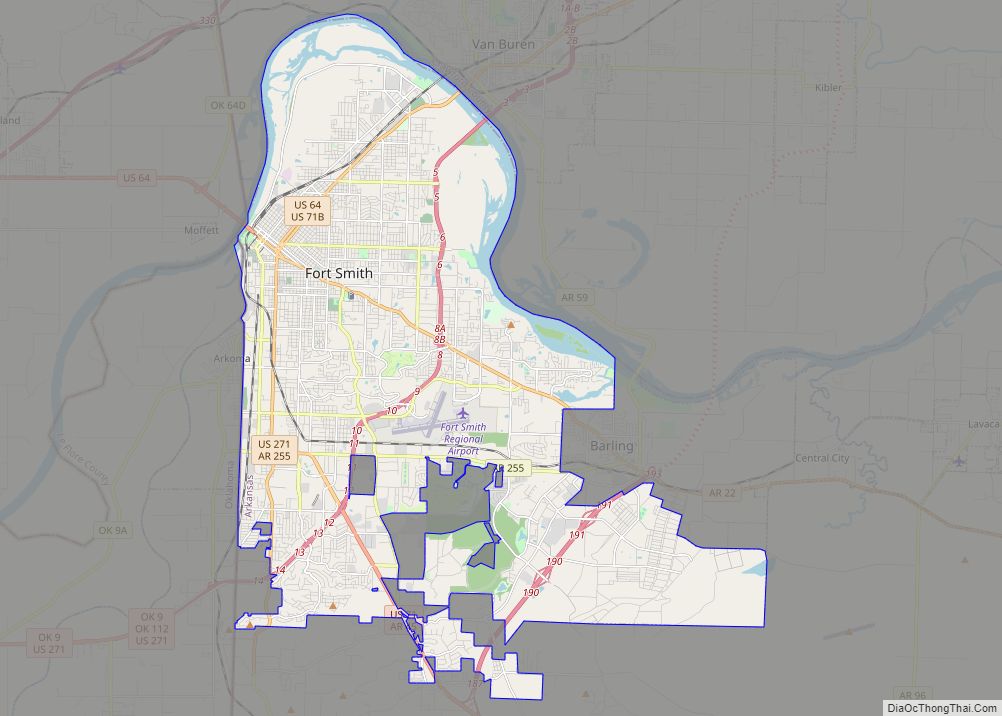
Fort Smith is the third-largest city in Arkansas and one of the two county seats of Sebastian County. As of the 2020 census, the population was 89,142. It is the principal city of the Fort Smith, Arkansas–Oklahoma Metropolitan Statistical Area, a region of 298,592 residents that encompasses the Arkansas counties of Crawford, Franklin, and Sebastian, and the Oklahoma counties of Le Flore and Sequoyah.
Fort Smith lies on the Arkansas–Oklahoma state border, situated at the confluence of the Arkansas and Poteau rivers, also known as Belle Point. Fort Smith was established as a western frontier military post in 1817, when it was also a center of fur trading. The city developed there. It became well known as a base for migrants’ settling of the “Wild West” and for its law enforcement heritage.
The city government is led by Mayor George McGill (D), who made history in 2018 when he was elected as the city’s first African American mayor, and a city Board of Directors composed of three members elected at-large and four members elected by ward.
| Name: | Fort Smith city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Arkansas |
| County: | Sebastian County |
| Founded: | 1817 |
| Incorporated: | December 24, 1842 |
| Elevation: | 463 ft (141.1 m) |
| Land Area: | 63.99 sq mi (165.74 km²) |
| Water Area: | 4.24 sq mi (10.98 km²) |
| Population Density: | 1,392.97/sq mi (537.83/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 72901-72906, 72908, 72913-72914, 72916-72919 |
| Area code: | 479 |
| FIPS code: | 0524550 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 0076952 |
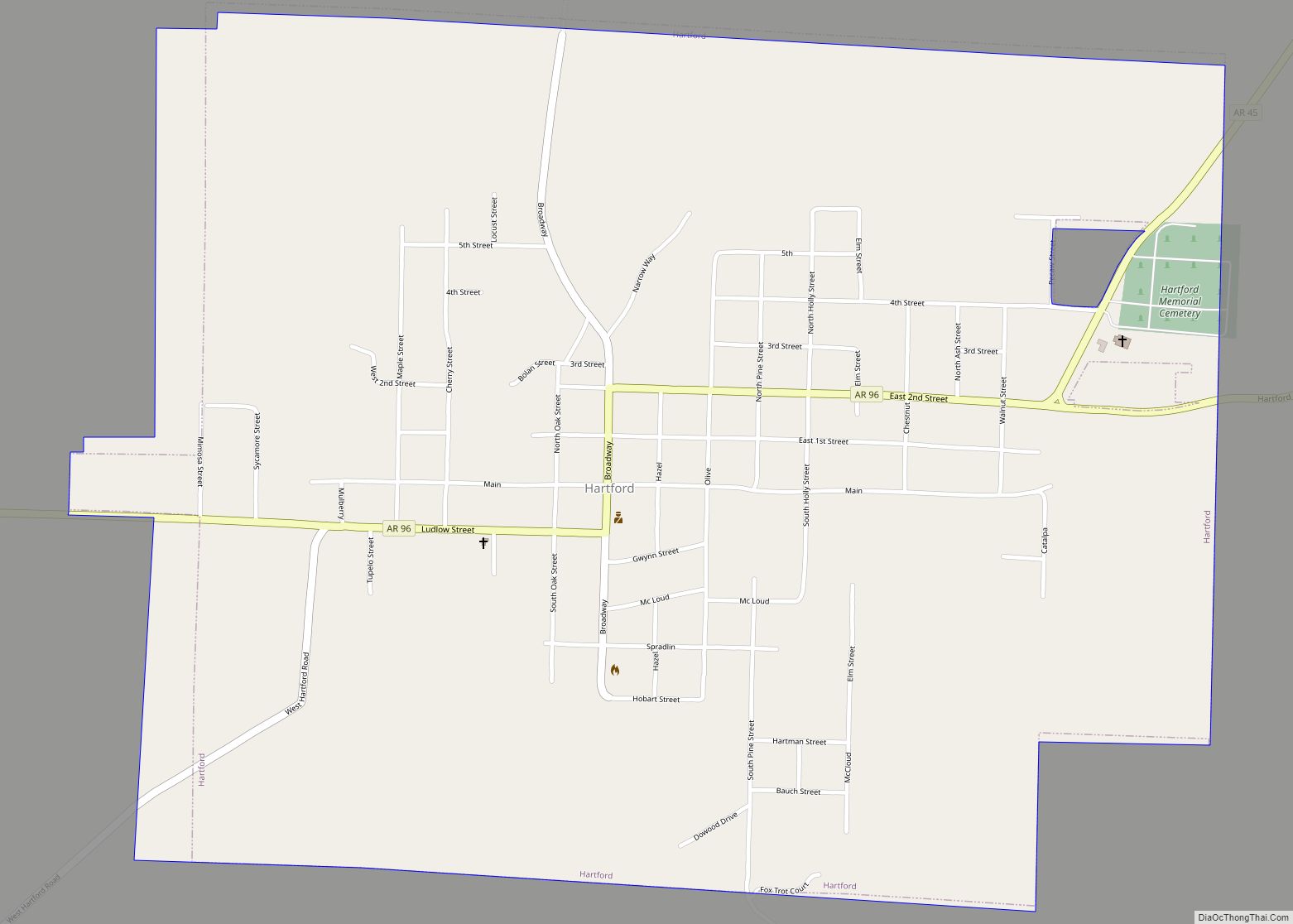
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
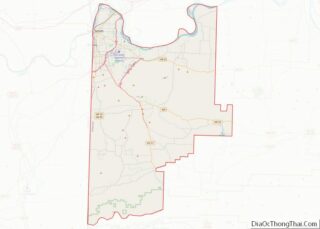
Fort Smith location map. Where is Fort Smith city?
History
The United States acquired the territory and large areas west of the Mississippi River from France in the Louisiana Purchase (1803). Soon after, the government sent the Pike Expedition (1806) to explore the areas along the Arkansas River. The US founded Fort Smith in 1817 as a military post. It was named after General Thomas Adams Smith (1781–1844), who commanded the United States Army Rifle Regiment in 1817, headquartered near St. Louis. General Smith had ordered Army topographical engineer Stephen H. Long (1784–1864) to find a suitable site on the Arkansas River for a fort. General Smith never visited the town or the forts that bore his name.
A stockade was built and occupied from 1817 until 1822 by a small troop of regulars commanded by Major William Bradford. A small settlement began forming around the fort, but the Army abandoned the first Fort Smith in 1824 and moved 80 miles further west to Fort Gibson. John Rogers, an Army sutler and land speculator, bought up former government-owned lands at this site and promoted growth of the new civilian town of Fort Smith.
Due to the strategic location of this site, the federal government re-established a military presence at Fort Smith during the Indian Removal era of the 1830s, primarily of tribes from the American Southeast to west of the Mississippi River in Indian Territory, which is present-day Oklahoma.
In 1838 the Army moved back into the old military post near Belle Point, and expanded the base. They used troops to forcibly relocate the Choctaw and Cherokee, from their ancestral homelands in the Southeast; they were the last of the tribes to leave. Remnants of the Five ‘Civilized’ Tribes remained in the southeast, and some of their descendants have reorganized and been federally recognized. The Cherokee called the forced migration the Trail of Tears, as some of their people and the people who were enslaved died from starvation, hypothermia, exhaustion and many illnesses along the way. The army enforced the removal of these tribes to the reserved Indian Territory, where the federal government set aside land that was less fertile while imposing detentes between distinct nations. Many displaced people stopped walking and settled in Fort Smith and adjoining Van Buren, Arkansas on the other side of the river.
The US Army also used Fort Smith as a base during the Mexican War (1846-1848). As a result, the US acquired large territories in the Southwest, and later annexed the Republic of Texas, which had been independent from 1836-1846.
Sebastian County was formed in 1851, separated from Crawford County north of the Arkansas River. In 1858, Fort Smith was designated as a Division Center of the Butterfield Overland Mail’s 7th Division route across Indian Territory from Fort Smith to Texas and as a junction with the mail route from Memphis, Tennessee, an important port on the east side of the Mississippi River.
For roughly a year of the U.S. Civil War, the fort was occupied by the Confederate Army. Union troops under General Steele took control of Fort Smith on September 1, 1863. A small fight occurred there on July 31, 1864, but the Union army maintained command in the area until the war ended in 1865. As a result, many refugee slaves, orphans, Southern Unionists, and others came here to escape the guerrilla warfare raging in Arkansas, Missouri, and the Border States. The slaves were freed under the Emancipation Proclamation of January 1863 by President Abraham Lincoln. Federal troops abandoned the post of Fort Smith for the last time in 1871. The town continued to thrive despite the absence of federal troops.
Two of Fort Smith’s most notable historic figures were Judge Isaac Parker and William Henry Harrison Clayton, also known as W.H.H. Clayton. In 1874, William Henry Harrison Clayton was appointed United States Attorney for the Western District of Arkansas by President Ulysses S. Grant. Fort Smith was a bustling community full of brothels, saloons and outlaws, just across the river from Indian Territory. William Clayton realized a strong judge would be necessary to bring law and order to the region. He knew that Isaac Parker was a strong judge. But Judge Parker had been appointed Chief Justice of Utah Territory and confirmed by the US Senate. With the help of President Grant and US Senator Powell Clayton, former governor of Arkansas, William Clayton was able to gain the appointment of Judge Parker in the Fort Smith district.
Judge Isaac Parker served as U.S. District Judge 1875–1896. He was nicknamed the “Hanging Judge”: in his first term after assuming his post, he tried 18 people for murder, convicted 15 of them, and sentenced eight of those to die. Six of these men were later hanged on the same day. Over the course of his career in Fort Smith, Parker sentenced 160 people to death. Of those, 79 were executed on the gallows. His courthouse is now marked as a National Historic Site, where “more men were put to death by the U.S. Government… than in any other place in American history.”
William Clayton served as US Attorney under four different presidents and later was appointed as Chief Justice of Indian Territory. He was instrumental in achieving statehood for Oklahoma in 1907, after Native American claims were extinguished by distribution of communal lands under the Dawes Act and the breakup of tribal governments. Together with Territorial Governor Frank Frantz, Clayton took a copy of the Oklahoma Constitution to President Theodore Roosevelt after the state was admitted to the Union in 1907. Governor Frantz and Judge Clayton both lost their territorial positions when Oklahoma became a state; a new governor was elected and the Roosevelt administration appointed a new judge.
During investment in the military prior to World War II, the Army returned to Fort Smith in 1941. It established the Fort Chaffee Military Reservation east of the city.
On April 21, 1996, a large tornado, part of the April 1996 tornado outbreak sequence, destroyed and heavily damaged much of historic downtown Fort Smith around the Garrison Avenue Bridge. The storm tracked from eastern Pittsburg County, Oklahoma into Fort Smith and Van Buren, Arkansas. The tornado left four people dead in western Arkansas. Days later, the damaged Eads Brothers Furniture building in downtown Fort Smith was destroyed by one of the largest fires in the city’s history.
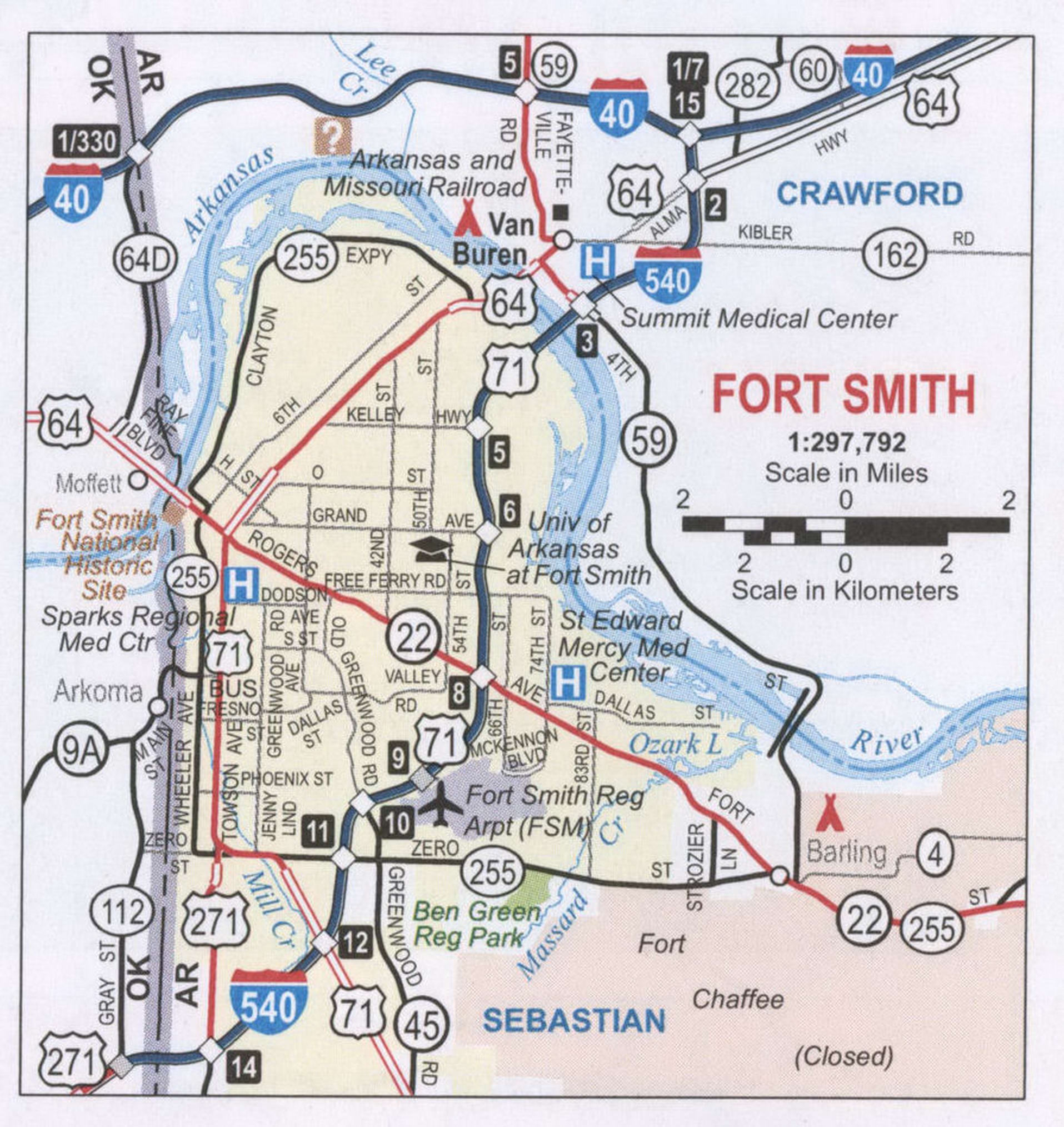
Fort Smith Road Map
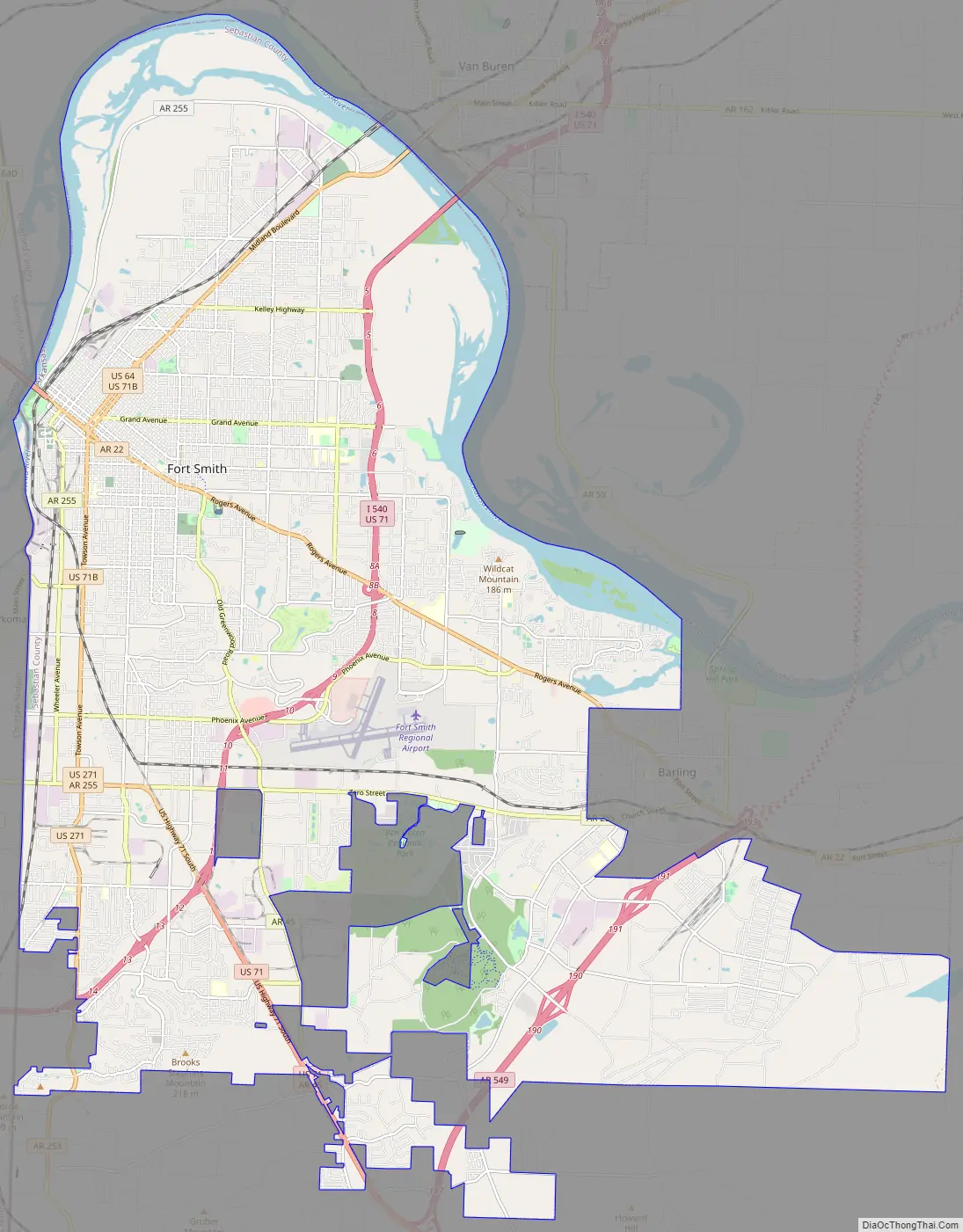
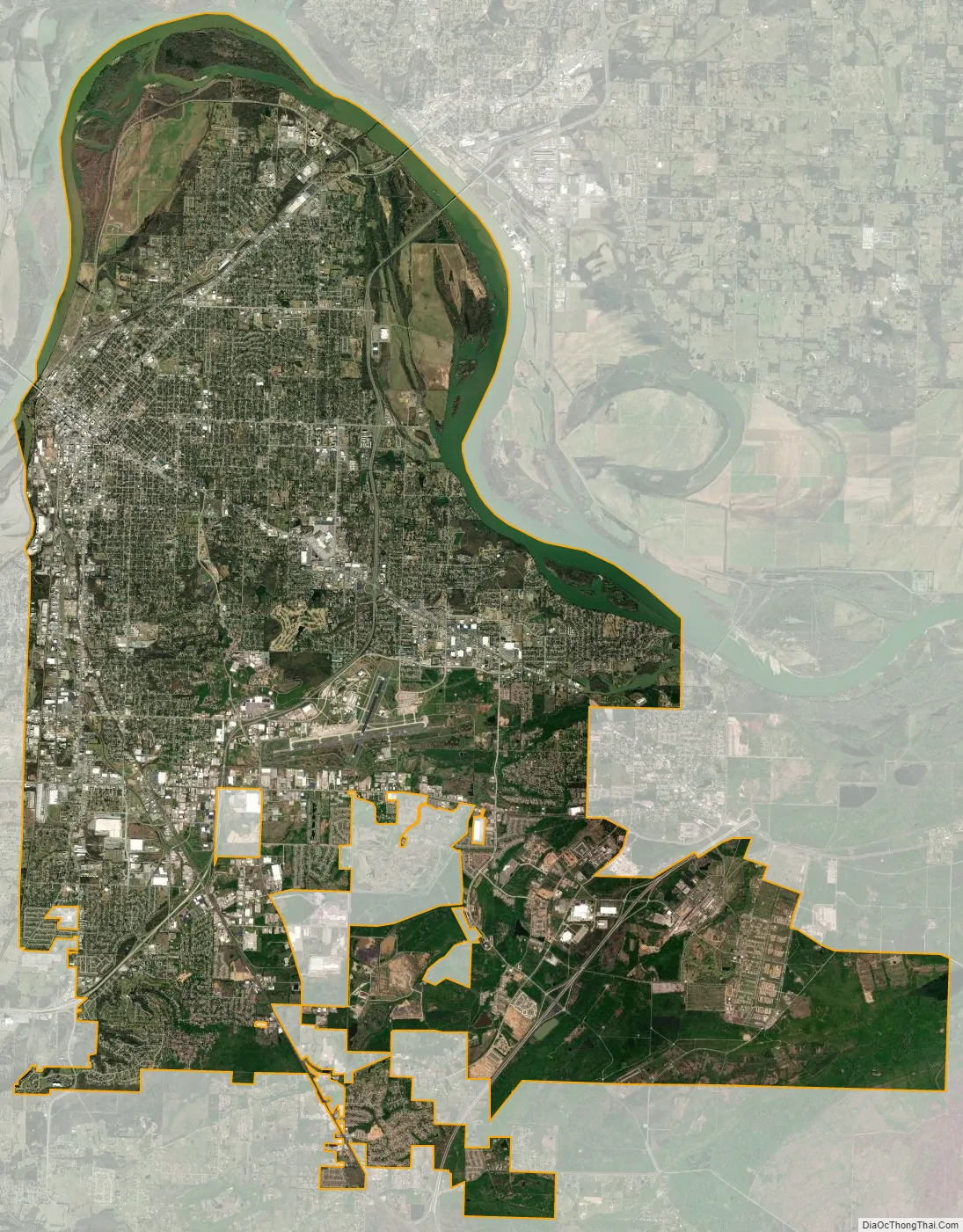
Fort Smith city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 64.6 square miles (167 km), of which 61.7 square miles (160 km) is land and 3.9 square miles (10 km) (6.3%) is water.
Climate
Fort Smith has a humid subtropical climate with generally mild winters and hot, humid summers. The monthly mean temperature ranges from 40.4 °F (4.7 °C) in January to 83.1 °F (28.4 °C) in July; on average, the high stays at or below freezing on 3.8 days, reaches 90 °F (32 °C) on 77.8 days, and 100 °F (38 °C) on 11.1 days annually. The average first and last occurrences for freezing temperatures are November 6 and March 25, respectively. Extreme temperatures range from −15 °F (−26 °C) on February 12, 1899 to 115 °F (46 °C) on August 3, 2011. Fort Smith is situated near an area known as Tornado Alley in the central United States. The city has been struck by three major tornadoes, which occurred in the years of 1898, 1927 and 1996.
See also
Map of Arkansas State and its subdivision:- Arkansas
- Ashley
- Baxter
- Benton
- Boone
- Bradley
- Calhoun
- Carroll
- Chicot
- Clark
- Clay
- Cleburne
- Cleveland
- Columbia
- Conway
- Craighead
- Crawford
- Crittenden
- Cross
- Dallas
- Desha
- Drew
- Faulkner
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Garland
- Grant
- Greene
- Hempstead
- Hot Spring
- Howard
- Independence
- Izard
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Johnson
- Lafayette
- Lawrence
- Lee
- Lincoln
- Little River
- Logan
- Lonoke
- Madison
- Marion
- Miller
- Mississippi
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Nevada
- Newton
- Ouachita
- Perry
- Phillips
- Pike
- Poinsett
- Polk
- Pope
- Prairie
- Pulaski
- Randolph
- Saint Francis
- Saline
- Scott
- Searcy
- Sebastian
- Sevier
- Sharp
- Stone
- Union
- Van Buren
- Washington
- White
- Woodruff
- Yell
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming