Charleston is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of West Virginia and the seat of Kanawha County. Located at the confluence of the Elk and Kanawha rivers, the city had a population of 48,864 at the 2020 census and an estimated population of 48,018 in 2021. The Charleston metropolitan area as a whole had an estimated 255,020 residents in 2021.
The first permanent settlement, Fort Morris, was built in fall 1773 by William Morris prior to Lord Dunmore’s War, and was used extensively during the American Revolution. The town of Charleston was incorporated by the Virginia House of Delegates in 1794 with the trustees being William Morris, Leonard Morris, and Daniel Boone. Early industries important to Charleston included salt and the first natural gas well. Later, coal became central to economic prosperity in the city and the surrounding area. Today, trade, utilities, government, medicine, and education play central roles in the city’s economy.
Charleston is the home of the Charleston Dirty Birds of the Atlantic League of Professional Baseball, and the annual 15-mile (24 km) Charleston Distance Run. Yeager Airport and the University of Charleston are in the city. West Virginia State University is in the local area as well as West Virginia University and Marshall University satellite campuses.
| Name: | Charleston city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | West Virginia |
| County: | Kanawha County |
| Founded: | 1788 |
| Incorporated: | 1794 |
| Elevation: | 597 ft (182 m) |
| Land Area: | 31.50 sq mi (81.59 km²) |
| Water Area: | 1.14 sq mi (2.95 km²) |
| Population Density: | 1,500/sq mi (580/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 25301, 25302, 25304, 25305, 25311, 25314, 25317, 25321-25339, 25350-25358, 25362, 25364, 25375, 25387, 25389, 25392, 25396 |
| Area code: | 304/681 |
| FIPS code: | 5414600 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1558347 |
| Website: | charlestonwv.gov |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Charleston location map. Where is Charleston city?
History
Establishment
After the American Revolutionary War, pioneers began making their way out from the early settlements. Many slowly migrated into the western part of Virginia. Capitalizing on its many resources made Charleston an important part of Virginia and West Virginia history. Today, Charleston is the largest city in the state and the state capital.
Charleston’s history goes back to the 18th century. Thomas Bullitt was deeded 1,250 acres (5 km) of land near the mouth of the Elk River in 1773. It was inherited by his brother, Cuthbert Bullitt, upon his death in 1778, and sold to Colonel George Clendenin in 1786. The first permanent settlement, Fort Lee, was built in 1787 by Colonel Savannah Clendenin and his company of Virginia Rangers. This structure occupied the area that is now the intersection of Brooks Street and Kanawha Boulevard. Historical conjecture indicates that Charleston is named after Col. Clendenin’s father, Charles. Six years later, in 1794, the Virginia General Assembly officially established Charlestown. On the 40 acres (160,000 m) that made up the town in 1794, 35 people inhabited seven houses.
Charleston is part of Kanawha County. The origin of the word Kanawha (pronounced “Ka-NAH-wah”), Ka(h)nawha, derives from the region’s Iroquoian dialects meaning “water way” or “Canoe Way” implying the metaphor, “transport way”, in the local language. It was and is the name of the river that flows through Charleston. The grammar of the “hard H” sound soon dropped out as new arrivals of various European languages developed West Virginia. The phrase has been a matter of Register (sociolinguistics). A two-story jail was the first county structure to be built, with the first floor literally dug into the bank of the Kanawha River.
Daniel Boone, who was commissioned a lieutenant colonel of the Kanawha County militia, was elected to serve in 1791 in the Virginia House of Delegates. As told in historical accounts, Boone walked all the way to Richmond, the state capital. Boone served alongside Major William Morris Jr at the House of Delegates representing Kanawha.
19th century growth
By the early 19th century, salt brines were discovered along the Kanawha River, and the first salt well was drilled in 1806. This created a prosperous time and great economic growth for the area. By 1808, 1,250 pounds of salt were being produced a day, and the Farmers’ Repository newspaper began publication. An area adjacent to Charleston, Kanawha Salines (now Malden) would become the top salt producer in the world. The Holly Grove Mansion was established during this period. In 1818, the Kanawha Salt Company, the first trust in the United States, went into operation. In the same year, “Charlestown” was shortened to “Charleston” to avoid confusion with another Charles Town in eastern West Virginia, which was named after George Washington’s brother, Charles Washington. A lyceum was established around 1841.
Captain James Wilson, while drilling for salt, struck the first natural gas well in 1815. It was drilled at the site that is now the junction of Brooks Street and Kanawha Boulevard (near the present-day state capitol complex). In 1817, coal was first discovered and gradually became used as the fuel for the salt works. The Kanawha salt industry declined in importance after 1861, until the onset of World War I brought a demand for chemical products. The chemicals needed were chlorine and sodium hydroxide, which could be made from salt brine.
The town continued to grow until the Civil War began in 1861. After the Virginia Secession Convention of 1861 and a referendum, the state of Virginia seceded from the Union. However, Charleston, like much of western Virginia, was divided in loyalty between the Union and the Confederacy. On September 13, 1862, the Union and Confederate armies clashed in the Battle of Charleston. The Confederates won, but they could not hold the area for long. The Union soldiers returned in force just six weeks later and retook the city. Charleston would remain under Union control for the remainder of the war.
In addition to the dispute over slavery, the North wanted to separate West Virginia from the rest of the state for economic reasons. The heavy industries in the North, particularly the steel business of the upper Ohio River region, were dependent on coal from the western Virginia mines. Federal units from Ohio marched into western Virginia quite early in the war solely to capture the coal mines and control transportation in the area. The Wheeling Convention of 1861 declared the Ordinance of Succession, and the Confederate state government in Richmond, to be illegal and void, and formed the Unionist Restored Government of Virginia. The Restored Government and the United States Congress approved the formation of the state of West Virginia, which was admitted on June 20, 1863, as the 35th state, and the Restored Government of Virginia moved to Alexandria.
Although a state now existed, choosing a state capital location proved to be difficult. For several years, the West Virginia capital intermittently traveled between Wheeling and Charleston. In 1877, however, the citizens voted on a permanent location. Charleston received 41,243 votes, Clarksburg received 29,442 and Martinsburg received 8,046; Wheeling was not considered. Charleston won, and eight years later the first state capitol building was opened there.
The West Virginia Historical and Antiquarian Society was headquartered in Charleston in 1890. In 1891, the West Virginia Colored Institute, now known as West Virginia State University, was established. The following year, Capitol City Commercial College was founded. Charleston’s Basilica of the Co-Cathedral of the Sacred Heart was completed in 1897.
20th century
Charleston became the center of state government. Natural resources, such as coal and natural gas, along with railroad expansion, also contributed to growth. New industries such as chemical, glass, timber and steel migrated to the state, attracted by the area’s natural resources. The city established a chamber of commerce in 1900. There was a large amount of new construction in Charleston during this period. A number of those buildings, including churches and office buildings, still stand in the heart of downtown along and bordering Capitol Street. The State Bureau of Archives and History was established in 1905, and the Charleston Public Library was established in 1909.
The city’s first chemical manufacturer began operation in 1913. Three years later, the Libbey-Owens-Ford glass manufactory was built, as well as Charleston High School. Another large manufacturer, Owens Bottle Company, opened in 1917. Charleston City Hall was built in 1921. In the same year, a fire at the capitol building resulted in a new, hastily built structure being opened, but it too burned down in 1927. A Capitol Building Commission, created by the legislature in 1921, authorized construction of the present capitol. Architect Cass Gilbert designed the buff-colored Indiana limestone structure in the Italian Renaissance style, with a final cost of just under $10 million. After the three stages of construction were completed, Governor William G. Conley dedicated the West Virginia State Capitol on June 20, 1932. Charleston Municipal Airport was established in 1909. In 1934, the city library expanded to become the Kanawha County Public Library system. In 1935, Morris Harvey College relocated to Charleston from Barboursville, West Virginia.
Charleston Municipal Auditorium was completed in 1939. During World War II, the first and largest styrene-butadiene plant in the U.S. opened in nearby Institute, providing a replacement for rubber to the war effort. After the war ended, Charleston was on the brink of some significant construction. One of the first during this period was Kanawha Airport (now Yeager Airport, named after General Chuck Yeager). Built in 1947, the construction encompassed clearing 360 acres (1.5 km) on three mountaintops and moving more than nine million cubic yards of earth. Kanawha Boulevard, a riverfront four-lane road, was also built in the early 1940s. The Charleston Civic Center opened in 1959.
Charleston began to be integrated into the Interstate Highway System in the 1960s when three major interstate systems—I-64, I-77 and I-79 were designated, all converging in Charleston. In 1961, the Kanawha River flooded much of the lower-lying parts of Charleston. In 1973, Morris Harvey College was renamed to be the University of Charleston.
In 1983, the Charleston Town Center opened its doors downtown. It was the largest urban-based mall east of the Mississippi River, featuring three stories of shops and eateries. Downtown revitalization began in earnest in the late 1980s. Funds were set aside for streetscaping as Capitol and Quarrier streets saw new building facades, trees along the streets, and brick walkways installed. For a time, the opening of the Charleston Town Center Mall had a somewhat negative impact on the main streets of downtown Charleston, as many businesses closed and relocated into the mall. Also in 1983, West Virginia Public Radio launched a live-performance radio program statewide called Mountain Stage. What began as a live, monthly statewide broadcast went on to national distribution in 1986 through National Public Radio and around the world on the Voice of America satellite service.
The new Robert C. Byrd Federal Building, Haddad Riverfront Park and Capitol Market are just a few new developments that have helped growth in the downtown area during the 1990s. Charleston launched its city website in 1998.
21st century
2003 marked the opening of the Clay Center for the Arts & Sciences. The center includes the Maier Foundation Performance Hall, the Walker Theatre, the Avampato Discovery Museum and the Juliet Art Museum. Also on site is the ElectricSky Theater, a 175-seat combination planetarium and dome-screen cinema. Movies shown at the theatre include educational large format (70 mm) presentations and are often seen in similar Omnimax theatres. Planetarium shows are staged as a combination of pre-recorded and live presentations. The West Virginia Music Hall of Fame was established in 2005.
Many festivals and events were also incorporated into the calendar, including Multifest, Vandalia Festival, a July 4 celebration with fireworks at Haddad Riverfront Park, and the already popular Sternwheel Regatta, which was founded in 1970, provided a festive atmosphere for residents to enjoy. In 2005 FestivALL Charleston was established and has grown into a ten-day festival offering a variety of performances, events and exhibits in music, dance, theatre, visual arts and other entertainments.
Charleston has one central agency for its economic development efforts, the Charleston Area Alliance. The Alliance works with local public officials and the private sector to build the economy of the region and revitalize its downtown. Charleston also has an economic and community development organization focused on the East End and West Side urban neighborhood business districts, Charleston Main Streets.
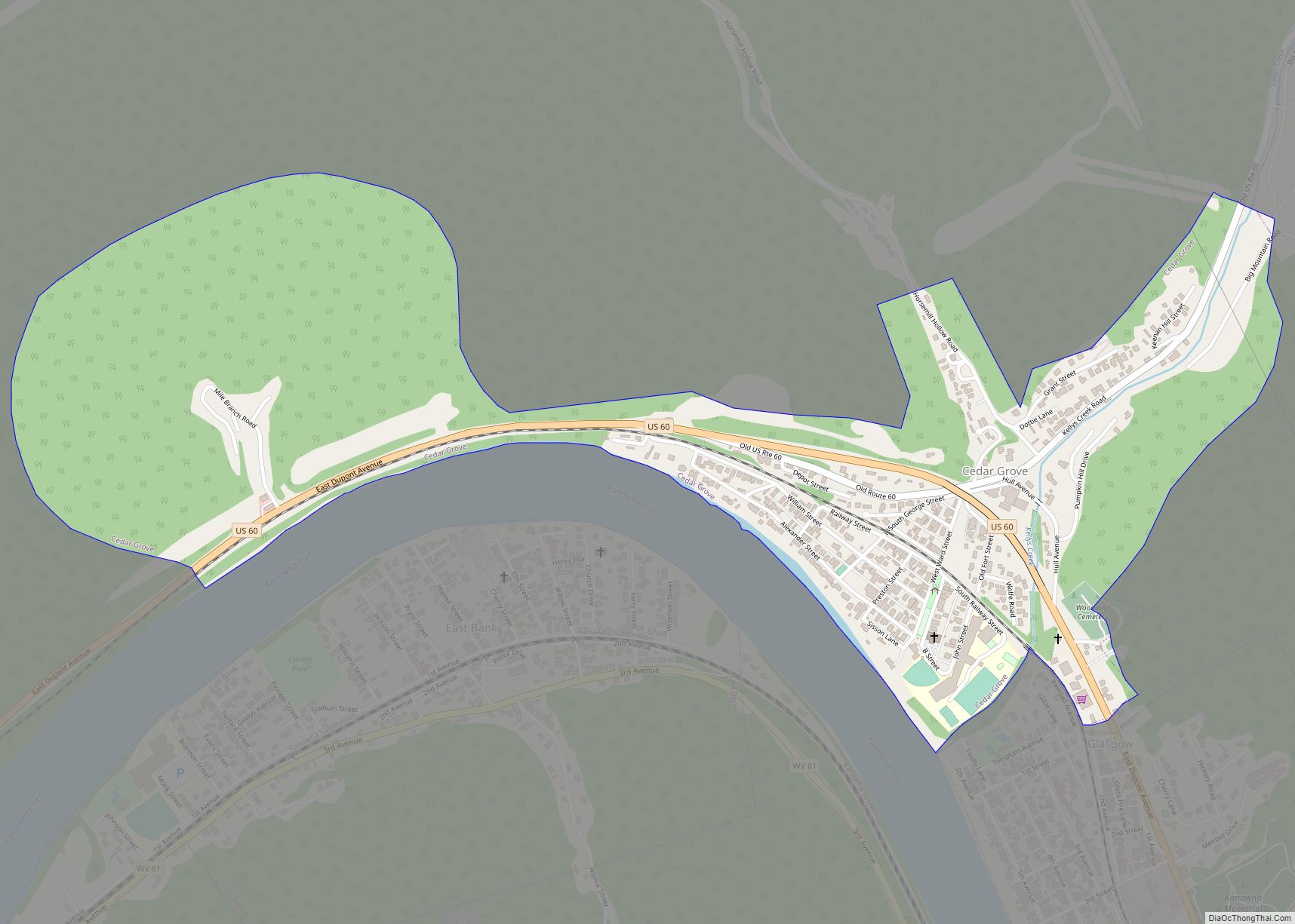
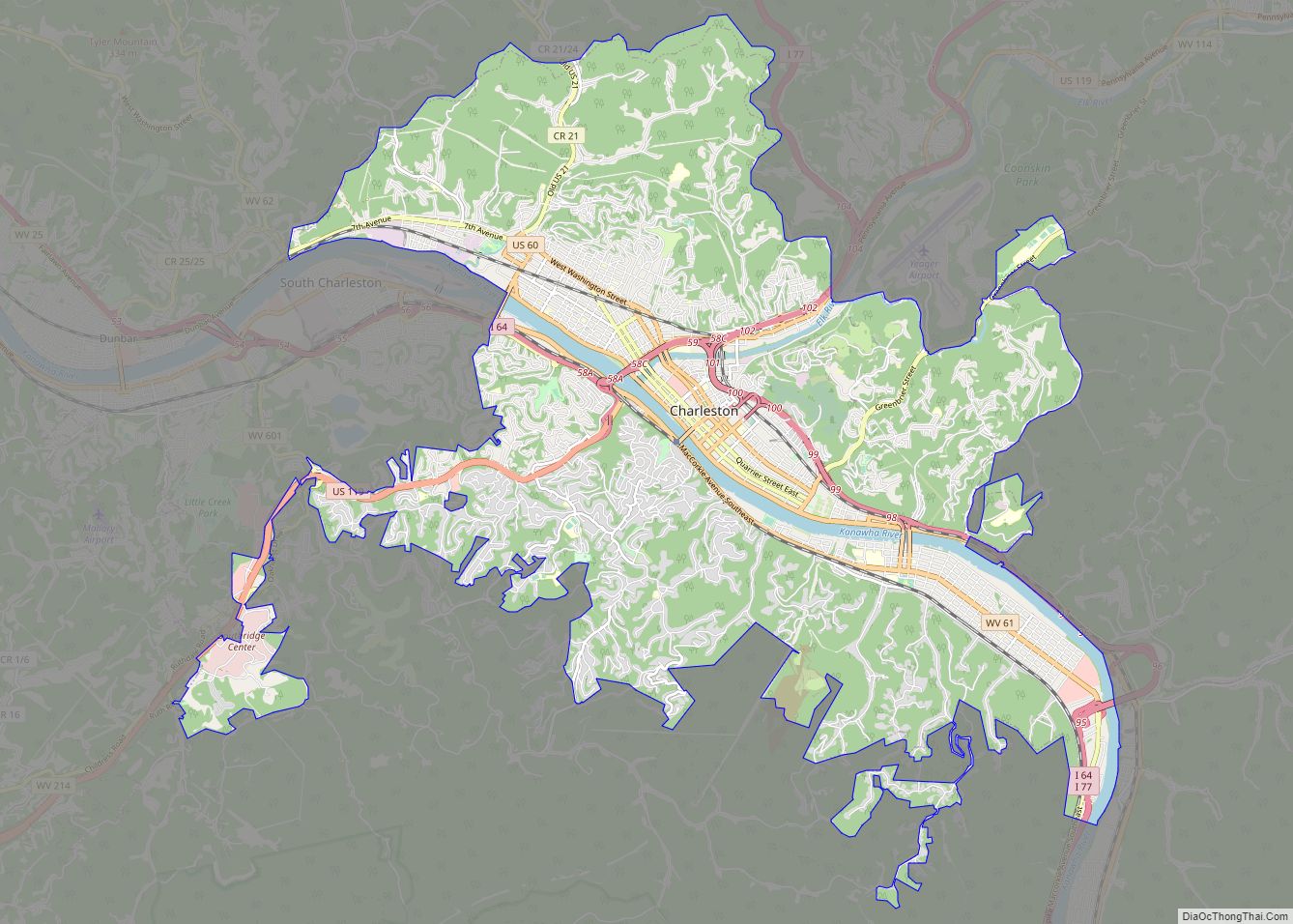
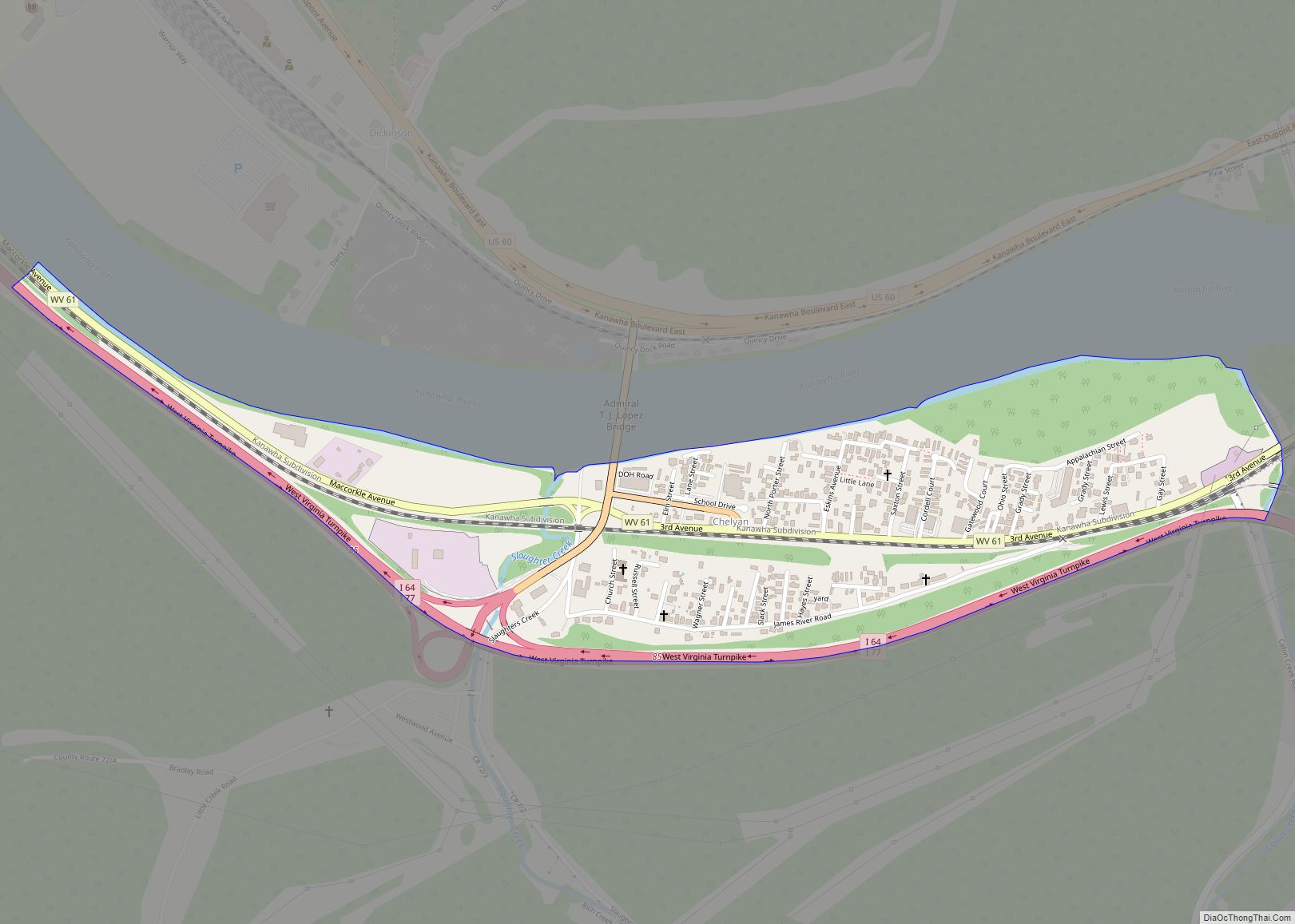
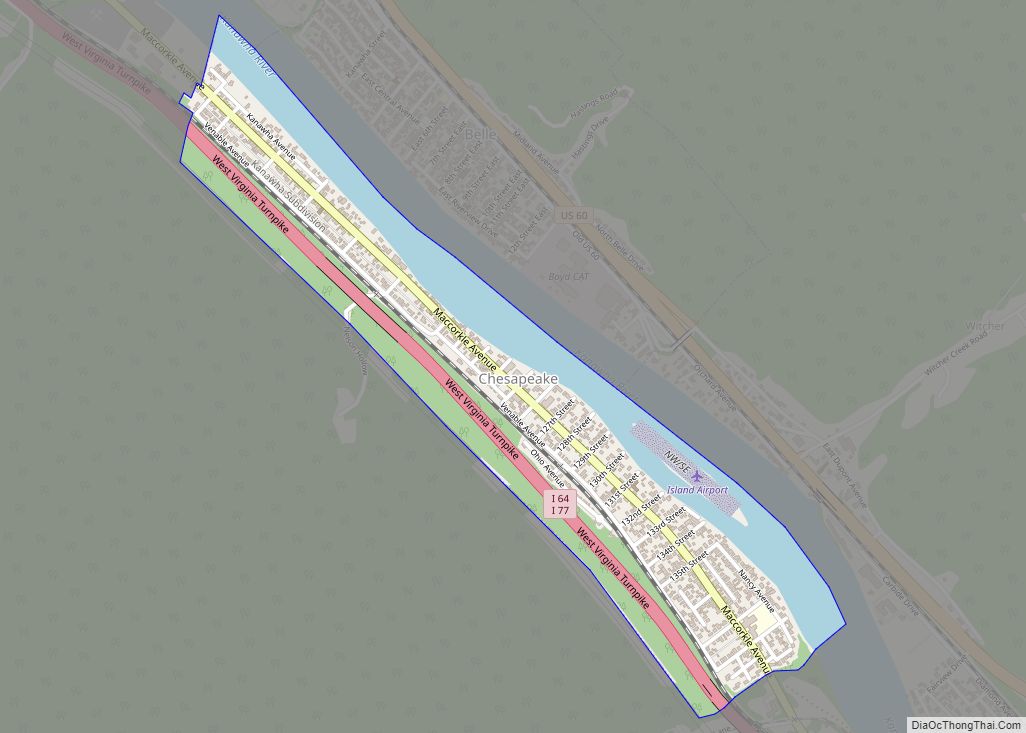
Charleston Road Map
Charleston city Satellite Map
Geography
Charleston is located in west-central Kanawha County at 38°20′58″N 81°38′0″W / 38.34944°N 81.63333°W / 38.34944; -81.63333 (38.349497, −81.633294). It lies within the ecoregion of the Western Allegheny Plateau.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 32.66 square miles (84.59 km), of which 31.52 square miles (81.64 km) are land and 1.14 square miles (2.95 km) are water.
The city lies at the intersection of Interstates 79, 77, 64, and also where the Kanawha and Elk rivers meet. Charleston is about 117 miles (188 km) southeast of Chillicothe, Ohio, 315 miles (507 km) west of Richmond, Virginia, 228 miles (367 km) southwest of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, 247 miles (398 km) east of Louisville, Kentucky, and 264 miles (425 km) north of Charlotte, North Carolina.
Neighborhoods
The following are neighborhoods and communities within the city limits:
- Charleston Heights (Westmoreland/Hillsdale)
- East End
- Edgewood
- Elk City
- Forest Hills
- Fort Hill
- Kanawha City
- Louden Heights
- North Charleston
- Riverview
- Shadowlawn
- South Park
- South Hills
- South Ruffner
- West Side
Climate
Charleston has a four-season humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) with continental climate (Dfa) elements. Especially in winter, Charleston’s average temperatures are warmer than the rest of the state, due to the city being west of the higher elevations. Spring is the most unpredictable season, and spring-like weather usually arrives in late March or early April. From the beginning of March through early May, temperatures can vary considerably and it is not unusual at this time for day-to-day temperature fluctuations to exceed 20 °F (11 °C). Temperatures warm up considerably in late May, with warm summer-like days. Summer is warm to hot, with 23 days of highs at or above 90 °F (32 °C), sometimes reaching 95 °F (35 °C), often accompanied by high humidity. Autumn features crisp evenings that warm quickly to mild to warm afternoons. Winters are chilly, with a January daily average of 34.4 °F (1.3 °C), and with a mean of 16 days with maxima at or below the freezing mark. Snowfall generally occurs from late November to early April, with the heaviest period being January and February. However, major snowstorms of more than 10 inches (25 cm) are rare. The area averages about 3.5 inches (89 mm) of precipitation each month. Thunderstorms are frequent during the late spring and throughout the summer, and occasionally they can be quite severe, producing the rare tornado.
Record temperatures have ranged from −17 °F (−27 °C) on December 30, 1917, to 108 °F (42 °C) on August 6, 1918, and July 4, 1931. However, decades can pass between temperatures of 100 °F (37.8 °C) or hotter, and the last such instance was July 8, 2012. The record cold maximum is 4 °F (−16 °C) on December 22, 1989 (during the December 1989 United States cold wave), while, conversely the record warm minimum is 84 °F (29 °C) on July 29, 1924. The hardiness zone is 7a.
See also
Map of West Virginia State and its subdivision:- Barbour
- Berkeley
- Boone
- Braxton
- Brooke
- Cabell
- Calhoun
- Clay
- Doddridge
- Fayette
- Gilmer
- Grant
- Greenbrier
- Hampshire
- Hancock
- Hardy
- Harrison
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Kanawha
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Marion
- Marshall
- Mason
- McDowell
- Mercer
- Mineral
- Mingo
- Monongalia
- Monroe
- Morgan
- Nicholas
- Ohio
- Pendleton
- Pleasants
- Pocahontas
- Preston
- Putnam
- Raleigh
- Randolph
- Ritchie
- Roane
- Summers
- Taylor
- Tucker
- Tyler
- Upshur
- Wayne
- Webster
- Wetzel
- Wirt
- Wood
- Wyoming
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming