Virginia State and its subdivision:- Barbour
- Berkeley
- Boone
- Braxton
- Brooke
- Cabell
- Calhoun
- Clay
- Doddridge
- Fayette
- Gilmer
- Grant
- Greenbrier
- Hampshire
- Hancock
- Hardy
- Harrison
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Kanawha
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Marion
- Marshall
- Mason
- McDowell
- Mercer
- Mineral
- Mingo
- Monongalia
- Monroe
- Morgan
- Nicholas
- Ohio
- Pendleton
- Pleasants
- Pocahontas
- Preston
- Putnam
- Raleigh
- Randolph
- Ritchie
- Roane
- Summers
- Taylor
- Tucker
- Tyler
- Upshur
- Wayne
- Webster
- Wetzel
- Wirt
- Wood
- Wyoming
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming