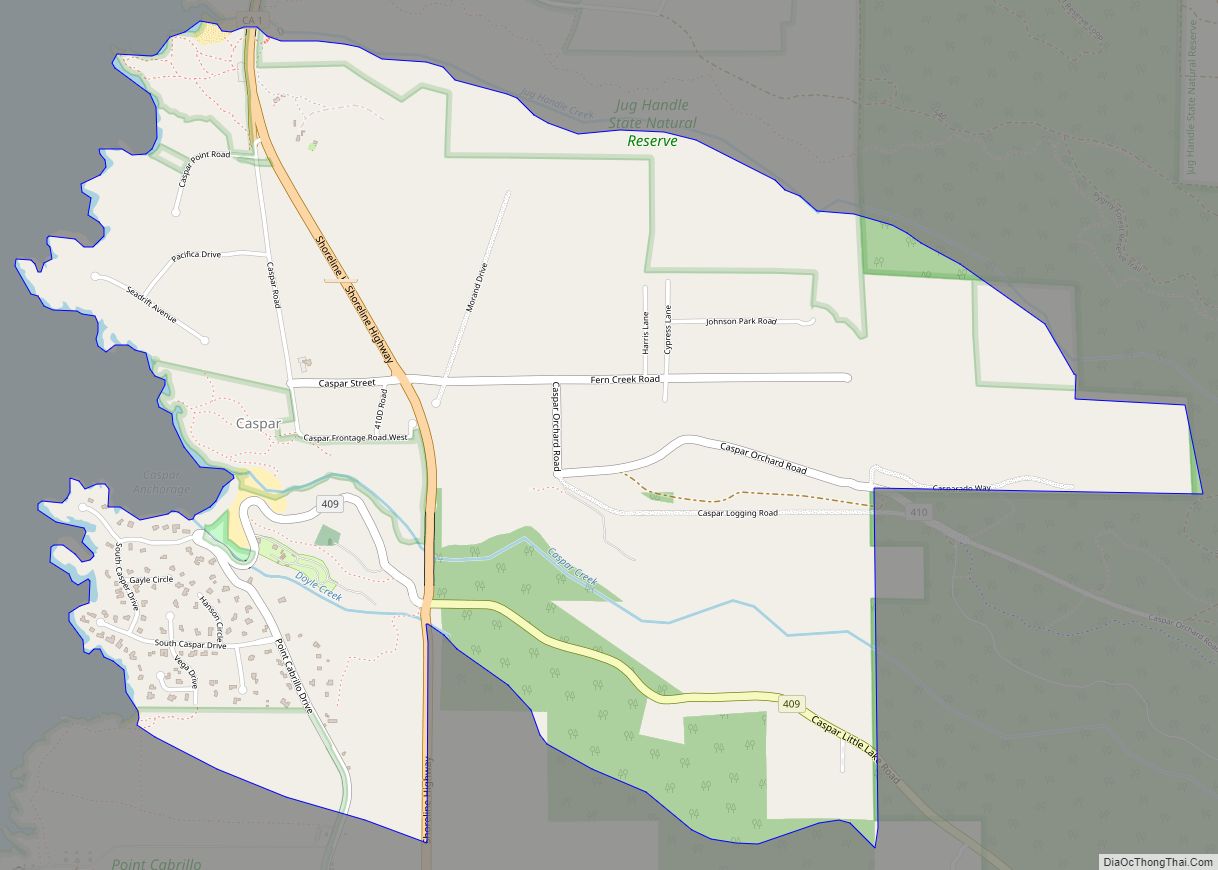
Caspar is a unincorporated community in Mendocino County, California, United States. It is located on the Pacific Ocean, 4 miles (6 km) north of Mendocino, at an elevation of 82 feet (25 m). It is bounded on three sides by state parks: the historic 1909 Point Cabrillo Light Station is nearby to the south, Jug Handle State Natural Reserve lies to the north, and its coast forms Caspar Headlands State Beach. The population was 500 at the 2020 census. For statistical purposes, the United States Census Bureau has defined Caspar as a census-designated place (CDP).
| Name: | Caspar CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Mendocino County |
| Elevation: | 82 ft (25 m) |
| Total Area: | 2.99 sq mi (7.7 km²) |
| Land Area: | 2.99 sq mi (7.7 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.0 km²) 0% |
| Total Population: | 500 |
| Population Density: | 167.11/sq mi (64.52/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 95420 |
| Area code: | 707 |
| FIPS code: | 0611768 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
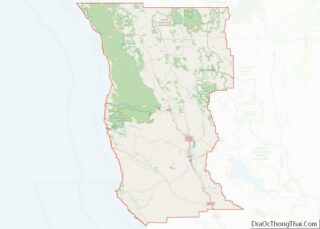
Caspar location map. Where is Caspar CDP?
History
Caspar was settled in 1857 by Siegfried Caspar, who later sold the land to Jacob Green Jackson, one of the founders of the Caspar Lumber Company, which turned Caspar into a significant logging town in Northern California from 1864 to 1955. Pilings from the mill can be seen on Caspar Beach south of the community. The mill was featured on the cover of a 1938 National Geographic magazine.
Multiple heirs to the Caspar Lumber Company sold their holdings to Georgia-Pacific and a pair of private investors in 1989. Ownership of the central parcels, consisting of more than 300 acres (120 ha) and comprising much of “downtown Caspar”, was taken over by the Caspar Cattle Company in 1997. The company’s principal immediately offered the land for sale. This offer was facilitated by a professor and team of graduate student community planners from the University of California, Berkeley. The process early on committed to consensus and inclusive self-governance, and identified several sacred spaces, principal among them the headlands, once the site of the Caspar Lumber Company’s mill, and managed the acquisition of the 30-acre (12 ha) headlands parcel in partnership with the Trust for Public Land and the Mendocino Land Trust, which acquired the adjoining beach in 1999. Funded by a California State Coastal Conservancy grant in May 2000, as well as state and federal funds, the headlands were transferred to California State Parks and designated as Caspar Headlands State Reserve in June 2002.
The Caspar Schoolhouse, built in the late 1800s during Caspar’s heyday, and expanded during the boom years after 1906, served as a Headstart school and a mail-order company office, then remained empty until it was sold by the Cattle Company to Caspar Community, Inc., the nonprofit entity that organized the community’s campaign to preserve its sacred spaces. CCI continues to attempt to acquire the remainder of the property in accordance with the vision of the community since its formation. As of July 2013, the majority of the land is still for sale.
Point Cabrillo Light Station
Church
Mill ruins at Caspar beach
The Caspar post office opened in 1874 and closed on November 15, 1986, when postmaster Georgia Johnson retired.
As of 2013, Caspar has a community center, church and a thriving nightclub. The Caspar Inn existed continuously as a roadhouse from its founding during the heyday of the logging era in 1906 until its closure in February 2013.
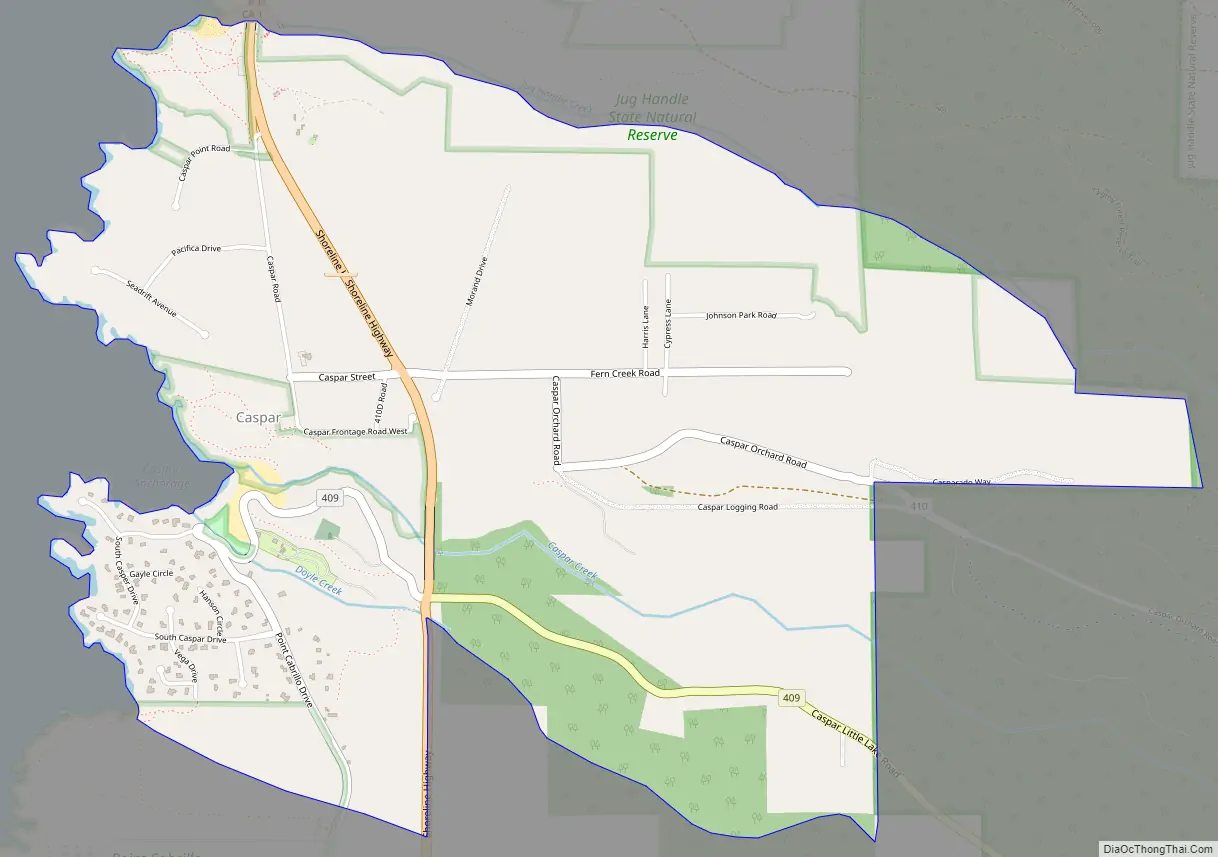
Caspar Road Map
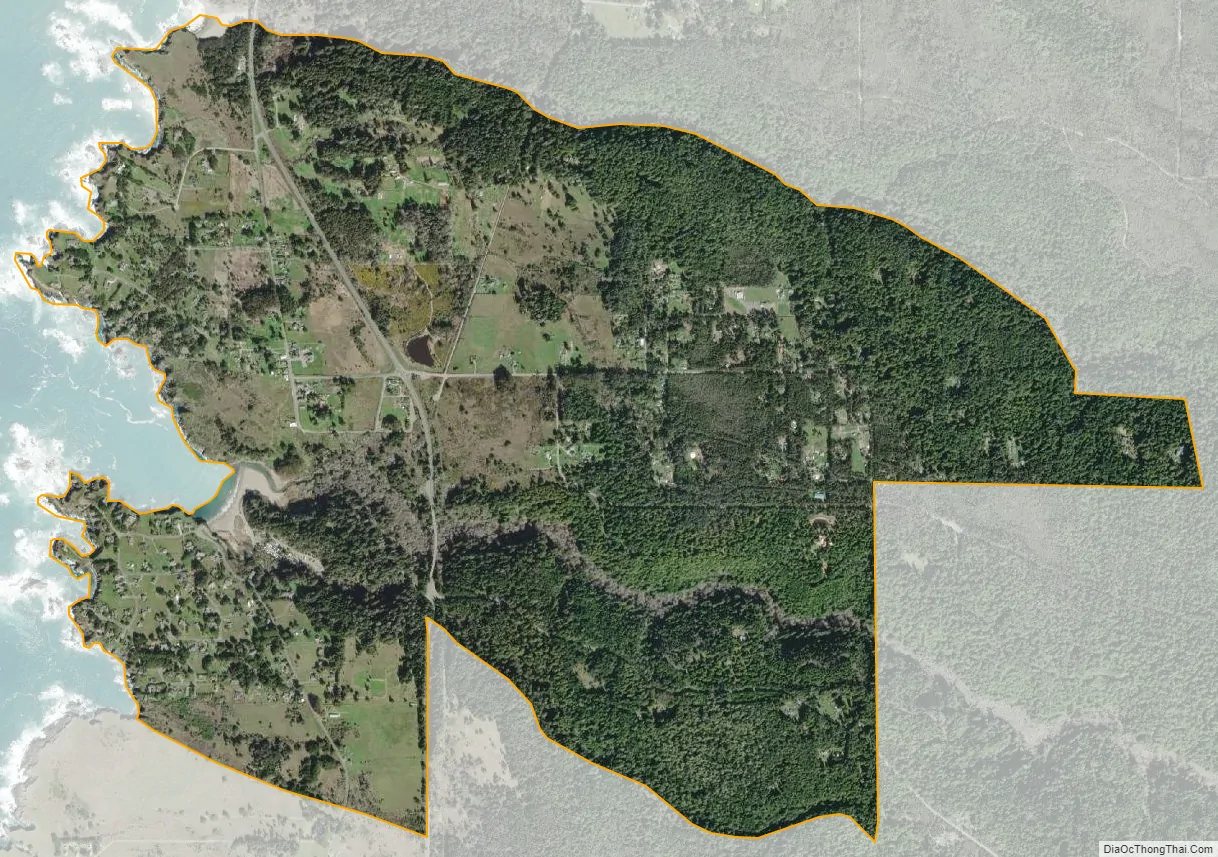
Caspar city Satellite Map
Geography
Caspar is along the western edge of Mendocino County and is traversed by California State Route 1, which leads north 6 miles (10 km) to Fort Bragg and south 4 miles (6 km) to Mendocino. Caspar Creek crosses the southern part of the community, entering the Pacific Ocean at Caspar Anchorage, a small cove which is bordered by Caspar State Beach.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP covers an area of 3.0 square miles (7.8 km), all of it land. The census bureau definition of the area as a CDP may not precisely correspond to local understanding of the area with the same name.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming