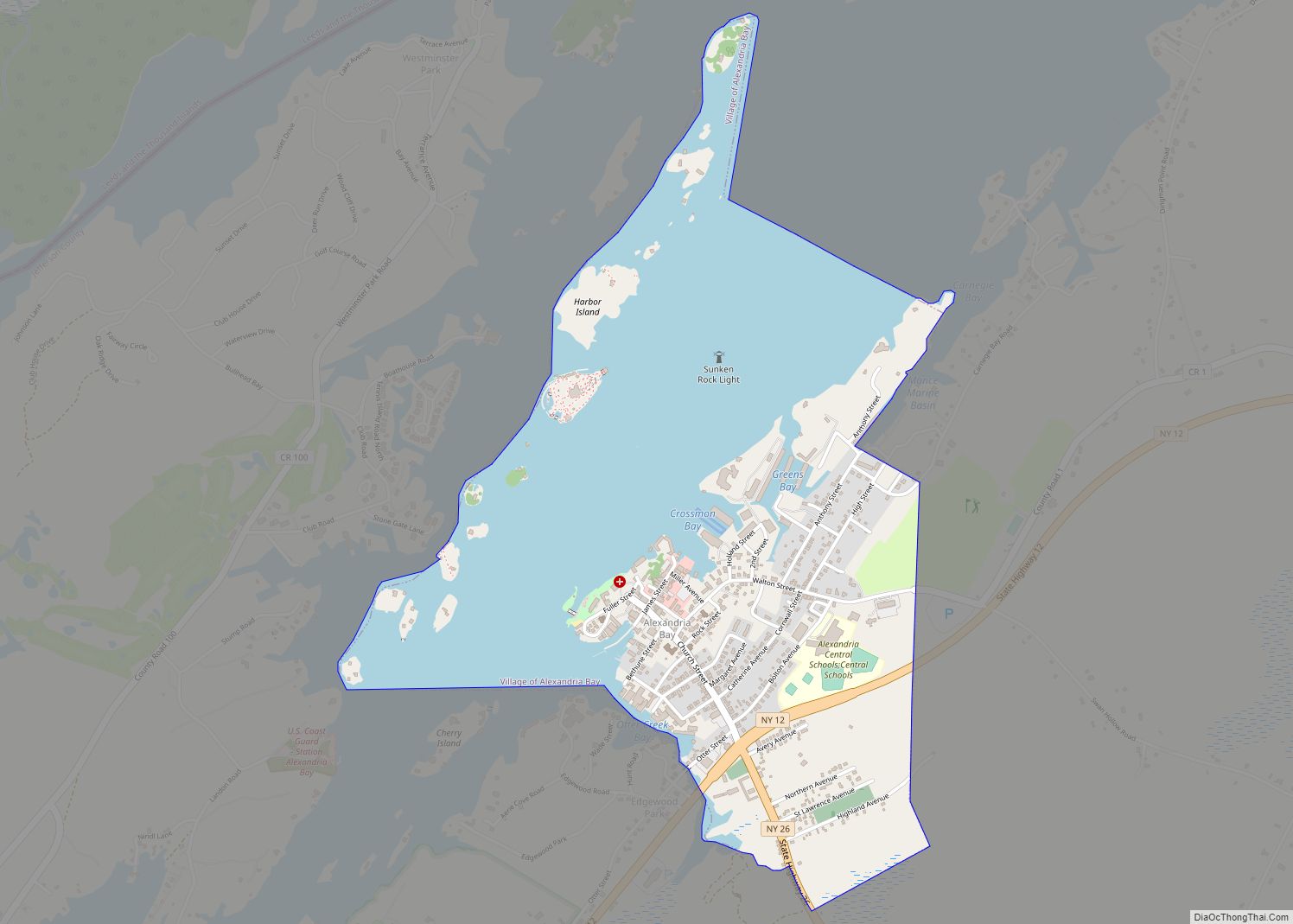
Thousand Island Park, also known as TI Park, is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the town of Orleans, Jefferson County, New York, United States, in the Thousand Islands region on the St. Lawrence River. Founded in 1875 as a holiday camp, the incorporated community remains a seasonal summer community; despite 323 housing units, there was only a population of 31 permanent residents as of the 2010 census.
The community is a national historic district, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1982. The district is notable for its outstanding concentration of substantially-intact late 19th-century and early 20th-century resort architecture. The park also contains Vivekananda Cottage, a Hindu sacred site visited by the Swami Vivekananda and his followers.
| Name: | Thousand Island Park CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | New York |
| County: | Jefferson County |
| Elevation: | 275 ft (84 m) |
| Total Area: | 0.63 sq mi (1.63 km²) |
| Land Area: | 0.30 sq mi (0.77 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.33 sq mi (0.86 km²) |
| Total Population: | 96 |
| Population Density: | 323.23/sq mi (124.89/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 13692 |
| FIPS code: | 3673726 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0967447 |
| Website: | www.tiparkcorp.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Thousand Island Park location map. Where is Thousand Island Park CDP?
History
1875–1912: Golden Era
In 1875, Thousand Island Park was founded by Rev. J.F. Dayan, as a Methodist summer, Chautauqua-like community. The main purpose was to enable families to secure pleasant lots for cottages or tents where they could spend a portion of the summer in a beautiful, cool, and salubrious place with religious purposes being secondary. The Park’s landmarks, homes, and way of life were nearly destroyed by fire. It is fortunate so much remains.
The Methodist summer camp colony that surrounded the Tabernacle was soon transformed from a tent city into a permanent village of summer residences. It was built on a scale far surpassing other similar associations. All roads lead to the Tabernacle centered prominently and squarely at the head of the Park on St. Lawrence Ave. The Tabernacle was the center for socialization and participation in Chautauqua-like programs which included religious studies, Sunday school institutes, outdoor recreation, travel lectures, temperance rallies and discussion of social reforms.
Campers leased lots, set up their tents on the preferred, prime lots closest to the Tabernacle. This grouping of tents was often called a tent city. The first diminutive cottages were tents constructed of wood on the original wooden tent platform. Individual owners also improvised, conceived and produced hybrids, combining styles and embellishing these small Tent Platform/Campground style structures, called the Landmark Shop, with fanciful gingerbread.
As the architecture on the Park evolved, larger structures came into vogue. Much of the look of these Victorian cottages derives its characteristics from the varied styles of nineteenth-century architecture. In addition to the charming Gothic Tent style cottages, Gothic Revival, Eastlake, Stick, Shingle, and Queen Anne became popular architectural styles. After the fire of 1912, Bungalow/Craftsman styles, Neoclassical Revival style, and vernacular cottages were added to the Park’s varied styles of architecture.
By 1890, the Park was firmly established with nearly 600 cottages and 7,000 summer inhabitants. A more liberal policy relaxed restrictions on curfews and the prohibition of cards and alcohol bringing more of a resort character to the Park. The Pavilion was the main entry to this Methodist retreat at a time when all travel to Wellesley Island was by water. The new, larger Pavilion was able to accommodate the landing of steamships and served as the gateway to the Park with hundreds of visitors seeking intellectual pursuits and entertainment by participating in the Chautauqua programs.
The destruction by fire in 1912 of the Park’s last great hotel, The Columbian and 99 cottages plus the business district, signaled the end of the Golden Era.
1913–1974: Mid-century changes
Following the fire, families continued to summer in the park but tourism in the region slowly declined. After the fire and through the Great Depression, barely half of the cottages were occupied and eventually, another 200 cottages were torn down.
In 1933, the Thousand Island Park Association corporation was foreclosed due to financial troubles and the property was sold to the new Wellesley Island Park Inc. TI Park continued to decline in the following two decades. Most of the Park’s hotels closed and many cottages were torn down; by 1950, there were only 12 businesses and 320 cottages on the Park, compared to 600 in the late 1800s. The park corporation was deeply in debt; in 1953, it became the Thousand Island Park Corporation. Families continued to enjoy the park during the summer and it became a mostly non-religious community in the 1960s and ’70s.
1975–present: Historic preservation and revival
In 1975, the Centennial Celebration served as a catalyst for change in the Park; the architectural charm and setting was once again appreciated. The Centennial Year Celebration inspired the formation of the Landmark Society in 1976, and the path that led to the Park regaining its architectural character and integrity. A small group of dedicated Landmark Society members initiated the nomination of Thousand Island Park to the National Register of Historic Places, finally achieved in 1982. The Thousand Island Park Landmark Society is supported today by individuals who promote the mission set forth by the Landmark founders.
The restoration and preservation of TI Park continued into the 2000s. In 2014, the park faced another serious fire when the building at the community’s four corners, containing The Guzzle, grocery store, volunteer fire department, a few small shops and offices, a plumbing company, and the post office, burned down. A smaller replacement building was rebuilt on that corner and opened in 2017.
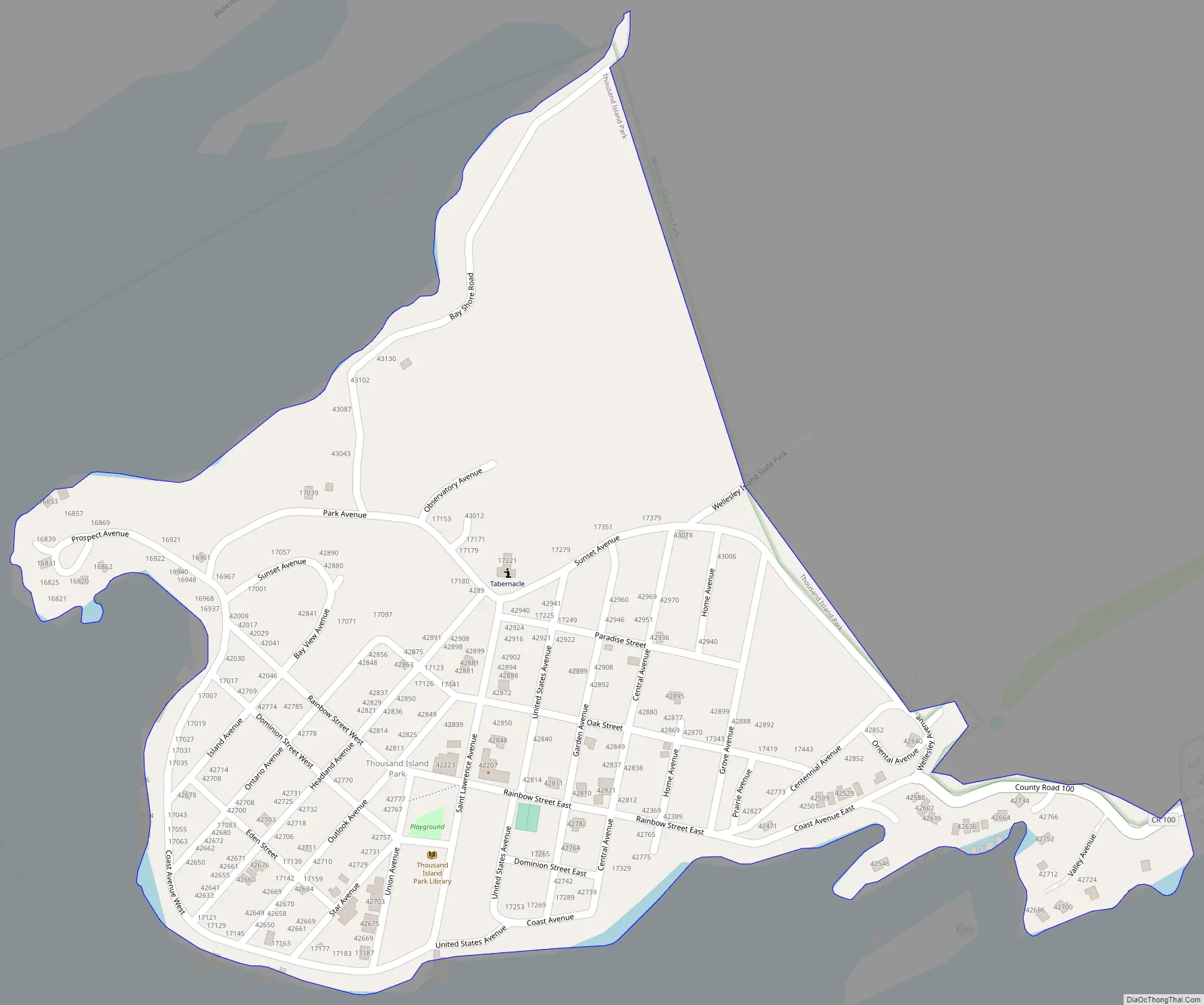
Thousand Island Park Road Map
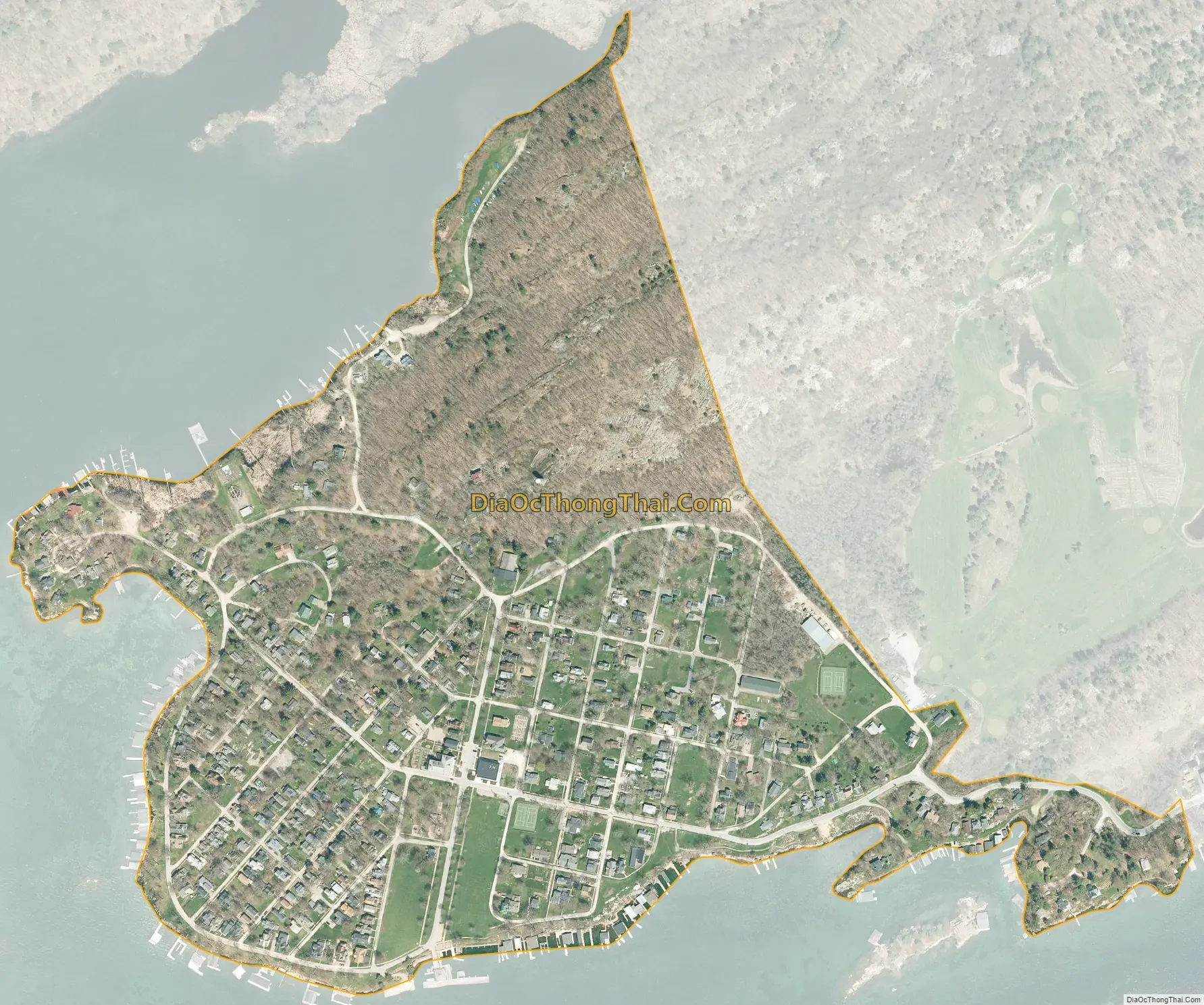
Thousand Island Park city Satellite Map
Geography
Thousand Island Park is in the northern part of the town of Orleans, at the southwest end of Wellesley Island, one of the largest of the Thousand Islands. It is bordered to the east by Wellesley Island State Park. The community is reached by automobile using County Route 100, which leads northeast 2.5 miles (4.0 km) to Interstate 81 at Exit 51.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the Thousand Island Park CDP has a total area of 0.29 square miles (0.76 km), all land.
Rock Island Light is 0.5 miles (0.8 km) southeast of Thousand Island Park in the middle of the south channel of the St. Lawrence, known as American Narrows, and Fishers Landing is directly across the narrows on the mainland, 1 mile (1.6 km) southeast of the community.
See also
Map of New York State and its subdivision:- Albany
- Allegany
- Bronx
- Broome
- Cattaraugus
- Cayuga
- Chautauqua
- Chemung
- Chenango
- Clinton
- Columbia
- Cortland
- Delaware
- Dutchess
- Erie
- Essex
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Genesee
- Greene
- Hamilton
- Herkimer
- Jefferson
- Kings
- Lake Ontario
- Lewis
- Livingston
- Madison
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Nassau
- New York
- Niagara
- Oneida
- Onondaga
- Ontario
- Orange
- Orleans
- Oswego
- Otsego
- Putnam
- Queens
- Rensselaer
- Richmond
- Rockland
- Saint Lawrence
- Saratoga
- Schenectady
- Schoharie
- Schuyler
- Seneca
- Steuben
- Suffolk
- Sullivan
- Tioga
- Tompkins
- Ulster
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Westchester
- Wyoming
- Yates
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming