San Fernando (Spanish for “St. Ferdinand”) is a general-law city in the San Fernando Valley region of Los Angeles County, California, in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. It is bordered on all sides by the City of Los Angeles. As of the 2010 census the population of San Fernando was 23,645.
| Name: | San Fernando city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Los Angeles County |
| Incorporated: | August 31, 1911 |
| Elevation: | 1,070 ft (326 m) |
| Total Area: | 2.37 sq mi (6.15 km²) |
| Land Area: | 2.37 sq mi (6.15 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km²) 0% |
| Total Population: | 23,645 |
| Population Density: | 10,245.16/sq mi (3,955.63/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 91340-91342, 91344-91346 |
| Area code: | 818, 747 |
| FIPS code: | 0666140 |
| Website: | www.ci.san-fernando.ca.us |
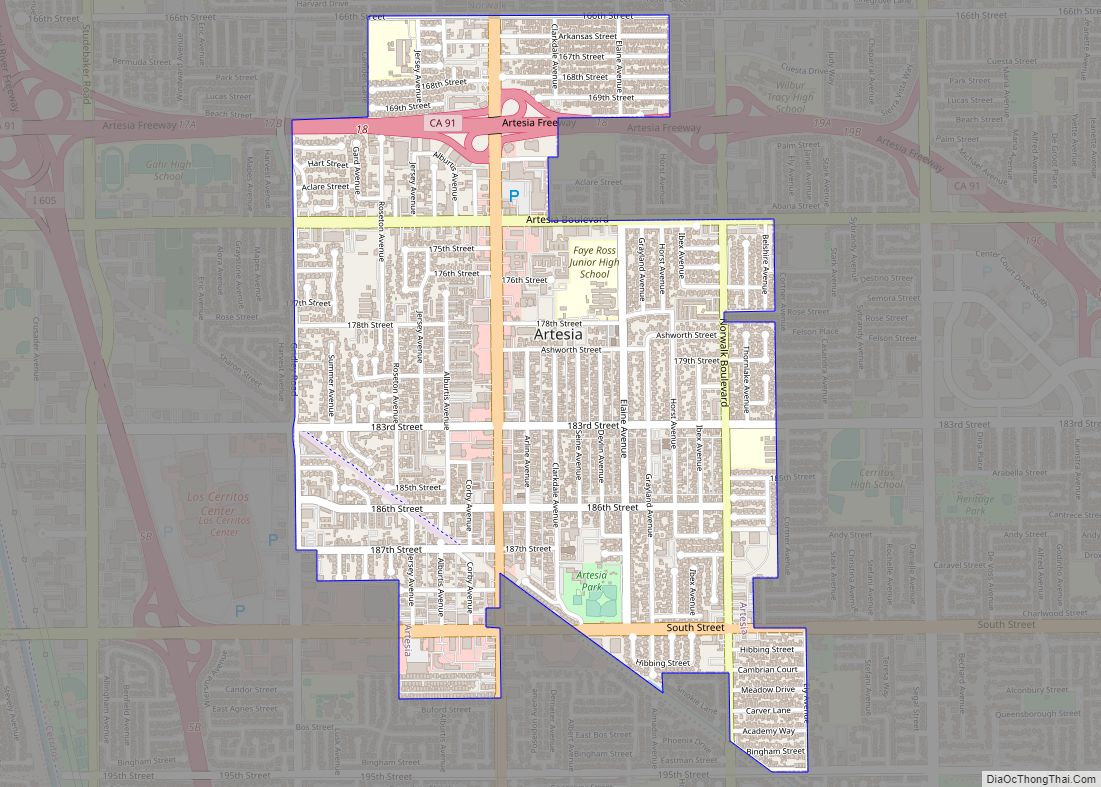
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
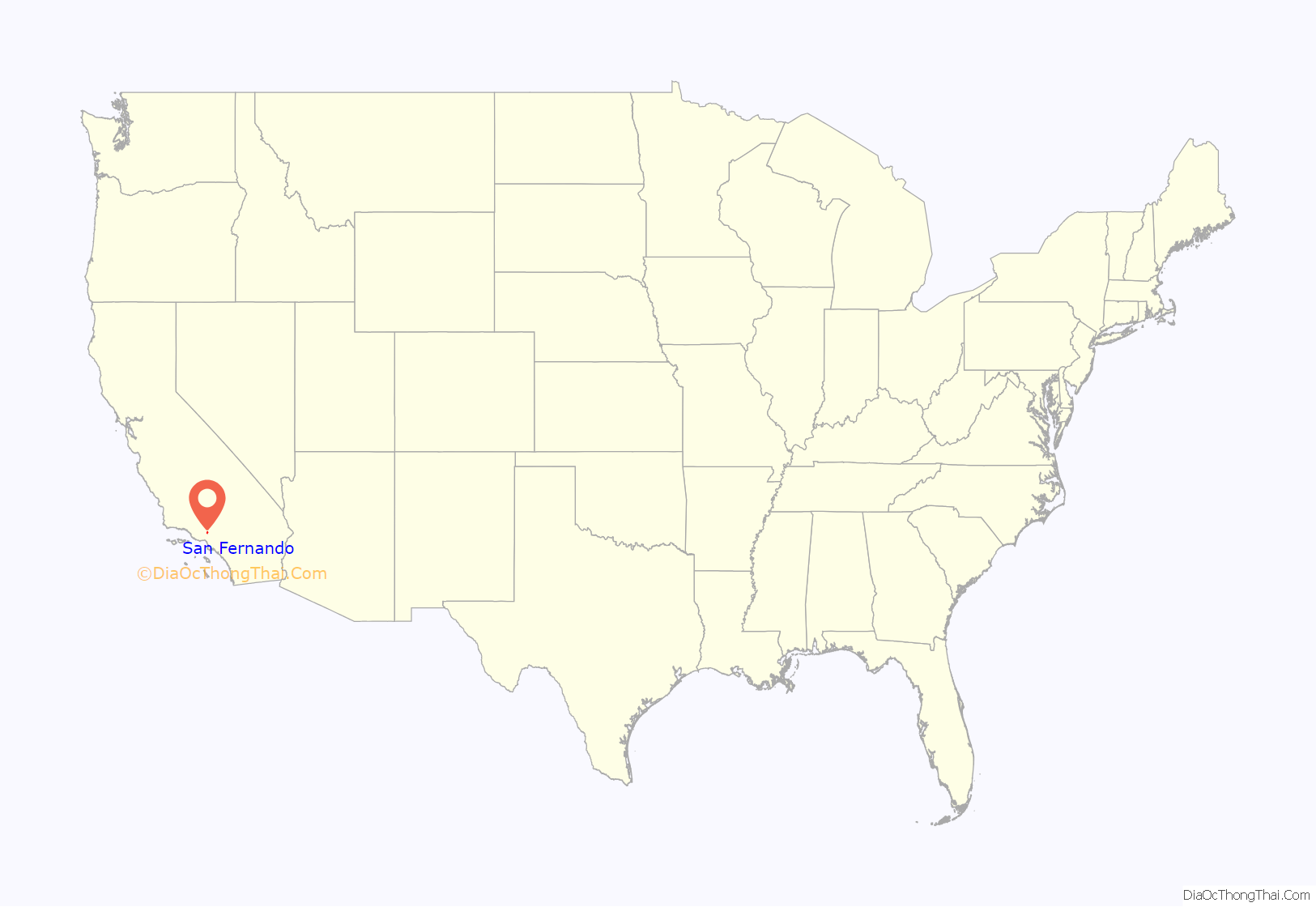
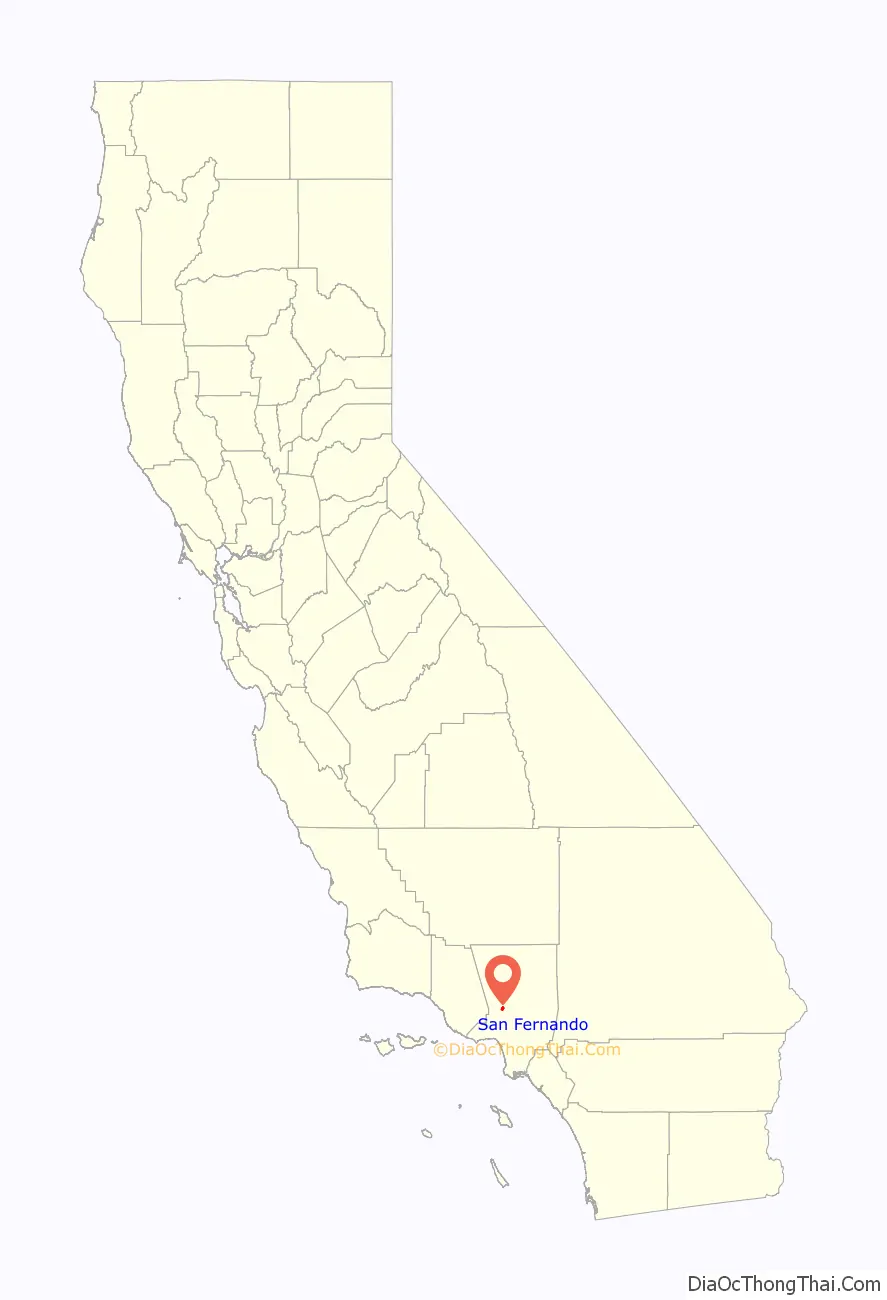
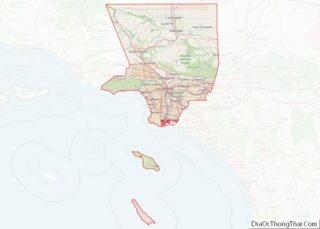
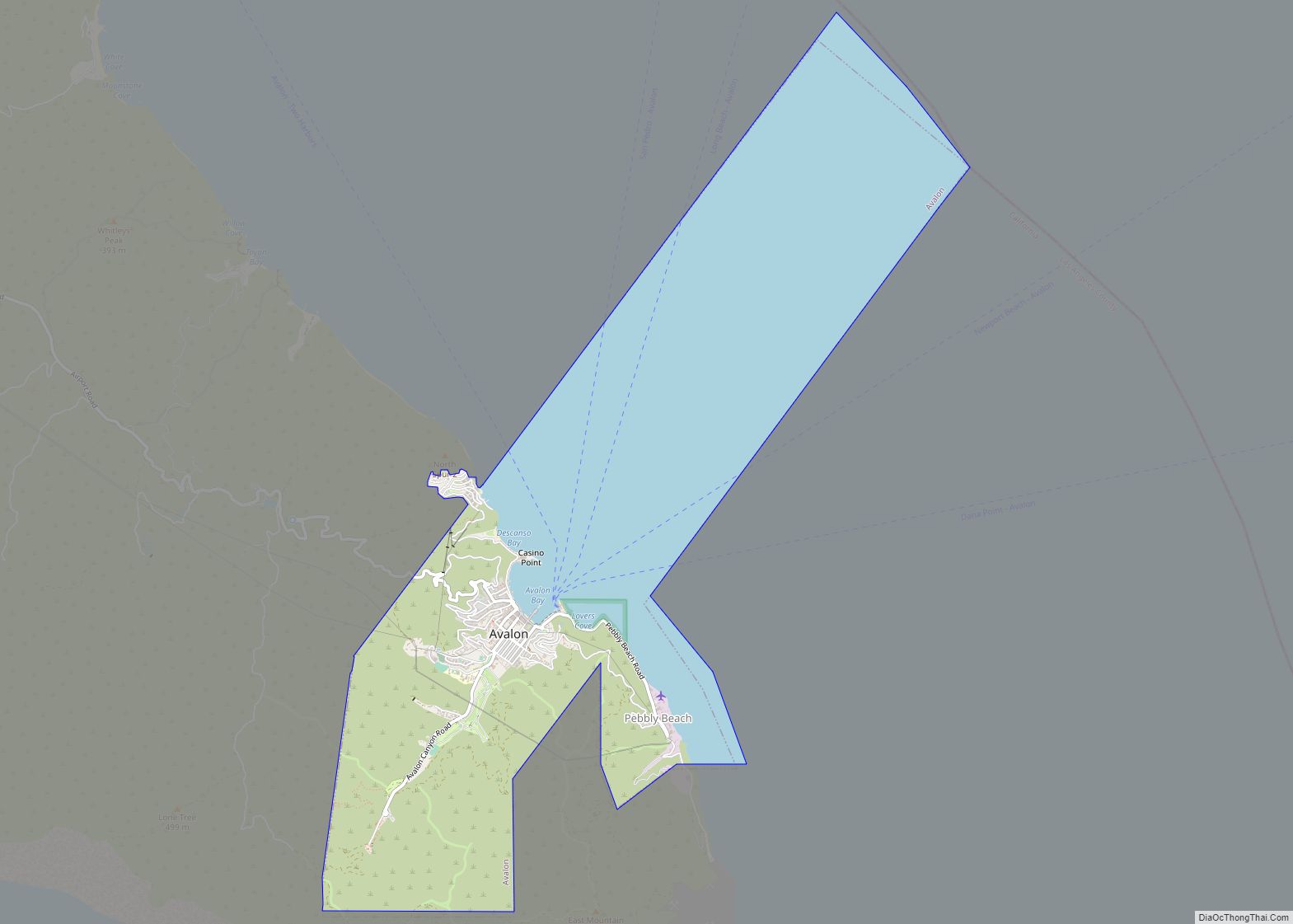
San Fernando location map. Where is San Fernando city?
History
Prior to the arrival of Spanish missionaries and soldiers, the area of San Fernando was in the northwestern extent of Tovaangar, or the homelands of the Tongva. The nearby village of Pasheeknga was a major site for the Tongva, being the most populous village in the San Fernando Valley at the time. The homelands of the Tataviam could be found to the north and the Chumash to the west.
Spanish colonial period
The Mission San Fernando Rey de España (named after St. Ferdinand) was founded in 1797 at the site of Achooykomenga, an agricultural rancho established by Juan Francisco Reyes for Pueblo de Los Ángeles worked by Ventureño Chumash, Fernandeño (Tongva), and Tataviam laborers.
In 1833, the mission was secularized by the Mexican government. During its time as a mission, 1,367 native children were baptized at San Fernando, of which 965 died in childhood. The high death rate of children and adults at the missions sometimes led those kept at the mission to run away.
Rancho land grant
In 1846, the area became part of the Mexican land grant of Rancho Ex-Mission San Fernando. In 1874, Charles Maclay, bought 56,000 acres (227 km) of the Rancho.
In 1882, cousins George K. Porter and Benjamin F. Porter, of future Porter Ranch, each received one-third of the total land. In 1885, Maclay founded the Maclay School of Theology, a Methodist seminary in San Fernando. After his death it became an affiliate and moved to the campus of the University of Southern California and then the Claremont School of Theology.
While most of the towns in the surrounding San Fernando Valley agreed to annexation by Los Angeles in the 1910s, eager to tap the bountiful water supply provided by the newly opened Los Angeles Aqueduct, San Fernando’s abundant groundwater supplies allowed it to remain a separate city.
Incorporation
In the first half of the 20th century after incorporation in 1911, the city of San Fernando tried to extend its city limits to Sylmar, Mission Hills and Pacoima, but the city of Los Angeles kept up their rapid annexation and caused many failed attempts.
By the 1950s, the city said that annexation was hard to do, due to the large bureaucracy of Los Angeles. As the San Fernando Valley transitioned from an agricultural area to a suburban one in the decades after World War II, San Fernando retained its independence.
As with much of the San Fernando Valley east of the San Diego Freeway, the city of San Fernando has seen a significant demographic shift in recent years. Declining birth-rates and an aging population of middle-class whites, who once dominated the area in the 1950s, has contributed to the movement into other parts of the San Fernando Valley. There has also been movement into the Santa Clarita and Antelope Valleys to the north.
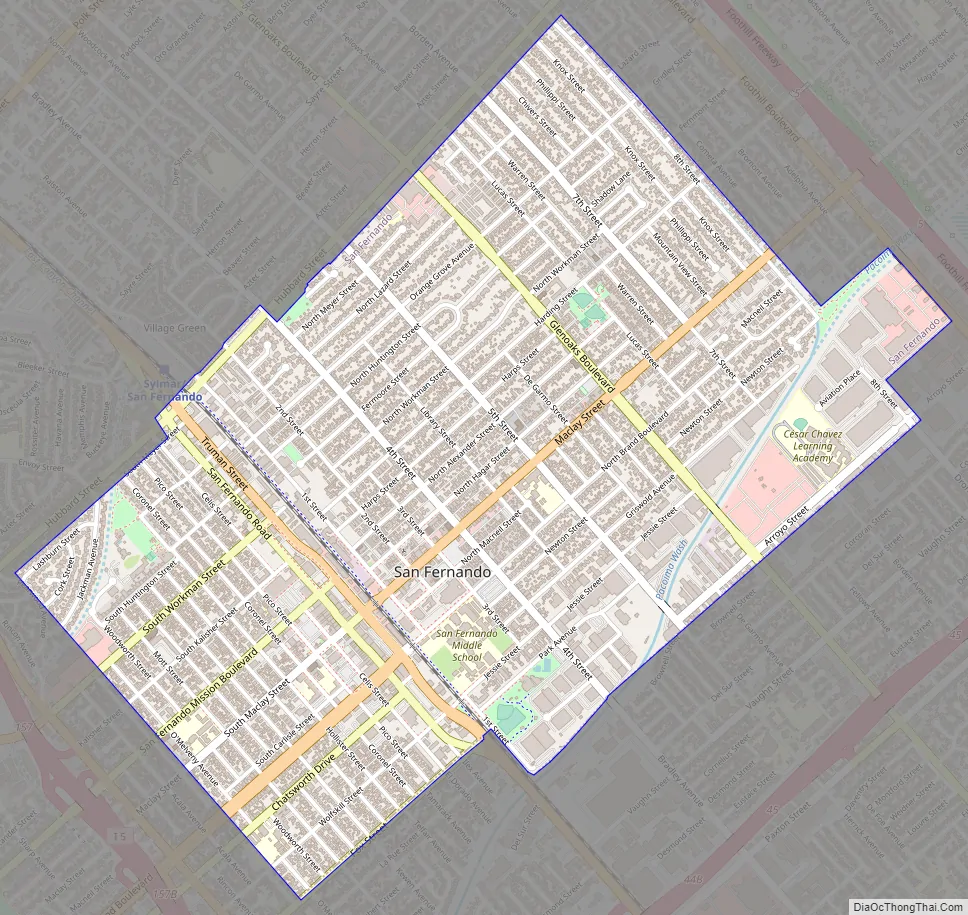
San Fernando Road Map
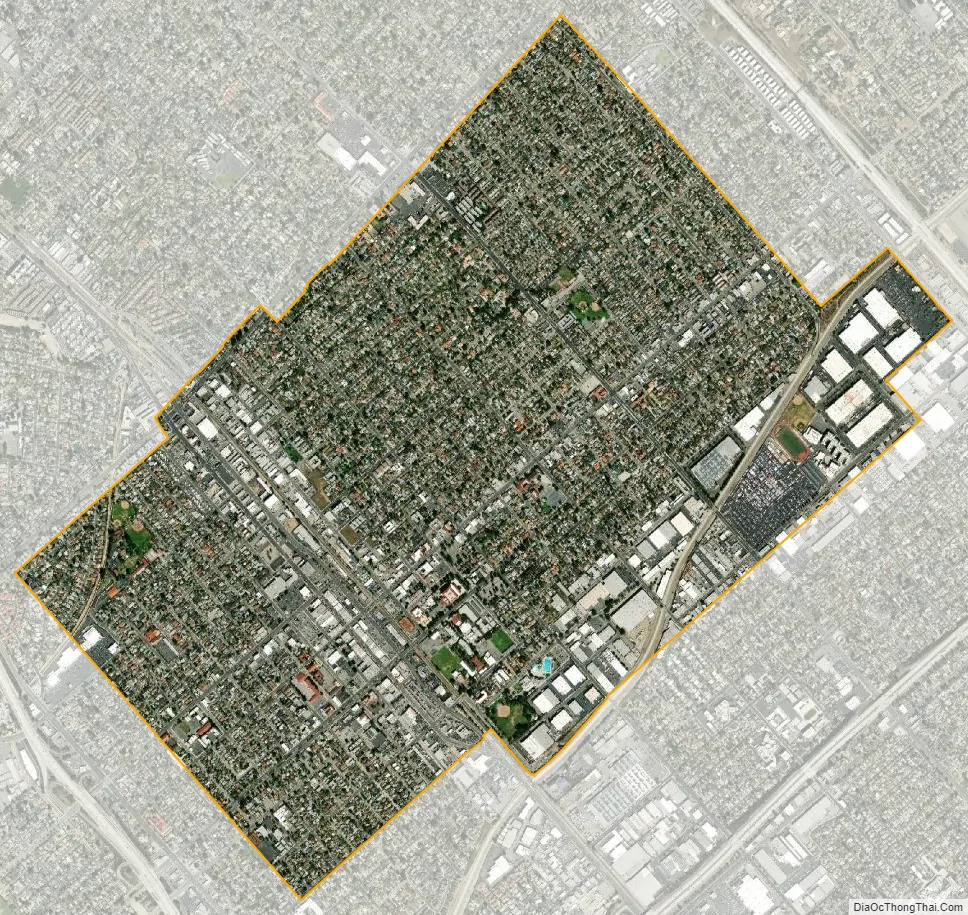
San Fernando city Satellite Map
Geography
San Fernando is completely surrounded by the city of Los Angeles, with the neighborhoods of Sylmar to the north, Lake View Terrace to the east, Pacoima to the south, and Mission Hills to the west. It is served by the Golden State (Interstate 5), Foothill (Interstate 210), Ronald Reagan (State Route 118), and San Diego (Interstate 405) freeways.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming