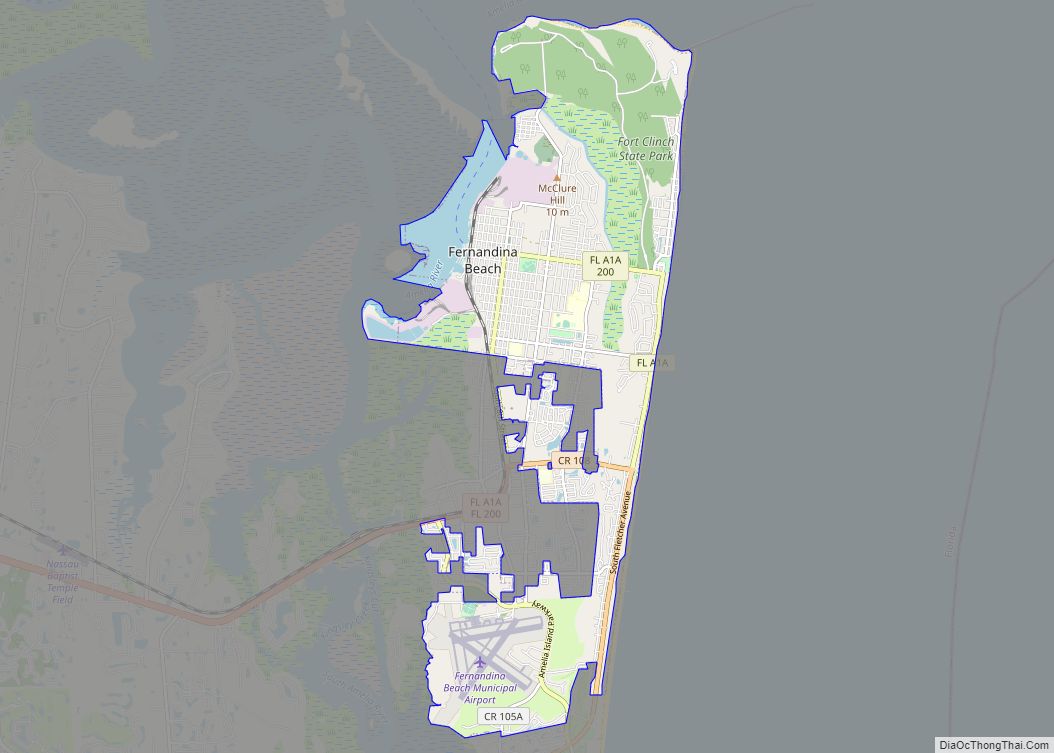
Fernandina Beach is a city in northeastern Florida and the county seat of Nassau County, Florida, United States. It is the northernmost city on Florida’s Atlantic coast, situated on Amelia Island, and is one of the principal municipalities comprising Greater Jacksonville. The area was first inhabited by the Timucuan Indian people. Known as the “Isle of 8 Flags”, Amelia Island has had the flags of the following nations flown over it: France, Spain, Great Britain, Spain (again), the Republic of East Florida (1812), the Republic of the Floridas (1817), Mexico, the Confederate States of America, and the United States.
The French, English, and Spanish all maintained a presence on Amelia Island at various times during the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries, but the Spanish established Fernandina. The town of Fernandina, which was about a mile from the present city, was named in honor of King Ferdinand VII of Spain by the governor of the Spanish province of East Florida, Enrique White. Fernandina has the distinction of being the last Spanish city platted in the Western Hemisphere, in 1811.
According to the 2010 census, the city population was 11,487. It is the seat of Nassau County. It is also the largest incorporated city in the county since Yulee is an unincorporated town.
| Name: | Fernandina Beach city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Florida |
| County: | Nassau County |
| Elevation: | 25 ft (7.6 m) |
| Total Area: | 12.62 sq mi (32.68 km²) |
| Land Area: | 11.83 sq mi (30.64 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.79 sq mi (2.04 km²) |
| Population Density: | 1,103.11/sq mi (425.92/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 32034-32035 |
| Area code: | 904 |
| FIPS code: | 1222175 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0294308 |
| Website: | www.fbfl.us. |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
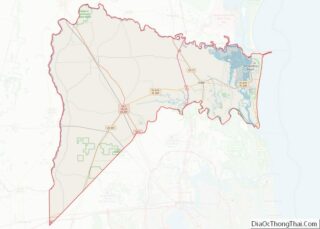
Fernandina Beach location map. Where is Fernandina Beach city?
History
Prior to the arrival of Europeans on what is now Amelia Island, Native Americans occupied the site of the original town of Fernandina. Native American bands associated with the Timucuan mound-building culture had settled on the island about 1000 CE, calling it Napoyca. They remained on the island until the early 18th century, when European settlement began.
Old Town Fernandina
On January 1, 1811, Enrique White, governor of Spain’s East Florida province, named the town of Fernandina, about a mile from the present city, in honor of King Ferdinand VII. On May 10 of that year, Fernandina became the last town platted under the Laws of the Indies in the Western hemisphere. The town was intended as a bulwark against U.S. territorial expansion. In the following years, it was captured and recaptured by a succession of renegades and privateers.
At the beginning of the Patriot War, with the approval of President James Madison and Georgia Governor George Mathews on March 13, 1812, insurgents known as the “Patriots of Amelia Island” seized the island. After raising a Patriot flag, they replaced it with the United States flag. American gunboats under the command of Commodore Hugh Campbell maintained control of the island. On May 15, 1812, the British brig. Sappho fired on Gunboat no. 168, which had fired on the loyalist merchant vessel Fernando to prevent her leaving. Outgunned, the American gunboat withdrew, which enabled several vessels to escape from the port. President Madison eventually denounced the filibustering of George Mathews, however, on the grounds that Mathews had violated his instructions.
Spanish pressure forced the American evacuation from the island in 1813. Spanish forces erected Fort San Carlos on the island in 1816. However, A Scottish soldier and adventurer named Gregor MacGregor with 55 musketeers seized Fort San Carlos in 1817, claiming the island on behalf of “the brethren of Mexico, Buenos Ayres, New Grenada and Venezuela”, and raised the Green Cross of Florida flag over the Spanish Fort San Carlos. MacGregor claimed to be Brigadier General of the armies of the United Provinces of New Grenada and Venezuela (where he had successfully fought and led troops), and General-in-Chief of the armies for the two Floridas, commissioned by the Supreme Director of Mexico.
Spanish soldiers forced MacGregor’s withdrawal, but their attempt to regain complete control was foiled by American irregulars organized by Ruggles Hubbard and former Pennsylvania congressman Jared Irwin. Hubbard and Irwin later joined forces with the French-born pirate Louis Aury, who laid claim to the island on behalf of the Republic of Mexico. U.S. Navy forces drove Aury from the island, and President James Monroe vowed to hold Amelia Island “in trust for Spain.”
Modern Fernandina
In 1847 construction of Fort Clinch began in nearby present-day Fernandina. The Third System fort was named after General Duncan Lamont Clinch who fought in the War of 1812 and the Seminole Wars. Senator David Levy Yulee, founder of the Florida Railroad, wanted the eastern terminus of his railroad line to end in Amelia Island. The Old Town Fernandina was too cut off by the marshes to be used as a terminal. Yulee wanted to end the railroad on the banks of the Amelia River one mile to the south. The leaders of Fernandina did not want a new community to grow and prosper to surpass their town. The leaders of Fernandina decided to move the town up to the railroad where the present-day Fernandina Beach stands. Yulee began construction of the railroad in 1855 and was completed in 1861.
On January 8, 1861, two days before Florida’s secession, Confederate sympathizers (the Third Regiment of Florida Volunteers) took control of Fort Clinch, already abandoned by the Federal workers who had been enlarging the structure. The Confederates erected batteries on the northern end of Amelia Island but lacked the resources to fortify Fort Clinch. Robert E. Lee, who was commanding coastal defenses in the Deep South, ordered cannons and troops withdrawn in early 1862.
Lee’s orders to withdraw the cannons and troops were too late. Union forces, consisting of 28 gunboats commanded by Commodore Samuel Dupont, occupied the island on March 3, 1862, and raised the American flag. In January 1863, the first all-black regiment of former slaves recruited to fight for the Union was read Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation at Fernandina. Three weeks later they set sail up the St. Marys River to engage the Confederate forces. The Union used the fort as a base for its operations in the area for the remainder of the war.
In 1891, Harmon Murray, who had been the leader of a criminal gang operating out of Gainesville, arrived in Fernandina, where his sister lived. Murray was soon committing burglaries and robberies in Fernandina and elsewhere on Amelia Island. Law officers chased a black suspect several times, who shot at them on one occasion. Murray taunted the police with a letter in early May, to the effect that he would not be taken alive, and would take the Nassau County sheriff and Fernandina police chief with him. Acting on a tip, on May 16 police surrounded the house Murray was staying in. Murray heard the officers getting into position, and shot and killed deputy sheriff Joseph W. Robinson. In the ensuing gun battle Murray wounded Fernandina Police Chief James Higgenbotham. Although grazed on the wrist and scalp, Murray was able to escape. Despite the intensive manhunt for him, Murray was able to slip off of Amelia Island to the mainland. The City of Fernandina offered a reward for the capture of Murray, “dead or alive”.
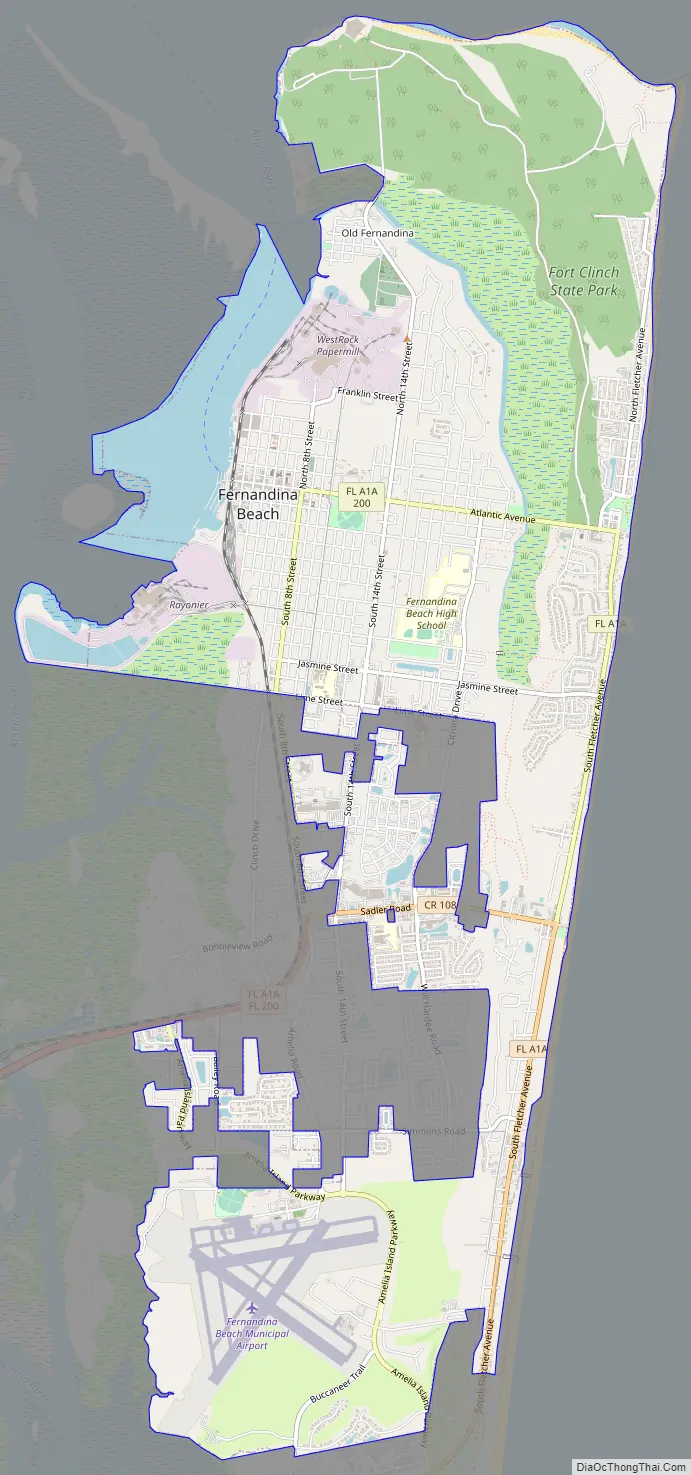
Fernandina Beach Road Map
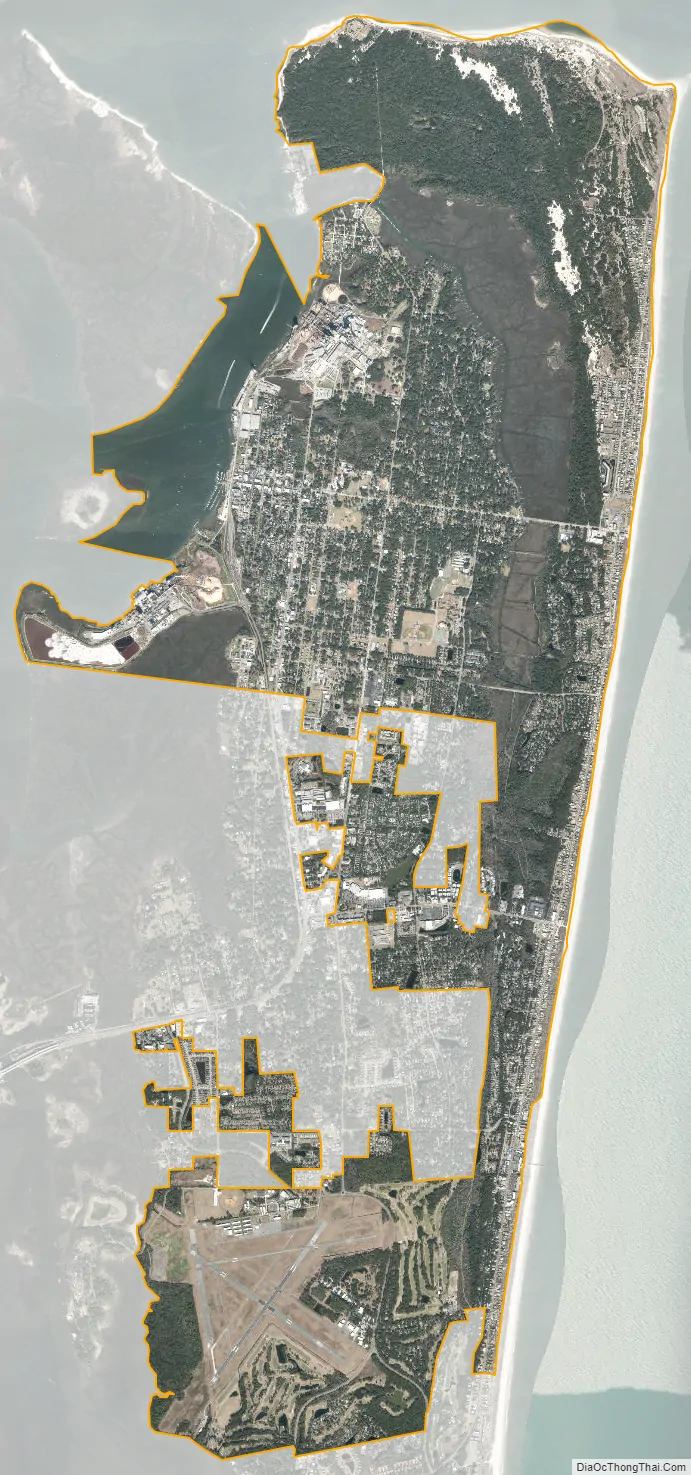
Fernandina Beach city Satellite Map
Geography
Fernandina Beach is located at 30°24′04″N 81°16′27″W / 30.4010°N 81.2742°W / 30.4010; -81.2742, approximately 25 miles (40 km) northeast of downtown Jacksonville.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 15.7 square miles (41 km), all land. It is the northernmost city on the eastern coast of Florida.
Climate
Fernandina Beach has a humid subtropical climate (Cfa) with long, hot, and rainy summers and short, mild winters.
See also
Map of Florida State and its subdivision:- Alachua
- Baker
- Bay
- Bradford
- Brevard
- Broward
- Calhoun
- Charlotte
- Citrus
- Clay
- Collier
- Columbia
- Desoto
- Dixie
- Duval
- Escambia
- Flagler
- Franklin
- Gadsden
- Gilchrist
- Glades
- Gulf
- Hamilton
- Hardee
- Hendry
- Hernando
- Highlands
- Hillsborough
- Holmes
- Indian River
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Lafayette
- Lake
- Lee
- Leon
- Levy
- Liberty
- Madison
- Manatee
- Marion
- Martin
- Miami-Dade
- Monroe
- Nassau
- Okaloosa
- Okeechobee
- Orange
- Osceola
- Palm Beach
- Pasco
- Pinellas
- Polk
- Putnam
- Saint Johns
- Saint Lucie
- Santa Rosa
- Sarasota
- Seminole
- Sumter
- Suwannee
- Taylor
- Union
- Volusia
- Wakulla
- Walton
- Washington
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming