Escondido is a city in San Diego County, California, United States. Located in the North County region, it was incorporated in 1888, and is one of the oldest cities in San Diego County. It has a population of 151,038 as of the 2020 census.
| Name: | Escondido city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | San Diego County |
| Incorporated: | October 8, 1888 (1888-10-08) |
| Elevation: | 646 ft (197 m) |
| Total Area: | 37.45 sq mi (97.00 km²) |
| Land Area: | 37.34 sq mi (96.72 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.11 sq mi (0.28 km²) 0.48% |
| Total Population: | 151,038 |
| Population Density: | 4,060.12/sq mi (1,567.61/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 92025–92027, 92029 |
| FIPS code: | 0622804 |
| Website: | www.escondido.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Escondido location map. Where is Escondido city?
History
The Escondido area was first settled by the Luiseño, who established campsites and villages along the creek running through the area. They named the place Mixéelum Pompáwvo or “Mehel-om-pom-pavo.” The Luiseno also had another village north of Mixéelum Pompáwvo called Panakare. The Kumeyaay migrated from areas near the Colorado River, settling both in the San Pasqual Valley and near the San Dieguito River in the southwestern and western portions of what is now Escondido. Most of the villages and campsites today have been destroyed by development and agriculture.
Spanish and Mexican eras
Spain controlled the land from the late 18th century to the early 19th century, and established many missions in California to convert the indigenous people. When Mexico gained its independence from Spain, the local land was divided into large ranchos. Most of what is now Escondido occupies the former Rancho Rincon del Diablo (“Devil’s Corner”), a Mexican land grant given to Juan Bautista Alvarado (not the governor of the same name) in 1843 by Governor Manuel Micheltorena. Alvarado was a Regidor of Los Angeles at the time, and the first Regidor of the pueblo of San Diego. The southern part of Escondido occupies the former Rancho San Bernardo, granted in 1842 and 1845.
In 1846, during the Mexican–American War, the Battle of San Pasqual was fought southeast of Escondido. This battle pitted Mexican forces under Andrés Pico (brother of then-California-governor Pío Pico) against Americans under Stephen W. Kearny, Archibald Gillespie, and Kit Carson. A park in Escondido is named for Carson.
American era
The city was home to a largely Spanish-speaking population in the first census, taken in 1850 when California became a state. After statehood, non-Hispanic settlers came to Southern California in increasing numbers. The decade of the 1880s is known as the “Southern California Land Boom” because so many people moved to the state.
In 1853, pro-Southern Copperheads proposed dividing the state of California to create a new Territory of Colorado (at this time the territory that would become the state of Colorado was named “Jefferson”). San Diego Judge Oliver S. Witherby suggested placing the capitol of the new territory in Rancho Rincon del Diablo. He envisioned a railroad connecting San Diego to Fort Yuma through an area about two miles (3 km) south of the current Escondido site, heading east through San Pasqual. With a series of deeds in 1855 and 1856, the rancho was transferred from the heirs of Juan Bautista Alvarado to Witherby. He planned to profit from the town that he believed would be established from the dividing point on the railroad below the eastern hills. The proposal for splitting the state and creating the new territory passed in the California legislature, but died in Congress in the run-up to the Civil War. It was effectively killed in 1861 when Congress organized the Territory of Colorado in the area previously occupied by the Jefferson Territory. With Witherby’s vision of owning a bustling state capitol unrealized, he set up a mining operation on the rancho instead.
In 1868, Witherby sold the rancho for $8000 to Edward McGeary and John, Josiah, and Matthew Wolfskill. McGeary owned half the rancho, while the three Wolfskill brothers each owned an equal share of the other half. John Wolfskill farmed sheep, horses, and cattle on the rancho for a number of years. Wolfskill had frequent conflicts with the Couts family, owners of the neighboring Guajome, Buena Vista, and San Marcos ranchos, over grazing lands and watering holes.
In October 1883, a group of Los Angeles investors purchased Rancho Rincon del Diablo. This group sold the land to the newly formed Escondido Company in 1884. On December 18, 1885, investors incorporated the Escondido Land and Town Company, and in 1886 this company purchased the 12,814-acre (52 km) area for approximately $100,000. Two years later, in 1888, Escondido was incorporated as a city; the vote was 64 in favor of cityhood with 12 votes against. Railroads such as the Santa Fe and Southern Pacific were laid in the 1880s. The opening of U.S. Route 395 in 1930 boosted economic growth in Escondido.
Escondido was primarily an agricultural community, growing muscat grapes initially. After a dam was built in 1894-1895 to form what is known today as Lake Wohlford, orange and lemon trees were planted in large numbers, as were olive and walnut trees. By the 1960s, avocados became the largest local crop. Since the 1970s, Escondido has lost most of its agricultural land to housing developments, but still retains a significant agricultural presence in the San Pascual Valley including vineyards, citrus orchards, and avocado orchards.
Escondido Road Map
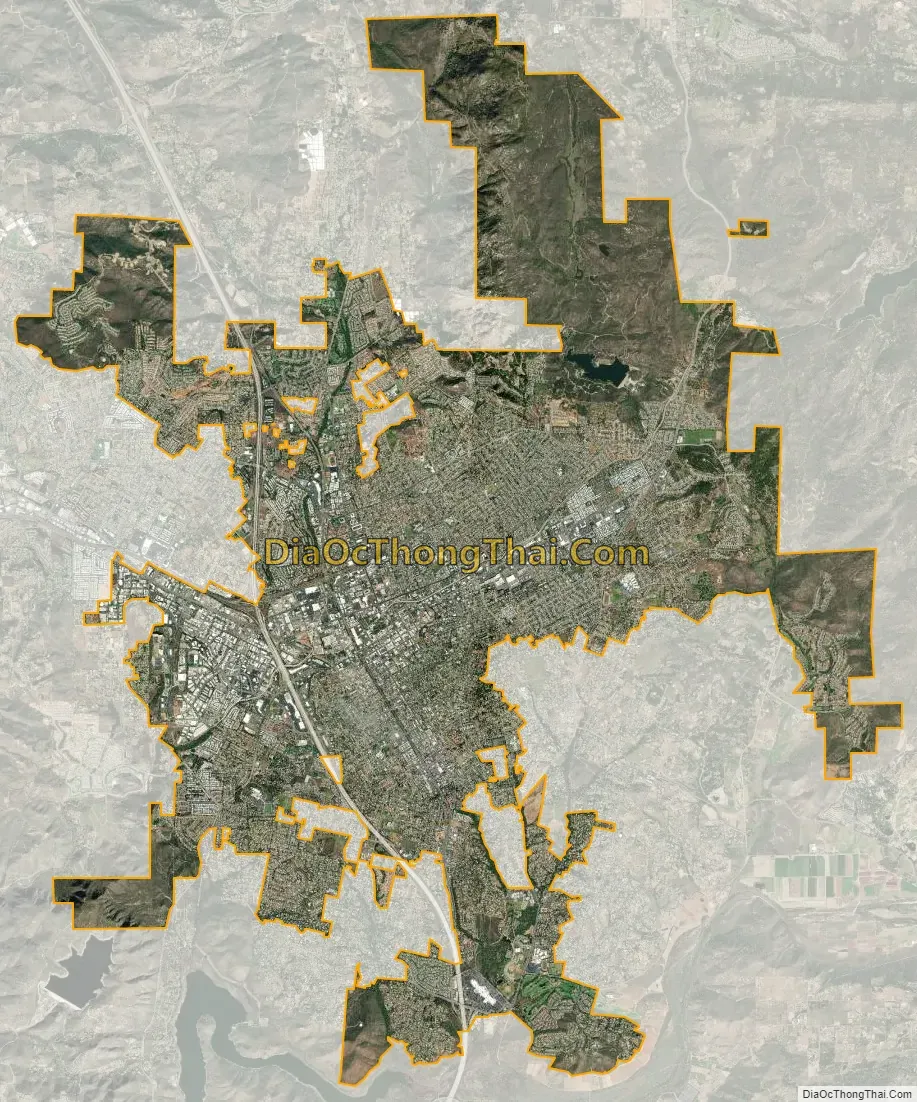
Escondido city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 37.0 square miles (96 km). 36.8 square miles (95 km) of it is land and 0.2 square miles (0.52 km) of it is water. The total area is 0.48% water.
The city is growing at a rapid rate. The city proper is surrounded by several sparsely populated unincorporated communities. These include Jesmond Dene and Hidden Meadows to the north; Felicita Park to the southwest; and Rincon Del Diablo to the southeast. Residents of these communities have Escondido mailing addresses and ZIP codes, and their children are sometimes assigned to Escondido schools, but residents of these communities cannot participate in city elections.
The city contains several neighborhoods, including:
- Downtown Escondido centers on Grand Avenue between Centre City Parkway and the site of the old Palomar Hospital. The city’s general plan defines the Downtown Specific Plan Area as approximately 460 acres (1.9 km) bounded by Centre City Parkway on the west, Hickory and Ivy Streets on the east, Washington Avenue on the north, and Fifth Avenue on the south, with an additional narrow section extending west along Valley Parkway to Interstate 15. Downtown Escondido includes a mix of coffee shops, restaurants, assorted retail, art galleries, bakeries, a comedy club, and the newly renovated historic Ritz Theater.Sunset aerial view of Downtown Escondido, California
- Old Escondido Historic District is bounded by Escondido Boulevard on the west, Chestnut Street on the east, Fifth Avenue on the north, and Thirteenth Avenue on the south. This area is made up of mostly single-family residential housing built in the late 1800s and early 1900s in the Victorian and Craftsman styles and is a 5 to 10 minute walk to Grand Avenue in Downtown Escondido.Neighborhood view in Old Escondido Historic District in Escondido, California
The Escondido Creek bisects the city. It originates at the Lake Wohlford Dam [ceb] in the northeast, passes through downtown and leaves the city through the Harmony Grove area in the southwest before eventually emptying into the San Elijo Lagoon. The creek path through the city was developed into a concrete flood control channel in the 1960s. A Class I bicycle path runs along most of the channel’s length.
The community of Valley Center is located just north of Escondido. Valley View Casino, owned by the San Pasqual Band of Diegueno Mission Indians, is located in Valley Center.
Natural vegetation types in the Escondido area include chaparral brushland, oak woodland, riparian (stream) woodland, and grassland. The Daley Ranch Preserve north of the city provides a good location to view these natural vegetation types.
Climate
Escondido has a borderline semi-arid climate (Köppen: Bsh) and hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen: Csa) with hot summers and cool wet winters. Owing to its inland setting it is considerably warmer than coastal cities like San Diego, Carlsbad or Oceanside during the summertime, and cooler in the winter. Yearly precipitation averages around 15 inches (380 mm) and can vary considerably from year to year. Rainfall totals are higher in the hills to the north and east, with 20-24 inches falling in most areas above 2,000 feet elevation, and over 30 inches on Palomar Mountain, 15 miles east. More than 80% of all precipitation takes place from November through March. Snow is virtually unheard of, though occasionally winter and springtime thunderstorms will drop small hail. The climate is mild enough to allow widespread cultivation of avocados and oranges. Escondido is located in a plant hardiness zone 10a. The hottest temperature recorded in Escondido was 115 °F on September 6, 2020. The coldest temperature recorded in Escondido was 13 °F on January 2, 1901, and January 7, 1913.
Dixon Lake
Dixon Lake is located in the north of Escondido. It is a popular place for picnics, camping, and fishing. Dixon Lake has been granted an Aquaculture Permit by the State of California Department of Fish and Wildlife, so that fishing licenses are no longer required. However, all anglers eight years and older will need daily lake fishing permits, which are available at the concession stand. Throughout the year, the city keeps stocking different types of fish, which include bass, bluegill, carp, catfish, crappie, and trout. Each year the Trout Derby event is also hosted at Dixon Lake.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming