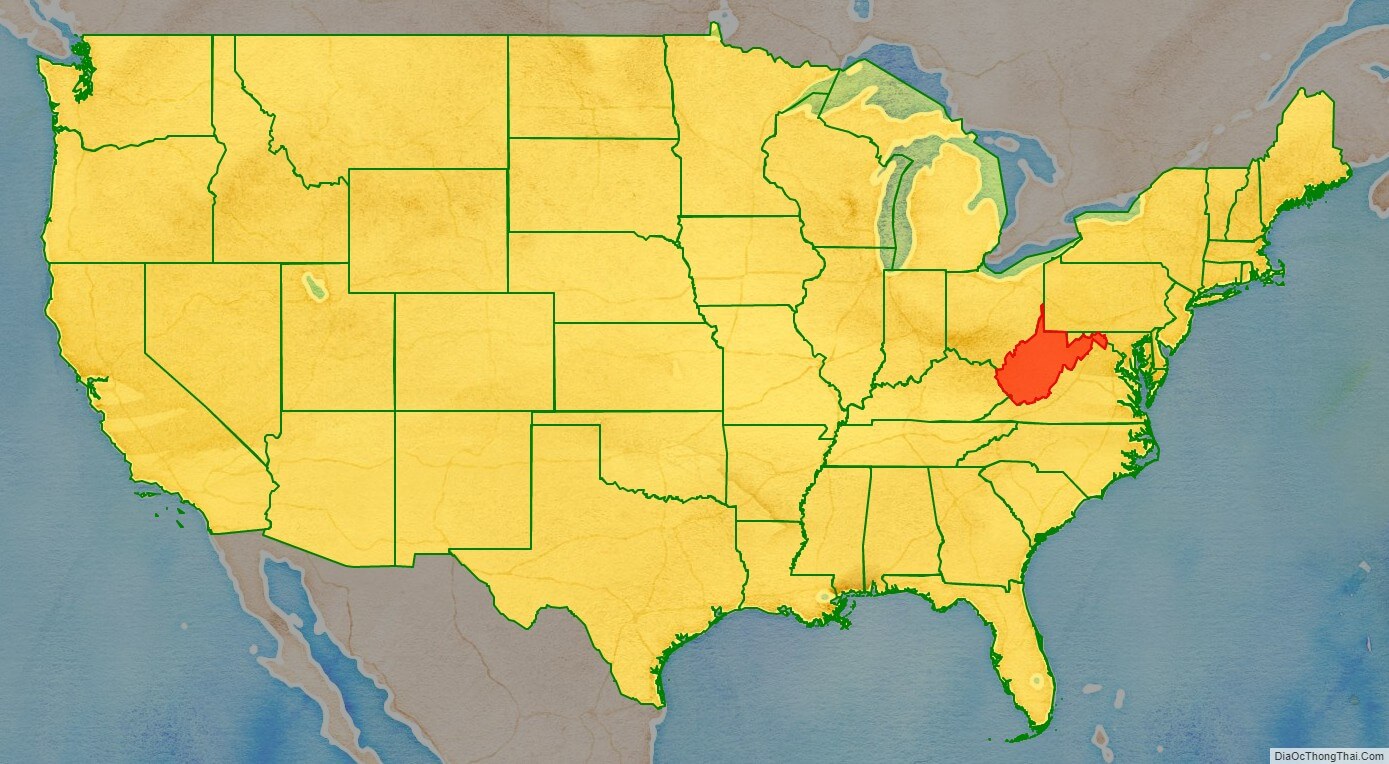
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered by Pennsylvania to the north and east, Maryland to the east and northeast, Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, and Ohio to the northwest. West Virginia is the 10th-smallest state by area and ranks as the 12th-least populous state, with a population of 1,793,716 residents. The capital and largest city is Charleston.
West Virginia was admitted to the Union on June 20, 1863, and was a key border state during the American Civil War. It was the only state to form by separating from a Confederate state, one of two states (along with Nevada) admitted to the Union during the Civil War, and the second state to separate from another state, after Maine separated from Massachusetts in 1820. Some of its residents held slaves, but most were yeoman farmers, and the delegates provided for the gradual abolition of slavery in the new state constitution. The state legislature abolished slavery in the state, and at the same time ratified the 13th Amendment abolishing slavery nationally on February 3, 1865.
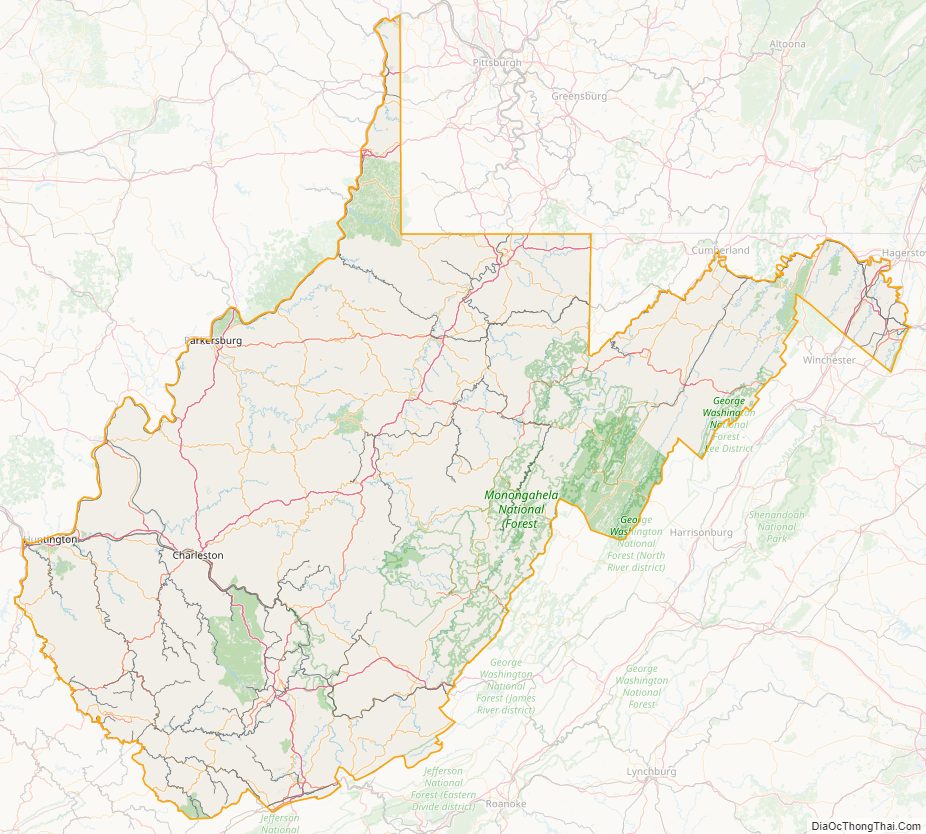
West Virginia’s Northern Panhandle extends adjacent to Pennsylvania and Ohio to form a tristate area, with Wheeling and Weirton just across the border from the Pittsburgh metropolitan area. Huntington in the southwest is close to Ohio and Kentucky, while Martinsburg and Harpers Ferry in the Eastern Panhandle region are considered part of the Washington metropolitan area, between Maryland and Virginia. West Virginia is often included in several U.S. geographical regions, including the Mid-Atlantic, the Upland South, and the Southeastern United States. It is the only state entirely within the area served by the Appalachian Regional Commission; the area is commonly defined as “Appalachia”.
The state is noted for its mountains and rolling hills, its historically significant coal mining and logging industries, and its political and labor history. It is also known for a wide range of outdoor recreational opportunities, including skiing, whitewater rafting, fishing, hiking, backpacking, mountain biking, rock climbing, and hunting. From the Great Depression to the 1990s, the state voted heavily for the Democratic Party due to its tradition of union-based politics. Since then, the state has become heavily Republican, and is considered a “deep red” state at the federal level.
Other nominated names for the state included Vandalia, Kanawha, Appalachia, and Western Virginia. The capital was originally Wheeling, before switching to Charleston, moving back to Wheeling, and finally back to Charleston. The first governor was Arthur Boreman.
| Before statehood: | Part of Virginia |
|---|---|
| Admitted to the Union: | June 20, 1863; 159 years ago (1863-06-20) (35th) |
| Capital: | Charleston |
| Capital – largest city: | largest city |
| Largest metro and urban areas: | Charleston–Huntington (combined) Huntington (metro and urban) |
| Elevation: | 1,513 ft (461 m) |
| Total Area: | 24,230 sq mi (62,755 km) |
| Area Rank: | 41st |
| Total Population: | 1,793,716 |
| Population Rank: | 39th |
| Population Density: | 77/sq mi (29.8/km) |
| Population Density Rank: | 29th |
| Median Household Income: | $43,469 |
| Income Rank: | 49th |
| Demonym(s): | West Virginian, Mountaineer |
| USPS abbreviation: | WV |
| ISO 3166 code: | US-WV |
| Website: | wv.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
West Virginia location map. Where is West Virginia state?
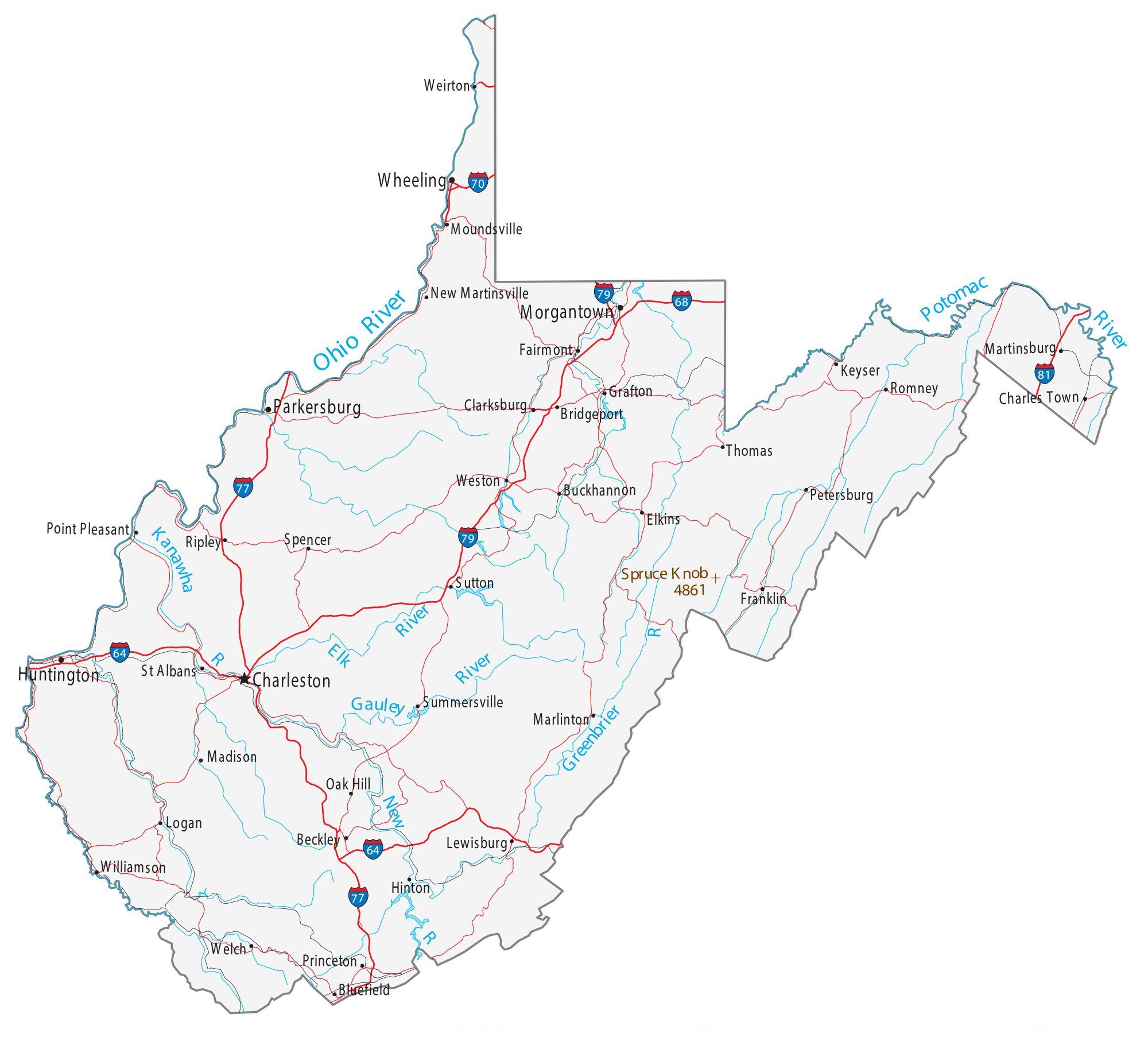
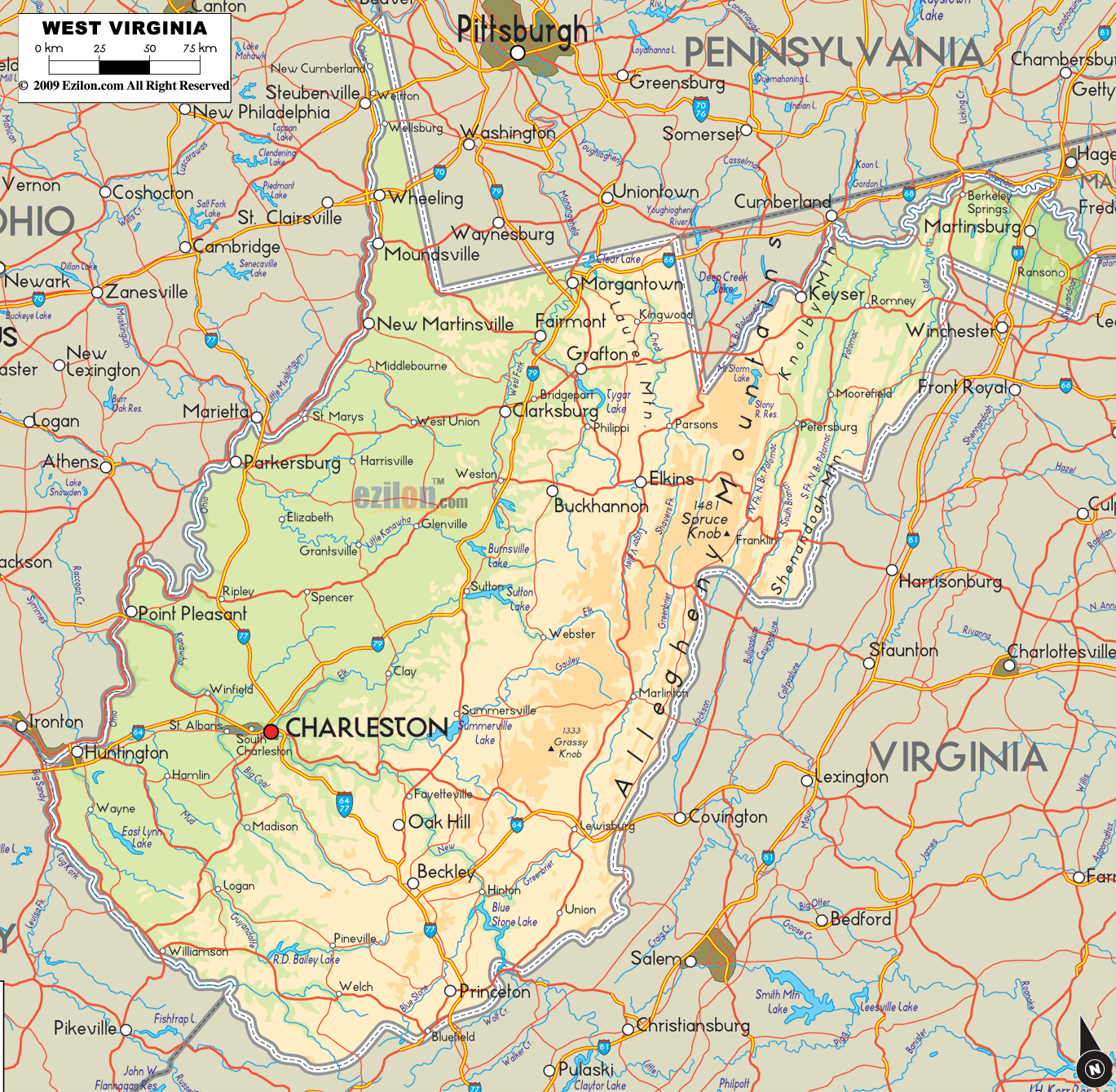
West Virginia Road Map
West Virginia Map – Roads & Cities
West Virginia Street Map
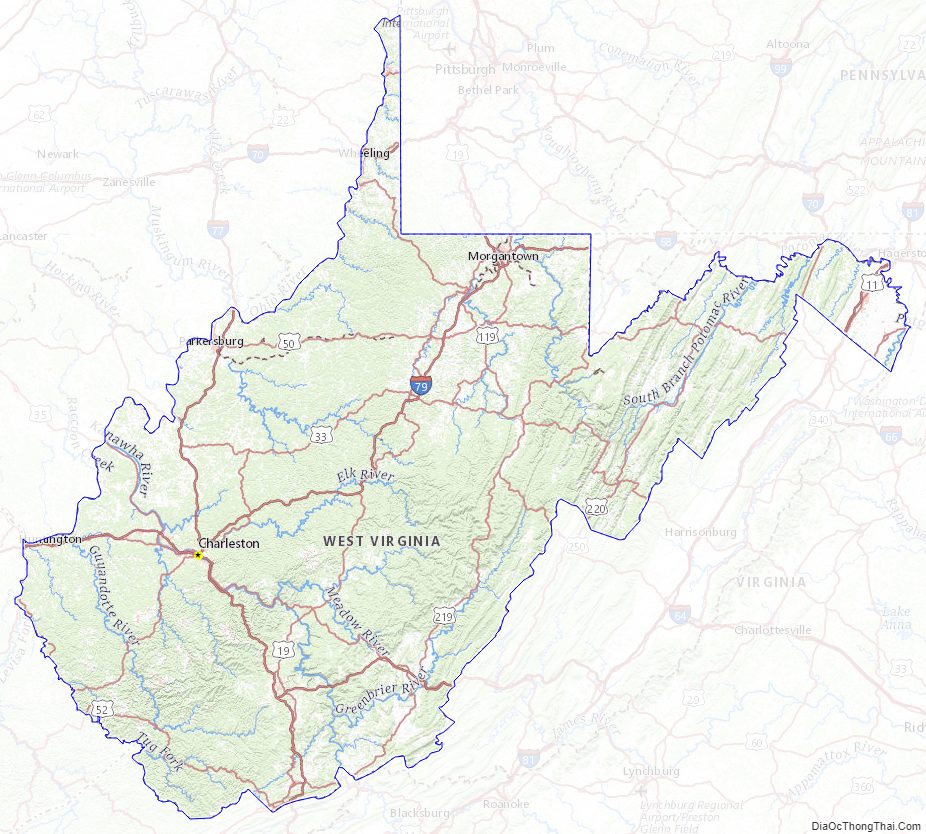
West Virginia State Map – Places and Landmarks
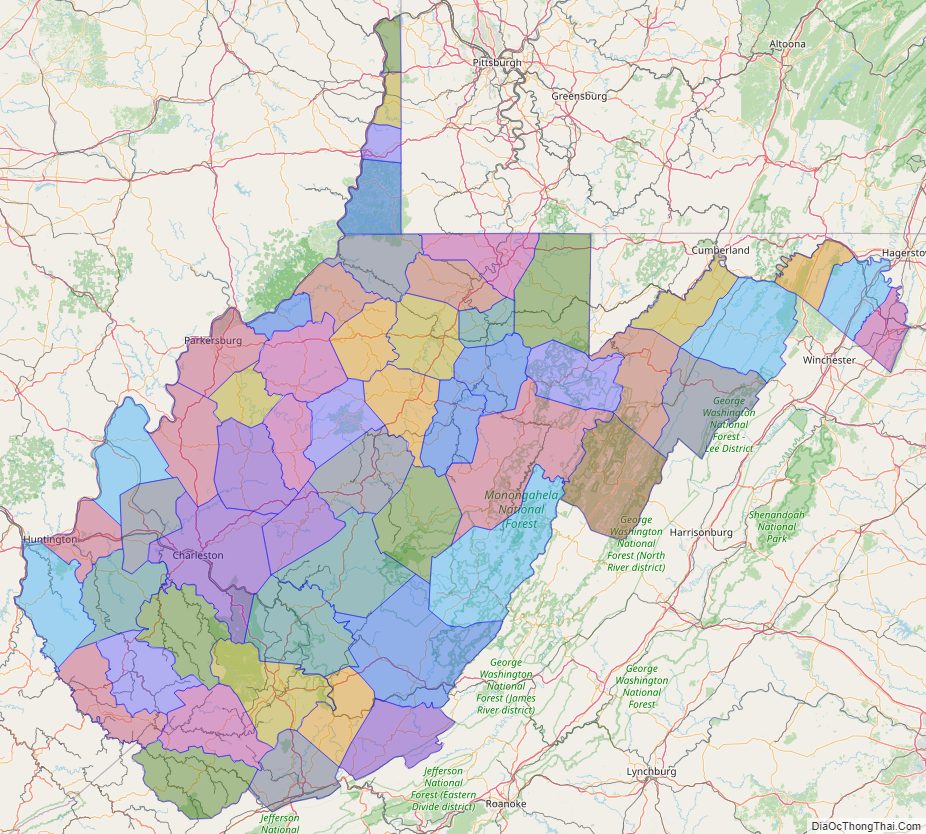
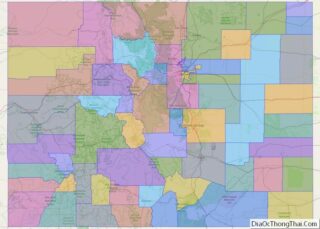
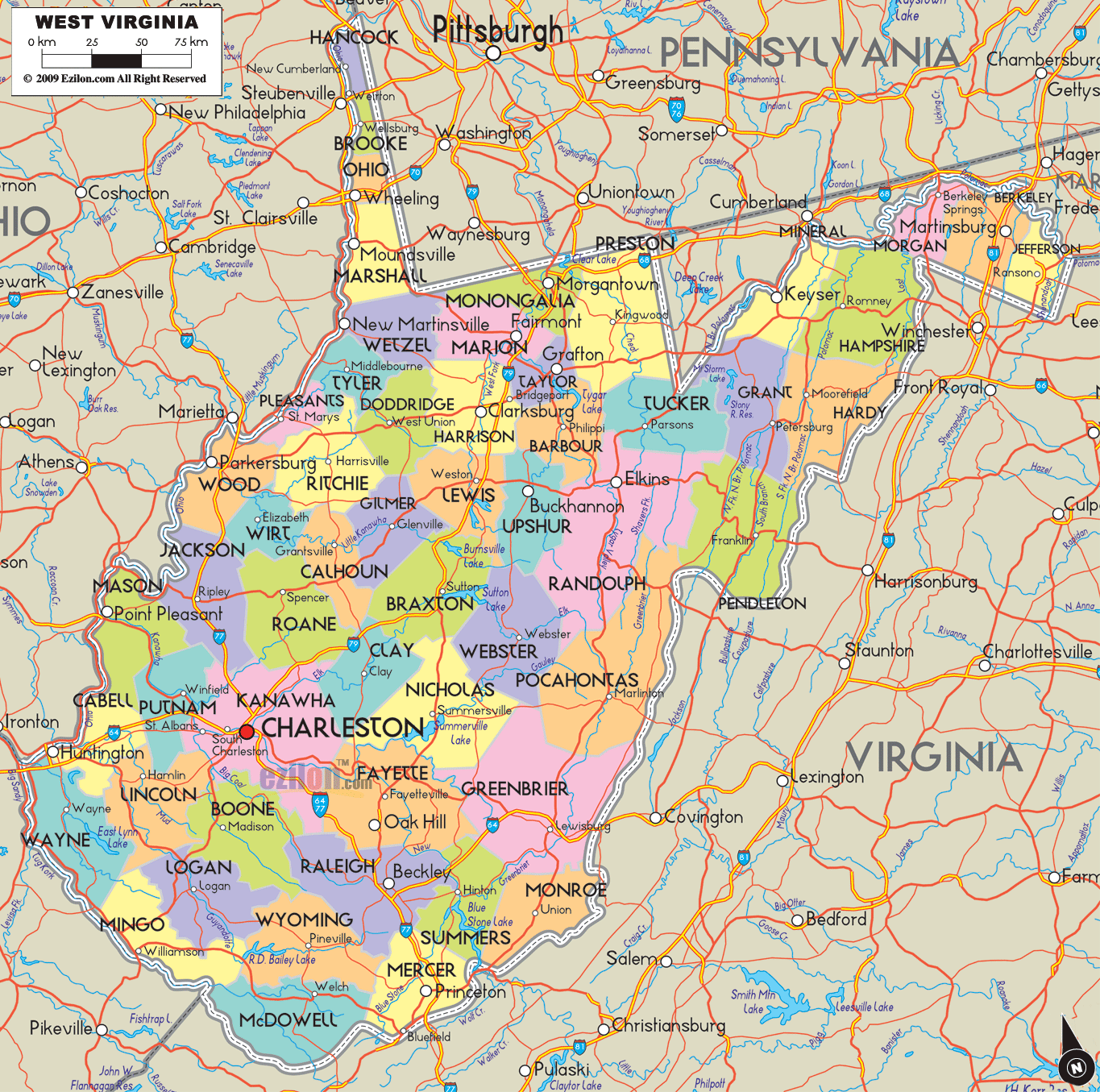
West Virginia Political Map
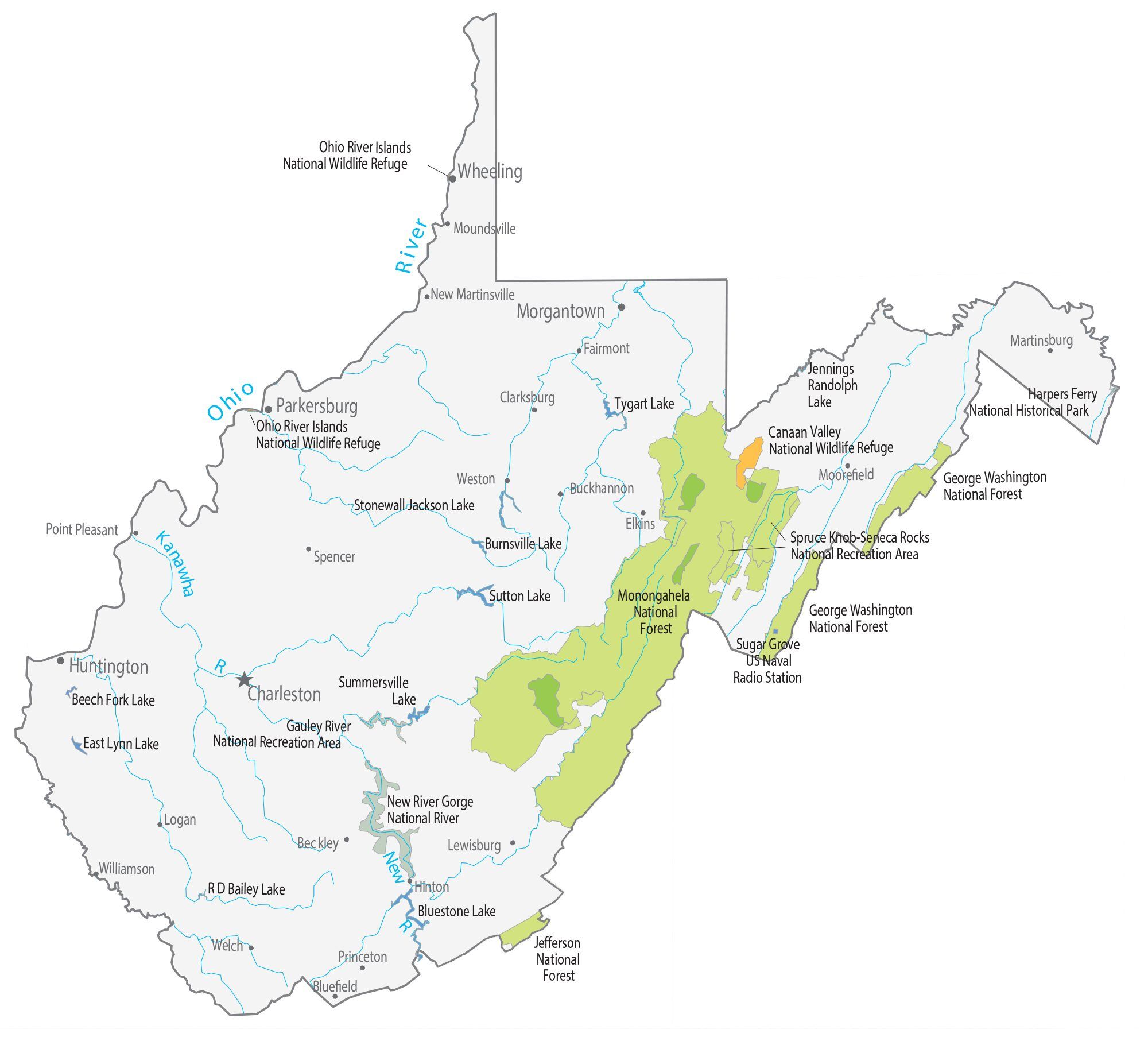
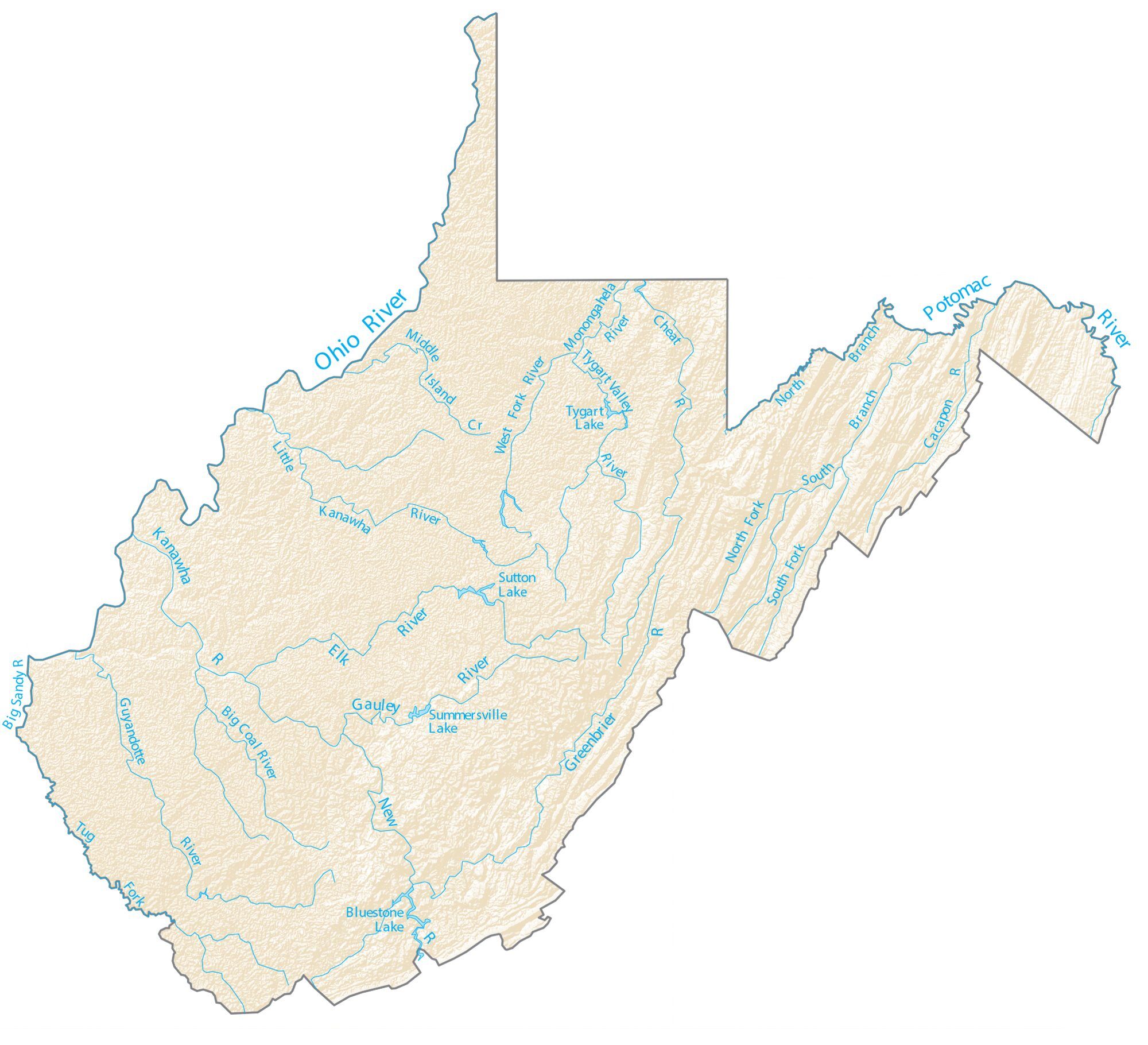
West Virginia Lakes and Rivers Map
Geography
Located in the Appalachian Mountain range, West Virginia covers an area of 24,229.76 square miles (62,754.8 km), with 24,077.73 square miles (62,361.0 km) of land and 152.03 square miles (393.8 km) of water, making it the 41st-largest state in the United States. West Virginia borders Pennsylvania and Maryland in the northeast, Virginia in the southeast, Ohio in the northwest, and Kentucky in the southwest. Its longest border is with Virginia at 381 miles (613 km), followed by Ohio at 243 miles (391 km), Maryland at 174 miles (280 km), Pennsylvania at 118 miles (190 km), and Kentucky at 79 miles (127 km).
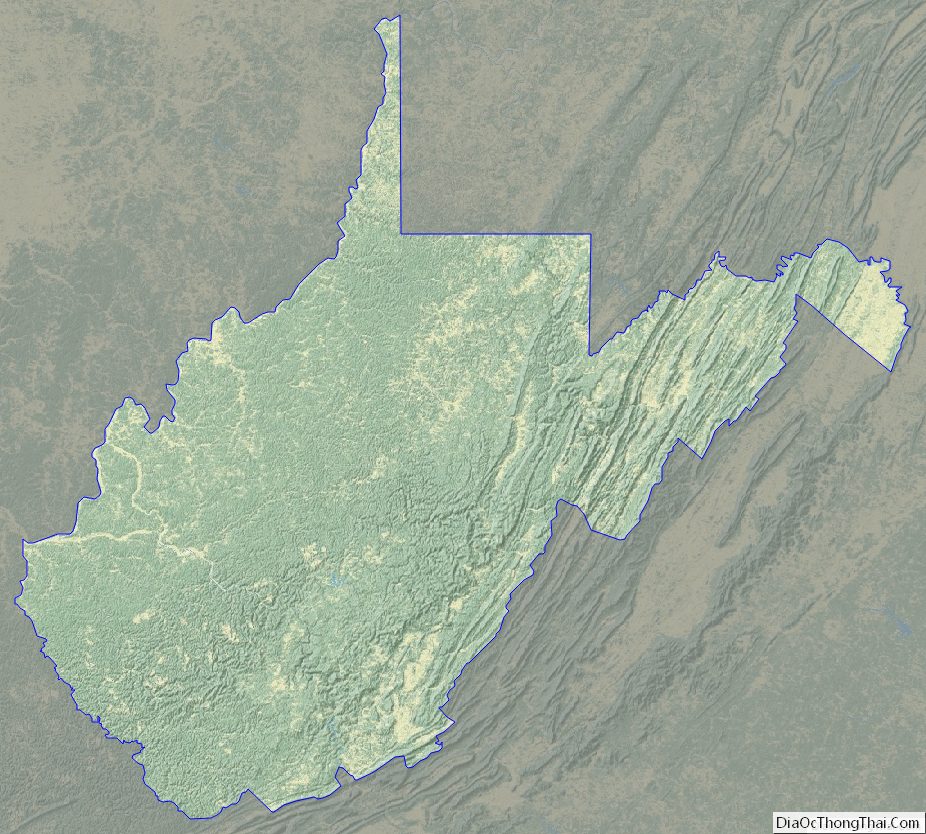
Geology and terrain
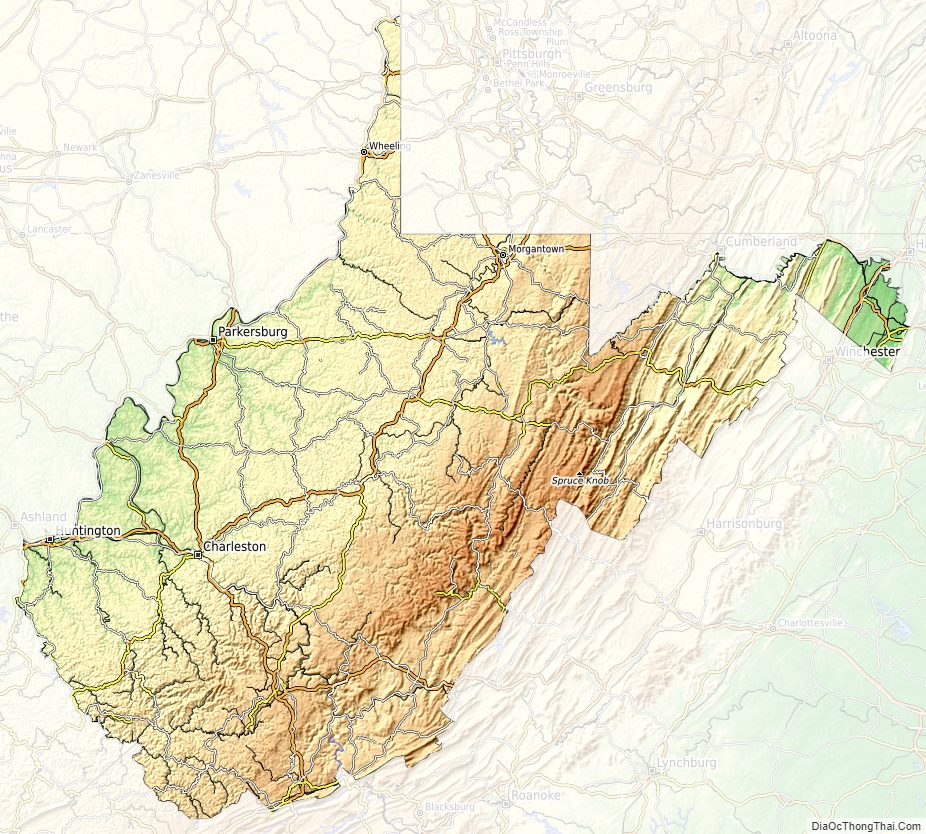
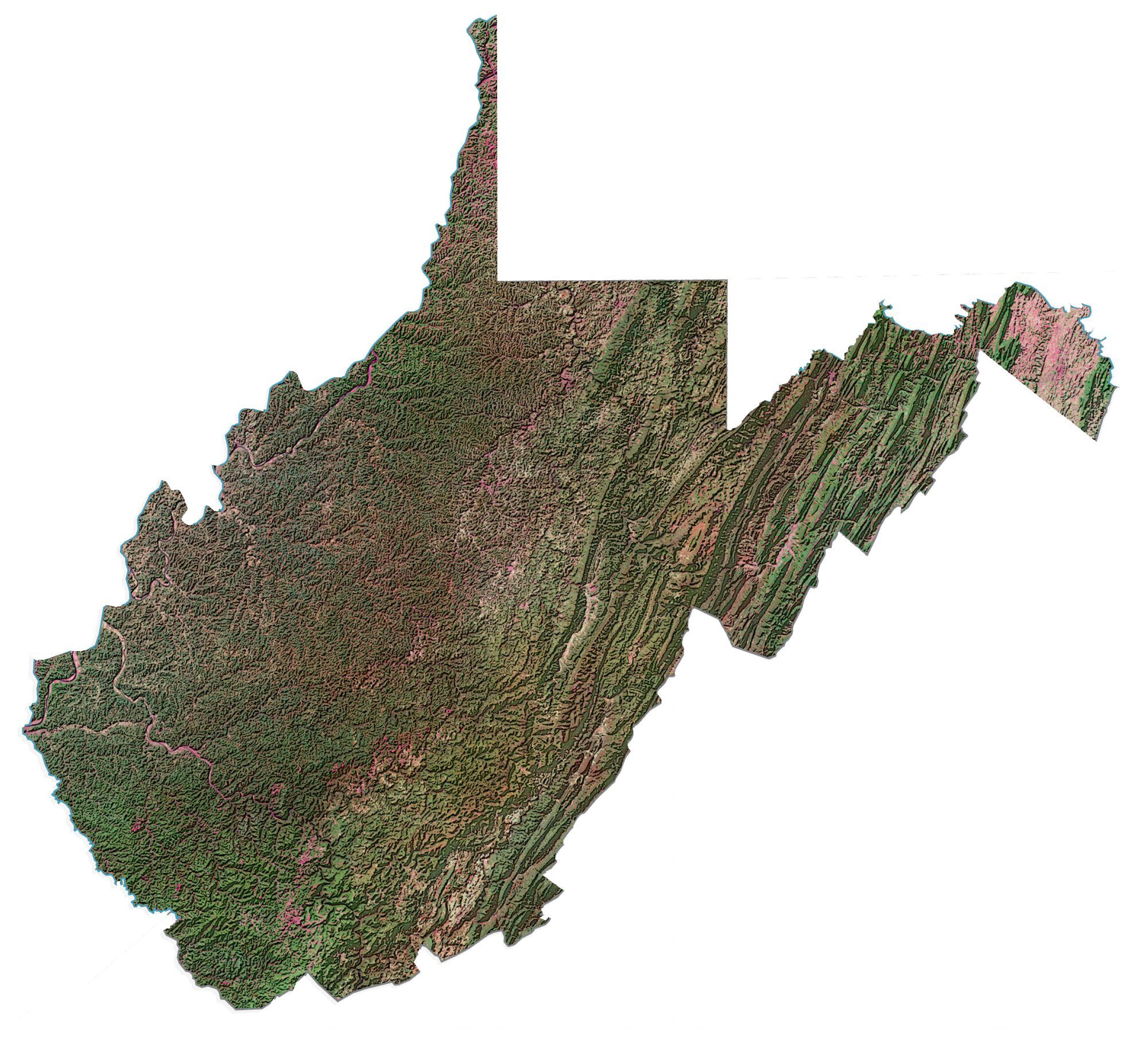
West Virginia is located entirely within the Appalachian Region, and the state is almost entirely mountainous, giving the reason for the nickname The Mountain State and the motto Montani Semper Liberi (“Mountaineers are always free”). The elevations and ruggedness drop near large rivers like the Ohio River or Shenandoah River. About 75% of the state is within the Cumberland Plateau and Allegheny Plateau regions. Though the relief is not high, the plateau region is extremely rugged in most areas. The average elevation of West Virginia is approximately 1,500 feet (460 m) above sea level, which is the highest of any U.S. state east of the Mississippi River.
On the eastern state line with Virginia, high peaks in the Monongahela National Forest region give rise to an island of colder climate and ecosystems similar to those of northern New England and eastern Canada. The highest point in the state is atop Spruce Knob, at 4,863 feet (1,482 m), and is covered in a boreal forest of dense spruce trees at altitudes above 4,000 feet (1,200 m). Spruce Knob lies within the Monongahela National Forest and is a part of the Spruce Knob–Seneca Rocks National Recreation Area. A total of six wilderness areas can also be found within the forest. Outside the forest to the south, the New River Gorge is a canyon 1,000 feet (300 m) deep, carved by the New River. The National Park Service manages a portion of the gorge and river that has been designated as the New River Gorge National Park and Preserve.
Other areas under protection and management include:
Most of West Virginia lies within the Appalachian mixed mesophytic forests ecoregion, while the higher elevations along the eastern border and in the panhandle lie within the Appalachian–Blue Ridge forests. The native vegetation for most of the state was originally mixed hardwood forest of oak, chestnut, maple, beech, and white pine, with willow and American sycamore along the state’s waterways. Many of the areas are rich in biodiversity and scenic beauty, a fact appreciated by native West Virginians, who refer to their home as Almost Heaven (from the song “Take Me Home, Country Roads” by John Denver). Before the song, it was known as “The Cog State” (Coal, Oil, and Gas) or “The Mountain State”.
The underlying rock strata are sandstone, shale, bituminous coal beds, and limestone laid down in a near-shore environment from sediments derived from mountains to the east, in a shallow inland sea on the west. Some beds illustrate a coastal swamp environment, some river delta, and some shallow water. Sea level rose and fell many times during the Mississippian and Pennsylvanian eras, giving a variety of rock strata. The Appalachian Mountains are some of the oldest on earth, having formed more than three hundred million years ago.
Climate
The climate of West Virginia is generally a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa, except Dfb at the higher elevations) with warm to hot, humid summers and chilly winters, increasing in severity with elevation. Some southern highland areas also have a mountain temperate climate (Köppen Cfb) where winter temperatures are more moderate and summer temperatures are somewhat cooler. However, the weather is subject in all parts of the state to change. The hardiness zones range from zone 5b in the central Appalachian mountains to zone 7a in the warmest parts of the lowest elevations.
In the Eastern Panhandle and the Ohio River Valley, temperatures are warm enough to see and grow subtropical plants such as southern magnolia (Magnolia grandiflora), crepe myrtle, Albizia julibrissin, American sweetgum and even the occasional needle palm and sabal minor. These plants do not thrive as well in other parts of the state. The eastern prickly pear grows well in many portions of the state.
Average January temperatures range from around 26 °F (−4 °C) near the Cheat River to 41 °F (5 °C) along sections of the border with Kentucky. July averages range from 67 °F (19 °C) along the North Branch Potomac River to 76 °F (24 °C) in the western part of the state. It is cooler in the mountains than in the lower sections of the state. The highest recorded temperature in the state is 112 °F (44 °C) at Martinsburg on July 10, 1936, and the lowest recorded temperature in the state is −37 °F (−38 °C) at Lewisburg on December 30, 1917.
Annual precipitation ranges from less than 32 inches (810 mm) in the lower eastern section to more than 56 inches (1,400 mm) in higher parts of the Allegheny Front. Valleys in the east have lower rainfall because the Allegheny mountain ridges to the west create a partial rain shadow. Slightly more than half the rainfall occurs from April to September. Dense fogs are common in many valleys of the Kanawha section, especially the Tygart Valley. West Virginia is also one of the cloudiest states in the nation, with the cities of Elkins and Beckley ranking 9th and 10th in the U.S. respectively for the number of cloudy days per year (over 210). In addition to persistent cloudy skies caused by the damming of moisture by the Alleghenies, West Virginia also experiences some of the most frequent precipitation in the nation, with Snowshoe averaging nearly 200 days a year with either rain or snow. Snow usually lasts only a few days in the lower sections but may persist for weeks in the higher mountain areas. An average of 34 inches (860 mm) of snow falls annually in Charleston, although during the winter of 1995–1996 more than three times that amount fell as several cities in the state established new records for snowfall. Average snowfall in the Allegheny Highlands can range up to 180 inches (4,600 mm) per year. Severe weather is somewhat less prevalent in West Virginia than in most other eastern states, and it ranks among the least tornado-prone states east of the Rockies.
Adjacent states
- Pennsylvania (North)
- Maryland (Northeast)
- Kentucky (Southwest)
- Virginia (East)
- Ohio (West)
Flora and fauna
West Virginia Physical Map
West Virginia Topographic Map
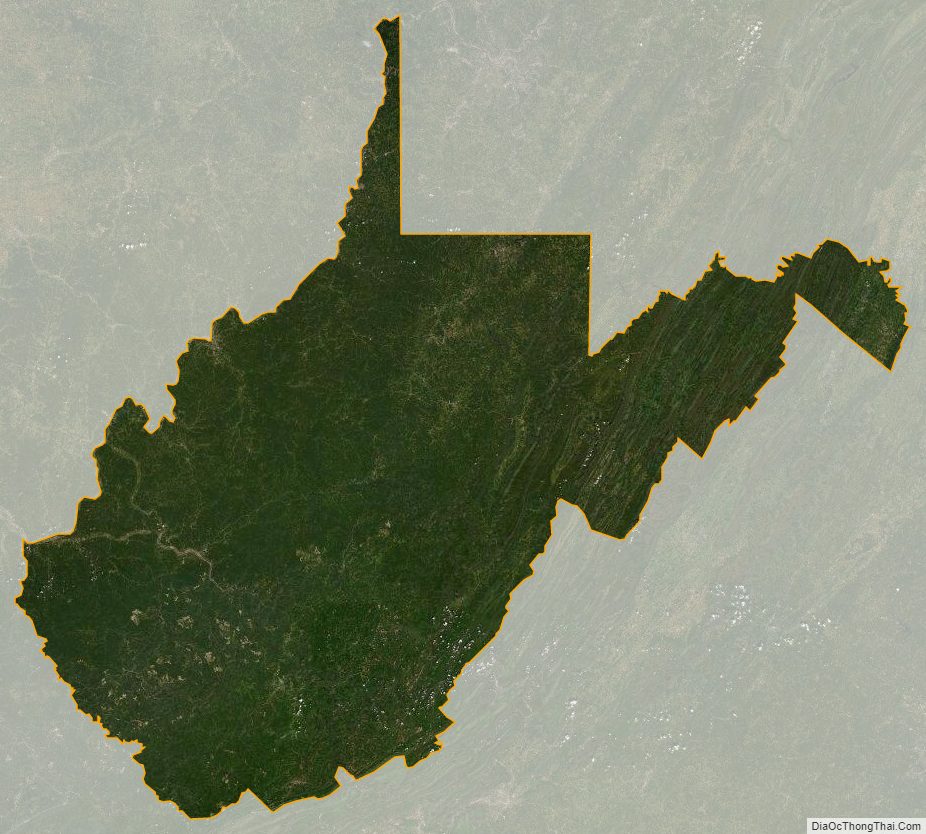
West Virginia Satellite Map
Others printable maps
West Virginia Outline Map
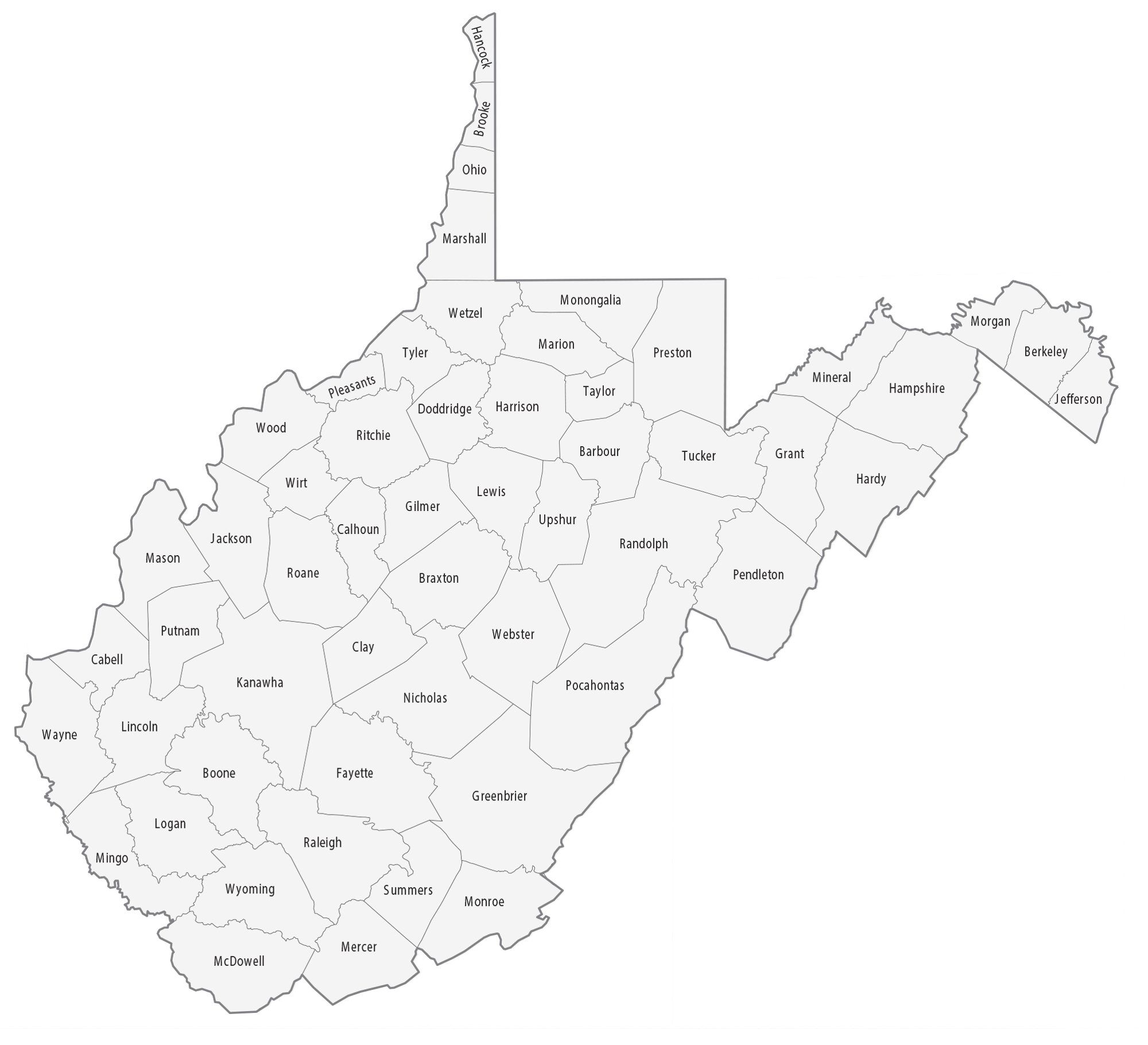
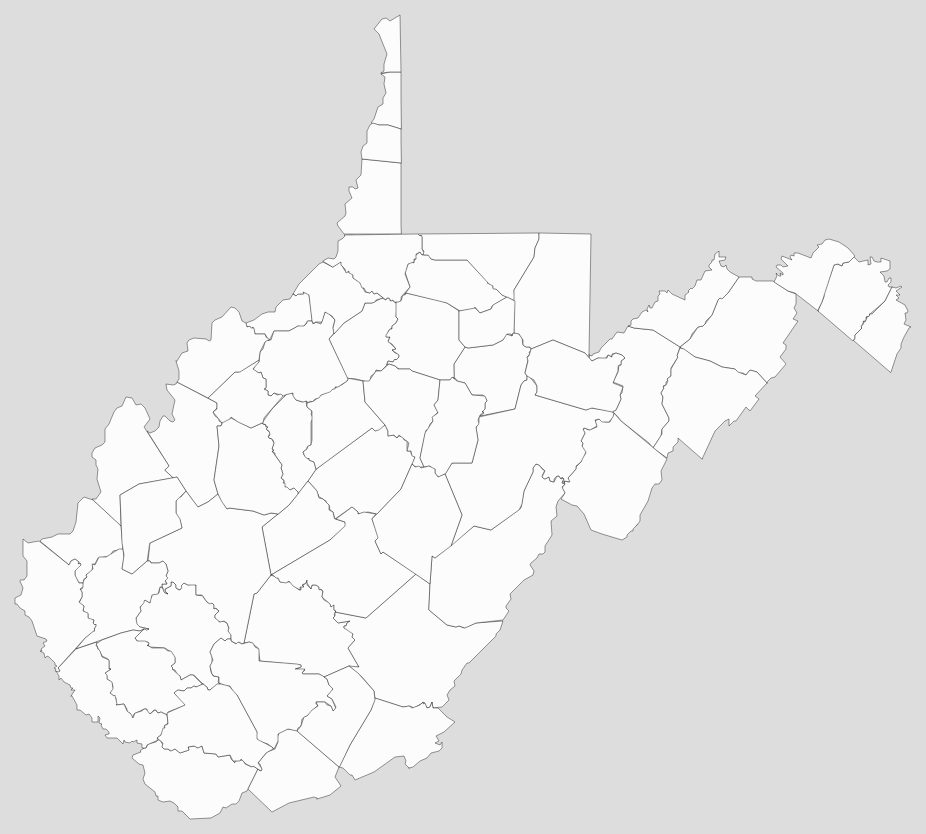
Blank West Virginia County Map
See also
Map of West Virginia State and its subdivision:- Barbour
- Berkeley
- Boone
- Braxton
- Brooke
- Cabell
- Calhoun
- Clay
- Doddridge
- Fayette
- Gilmer
- Grant
- Greenbrier
- Hampshire
- Hancock
- Hardy
- Harrison
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Kanawha
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Marion
- Marshall
- Mason
- McDowell
- Mercer
- Mineral
- Mingo
- Monongalia
- Monroe
- Morgan
- Nicholas
- Ohio
- Pendleton
- Pleasants
- Pocahontas
- Preston
- Putnam
- Raleigh
- Randolph
- Ritchie
- Roane
- Summers
- Taylor
- Tucker
- Tyler
- Upshur
- Wayne
- Webster
- Wetzel
- Wirt
- Wood
- Wyoming
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming