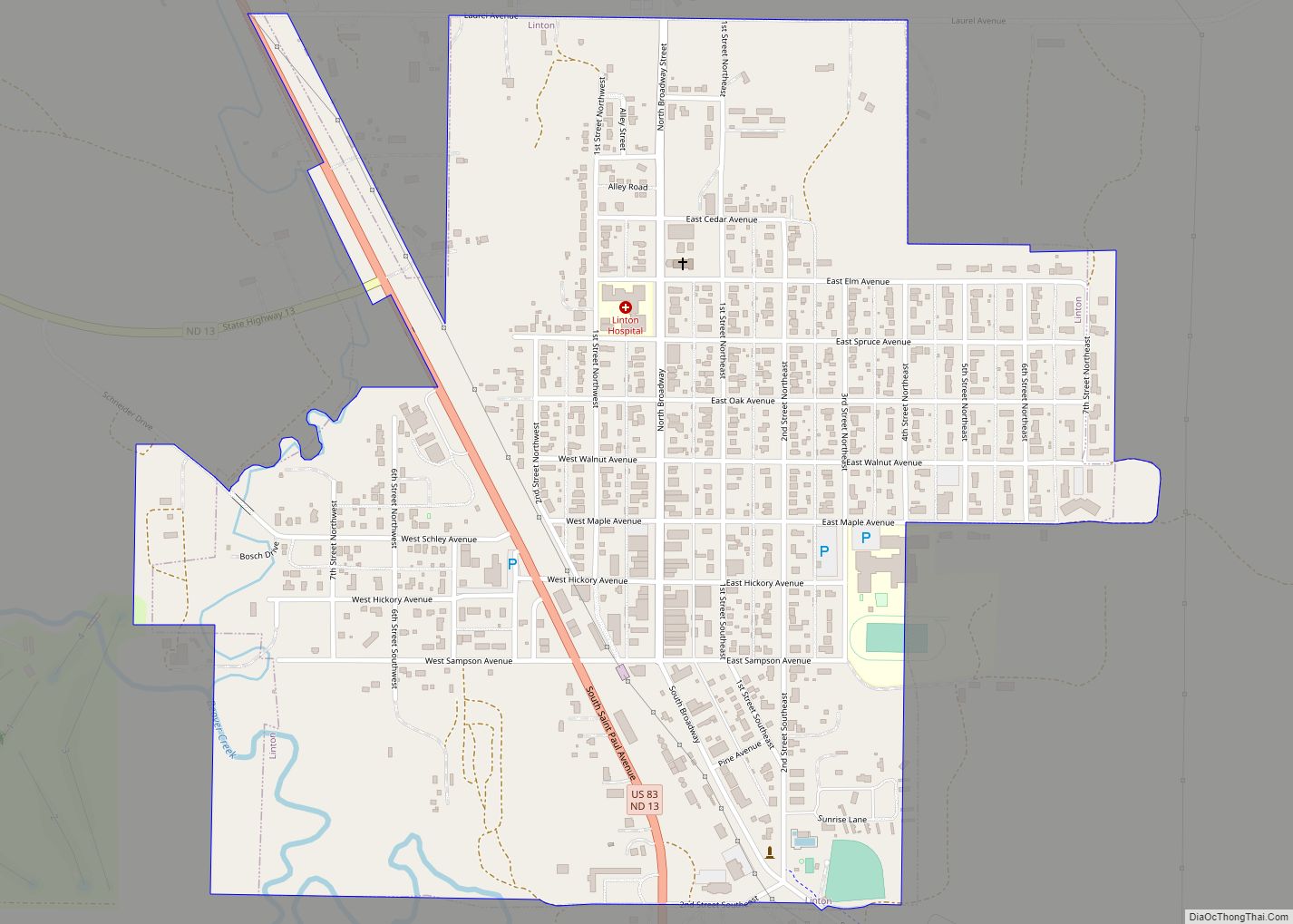
Linton is a city in and the county seat of Emmons County, North Dakota, United States. The population was 1,071 at the 2020 census. When compared with the other 356 cities in North Dakota, Linton ranks in the top twelve percent based on the number of its residents. The city serves as a governmental, commercial and business hub for Emmons County.
A nearby historic site listed on the National Register of Historic Places is Sacred Heart Cemetery, Wrought-Iron Cross Site, in or near Linton.
| Name: | Linton city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | North Dakota |
| County: | Emmons County |
| Founded: | 1899 |
| Elevation: | 1,719 ft (524 m) |
| Total Area: | 0.79 sq mi (2.03 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.79 sq mi (2.03 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) |
| Total Population: | 1,071 |
| Population Density: | 1,364.33/sq mi (526.84/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 58552 |
| Area code: | 701 |
| FIPS code: | 3846980 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1029917 |
| Website: | lintonnd.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Linton location map. Where is Linton city?
History
In August 1898, land located in the geographic center of Emmons County in Section 7 of Township 132 North, Range 76 West, of the Fifth Principal Meridian, was surveyed and platted by W.E. Petrie into lots, streets and alleys explicitly for the purpose of creating a seat for Emmons County. The site was named Linton, after George W. Lynn, who had settled in Emmons County in 1885. He was a farmer, lawyer, Emmons County’s first States Attorney and for a while was the publisher of the Emmons County Free Press. The plat was filed with the register of deeds on December 30, 1898. Linton was incorporated as a village on April 26, 1906; and incorporated as a city on April 6, 1914. Charles Patterson, editor of the Emmons County Republican, was Linton’s first postmaster, having received his commission for the post in March 1899.
Linton received its first connection via long-distance telephone in 1905 when the Northwestern Telephone Exchange Company established a line from Fargo to Bismarck and created a branch line to Linton. At the same time Bismarck was connected to the line of the South Dakota system so that each of the communities could communicate with each other in this way.
Notable persons from Linton
The Hollywood agent Bill Daly, of Bill Daly Associates, was the manager for Lawrence Welk and the lightweight world boxing champion Carlos Ortiz, among others. Daly was the nephew of Linton physician Dr. Rolly Hogue’s daughter-in-law Kathleen Hogue. Roman Catholic bishop Austin Anthony Vetter was born in Linton.
The creation of Linton
.
The creation of Linton was the result of a political dispute between residents in the northern half of Emmons County and those in the southern half. In 1885, two years after the county was officially organized, the county seat was in the town of Williamsport, which was located in the northern half of the county in Township 135N, Range 76W, Section 15 on the east side of what is today 9th Ave. SE between 62nd St. SE and the vacated 63rd St. SE, two and a half miles northeast of Hazelton. The people in the southern half were upset because the county seat was so far away and most of the county leaders were from the north. Moreover, the northern part was more densely settled than the southern part, so this created problems when it came time to vote because the higher population numbers gave “Northerners” greater influence on issues. Eventually, it was decided to take a vote to see if residents favored dividing the county in two. If successful, the northern half would continue to be named Emmons—with Williamsport remaining the county seat—while the southern half would be named Winona with the town of Winona serving as the new county seat of government.
When the votes were tallied, residents had decided against splitting the county. However this did not end the dispute, and the effort to move the seat of government from Williamsport to Winona continued. Three votes were taken during the 1880s and 1890s. The first two failed completely. The third resulted in a decision to move the county seat to the center of the county and create a new town, which eventually become the city of Linton. People in the North still wanted to keep the seat at Williamsport, however, so they preferred charges claiming that the election was “fraudulent and illegal”, and obtained a court injunction to prevent the move. Southerners became so incensed by this action that they went to Williamsport in January 1899 to take possession of the county records and transfer them to the new county seat. The men were armed, and they met no resistance and took the records, including, according to an account by then-constable John Bartu, a two-ton safe (this safe is now in the collection of the Emmons County Museum in Linton). No charges were brought against the men, although the Williamsport interests succeeded in having the records brought back to their city and causing another election to be ordered which would require the approval of a majority of two-thirds of the voters to have Linton retain its position as county seat (this election was never held). Although the records were brought back to Linton, the case dragged on in the courts for several months, during which time it was expected that it would end up in the state supreme court. The matter was finally settled when E.S. Allen, the attorney for the people of Williamsport, moved that the case be dismissed, whereby the city of Linton prevailed and the seat of Emmons County has remained there ever since. As a result of losing its position as the county seat, and because the Northern Pacific Railway preferred the Linton location when they built a branch to the area in about 1897, Williamsport ceased to exist as a community by the early years of the 20th century and the site today is occupied by farmland.
The community’s oldest newspaper, The Emmons County Record, began publication with 75 copies printed on June 10, 1884 in Williamsport but was relocated to Linton by Darwin R. Streeter, its founder, in 1899. Streeter continued as the newspaper’s publisher until January 1914, at which time full control of it passed into the hands of his son Frank. The newspaper has been published continuously since the time of its founding.
Linton Road Map
Linton city Satellite Map
Geography
Linton is located at 46°16′6″N 100°13′56″W / 46.26833°N 100.23222°W / 46.26833; -100.23222 (46.268360, -100.232110).
Another method of locating Linton is by tracing the intersection of US Highway 83 and ND Highway 13.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 0.75 square miles (1.94 km), all land.
According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Linton has a warm-summer humid continental climate, abbreviated “Dfb” on climate maps.
See also
Map of North Dakota State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Barnes
- Benson
- Billings
- Bottineau
- Bowman
- Burke
- Burleigh
- Cass
- Cavalier
- Dickey
- Divide
- Dunn
- Eddy
- Emmons
- Foster
- Golden Valley
- Grand Forks
- Grant
- Griggs
- Hettinger
- Kidder
- Lamoure
- Logan
- McHenry
- McIntosh
- McKenzie
- McLean
- Mercer
- Morton
- Mountrail
- Nelson
- Oliver
- Pembina
- Pierce
- Ramsey
- Ransom
- Renville
- Richland
- Rolette
- Sargent
- Sheridan
- Sioux
- Slope
- Stark
- Steele
- Stutsman
- Towner
- Traill
- Walsh
- Ward
- Wells
- Williams
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming