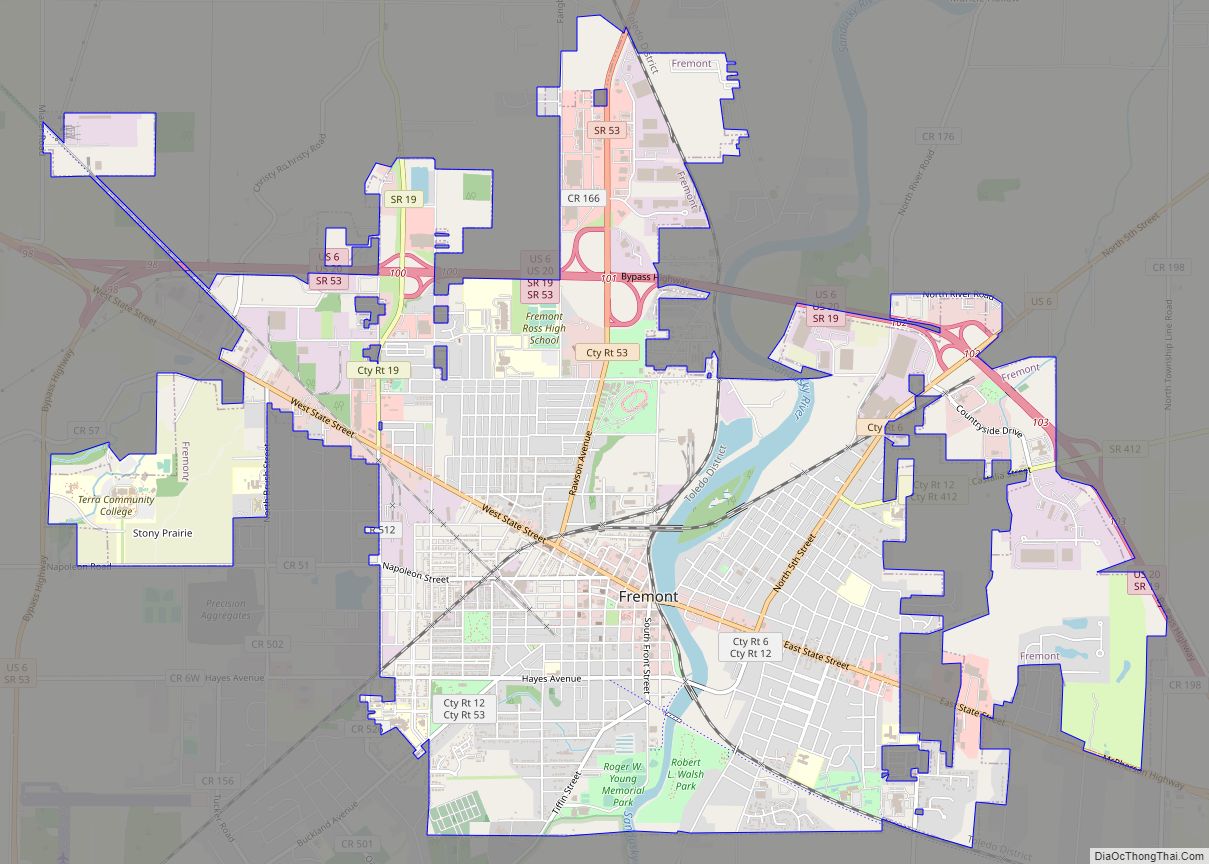
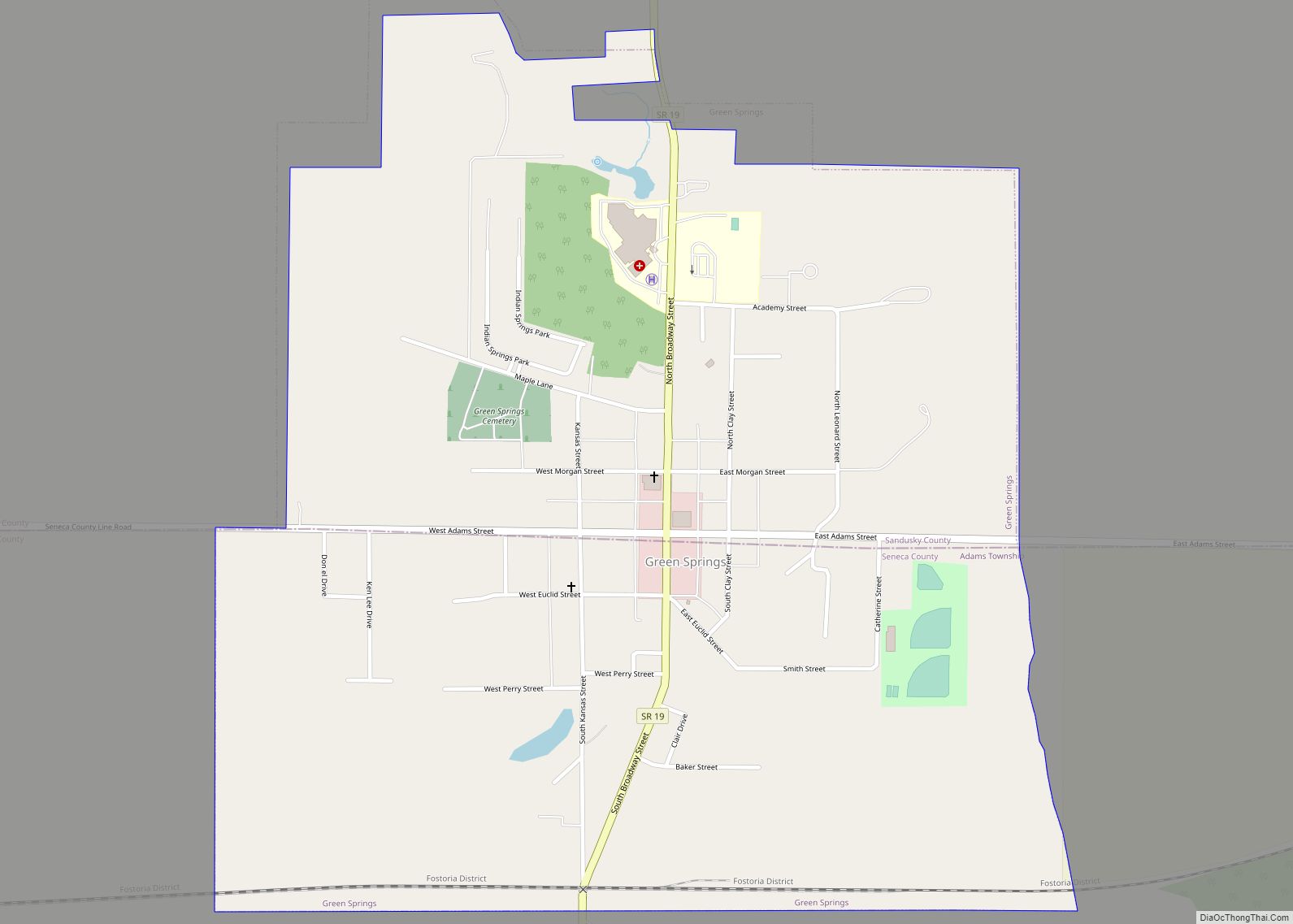
Fremont is a city in and the county seat of Sandusky County, Ohio, United States, located along the banks of the Sandusky River. It is about 35 miles (56 km) from Toledo and 25 miles (40 km) from Sandusky. It is part of the Toledo metropolitan area. The population was 15,930 at the 2020 census.
The city was the home of Rutherford B. Hayes, who served as President of the United States from 1877 to 1881. The Rutherford B. Hayes Presidential Center was the first presidential library and is one of the focal points of the city. The National Arbor Day Foundation has designated Fremont as a Tree City USA since 1986.
| Name: | Fremont city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Ohio |
| County: | Sandusky County |
| Elevation: | 627 ft (191 m) |
| Total Area: | 8.74 sq mi (22.64 km²) |
| Land Area: | 8.52 sq mi (22.07 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.22 sq mi (0.57 km²) |
| Total Population: | 15,930 |
| Population Density: | 1,869.28/sq mi (721.70/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 43420 |
| Area code: | 419, 567 |
| FIPS code: | 3928826 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1040674 |
| Website: | www.fremontohio.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
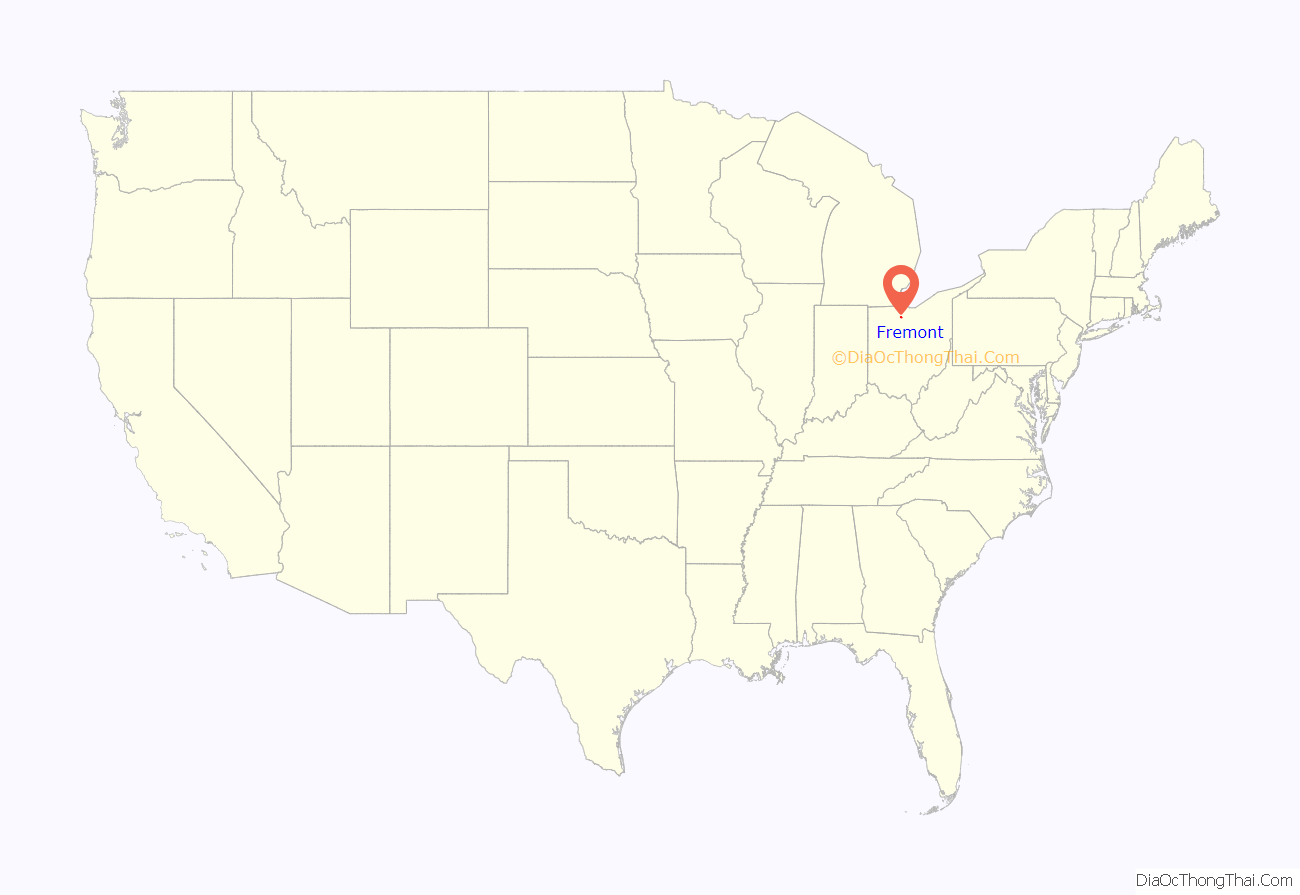
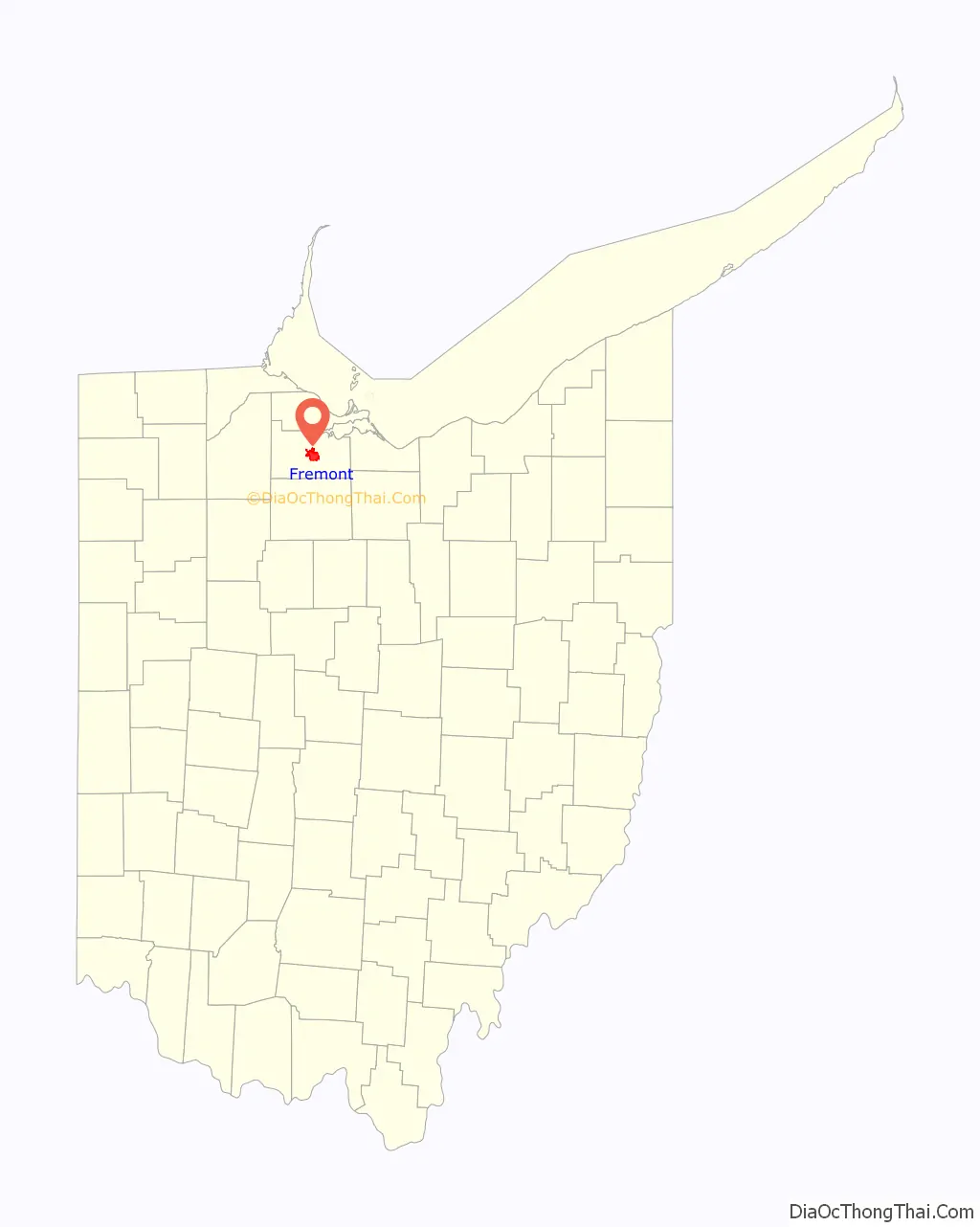
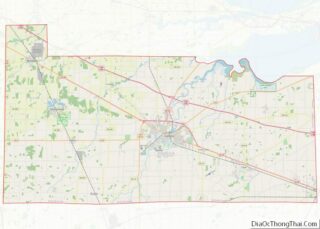
Fremont location map. Where is Fremont city?
History
Fremont is located on the former site of Junquindundeh, an historic Wyandot village on the west bank of the lower Sandusky River, near the falls and about 15 miles (24 km) upstream from its mouth at Sandusky Bay. French merchants established a trading post there in the 1750s, but British forces took over the trading post and rest of the area after their victory in the French and Indian War.
In 1787, the newly independent United States created the Northwest Territory to include all land west of the Ohio River. In 1803 the southeastern portion of the Northwest Territory was admitted to the Union as the new state of Ohio. Under the terms of Ohio’s statehood, the area of Lower Sandusky was defined as Indian Territory. American settlers who entered the area were in violation of the 1795 Treaty of Greenville, which was meant to preserve at least some land for the Native Americans. During the War of 1812 the United States Army considered removing by force the white settlers who were violating the Treaty of Greenville, but they did not carry out the threat.
Tensions with Great Britain increased in the early 1800s, and the United States government declared a boycott on all trade with the British, including those in Canada. The U.S. Army built Fort Sandusky near the river to protect an important supply depot. The post’s name was changed to Fort Stephenson during the War of 1812. In August 1813, British forces attacked and the Battle of Fort Stephenson took place. Major George Croghan and his U.S. Army garrison successfully fought off the invaders.
With the return of peace, a settlement grew up around the fort and became known as Lower Sandusky, since it was located on the lower part of the Sandusky River. In 1821 Lower Sandusky was designated as the county seat of Sandusky County. The town gradually increased in size, with the primary occupations being shipbuilding, fishing, and agricultural processing. Sandusky Bay leads to Lake Erie, and there was good fishing for walleye in the river, which return annually to spawn upriver. By the 1830s, the population included more white settlers, despite the area being a declared reserve only for Native Americans. Numerous Wyandot people still lived in the area, and some runaway African American slaves had made it their home after reaching safety in the free state of Ohio. The city had grain and sawmills, and the first sugar mill in Ohio.
In 1849 the residents changed the name of Lower Sandusky to Fremont, to honor John C. Frémont, who helped acquire California during the Mexican–American War.
In 1873, a few years before gaining national office, future president Rutherford B. Hayes moved into a family mansion in Fremont called Spiegel Grove, which was built by his late maternal uncle. That year Hayes announced his uncle Sardis Birchard’s bequest in his will, donating property in his estate worth $50,000 to the City Council in order to establish a public library. It opened the following year on Front Street. A few years later, a new building was constructed for it in 1878 on the grounds of the Fort Stephenson State Park, per his bequest. It is now known as the Birchard Public Library of Sandusky County. Spiegel Grove was incorporated into the Rutherford B. Hayes Presidential Center, founded in 1916 as the first presidential library in the United States.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Fremont became a major center for the production of cutlery, with several manufacturing plants, as well as other industries. The cutlery industry has declined, but the city still has a large Heinz plant for producing ketchup.
Commemoration of Battle of Fort Stephenson
The city set aside Fort Stephenson Park to preserve and commemorate the site of the fort that had a role in the War of 1812. Only its stone foundations are still visible. In 1885 the Sandusky County Soldiers Monument was installed in the park near Croghan Street, which was named after the commanding major of the fort. (He was promoted to colonel afterward for his success.) Former president Rutherford B. Hayes attended the ceremony.
In 1906 Colonel Croghan’s remains were brought from his hometown in Kentucky to Fremont and reinterred under the Soldiers Monument. In the same ceremony, the Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) unveiled a plaque to the Soldiers Monument to commemorate Croghan and his garrison in their victory in the Battle of Fort Stephenson.
What is now the main building of the Birchard Public Library, which serves the entire county, was constructed in 1878 in Fort Stephenson Park, by the terms of the bequest from Sardis Birchard, who bequeathed $50,000 in assets to endow a public library in 1873. The first facility opened in 1874 in a building on Front Street.
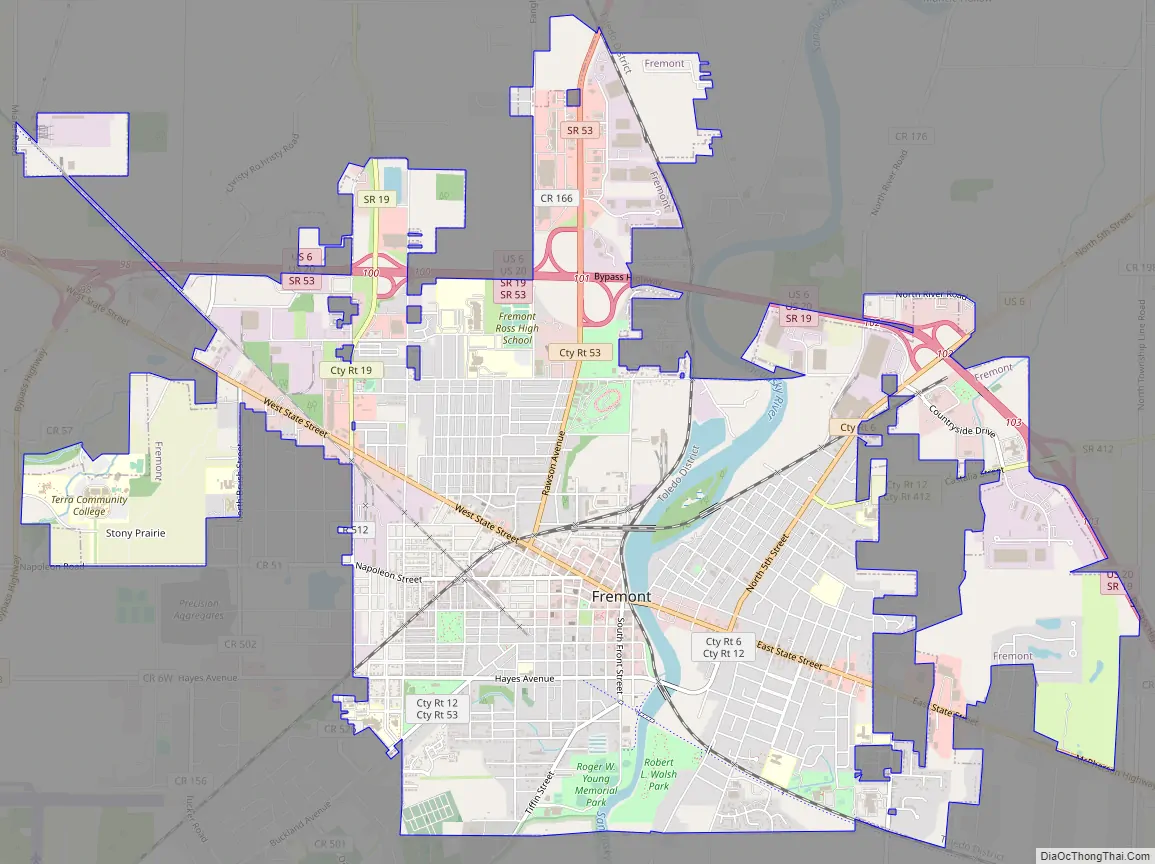
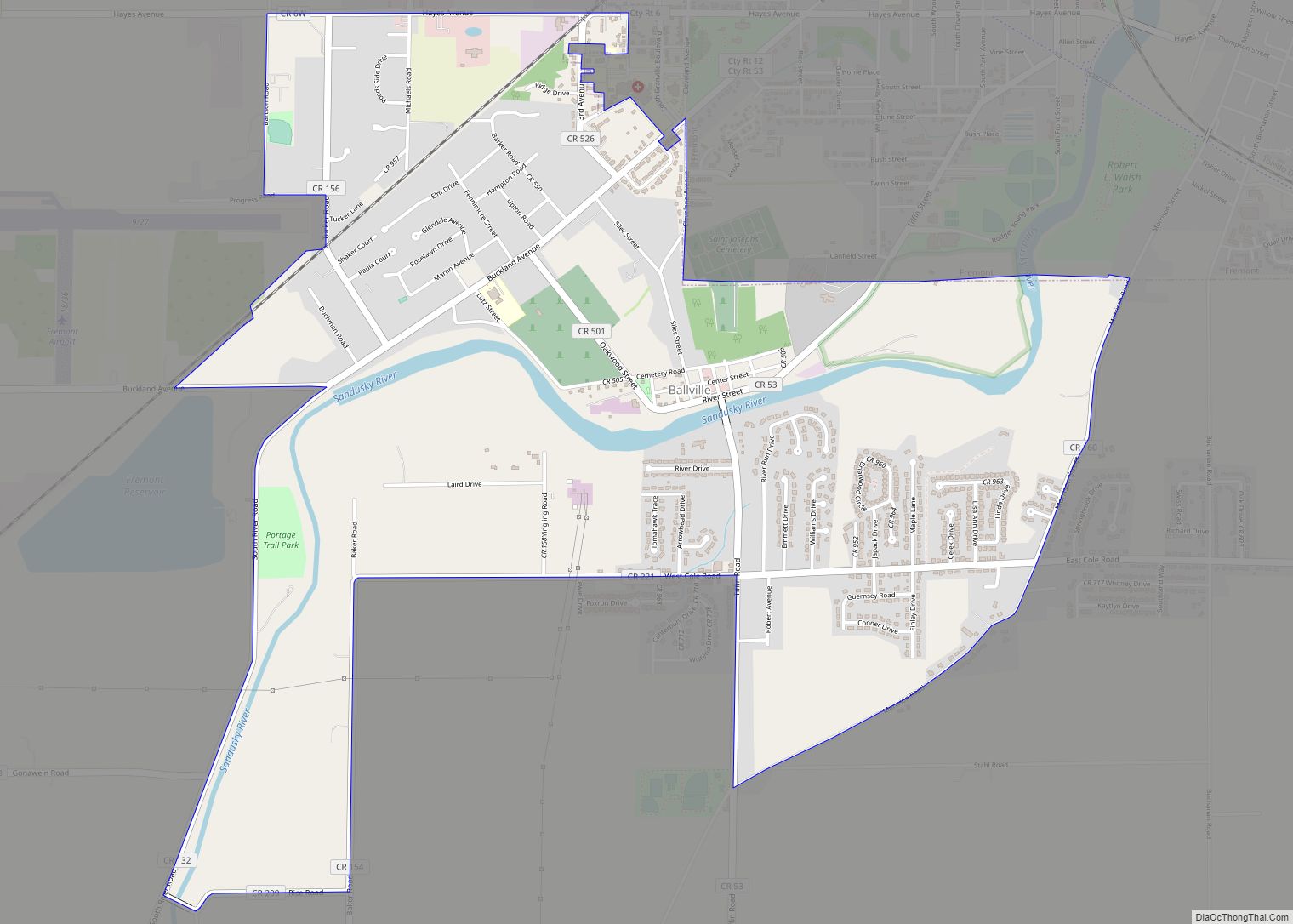
Fremont Road Map
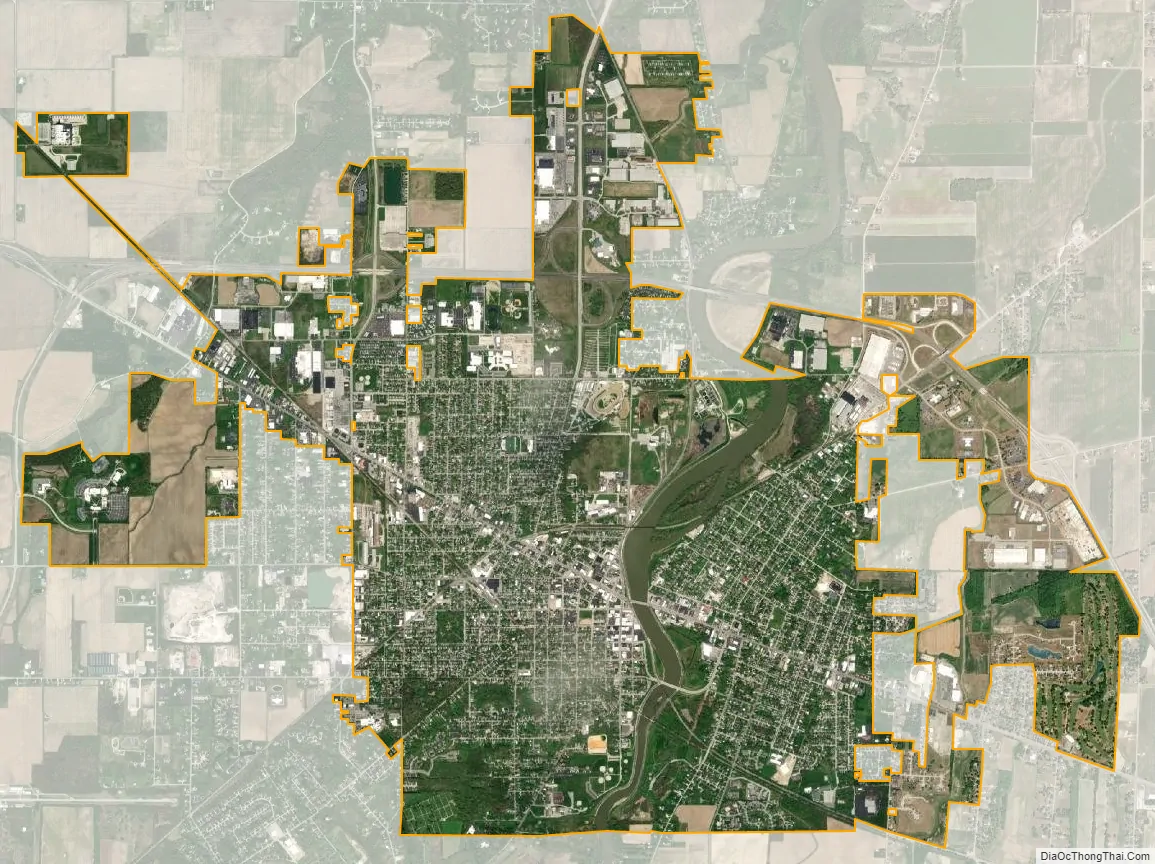
Fremont city Satellite Map
Geography
Fremont is located on both sides of the Sandusky River.
The city has a total area of 8.57 square miles (22.20 km), of which 8.35 square miles (21.63 km) is land and 0.22 square miles (0.57 km) is water.
Climate
See also
Map of Ohio State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Allen
- Ashland
- Ashtabula
- Athens
- Auglaize
- Belmont
- Brown
- Butler
- Carroll
- Champaign
- Clark
- Clermont
- Clinton
- Columbiana
- Coshocton
- Crawford
- Cuyahoga
- Darke
- Defiance
- Delaware
- Erie
- Fairfield
- Fayette
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Gallia
- Geauga
- Greene
- Guernsey
- Hamilton
- Hancock
- Hardin
- Harrison
- Henry
- Highland
- Hocking
- Holmes
- Huron
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Knox
- Lake
- Lake Erie
- Lawrence
- Licking
- Logan
- Lorain
- Lucas
- Madison
- Mahoning
- Marion
- Medina
- Meigs
- Mercer
- Miami
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Morgan
- Morrow
- Muskingum
- Noble
- Ottawa
- Paulding
- Perry
- Pickaway
- Pike
- Portage
- Preble
- Putnam
- Richland
- Ross
- Sandusky
- Scioto
- Seneca
- Shelby
- Stark
- Summit
- Trumbull
- Tuscarawas
- Union
- Van Wert
- Vinton
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Williams
- Wood
- Wyandot
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming