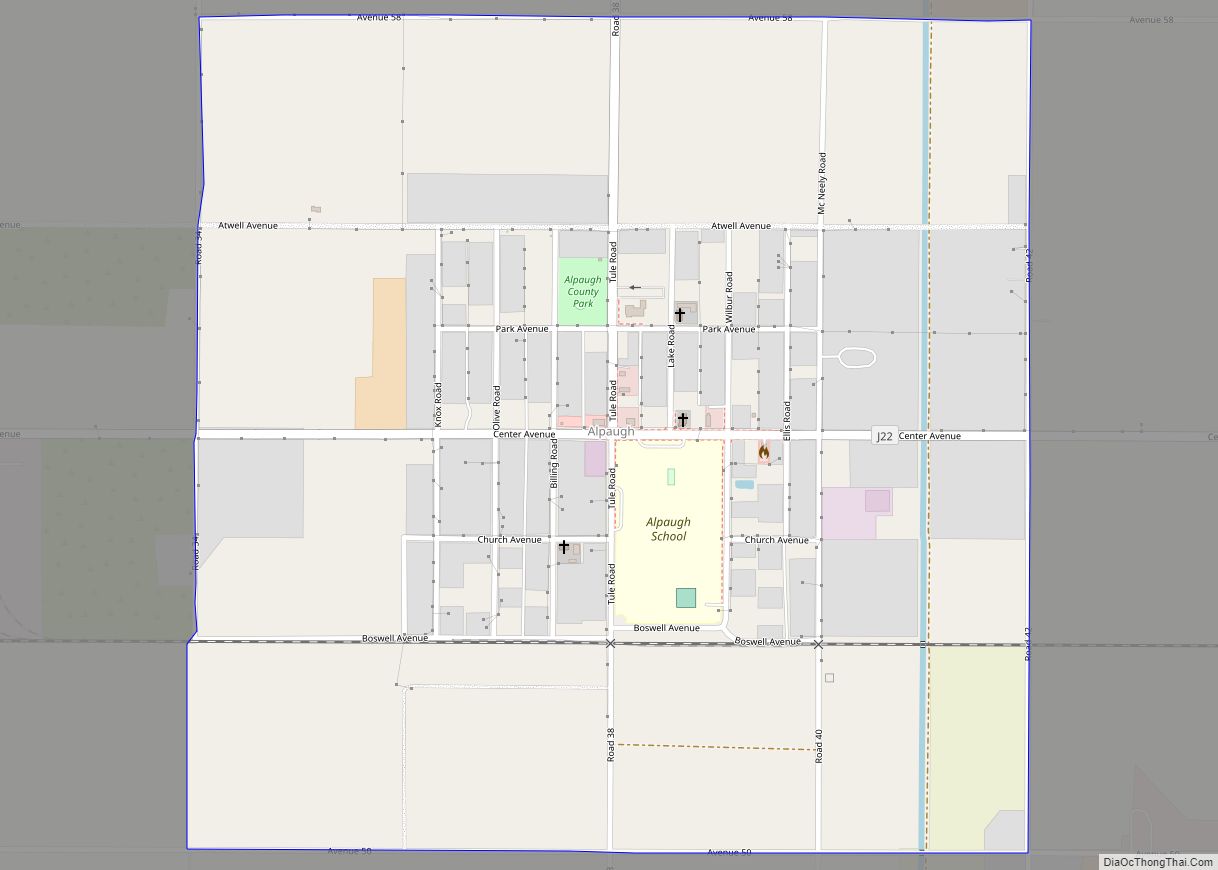
Alpaugh is a census-designated place (CDP) in Tulare County, California, United States. The population was 1,026 at the 2010 census, up from 761 at the 2000 census.
It is named for John Alpaugh, one of the officers of the Home Extension Colony which reclaimed (or land speculated on) the land the town is built on.
| Name: | Alpaugh CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Tulare County |
| Elevation: | 213 ft (65 m) |
| Total Area: | 0.42 sq mi (1.08 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.42 sq mi (1.08 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) 0% |
| Total Population: | 871 |
| Population Density: | 2,083.73/sq mi (804.37/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 93201 |
| Area code: | 559 |
| FIPS code: | 0601164 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1660246 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Alpaugh location map. Where is Alpaugh CDP?
History
Alpaugh’s location (once also called Hog Island, Root Island, and Atwell’s Island) was once either on an island or a narrow peninsula near the south end of the huge and rich Tulare Lake. A.J. Atwell was a Visalia attorney (and newspaper owner) who raised hogs on the island. The lake at different times supported a very large Native American population, a commercial fishery, herds of tule elk, countless game birds, and much more. The island was a regular port of call for the lake’s commercial ferry service. The last time the lake was brim full and overflowed into the San Joaquin River to the sea was 1878. Water diversions of its source waters have since caused the lake to shrink into the tiny remnant of today. Local efforts have been undertaken to increase the lake’s size for water storage and wildlife.
Los Angeles real estate developers, the California Home Extension Association, promoted, developed or founded Alpaugh, nearby Wasco, and several other California towns. It has also been referred to as “W.H. Wilber’s Second Home Extension Coloney [that] purchased eight-thousand acres of land surrounding [Alpaugh].” Los Angeles newspaper articles of the time explained that they were not the original landowners. “The California Home Extension association does not represent land owners; it has no lands of its own for sale.’.”
On 17 December 1905, an article headlined “BUY IN TOWN OF ALPAUGH, CAL” ran in the Los Angeles Herald with the subheadline: “PURCHASE OF 11,000 ACRES BY COLONISTS.” It says in part:
On 21 January 1906 — Page 19, an article headlined “ALL ABOARD FOR ALPAUGH” ran in the Los Angeles Herald with the subheadline: “Day Fixed for Distribution of Town Lots to Enthusiastic Colonists”, it says:
However, just one week before, that newspaper printed this, headline
NEW INDUSTRY AT ALPAUGH
In 1920 and 1921 both oil and large gas fields were found near Alpaugh.
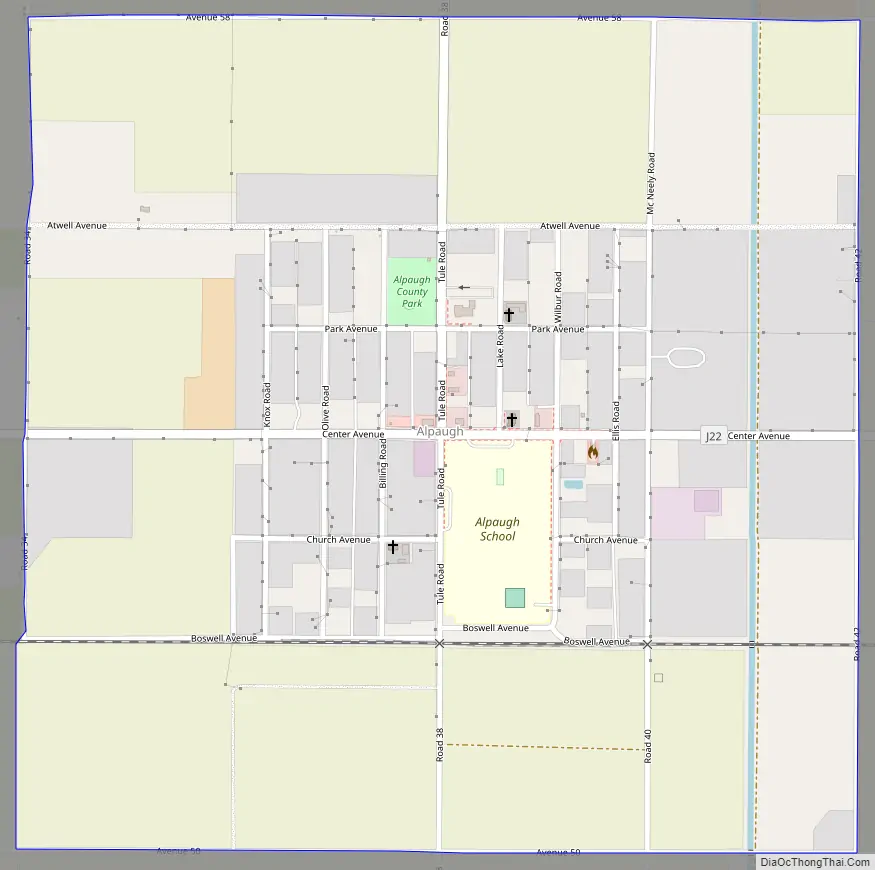
Alpaugh Road Map
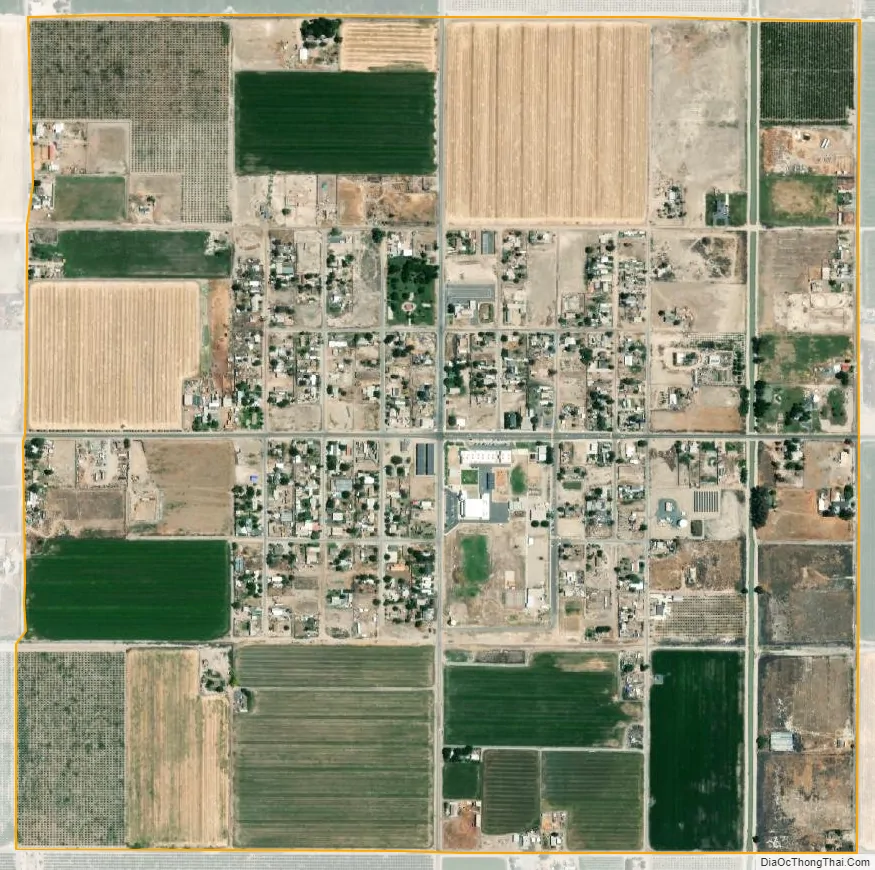
Alpaugh city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of 1.0 square mile (2.6 km), all of it land.
The site is located on the historic shoreline of Tulare Lake, once the largest freshwater lake in the USA outside of the Great lakes. Other towns built on its historic shores include Lemoore and Kettleman City.
Despite being on the edge of the ancient Tulare lakebed, the town is without access to safe drinking water, as high levels of Arsenic are found in the municipal water supply. Locals are forced to drink, cook and bathe using bottled water or expose themselves to this hazard. {https://environmentalintegrity.org/wp-content/uploads/CA-Arsenic-Report.pdf}
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming