Lake Riverside is a census-designated place in the south western part of Riverside County, California. Lake Riverside sits at an elevation of 3,379 feet (1,030 m). The 2010 United States census reported Lake Riverside’s population was 1,173. The community is named after the man-made Lake that the community surrounds.
| Name: | Lake Riverside CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Riverside County |
| Elevation: | 3,397 ft (1,035 m) |
| Total Area: | 7.277 sq mi (18.845 km²) |
| Land Area: | 7.193 sq mi (18.629 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.084 sq mi (0.217 km²) 1.15% |
| Total Population: | 1,173 |
| Population Density: | 160/sq mi (62/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 92536 |
| Area code: | 951 |
| FIPS code: | 0639715 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 2583052 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Lake Riverside location map. Where is Lake Riverside CDP?
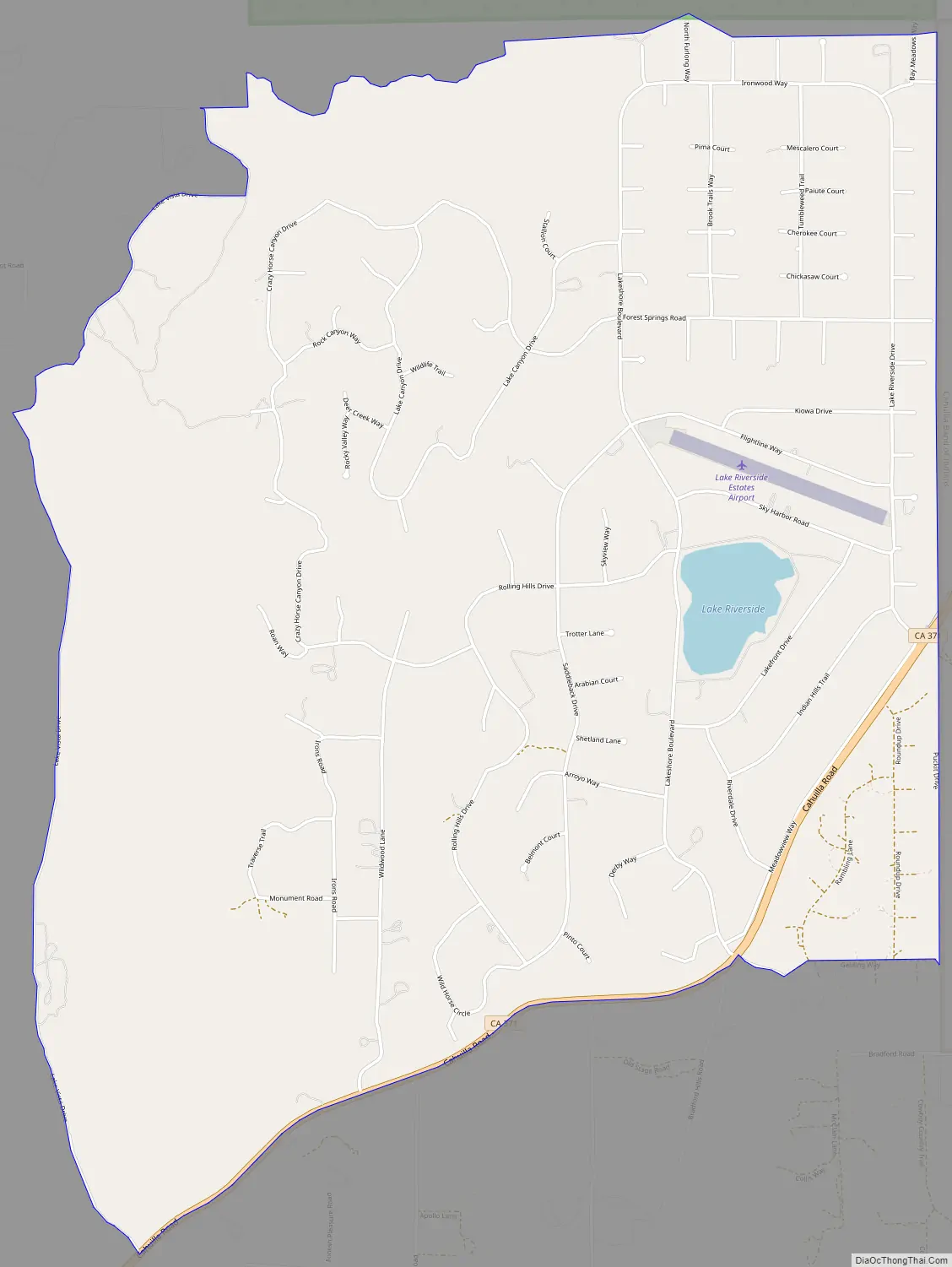
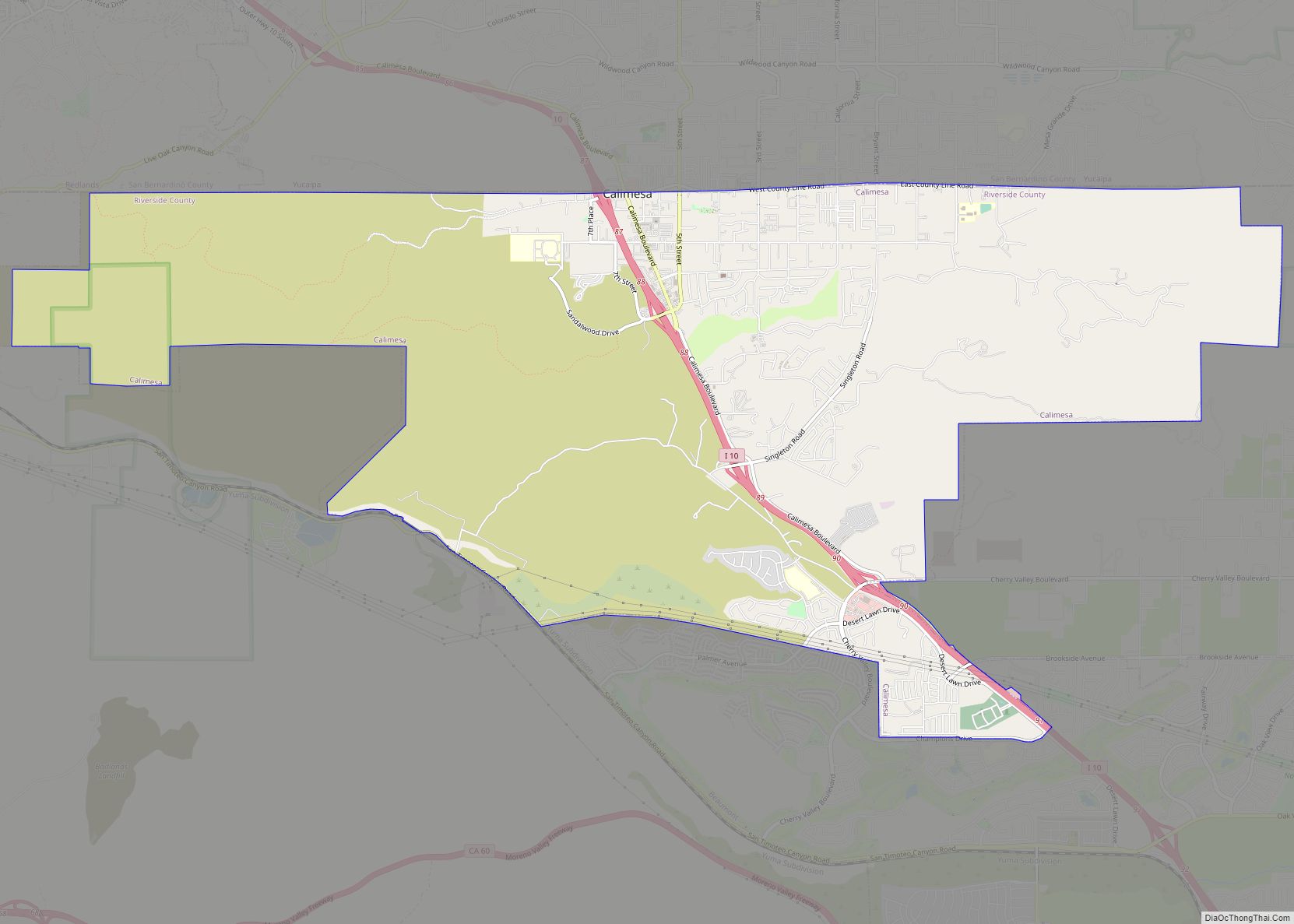
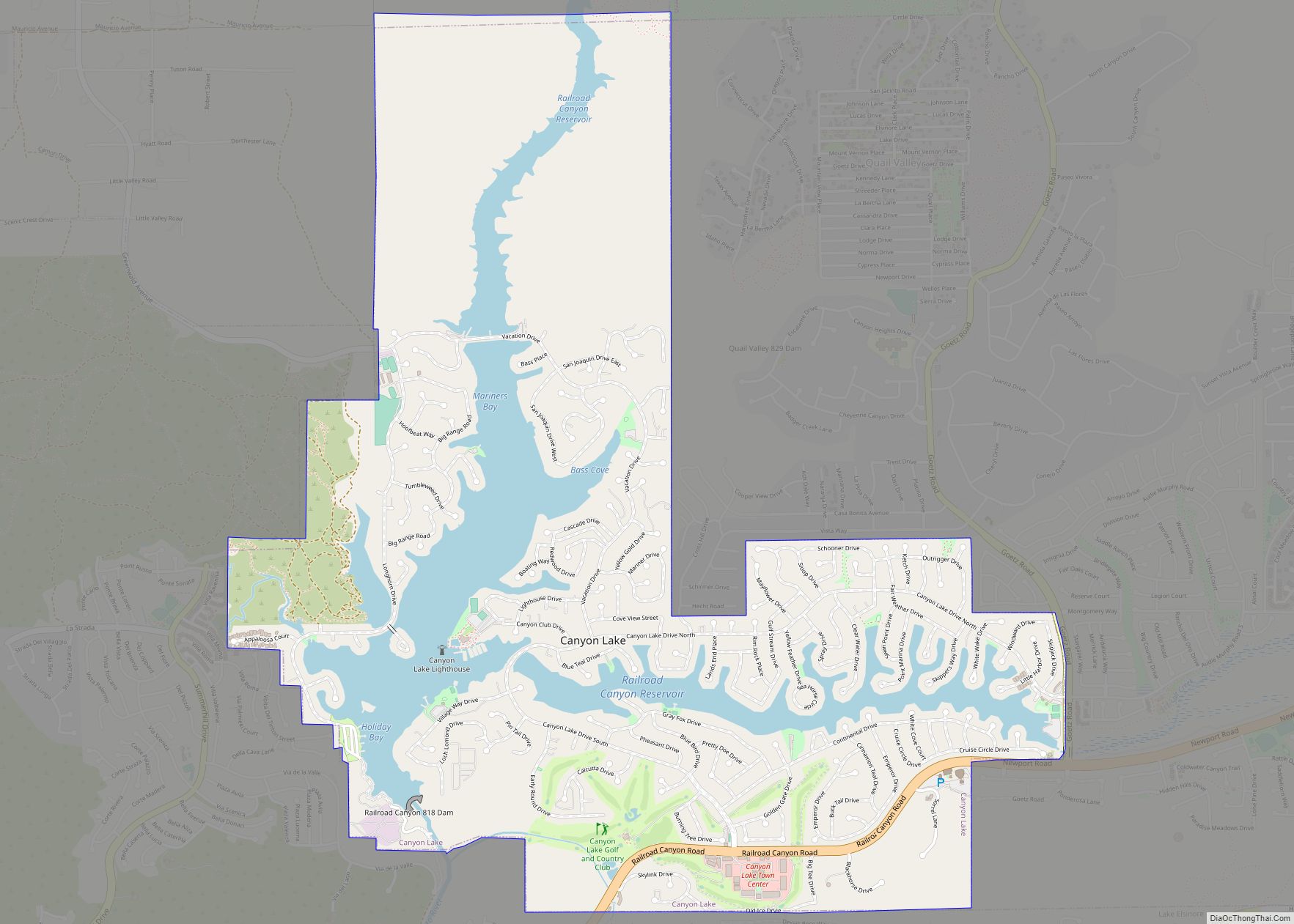
Lake Riverside Road Map
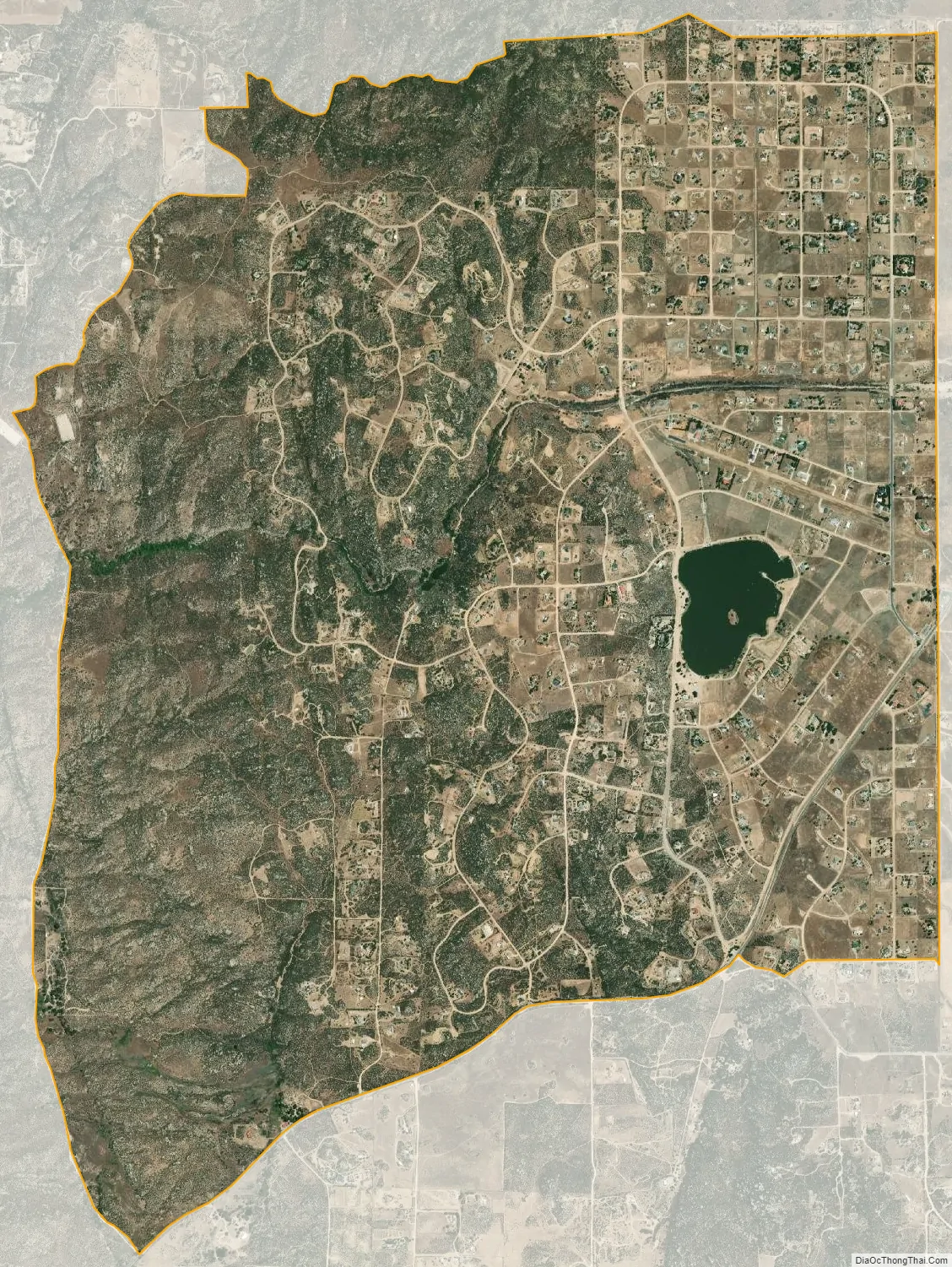
Lake Riverside city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the census-designated place (CDP) covers an area of 7.3 square miles (18.8 km), 98.85% of it land, and 1.15% of it water.
The water part of the CDP, Lake Riverside, was artificially made when a private farming-ranching company owning the land needed a water reservoir for its operation. With the approval of the Army Corps of Engineers, a well was dug in 1962 to pipe water from underground springs to create the Lake in the low lying areas of the Cahuilla Creek watershed and to sustain it. The Lake was enlarged to 55 acres (0.22 km) in 1970, after the property was purchased by a private developer to turn it into a rural residential subdivision. The original well from 1962 lasted to 1994, and a new well was dug in 1995 to sustain the Lake.
From early 2016 to late 2019, a swarm of small earthquakes occurred — ranging in magnitude from 0.7 to 4.4 — the strongest one occurred in August 2018, south of Lake Riverside, just off Cahuilla Road (SR 371). The remaining more than 22,000 individual seismic events occurred near the western edge of the Cahuilla Reservation stretching 4 km (2.5 mi) northward to just east of the Lake and never generated any significant damage in four years. The cause of this Cahuilla seismic swarm was traced to a deep natural underground reservoir of fluid, about 8 km (5.0 mi) below the surface, injecting fluid into the base of the fault zone, triggering the swarm of seismic events as it diffused slowly up into the fault zone over the four years.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming