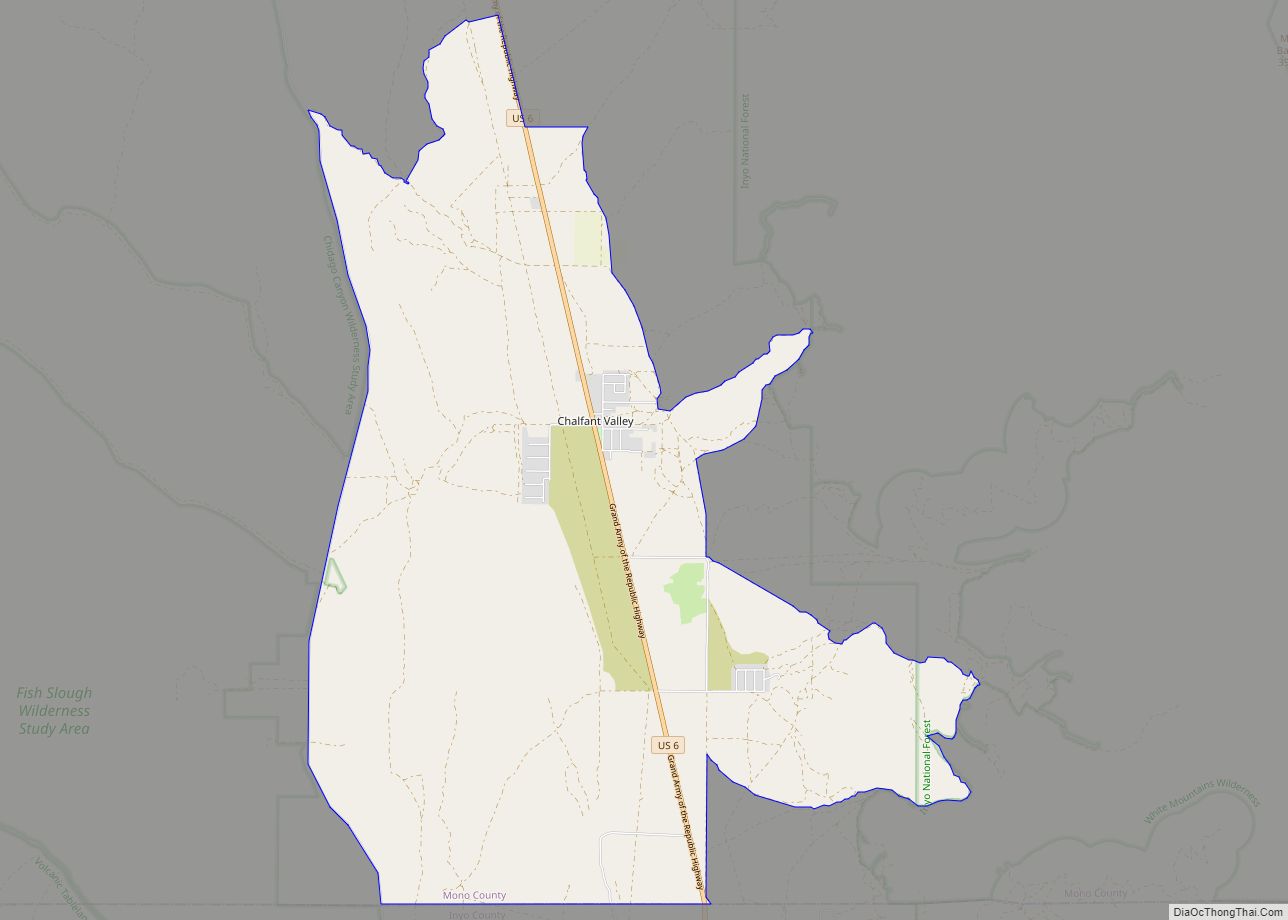
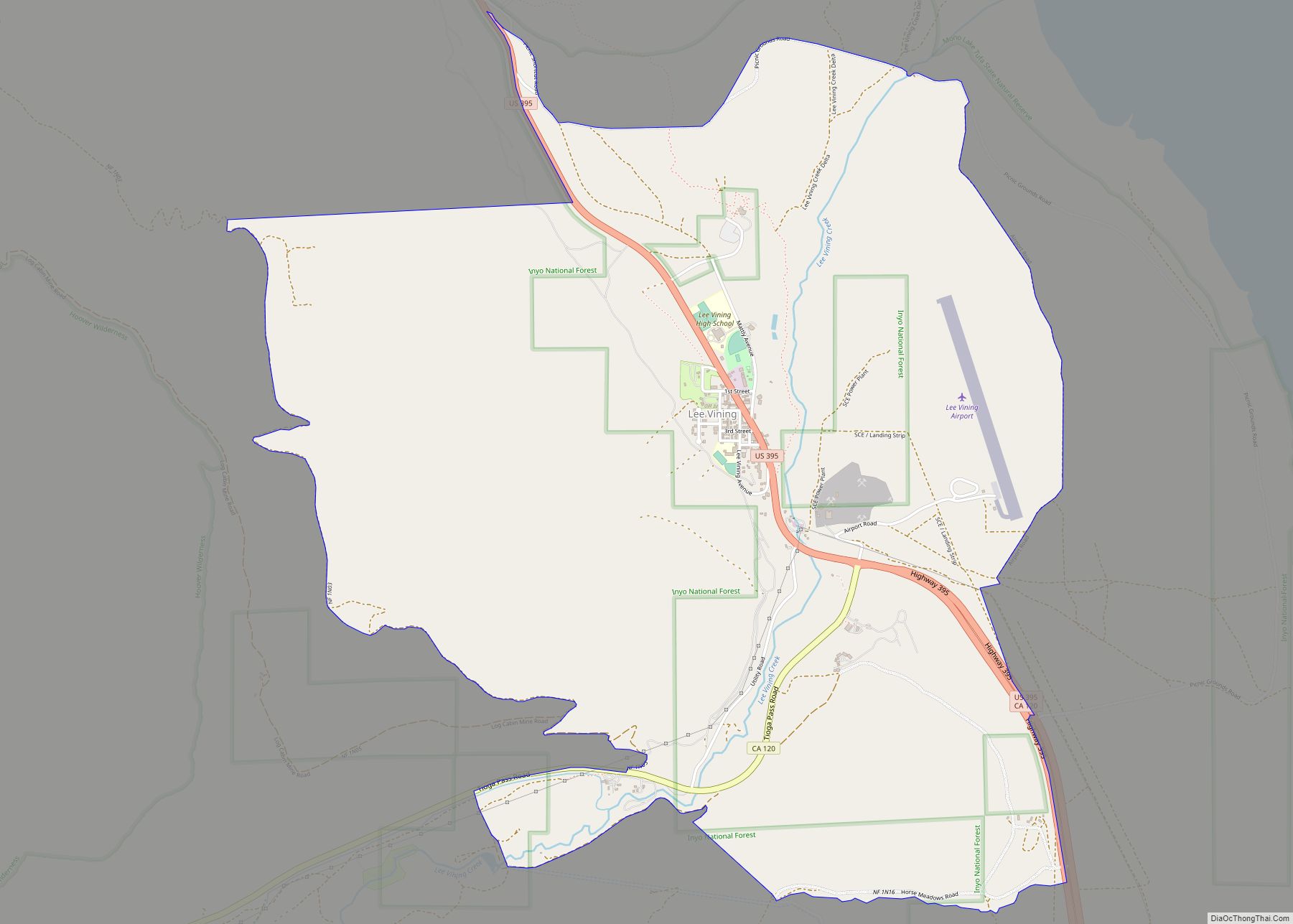
Lee Vining (formerly Leevining, Poverty Flat, and Lakeview) is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Mono County, California, United States. It is located 25 miles (40 km) south-southeast of Bridgeport, at an elevation of 6,781 feet (2,067 m). Lee Vining is located on the southwest shore of Mono Lake. The population was 217 as of the 2020 census.
| Name: | Lee Vining CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Mono County |
| Elevation: | 6,781 ft (2,067 m) |
| Total Area: | 5.208 sq mi (13.490 km²) |
| Land Area: | 5.206 sq mi (13.484 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.002 sq mi (0.006 km²) 0.05% |
| Total Population: | 217 |
| Population Density: | 42/sq mi (16.1/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 93541 |
| FIPS code: | 0640998 |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Lee Vining location map. Where is Lee Vining CDP?
History
The town was named after Leroy Vining, who founded the town in 1852 as a mining camp. In 1926, the town was laid out by Chris Mattly and named “Lakeview”, but when a post office was sought in 1928, it was learned that another town, Lakeview, California, already had the name. The name of Lee Vining was chosen in 1953. The place was also called “Poverty Flat” for its unfavorable conditions for agriculture.
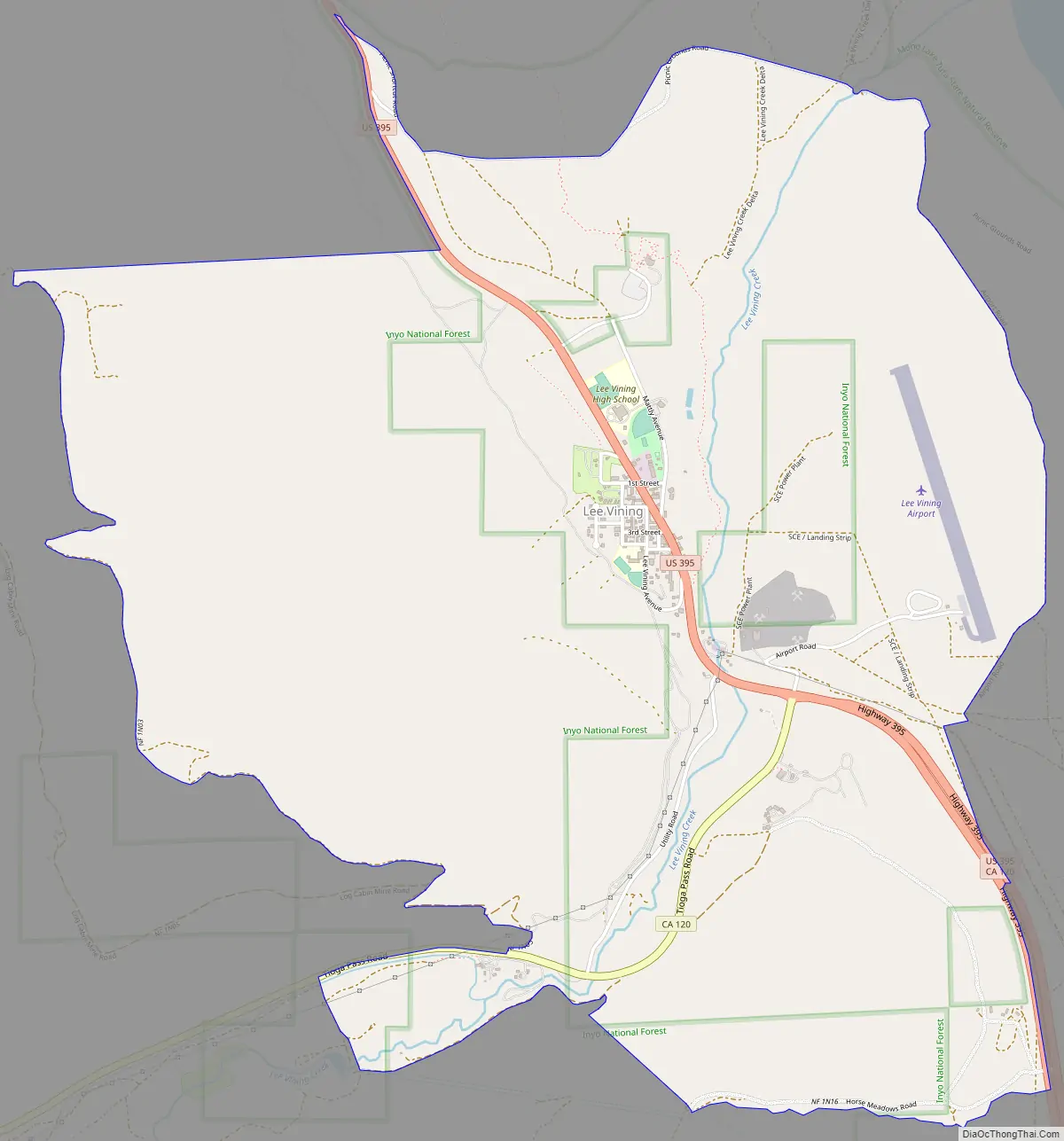
Lee Vining Road Map
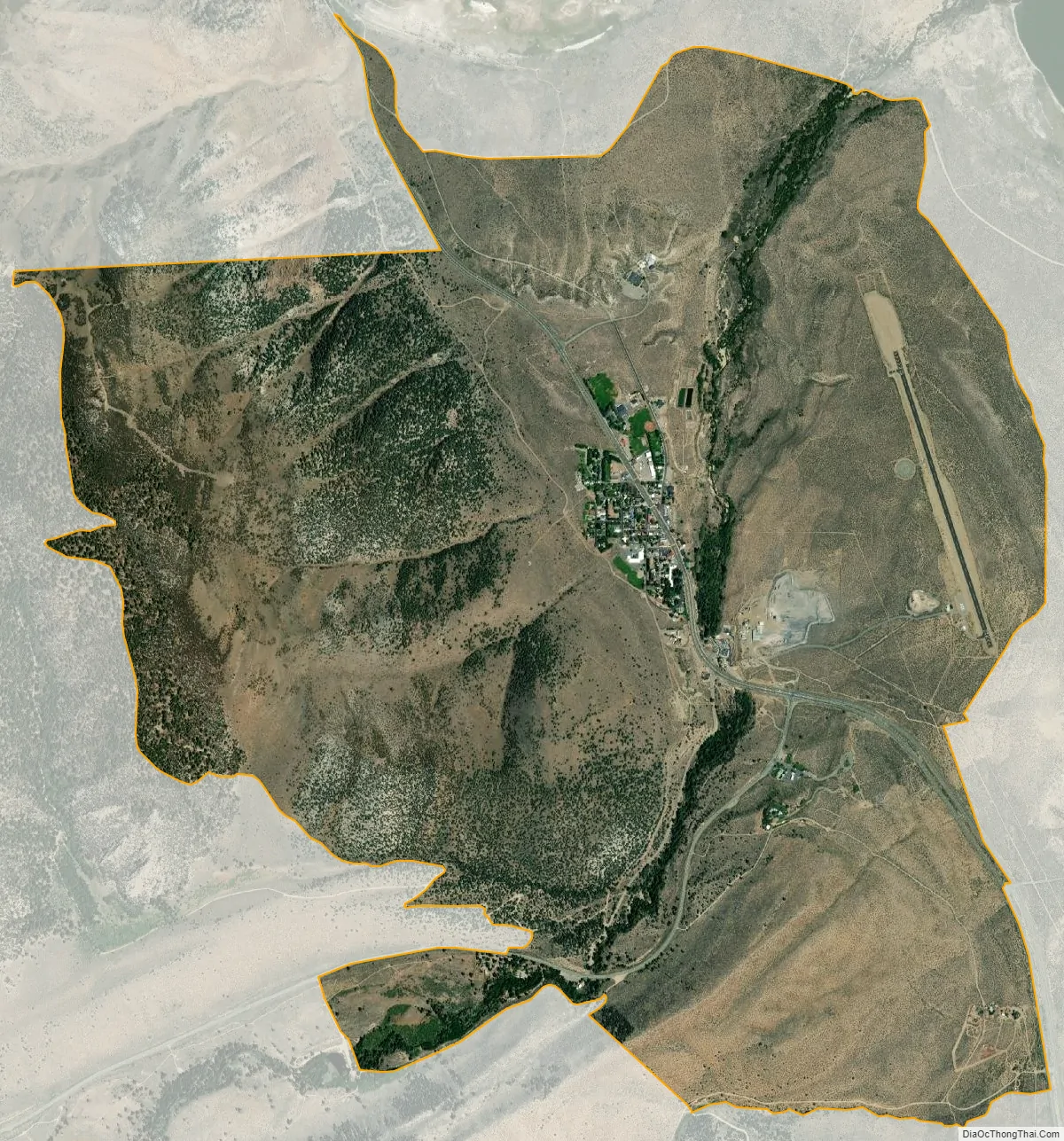
Lee Vining city Satellite Map
Geography
Lee Vining is in western Mono County along U.S. Route 395, at the eastern base of the Sierra Nevada. US 395 leads northwest 25 miles (40 km) to Bridgeport, the Mono county seat, and southeast the same distance to the junction for Mammoth Lakes. California State Route 120 climbs west from Lee Vining 12 miles (19 km) to the top of Tioga Pass, the east entrance to Yosemite National Park. According to the United States Census Bureau, the Lee Vining CDP covers an area of 5.2 square miles (13 km), 99.95% of it land and 0.05% of it water.
Climate
Lee Vining, on the boundary between the Sierra Nevada and Great Basin ecoregions, has a transitional climate: warmer and drier than the mountains to the west but cooler and much snowier than the vast desert to the east. Despite only getting 14 inches (360 mm) of water-equivalent precipitation annually, the town averages nearly 6 feet (1.8 m) of snow, sometimes falling as late as April or even May. Precipitation is highest in the winter months of December through March, but some can be expected to fall every month of the year, and the town does not typically experience the four to six month dry spells of more coastal parts of California.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming