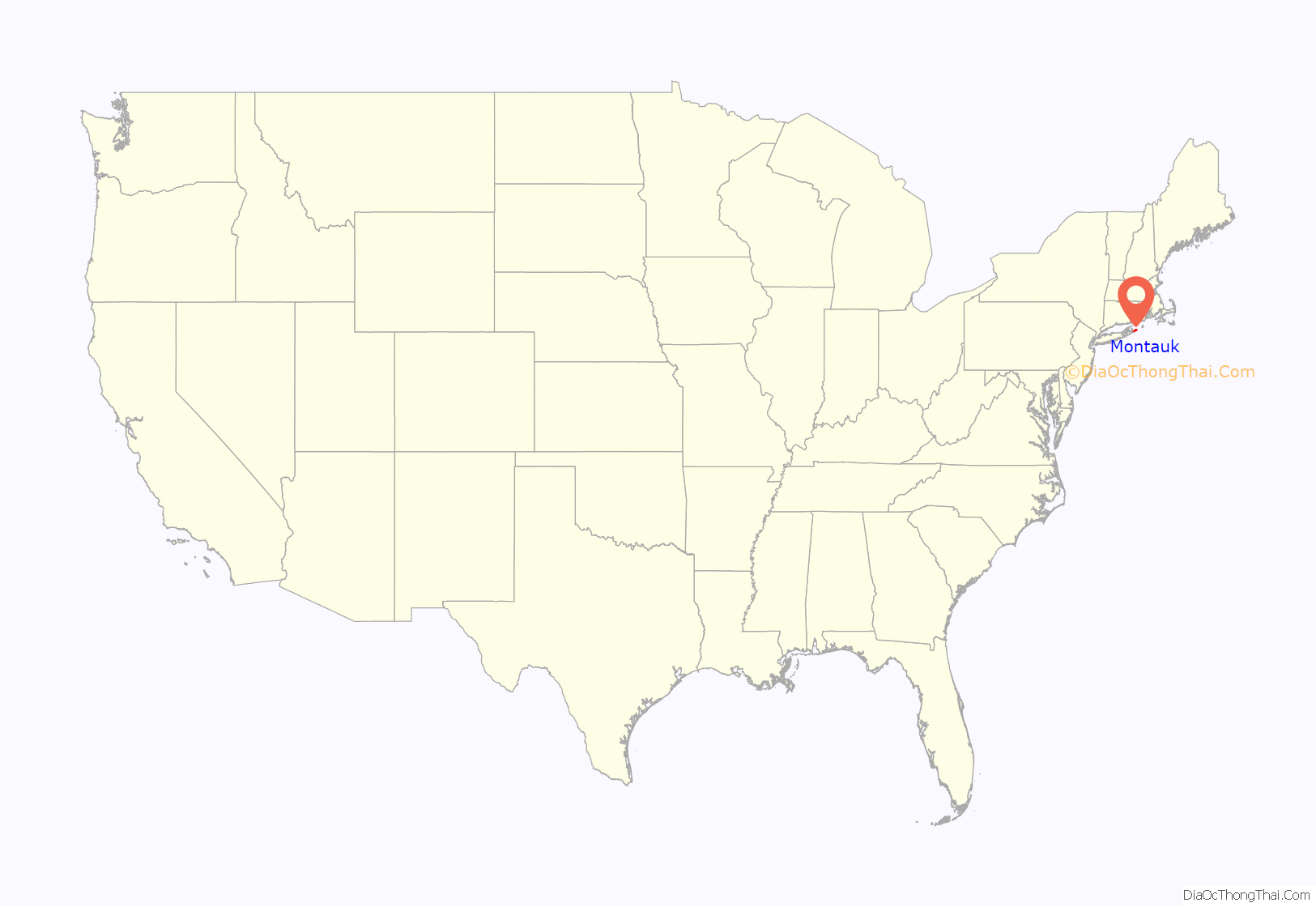
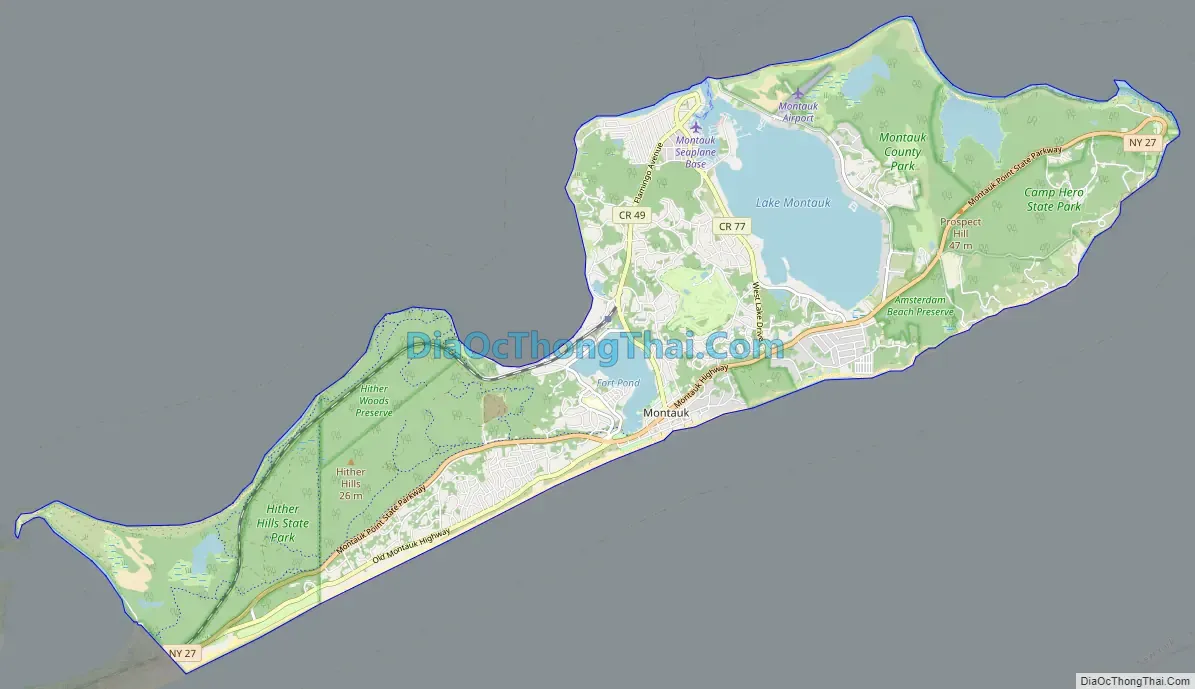
Montauk (/ˈmɒntɔːk/ MON-tawk) is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Town of East Hampton in Suffolk County, New York, on the eastern end of the South Shore of Long Island. As of the 2020 United States census, the CDP’s population was 4,318.
The CDP encompasses an area that stretches approximately 13 miles (21 km) from Napeague, New York, to the easternmost tip of New York State at Montauk Point Light. The hamlet encompasses a small area about halfway between the two points.
Located at the tip of the South Fork peninsula of Long Island, 118 miles (190 km) east of Midtown Manhattan, Montauk has been used as an Army, Navy, Coast Guard, and Air Force base. The Montauk Point Light was the first lighthouse in New York state and is the fourth oldest active lighthouse in the United States.
Montauk is a major tourist destination and has six state parks. It is particularly famous for its fishing, claiming to have more world saltwater fishing records than any other port in the world. Located 20 miles (32 km) off the Connecticut coast, it is home to the largest commercial and recreational fishing fleet in New York state.
| Name: | Montauk CDP |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 57 |
| LSAD Description: | CDP (suffix) |
| State: | New York |
| County: | Suffolk County |
| Elevation: | 33 ft (10 m) |
| Total Area: | 35.83 sq mi (92.81 km²) |
| Land Area: | 18.49 sq mi (47.89 km²) |
| Water Area: | 17.34 sq mi (44.92 km²) |
| Total Population: | 4,318 |
| Population Density: | 233.53/sq mi (90.17/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 11954 |
| Area code: | 631, 934 |
| FIPS code: | 3648054 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 957540 |
| Website: | ehamptonny.gov/333/Montauk |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
Montauk location map. Where is Montauk CDP?
History
17th century
Montauk derives its name from the Montaukett tribe, an Algonquian-speaking tribe who lived in the area. In 1614, Dutch explorer Adriaen Block encountered the tribe at Montauk Point, which he named Hoeck van de Visschers, or “Point of the Fishers”. Two decades later, in 1637, the Montauketts sided for their own protection with the New England settlers in the Pequot War in Connecticut. In the aftermath the Montauketts were to sell Gardiners Island. In 1648 what would become the Town of Easthampton (first Maidstone) was sold to settlers by the colony of Connecticut and the colony of New Haven while retaining the lands to the east, from the hills rising above where the first fort stood (Napeague, New York) to Montauk Point. The western boundary of today’s Hither Hills State Park is also known as the 1648 purchase line.
In 1653, Narragansetts under Ninigret attacked and burned the Montaukett village, killing 30 and capturing one of Chief Wyandanch’s daughters. The daughter was recovered with the aid of Lion Gardiner (who in turn was given a large portion of Smithtown, New York in appreciation). The Montauketts, ravaged by smallpox and fearing extermination by the Narragansetts, were provided temporary refuge by white settlers in East Hampton. Many short but famous battles ensued. The skirmishes ended in 1657. Fort Pond Bay derives its name from a Montaukett “fort” on its shore. A deed was issued in 1661 titled “Ye deed of Guift” which granted all of the lands east of Fort Pond to be for the common use of both the indigenous people and the townsmen.
Further purchase agreements were entered into in 1661, 1672 and 1686 which, among other things, allowed a group of Easthampton townsmen to graze cattle on the Montaukett lands. While some lands were protected in the agreements as forest land, for the most part, all of Montauk was maintained by the townsmen as a private livestock and fisheries operation. As a result of Montauk being operated as a livestock operation, it is considered to be the oldest cattle ranch in the United States.
In 1660, Wyandanch’s widow sold all of Montauk from Napeague to the tip of the island for 100 pounds to be paid in 10 equal installments of “Indian corn or good wampum at six to a penny”. However, the tribe was to be permitted to stay on the land, to hunt and fish at will on the land, and to harvest the tails and fins of whales that washed up dead on the East Hampton shores. Town officials who bought the land were to file for reimbursement for rum they had plied the tribe. The tribe was to continue residence until the 19th century in the area around Big Reed Pond in what was to be called “Indian Fields”.
In 1686, Governor of New York Thomas Dongan issued a patent creating the governing system for East Hampton. The patent did not extend beyond Napeague to Montauk. This lack of authority has formed the basis for various control disputes ever since.
18th century
During the Siege of Boston in the Revolutionary War, a British ship visited Fort Pond Bay in 1775 in search of provisions—notably cattle. John Dayton, who had limited troops at his disposal on a hill above the bay, feigned that he had more by walking them back and forth across a hill turning their coats inside out to make it look like there were more of them (a tactic referred to as “Dayton’s Ruse”).
In 1781, the British HMS Culloden ran aground near what today is called Culloden Point while pursuing a French frigate. The ship was scuttled, but its remains were discovered in the 1970s. It is now on the National Register of Historic Places and is the only underwater park in the state of New York.
The first hamlet of Montauk was built on Fort Pond Bay near what is now the train station for the Long Island Rail Road.
In 1792, Congress authorized construction of the Montauk Lighthouse. It was completed in 1796.
19th century
In 1839, slaves who had seized the schooner La Amistad came ashore in the hamlet looking for provisions after being told by the white crew they had returned to Africa. American authorities were alerted, and the slaves were recaptured and ultimately freed in a historically significant trial.
A judgment was entered in 1851 against the Trustees of the Freeholders and Commonalty of the Town of Easthampton, and on March 9, 1852, a deed to Montauk was given to plaintiffs Henry P. Hedges and others, because their predecessors had contributed the money to purchase Montauk from the native Montaukett Indians in the 1600s. This deed caused the lands covered by the Dongan Patent to be split, leaving the still unsettled lands at Montauk without government. Less than one month later, on April 2, 1852, a state law was passed that incorporated the Proprietors Montauks, establishing the corporation of the trustees of Montauk and affirming its right to govern.
Stephen Talkhouse was displayed in 1867 by P. T. Barnum as “the last king of the Montauks.” Talkhouse became famous for his walks from Indian Fields to New York City.
In 1879, Arthur W. Benson paid US$151,000 for 10,000 acres (40 km) for the east end. The deed releasing claim to Montauk was entered on March 9, 1852. Benson also received clear title to the Montaukett property at Big Reed Pond, buying it from tribesmen for $10 each, and in one case one of the tribesmen’s houses was burned down. The legitimacy of the transaction is still being contested in court by the tribe. Construction began in 1882 on seven Shingle-style “cottages” designed by Stanford White, which were the centerpiece of Benson’s plans. The most prominent of the six Montauk Association houses is Tick Hall, which was owned by entertainer Dick Cavett from 1967 to October 2021, when he sold it for $23.6 million.
The first train from the Austin Corbin extension of the Long Island Rail Road pulled into Montauk in 1895, the land having been bought in 1882. Corbin planned to turn Montauk into a “shortcut”, saving a day each way for voyages between New York City and London: ships would dock at the Fort Pond Bay terminal and passengers would travel by rail to New York City at 60 miles per hour (97 km/h)). Corbin built the dock on Fort Pond Bay, but the plans never materialized when, among other things, Fort Pond Bay was found to be too shallow and rocky to handle oceangoing ships.
In 1898, after the Benson/Corbin plan did not work out as planned, the United States Army bought the Benson property to establish a base called Camp Wikoff to quarantine Army personnel returning from the Spanish–American War. The most prominent of the returning quarantined soldiers were Theodore Roosevelt and his Rough Riders. Several soldiers died during the quarantine, prompting a visit from President William McKinley.
20th century
In 1924, Robert Moses began condemning the Benson land to establish state parks on either end of Montauk − Hither Hills State Park in the west and Montauk Point State Park in the east. The two parks were to be connected via the Montauk Point State Parkway.
In 1926, Carl G. Fisher bought most of the East End of Long Island (10,000 acres (40 km)) for only $2.5 million. He planned to turn Montauk into the “Miami Beach of the North”, a “Tudor village by the sea”. His projects included blasting a hole through the freshwater Lake Montauk to access Block Island Sound to replace the shallow Fort Pond Bay as the hamlet’s port; establishing the Montauk Yacht Club and the Montauk Downs Golf Course; and building Montauk Manor, a luxury resort hotel; the Montauk Tennis Auditorium, which became a movie theater (and is now the Montauk Playhouse); and the six-story Carl Fisher Office Building (later the Montauk Improvement Building and now The Tower at Montauk, a residential condominium). This last building remains East Hampton’s tallest occupied building, as zoning ordinances restricted heights of later buildings. The 30 or so buildings Fisher put up between 1926 and 1932 were designed in the Tudor Revival style. Fisher had successfully developed Miami Beach before beginning his Montauk project, but although he continued to pour his money into the development, to the extent of $12 million in total, he eventually lost his fortune due to the Wall Street Crash of 1929, and most of his enterprises were shut down. Other hotels that opened at the time of Fisher’s project include Gurney’s Inn, built by W. J. and Maude Gurney, who had managed a Fisher hotel in Miami Beach.
In the Great Hurricane of 1938, water flooded across Napeague, turning Montauk into an island. Floodwaters from the hurricane inundated the main downtown, and it was moved 3 miles (5 km) to the south, immediately next to the Atlantic Ocean.
During World War II the United States Navy bought most of the east end, including Montauk Manor, to turn it into a military base. Fort Pond Bay became a seaplane base. The U.S. Army established Camp Hero with 16-inch (410 mm) guns to protect New York shipping lanes. Several concrete bunker observation posts were built along the coast, including one immediately to the east of the Montauk Lighthouse. Base buildings were disguised so they would appear from above as a New England fishing village.
In 1951, sport fisherman Frank Mundus began to lead charter fishing trips out of Lake Montauk, initially looking for bluefish but soon found fishing for sharks was more lucrative. The sport of “monster fishing” became Montauk’s signature draw.
On September 1, 1951, the Pelican, captained by Eddie Carroll, capsized in the shoals off Montauk Point, resulting in the deaths of 45 passengers and crew. The 42-foot (13 m) Pelican was carrying 64 people, most of whom had taken the Fisherman’s Special trains to the Montauk LIRR station from New York City. The boat left the Fishangrila Dock at Fort Pond Bay at 7:30 a.m., severely overloaded. After fishing in the Atlantic Ocean on the south side of Montauk for several hours, it returned home, encountering engine trouble on the way. The weather turned stormy, and a northeast wind developed against an outgoing tide, resulting in standing waves of several feet at Endeavor Shoals, just off the Point. The vessel, wallowing in the heavy seas, became unstable in its overloaded state, capsized and then foundered at 2:10 p.m. Nearby vessels were only able to rescue 19 passengers. The wreck was secured by fabled sport fisherman Frank Mundus and towed into Lake Montauk by the Coast Guard. As a result of the disaster, strict new regulations regarding overloading of fishing vessels were adopted nationwide.
In 1957, the Army closed Camp Hero, and it was taken over by the United States Air Force, which in 1958 built a 100-foot-wide (30 m) AN/FPS-35 radar. A massive building was erected to house its computers.
In 1959, following the Kitchen Debate between United States Vice President Richard Nixon and Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev, the designers of the kitchen, including Raymond Loewy, announced plans to sell affordable prefabricated houses, called Leisurama, to be used for second homes. One of the houses was exhibited on the 9th floor of Macy’s. Two hundred of the houses, the largest installation, were assembled at Culloden Point in Montauk.
In 1967, the United States Coast Guard announced plans to tear down the Montauk Lighthouse and replace it with a taller steel tower. Erosion had reduced its buffer from the edge of a cliff from 300 feet (91 m) when it was built to less than 100 feet (30 m). After protests, the Coast Guard backed down from the plan. In 1982, the Air Force base formally closed, and the military began selling its surplus property.
Montauk Friends of Olmsted Parks LLC was established in 1994 to protect an extensive system of beaches and waterfront properties and roadways.
In 1995, Montauk became the birthplace of the extreme surfcasting technique known as skishing. The sport involves donning a wetsuit and flippers and swimming into the ocean with rod and reel to catch fish while drifting offshore.
21st century
In October 2007, a fishing boat dragged up a large 19th-century anchor, which was speculated to have been lost by the SS Great Eastern in 1862. In 2008, an unidentifiable carcass known as the “Montauk Monster” was discovered near the hamlet’s business district, with much speculation as to its identity. In August 2016 OCEARCH designated the waters off of Montauk and the rest of the South Shore of Long Island as a birthing ground for great white sharks.
Montauk Road Map
Montauk city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the hamlet has a total area of 19.8 square miles (51 km), of which 17.5 square miles (45 km) is land and 2.3 square miles (6.0 km), or 11.53%, is water.
Climate
Montauk has a humid subtropical climate (Cfa), under the Köppen climate classification, and using the 0 °C (32 °F) isotherm, is one of the northernmost locations in North America with this climate type. The presence of the Atlantic Ocean brings warmer winters than inland areas of the same latitude as well as cooler springs and summers: despite an extensive urban heat island and warmer lows throughout much of the year, Central Park in Manhattan, as compared to Montauk, averages twice as many days with a low reaching 10 °F (−12 °C) or below. The monthly daily average temperature ranges from 34.4 °F (1.3 °C) in January to 74.0 °F (23.3 °C) in July. There is 44.31 inches (1,130 mm) of precipitation annually, with a slight dry season in summer and wet season in late fall and early winter. Montauk’s warm subtropical climate makes it a popular vacation destination in the winter for New Yorkers and people from upstate New York.
According to the United States Department of Agriculture’s Agricultural Research Service, Montauk is in Plant Hardiness Zone 7b/8a, with an annual average extreme minimal temperature of 10 degrees Fahrenheit, which allows tropical plants to grow that would otherwise only be able to grow in the Deep South.
See also
Map of New York State and its subdivision:- Albany
- Allegany
- Bronx
- Broome
- Cattaraugus
- Cayuga
- Chautauqua
- Chemung
- Chenango
- Clinton
- Columbia
- Cortland
- Delaware
- Dutchess
- Erie
- Essex
- Franklin
- Fulton
- Genesee
- Greene
- Hamilton
- Herkimer
- Jefferson
- Kings
- Lake Ontario
- Lewis
- Livingston
- Madison
- Monroe
- Montgomery
- Nassau
- New York
- Niagara
- Oneida
- Onondaga
- Ontario
- Orange
- Orleans
- Oswego
- Otsego
- Putnam
- Queens
- Rensselaer
- Richmond
- Rockland
- Saint Lawrence
- Saratoga
- Schenectady
- Schoharie
- Schuyler
- Seneca
- Steuben
- Suffolk
- Sullivan
- Tioga
- Tompkins
- Ulster
- Warren
- Washington
- Wayne
- Westchester
- Wyoming
- Yates
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming