Tallahassee (/ˌtæləˈhæsi/ TAL-ə-HASS-ee) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Florida. It is the county seat and only incorporated municipality in Leon County. Tallahassee became the capital of Florida, then the Florida Territory, in 1824. In 2020, the population was 196,169, making it the eighth-largest city in the state of Florida. The population of the Tallahassee metropolitan area was 385,145 as of 2018. Tallahassee is the largest city in the Florida Big Bend and Florida Panhandle region, and the main center for trade and agriculture in the Florida Big Bend and Southwest Georgia regions.
With a student population exceeding 70,000, Tallahassee is a college town, home to Florida State University, ranked the nation’s 19th-best public university by U.S. News & World Report; Florida A&M University, ranked the nation’s best public historically black university by U.S. News & World Report; and Tallahassee Community College, a large state college that serves mainly as a feeder school to Florida State and Florida A&M.
As the capital, Tallahassee is the site of the Florida State Capitol, Supreme Court of Florida, Florida Governor’s Mansion, and nearly 30 state agency headquarters. The city is also known for its large number of law firms, lobbying organizations, trade associations and professional associations, including the Florida Bar and the Florida Chamber of Commerce. It is a recognized regional center for scientific research, and home to the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory. In 2015, Tallahassee was awarded the All-American City Award by the National Civic League for the second time.
| Name: | Tallahassee city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Florida |
| County: | Leon County |
| Elevation: | 203 ft (62 m) |
| Total Area: | 104.74 sq mi (271.27 km²) |
| Land Area: | 101.85 sq mi (263.80 km²) |
| Water Area: | 2.89 sq mi (7.47 km²) |
| Total Population: | 196,169 |
| Population Density: | 1,926.00/sq mi (743.64/km²) |
| Area code: | 850 |
| FIPS code: | 1270600 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 308416 |
| Website: | www.talgov.com |
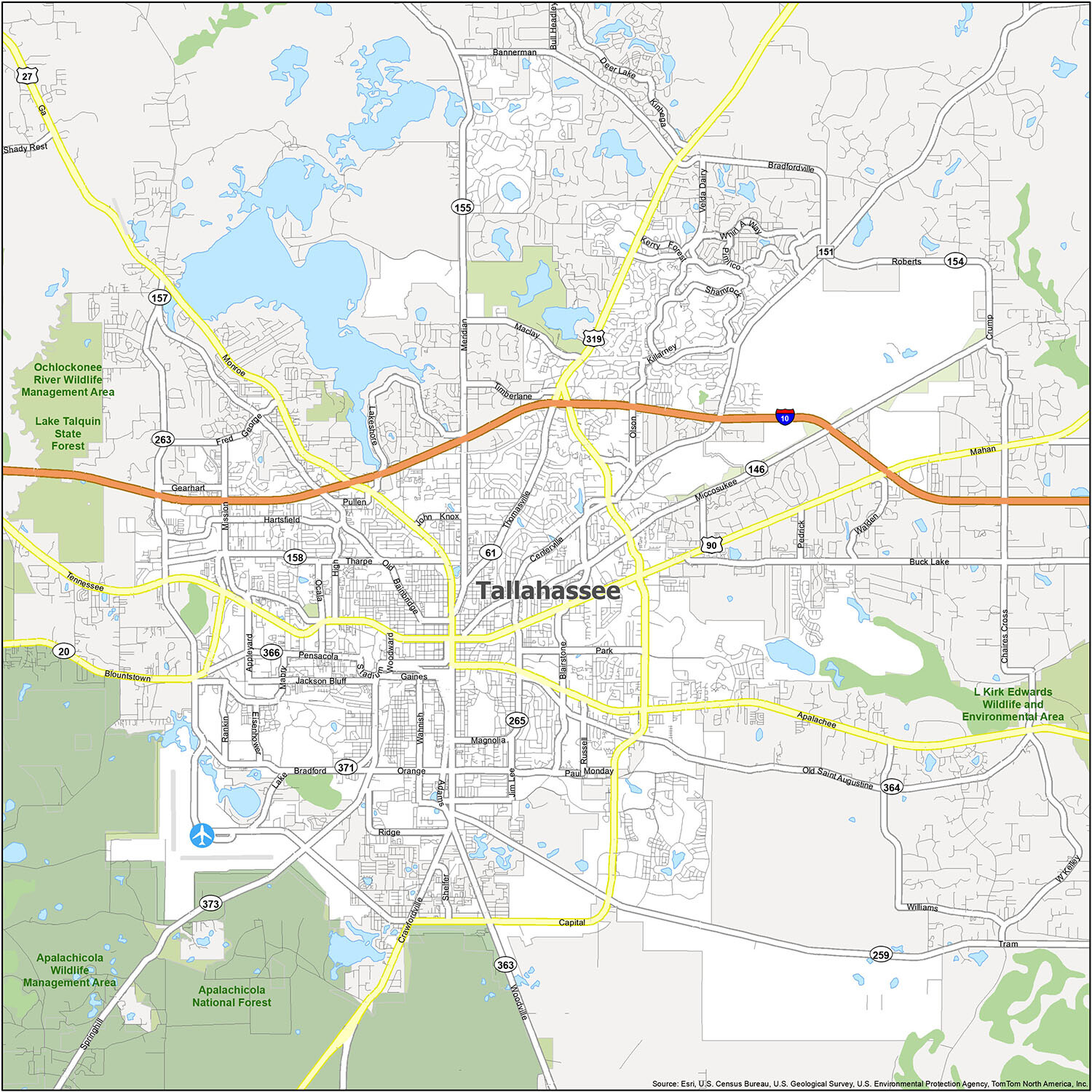
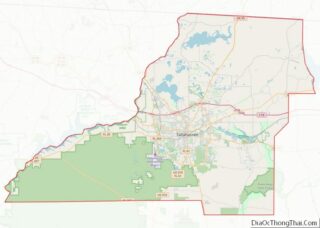
For those who are new to Tallahassee, our Tallahassee city map is the perfect way to get to know the city. The map highlights major roads, highways, and things to do. Download it and start exploring the area!
Tallahassee is a great place to explore and with our Tallahassee city map, you can easily find your way around the city. The map highlights major roads, highways, and things to do. Download it and start exploring the area today!
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Take a tour of your city, find out about the local entertainment and see what’s happening in any neighborhood. Explore Tallahassee Florida’s best attractions, restaurants, hotels, and more with this map. This interactive map will help you explore Tallahassee. From the top attractions to the best local spots, this interactive map has you covered.
Tallahassee location map. Where is Tallahassee city?
History
Indigenous peoples occupied this area for thousands of years before European encounter. Around 1200 CE, the large and complex Mississippian culture had built earthwork mounds near Lake Jackson which survive today; they are preserved in the Lake Jackson Archaeological State Park.
The Spanish Empire established their first colonial settlement at St. Augustine. During the 17th century they established several missions in Apalachee territory to procure food and labor to support their settlement, as well as to convert the natives to Roman Catholicism. The largest, Mission San Luis de Apalachee in Tallahassee, has been partially reconstructed by the state of Florida.
The expedition of Pánfilo de Narváez encountered the Apalachee people, although it did not reach the site of Tallahassee. Hernando de Soto and his mid-16th century expedition occupied the Apalachee town of Anhaica (at what is now Tallahassee) in the winter of 1538–39. Based on archaeological excavations, this Anhaica site is now known to have been about 0.5 miles (800 m) east of the present Florida State Capitol. The De Soto encampment is believed to be the first place Christmas was celebrated in the continental United States, although there is no historical documentation to back this claim.
The name Tallahassee is a Muskogean language word often translated as “old fields” or “old town”. It was likely an expression of the Creek people who migrated from Georgia and Alabama to this region in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, under pressure from European-American encroachment on their territory. They found large areas of cleared land previously occupied by the Apalachee tribe. (The Creek and later refugees who joined them developed as the Seminole Indians of Florida. The Talimali Band of Apalachee Indians in Louisiana identify as present-day descendants of the Apalachee Indians.)
During the First Seminole War, General Andrew Jackson fought two separate skirmishes in and around Tallahassee, which was then Spanish territory. The first battle took place on November 12, 1817. After Chief Neamathla, of the village of Fowltown just west of present-day Tallahassee, refused Jackson’s orders to relocate, Jackson entered the village, burnt it to the ground, and drove off its occupants. The Indians retaliated, killing 50 soldiers and civilians. Jackson reentered Florida in March 1818. According to Jackson’s adjutant, Colonel Robert Butler, they “advanced on the Indian village called Tallahasse (sic) [where] two of the enemy were made prisoner.”
State capital
Florida became an American territory in September 1821, in accordance with the Adams-Onís Treaty of 1819.
The first session of the Legislative Council of the Territory of Florida met on July 22, 1822, at Pensacola, the former capital of West Florida. Members from St. Augustine, the former capital of East Florida, traveled 59 days by water to attend. The second session was in St. Augustine, and western delegates needed 28 days to travel perilously around the peninsula to reach St. Augustine. During this session, delegates decided to hold future meetings at a halfway point. Two appointed commissioners selected Tallahassee, at that point an Apalachee settlement (Anhaica) virtually abandoned after Andrew Jackson burned it in 1818, as a halfway point. In 1824 the third legislative session met there in a crude log building serving as the capitol.
From 1821 through 1845, during Florida’s territorial period, the rough-hewn frontier capital gradually developed as a town. The Marquis de Lafayette, French hero of the American Revolution, returned to the United States in 1824 for a tour. The U.S. Congress voted to give him $200,000 (the same amount he had given the colonies in 1778), US citizenship, and the Lafayette Land Grant, 36 square miles (93 km) of land that today includes large portions of Tallahassee. In 1845 a Greek revival masonry structure was erected as the Capitol building in time for statehood. Now known as the “old Capitol”, it stands in front of the high-rise Capitol building built in the 1970s.
Tallahassee was in the heart of Florida’s Cotton Belt—Leon County led the state in cotton production—and was the center of the slave trade in Florida. During the American Civil War, Tallahassee was the only Confederate state capital east of the Mississippi River not captured by Union forces, and the only one not burned. A small engagement, the Battle of Natural Bridge, was fought south of the city on March 6, 1865, just a month before the war ended.
During the 19th century, the institutions that would develop into what is now Florida State University were established in Tallahassee; it became a university town. These included the Tallahassee Female Academy (founded 1843) and the Florida Institute (founded 1854). In 1851, the Florida legislature decreed two seminaries to be built on either side of the Suwannee River, East Florida Seminary and West Florida Seminary. In 1855 West Florida Seminary was transferred to the Florida Institute building (which had been established as an inducement for the state to place the seminary in Tallahassee). In 1858, the seminary absorbed the Tallahassee Female Academy and became coeducational. Its main building was near the northwest corner of South Copeland and West Jefferson streets, approximately where FSU’s Westcott Building is today.
In 1887, the Normal College for Colored Students, the ancestor of today’s FAMU, opened its doors. The legislature decided Tallahassee was the best location in Florida for a college serving African-American students; the state had segregated schools. Four years later its name was changed to State Normal and Industrial College for Colored Students, to teach teachers for elementary school children and students in industrial skills.
After the Civil War much of Florida’s industry moved to the south and east, a trend that continues today. The end of slavery and the rise of free labor reduced the profitability of the cotton and tobacco trade, at a time when world markets were also changing. The state’s major industries shifted to citrus, lumber, naval stores, cattle ranching, and tourism. The latter was increasingly important by the late 19th century. In the post-Civil War period, many former plantations in the Tallahassee area were purchased by wealthy northerners for use as winter hunting preserves. This included the hunting preserve of Henry L. Beadel, who bequeathed his land for the study of the effects of fire on wildlife habitat. Today the preserve is known as the Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy, nationally recognized for its research into fire ecology and the use of prescribed burning.
1900–99
Until World War II, Tallahassee remained a small Southern town with virtually the entire population living within one mile (1.6 km) of the Capitol. The main economic drivers were the colleges and state government, where politicians met to discuss spending money on grand public improvement projects to accommodate growth in places such as Miami and Tampa Bay, hundreds of miles away from the capital.
Tallahassee was also active in protest during the civil rights era. The Tallahassee bus boycott was a citywide boycott in Tallahassee, Florida that sought to end racial segregation in the employment and seating arrangements of city buses. On May 26, 1956, Wilhelmina Jakes and Carrie Patterson, two Florida A&M University students, were arrested by the Tallahassee Police Department for “placing themselves in a position to incite a riot”. Robert Saunders, representing the NAACP, and Rev. C. K. Steele began talks with city authorities while the local African-American community started boycotting the city’s buses. The Inter-Civic Council ended the boycott on December 22, 1956. On January 7, 1957, the City Commission repealed the bus-franchise segregation clause because of the United States Supreme Court ruling Browder v. Gayle (1956). In the 1960s there was a movement to transfer the capital to Orlando, closer to the state’s growing population centers. That movement was defeated; the 1970s saw a long-term commitment by the state to the capital city, with the construction of the new capitol complex and preservation of the old Florida State Capitol building.
In 1970, the Census Bureau reported the city’s population as 74.0% white and 25.4% black. In 1971, the city elected James R. Ford to the 5-member City Commission, and he became the city’s first African-American mayor in 1972 (commissioners rotated into the position serving a one-year term).
Bobby Bowden became the head coach of Florida State Seminoles football in 1976, and turned Tallahassee into a city dominated by college football, Bowden became very successful very quickly at Florida State. By his second year, Bowden had to deny many rumors that he would leave for another job; the team went 9–2, compared to the four wins total in the three seasons before Bowden. During 34 years as head coach he had only one losing season–his first, in 1976.
In 1977 the 22-story high-rise Capitol building, designed by architect Edward Durell Stone, was completed. It is now (2021) the third-tallest state capitol building in the United States. In 1978 the Old Capitol, directly in front of the new capitol, was scheduled for demolition, but state officials decided to keep the Old Capitol as a museum. In 1986, Jack McLean served as mayor, the second African-American to hold the position.
2000–present
Tallahassee was the center of world attention for six weeks during the 2000 United States Presidential election recount, which involved numerous rulings by the Florida Secretary of State and the Florida Supreme Court.
In 2016, the city suffered a direct hit by Hurricane Hermine, causing about 80% of the city proper to lose power, including Florida State University, and knocking down many trees.
In 2018, the city suffered another natural disaster when Hurricane Michael hit the panhandle.
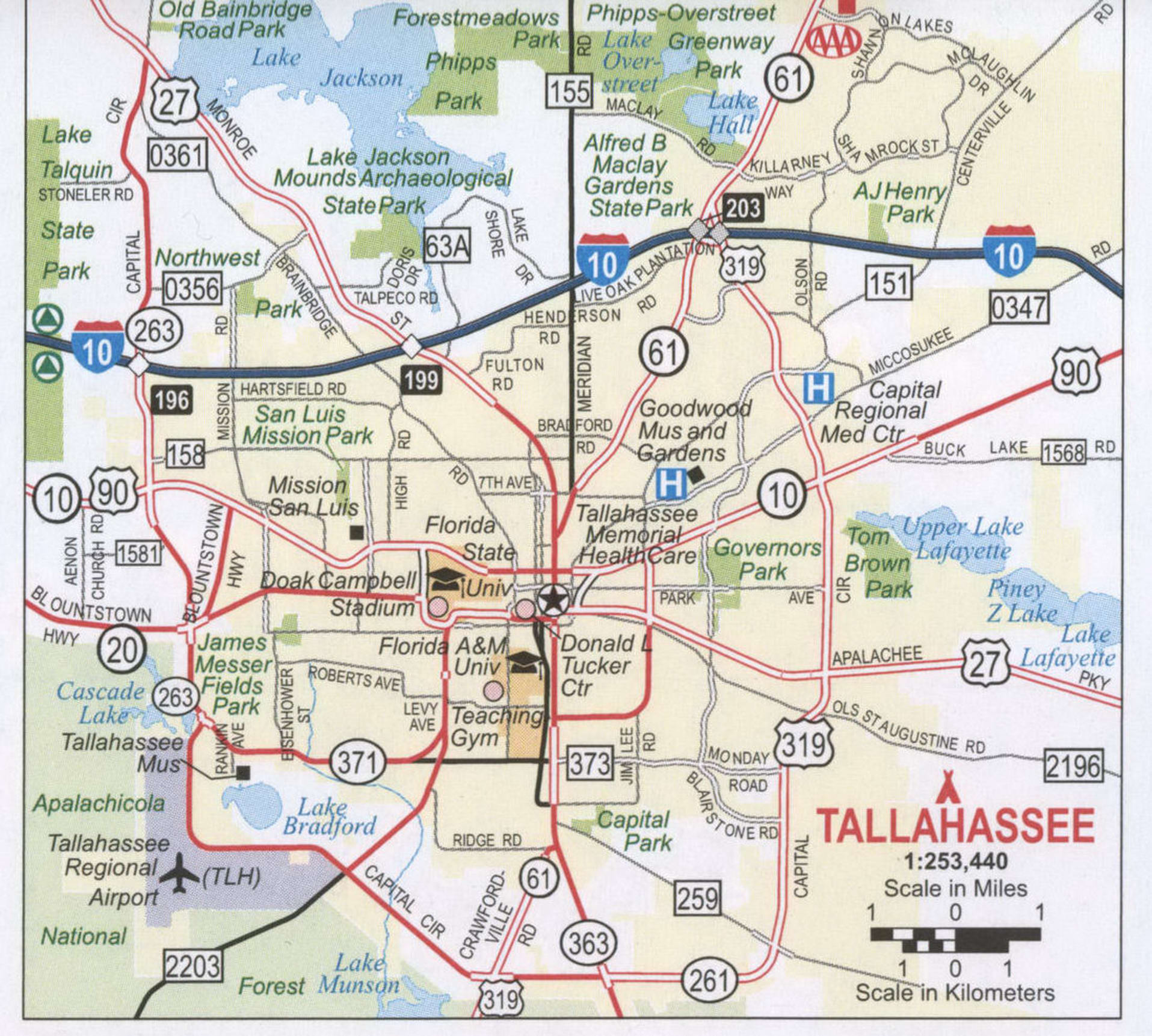
Tallahassee Road Map
There is no better way to get to know the city than by exploring it with a Tallahassee road map. Save yourself from spending hours driving around town looking for the best place or the best place for you. You can explore every interstate, highway, and major road of this beautiful city in just a few minutes. But for any road trips outside the city, check out our free Florida road map for statewide highway information.
Interstate Highways: I-10
US Highways: 20, 27, 61, 90, 151, 155, 158, 259, 263, 265, 319, 366, 371, 373, Blountstown Hwy,
Parkways: Apalachee Pky, Kerry Forest Pky
Major Roads: Adams St, Capital Cir, Crawfordville Rd, Fred George Rd, Gaines St, Hospitality St, Jefferson St, Lake Bradford Rd, Madison St, Magnolia Dr, Mahan Dr, Meridian Rd, Monroe St, Orange Ave, Paul Russell Rd, Pensacola St, Saint Augustine St, Springhill Rd, Stadium Dr, Tennessee St, Thomasville Rd, Tram Rd, Woodville Hwy, Woodward Ave
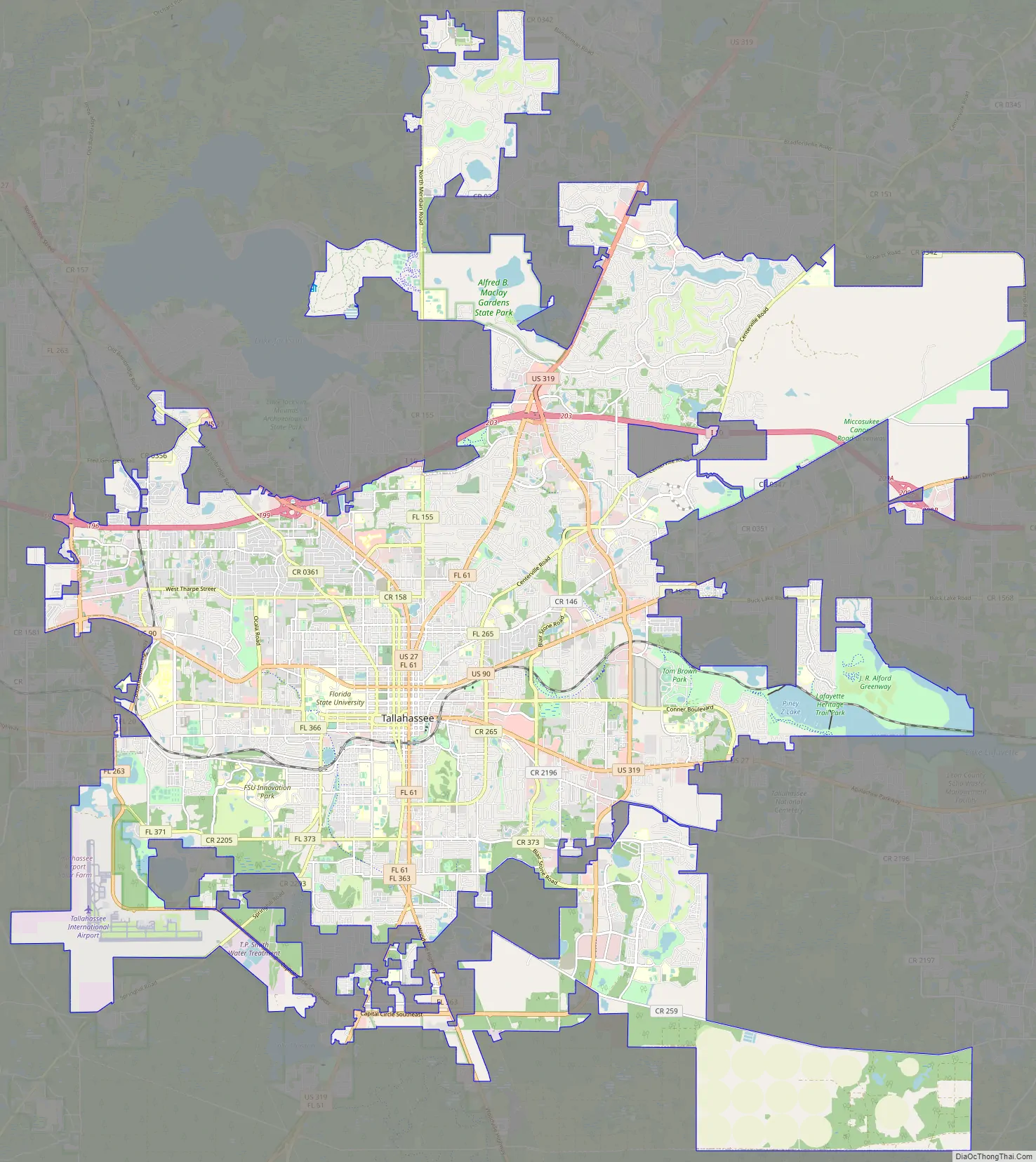
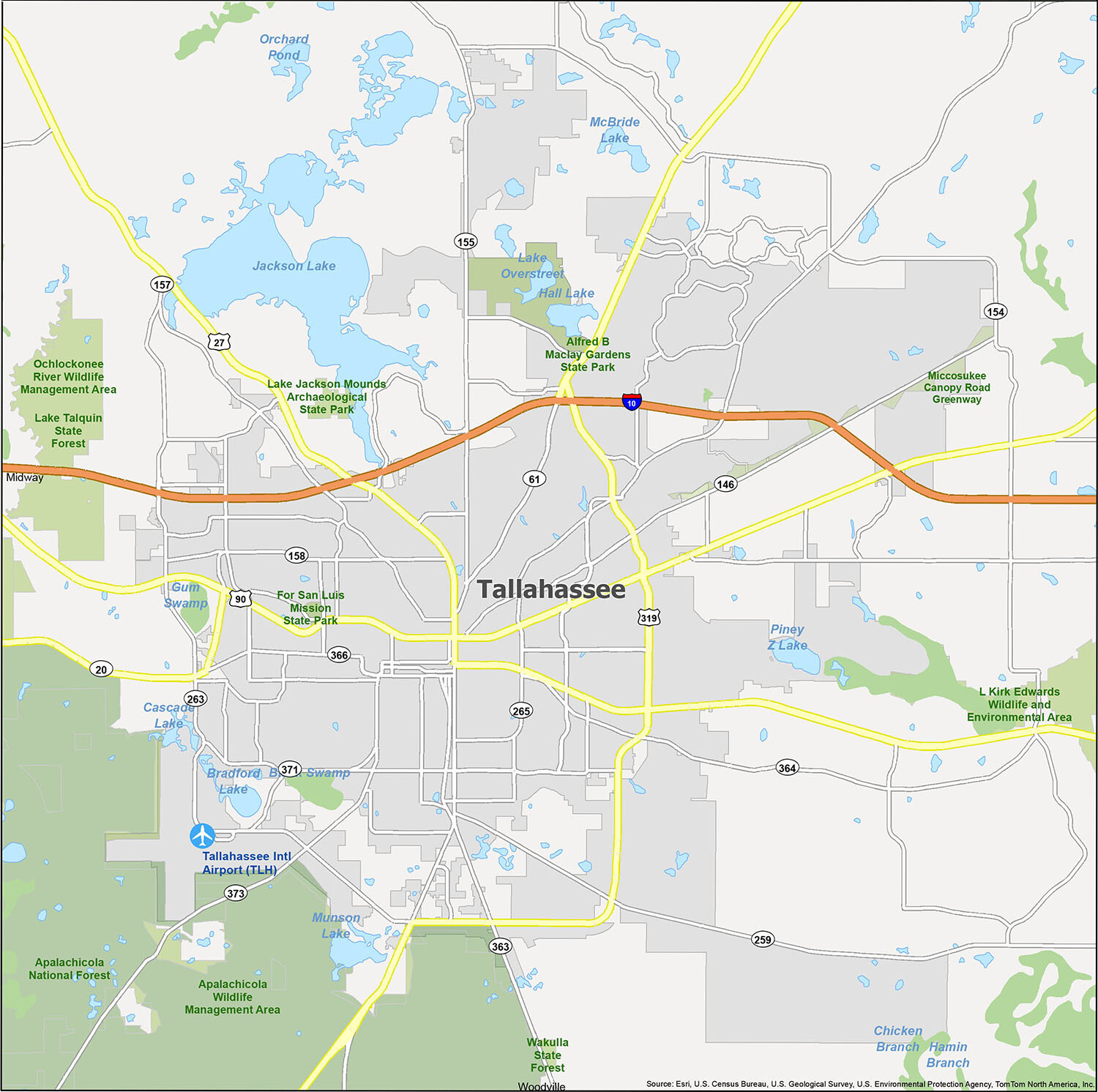
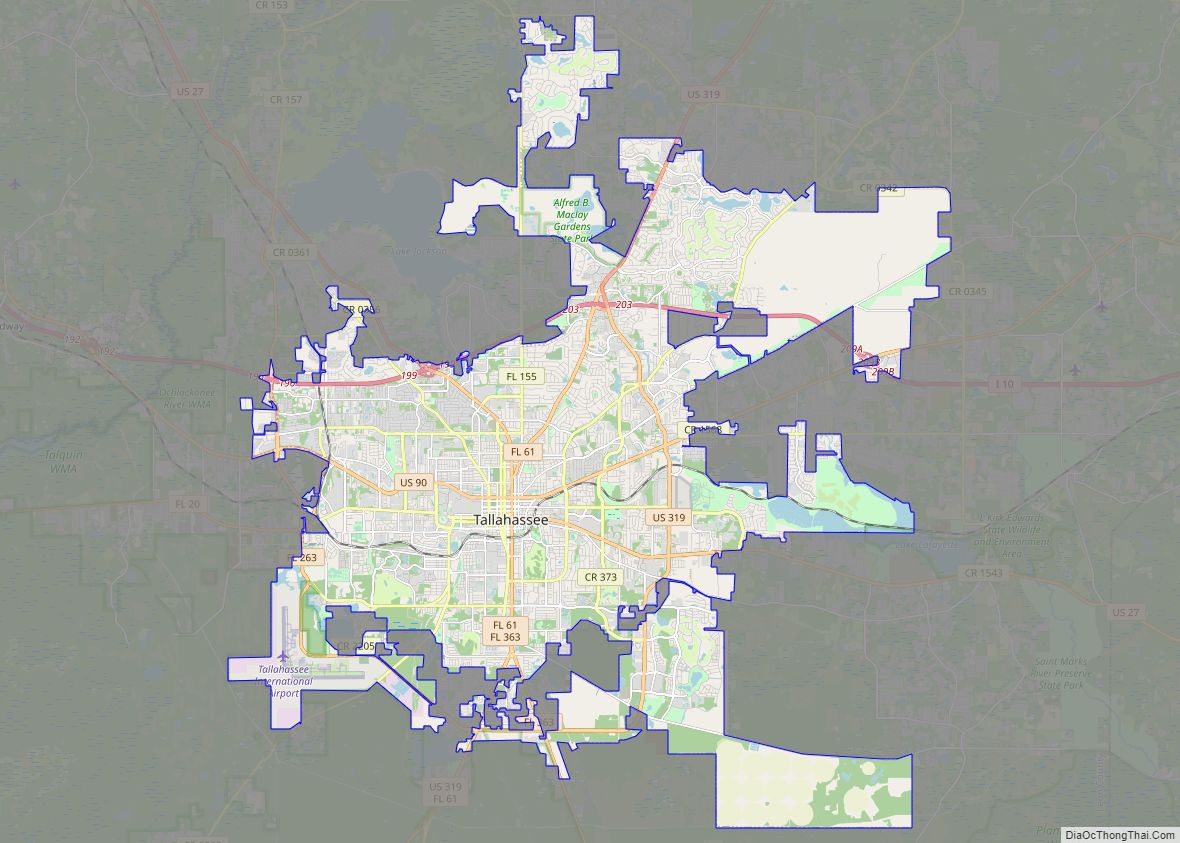
Tallahassee is an exciting city with plenty of attractions and activities for visitors of all ages. From outdoor recreation to historical sites, this map of Tallahassee provides an overview of the city’s points of interest. Whether you’re looking for a fun-filled vacation or an educational experience, Tallahassee has something for everyone. This map covers the entire city and includes points of interest, rivers, lakes, and populated places. It also includes information on local airports, cities, census-designated places, lakes, rivers, and parks and recreation areas.
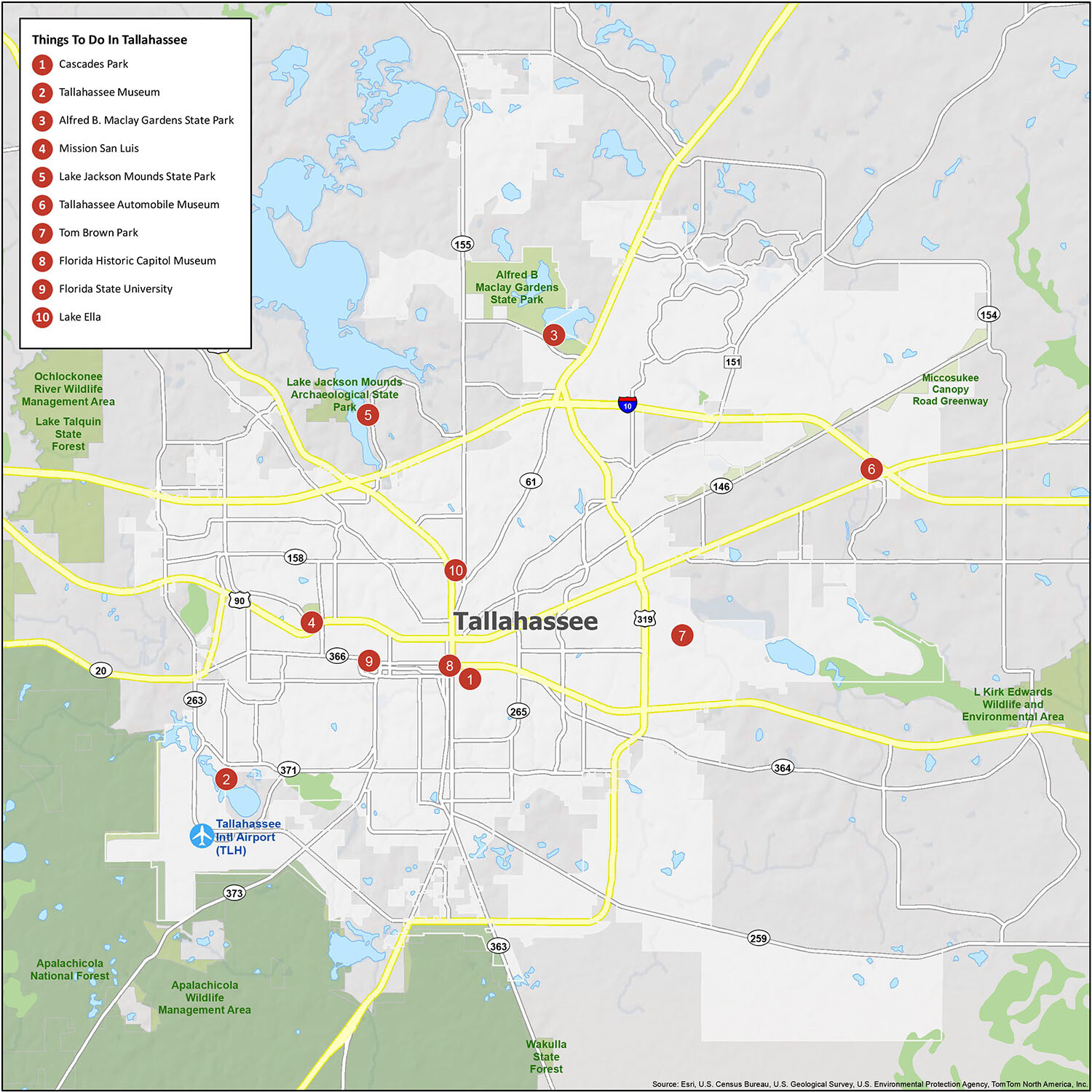
10 things to do in Tallahassee city
Whether you’re looking for a day of adventure or a relaxing day in nature, Tallahassee has something for everyone. With this Tallahassee map, you can explore the city’s best attractions and find the perfect way to explore Tallahassee, Florida.
Discover the best of Tallahassee, Florida with this map of all the things to do. From Cascades Park to the Tallahassee Museum, you’ll find all the places to see in the area. Explore the city’s best attractions and find the perfect way to explore Tallahassee, Florida.
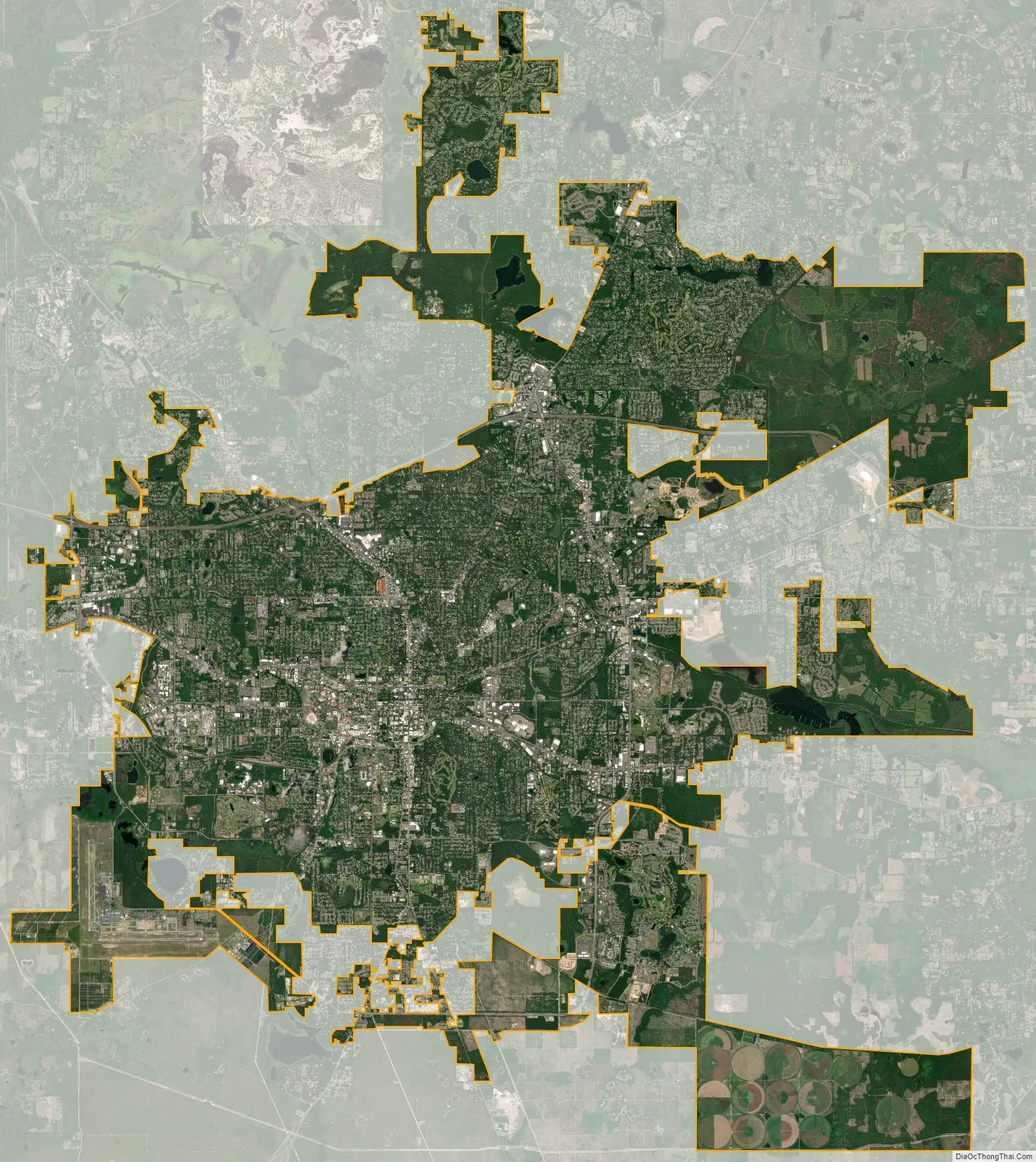
Tallahassee city Satellite Map
Geography
Tallahassee has an area of 98.2 square miles (254.3 km), of which 95.7 square miles (247.9 km) is land and 2.5 square miles (6.5 km) (2.59%) is water.
Tallahassee’s terrain is hilly by Florida standards, being at the southern end of the Red Hills Region, just above the Cody Scarp. The elevation varies from near sea level to just over 200 feet (61 m), with the state capitol on one of the highest hills in the city. The city includes two large lake basins, Lake Jackson and Lake Lafayette, and borders the northern end of the Apalachicola National Forest.
The flora and fauna are similar to those found in the mid-south and low country regions of South Carolina and Georgia. The palm trees are the more cold-hardy varieties like the state tree, the Sabal palmetto. Pines, magnolias, hickories, and a variety of oaks are the dominant trees. The Southern Live Oak is perhaps the most emblematic of the city.
Nearby cities and suburbs
- Crawfordville
- Havana
- Lamont
- Lloyd
- Midway
- Monticello
- Quincy
Cityscape
Tallahassee has many neighborhoods inside the city limits. Some of the most known and defined include All Saints, Apalachee Ridge, Betton Hills, Buck Lake, Callen, Frenchtown (the oldest historically black neighborhood in the state), Killearn Estates, Killearn Lakes Plantation, Lafayette Park, Levy Park, Los Robles, Midtown, Holly Hills, Jake Gaither/University Park, Indian Head Acres, Myers Park, Smokey Hollow, SouthWood, Seminole Manor and Woodland Drives.
Tallahassee is also home to some gated communities, including Golden Eagle, Ox Bottom, Lafayette Oaks and The Preserve at San Luis; the Tallahassee Ranch Club is to the southeast of the city.
Urban planning and expansion
The first plan for the Capitol Center was the 1947 Taylor Plan, which consolidated several government buildings in one downtown area. In 1974, the Capitol Center Planning Commission for the City of Tallahassee, Florida responded to growth of its urban center with a conceptual plan for the expansion of its Capitol Center. Hisham Ashkouri, working for The Architects’ Collaborative, led the urban planning and design effort. Estimating growth and related development for approximately the next 25 years, the program projected the need for 2.3 million square feet (214,000 m) of new government facilities in the city core, with 3,500 dwelling units, 100 acres (40 ha) of new public open space, retail and private office space, and other ancillary spaces. Community participation was an integral part of the design review, welcoming Tallahassee residents to provide input as well as citizens’ groups and government agencies, resulting in the creation of six separate design alternatives.
Sprawl and compact growth
The Tallahassee-Leon County Planning Department implements policies aimed at promoting compact growth and development, including the establishment and maintenance of an Urban Service Area. The intent of the Urban Service Area is to “have Tallahassee and Leon County grow in a responsible manner, with infrastructure provided economically and efficiently, and surrounding forest and agricultural lands protected from unwarranted and premature conversion to urban land use.” The result of compact growth policies has been a significant overall reduction in the Sprawl Index for Tallahassee between 2000 and 2010. CityLab reported on this finding, stating “Tallahassee laps the field, at least as far as the Sprawl Index is concerned.”
Climate
Tallahassee has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa), with long, tropical summers and short, mild winters, as well as warm to hot, drier springs and autumns. Tallahassee falls in USDA hardiness zones 8b (15 °F to 20 °F) Summer maxima here are hotter than in the Florida peninsula and it is one of the few cities in the state to occasionally record temperatures above 100 °F or 37.8 °C; there are an average of 11.2 days per year that have temperatures at least that high. The record high of 105 °F (41 °C) was set on June 15, 2011.
Summer is characterized by brief intense showers and thunderstorms that form along the afternoon sea breeze from the Gulf of Mexico. The daily mean temperature in July, the hottest month, is 82.9 °F (28.3 °C). Conversely, the winter is markedly cooler, with a January daily average temperature of 51.0 °F (10.6 °C). There is an average of 34.6 nights with a minimum at or below freezing, and on average, the window for freezing temperatures is from November 22 thru March 16, allowing a growing season of 250 days. With the data from the 1991–2020 normals, Tallahassee is in USDA zone 9a by a small margin, the coldest temperature of the year usually being about 20.2 °F (−6.6 °C). Temperature readings below 15 °F (−9 °C) are very rare, having last occurred on January 11, 2010.
During the Great Blizzard of 1899 the city reached −2 °F (−19 °C) on February 13, which remains Florida’s only recorded subzero reading. At the time, Tallahassee’s record low was colder than the record low in Tromsø, Norway. The record cold daily maximum is 22 °F (−6 °C), set on the same day as the all-time record low. More recently, a 28 °F (−2 °C) daily maximum was recorded in 1985. Conversely, the record warm daily minimum is 81 °F (27 °C) on July 15, 1980. However, the city itself is considerably warmer than the airport where the National Weather Service records its data from, even though the National Weather Service does not record data from it. This is due to an urban heat island, which creates an average disparity of 5.8 °F (3.2 °C) and is especially pronounced during winter.
Snow and ice are rare in Tallahassee, not occurring during most winters. Historically, at least flurries are recorded every three to four years, but measurable snowfall of 0.1 inches (0.3 cm) or more has only happened once in the 1991-2020 time period. The closest location that receives regular yearly snowfalls is Macon, Georgia, 200 miles (320 km) north of Tallahassee. Nonetheless, Tallahassee has recorded a few accumulating snowfalls over the last 100 years; the heaviest snowfall was 2.8 inches (7 cm) on February 13, 1958. Tallahassee’s other recorded measurable snowfalls were 1.0 inch (2.5 cm) on February 12–13, 1899, and December 22–23, 1989; 0.4 inches (1.0 cm) on March 28, 1955, and February 10, 1973; 0.2 inches (0.5 cm) on February 2, 1951; and 0.1 inches (0.3 cm) on January 3, 2018.
Although several hurricanes have brushed Tallahassee with their outer rain and wind bands, in recent years only Hurricane Kate, in 1985, and Hurricane Hermine, in 2016, have struck Tallahassee directly. Hurricane Michael passed 50 miles to the west after making landfall near Mexico Beach, Florida in October 2018 as a Category 5 storm, resulting in 95% of Leon County being without power.
The Big Bend area of North Florida sees several tornadoes each year during the season, but they are generally weak, cause little structural damage, and rarely hit the city. On April 19, 2015, a tornado touched down in Tallahassee. The tornado was rated EF1, and created a path as wide as 350 yards (320 m) for almost 5 miles (8 km) near Maclay Gardens. Damage included numerous downed tree limbs and a car crushed by a falling tree. During extremely heavy rains, some low-lying parts of Tallahassee may flood, notably the Franklin Boulevard area adjacent to the downtown and the Killearn Lakes subdivision, outside the Tallahassee city limits, on the north side.
The most recent tornado to hit Tallahassee occurred on January 27, 2021. It was rated as EF0 tornado. The tornado caused damage to the city and the Tallahassee International Airport.
See also
Map of Florida State and its subdivision:- Alachua
- Baker
- Bay
- Bradford
- Brevard
- Broward
- Calhoun
- Charlotte
- Citrus
- Clay
- Collier
- Columbia
- Desoto
- Dixie
- Duval
- Escambia
- Flagler
- Franklin
- Gadsden
- Gilchrist
- Glades
- Gulf
- Hamilton
- Hardee
- Hendry
- Hernando
- Highlands
- Hillsborough
- Holmes
- Indian River
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Lafayette
- Lake
- Lee
- Leon
- Levy
- Liberty
- Madison
- Manatee
- Marion
- Martin
- Miami-Dade
- Monroe
- Nassau
- Okaloosa
- Okeechobee
- Orange
- Osceola
- Palm Beach
- Pasco
- Pinellas
- Polk
- Putnam
- Saint Johns
- Saint Lucie
- Santa Rosa
- Sarasota
- Seminole
- Sumter
- Suwannee
- Taylor
- Union
- Volusia
- Wakulla
- Walton
- Washington
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming