Hartford is a city in Washington and Dodge counties in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2010 census, the city had a population of 14,223. All of this population resided in the Washington County portion of the city. The portion of the city in Dodge County consists of only industrial/commercial parcels. Located approximately 38 miles (61 km) northwest of Downtown Milwaukee and 22 miles (35 km) from city limits, Hartford is located on the outer edge of the Milwaukee metropolitan area.
| Name: | Hartford city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Wisconsin |
| County: | Dodge County, Washington County |
| Elevation: | 981 ft (299 m) |
| Total Area: | 8.51 sq mi (22.04 km²) |
| Land Area: | 8.43 sq mi (21.83 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.08 sq mi (0.21 km²) |
| Total Population: | 14,223 |
| Population Density: | 1,832.58/sq mi (707.57/km²) |
| Area code: | 262 |
| FIPS code: | 5533000 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1566104 |
| Website: | www.ci.hartford.wi.us |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
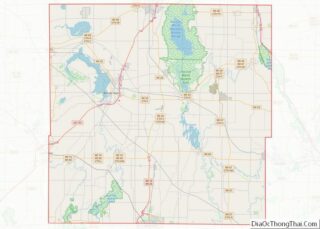
Hartford location map. Where is Hartford city?
History
Early history and settlement
In the early 19th century, Hartford was inhabited by the Potawatomi and Menominee people, who had a trading post on the Rubicon River and a village on the eastern shore of Pike Lake. In 1831, the Menominee surrendered their claims to the land to the United States Federal Government through the Treaty of Washington, and the Potawatomi surrendered their land claims in 1833 through the 1833 Treaty of Chicago, which (after being ratified in 1835) required them to leave the area by 1838. However, when the first White settlers arrived in 1843, they found that the Potawatomi were still living at the Pike Lake village. Some Native Americans remained in the area and were referred to as “strolling Potawatomi” in contemporary documents because many of them were migrants who subsisted by squatting on their ancestral lands, which were now owned by White settlers. Eventually the Potawatomi who evaded forced removal gathered in northern Wisconsin, where they formed the Forest County Potawatomi Community.
In July 1843, Timothy Hall became the first White person to purchase and settle land in the Hartford area, although when he arrived he found a Canadian named Jehial Case squatting near his land. Later that year, German immigrant settlers John Theil and Nicolaus Simon surveyed the Hartford area and determined that the Rubicon River would be a suitable location for a hydropowered mill. The following year, James and George Rossman joined Simon and Theil’s venture. The men purchased forty acres abutting the rapids of the Rubicon River and constructed a dam and a sawmill that harnessed the river’s power to make lumber from the old-growth forests covering the area. In 1846, a third Rossman brother, Charles, arrived in Hartford and constructed a gristmill to process grain grown by the settlers. On January 31, 1846, the land incorporated as the Town of Wright, before the name was changed to the Town of Hartford in February 1847, after Hartford, Connecticut. Many of the original settlers were Yankees from New England and were part of a wave of farmers who headed west in the early 1800s, though some other settlers—including Theil and Simon—were German immigrants. The early settlers cleared land for farming; constructed roads; created a post office; erected churches, starting with the First Congregational Church of Hartford which formed in 1847 and followed by Methodist, Baptist, Lutheran, and Catholic churches in the 1850s; and established businesses to serve the town’s agricultural economy, including equipment wholesalers, general stores, and dry goods dealers.
The La Crosse and Milwaukee Railroad was constructed through the community in 1855, and while rail connections were important to Hartford’s growth into the early 1900s, the company failed in 1861. Many local landowners had taken out mortgages on land for the railroad in exchange for company shares. The company’s failure left the landowners with mortgages to pay off, creating a local crisis in which some families were forced to sell their farms. The Hartford Home League newspaper started during the crisis to advocate for the farmers.
The community’s early years saw increasing tension between the settlers and Native Americans. For example, on August 25, 1861, a group of approximately a dozen Native Americans were living near Horicon Marsh, northwest of Hartford. They owned a horse, which got loose and wandered into a neighboring settler’s cornfield. The settler shot and killed the horse, and the Native Americans vowed to take revenge. The story traveled quickly, becoming increasingly exaggerated as it spread. By the time the story reached Hartford on August 26, the dozen peaceful Native Americans had been transfigured into an army of 5,000 warriors preparing to massacre the settlers in the area. Many able-bodied men in Hartford armed themselves, formed a war party, and set out to fight the Native Americans. But when they arrived at Horicon Marsh they found that the threat was entirely fictional. The incident caused widespread fear among the local Native American community as well as in the surrounding settler communities.
Growth and industrialization
Hartford incorporated as a city in 1883. While Hartford had a large German-American population in the 19th century and was home to several German cultural associations, including the Hartford Turners, the Hartford Schützenverein, and a chapter of the Sons of Hermann, the Germans in Hartford tended to be more assimilated than Germans in other Washington County communities. In 1912, one historian observed that in Washington County “there have always been places where the American [culture] predominated. Take the example of the two cities in the county. Hartford always was more of an American community than West Bend.”
In the final decades of the 1800s and first years of the 1900s, Hartford’s economy shifted from being a small market town serving the local farmers to being a larger industrial community. In 1906, the Kissel Motor Car Company opened and quickly became the community’s largest employer, creating hundreds of jobs and bringing European immigrant laborers into the community. Hartford was also home to the International Stamping Company, which manufactured automobile parts; the Hartford Canning Company, which processed local farmers’ crops such as peas, which were a cash crop in the area; the knitting mills of the Paramount Knitting Company; a glove factory; three tanneries and a brewery.
During World War II, Hartford’s factories contributed to the war effort. The Kissel car factory, which was sold to the West Bend Aluminum Company in 1944, was retooled to make shell casings, rocket containers, affordable kitchenware and canisters for gas masks. The Hartford Canning Company produced military rations. In the summer of 1944, the U.S. military tried to fill labor shortages in the Hartford area by contracting German prisoners of war to work on pea farms. Initially, the prisoners were transported from a requisitioned hotel on Lake Keesus in Waukesha County. In October 1944, the military requisitioned the Schwartz Ballroom on Jefferson Street (operating as the “Chandelier Ballroom” as of 2020) to serve as a prisoner of war camp for 600 Germans. The prisoners were contracted to work on farms as well as in canneries, hemp mills, dairy facilities and tanneries. The camp closed in January 1946 and the prisoners were repatriated to Germany.
Hartford’s population grew during the post–World War II economic expansion. The population more than doubled between 1950 and 1960, and the community has continued to grow in subsequent decades. While many of the early 20th century manufacturers, including the Kissel Motor Car Company, have closed, Hartford is home to several large manufacturers, including Broan-NuTone, which manufactures ventilation systems. In 1990, the city annexed land from the neighboring Town of Rubicon in Dodge County to expand its industrial zone.
Historic landmarks
Several buildings are listed on the National Register of Historic Places and among them are some of the Kissel houses as well as houses they built for others.
The Hartford post office contains an oil on canvas mural, Autumn Wisconsin Landscape, painted in 1940 by Ethel Spears. It was produced for the Section of Painting and Sculpture (later the Section of Fine Arts) of the Treasury Department as part of the WPA Depression-era employment projects.
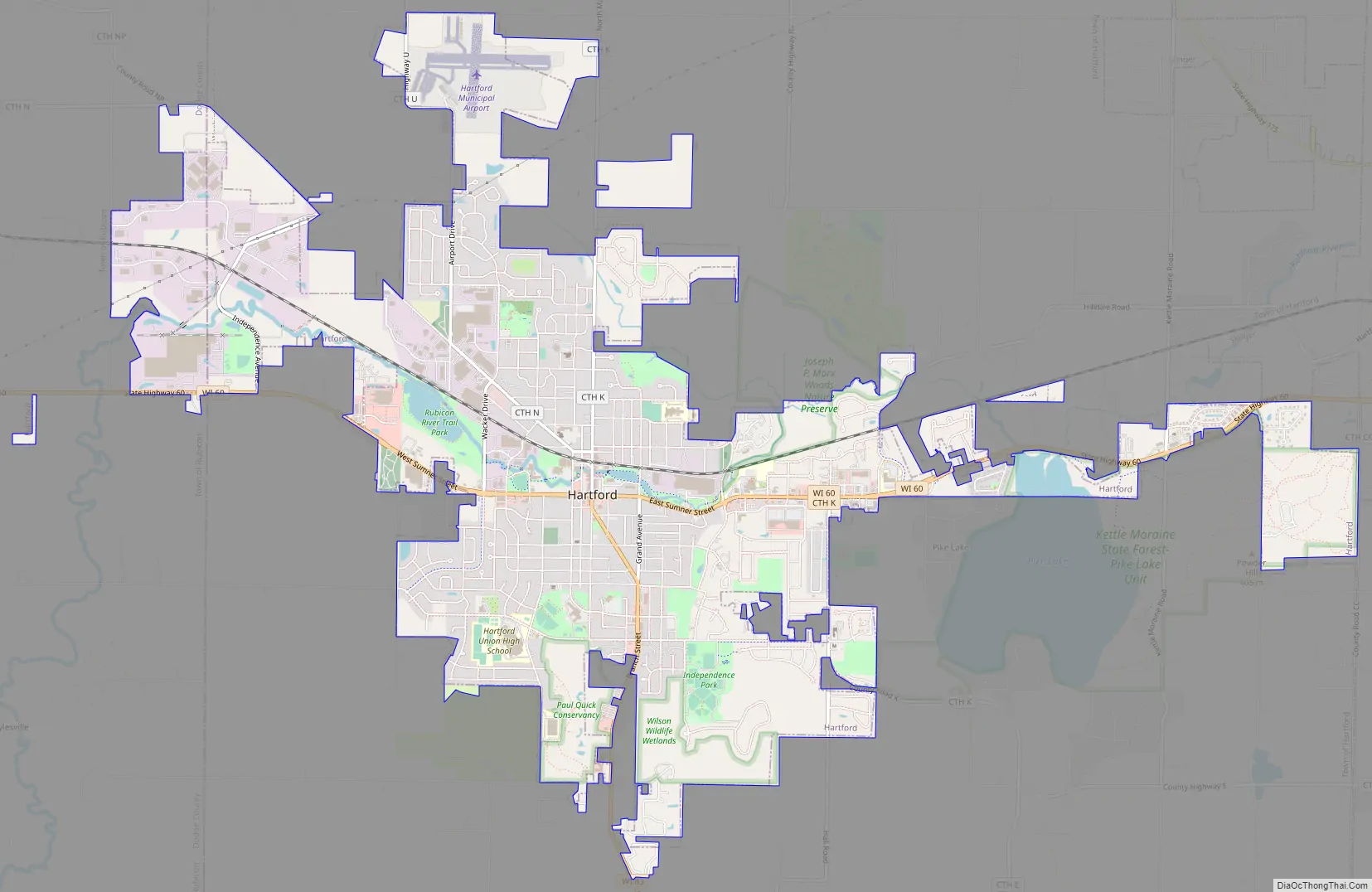
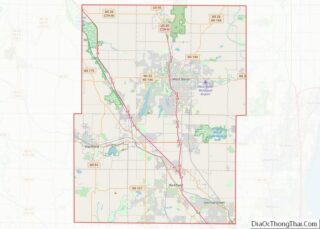
Hartford Road Map
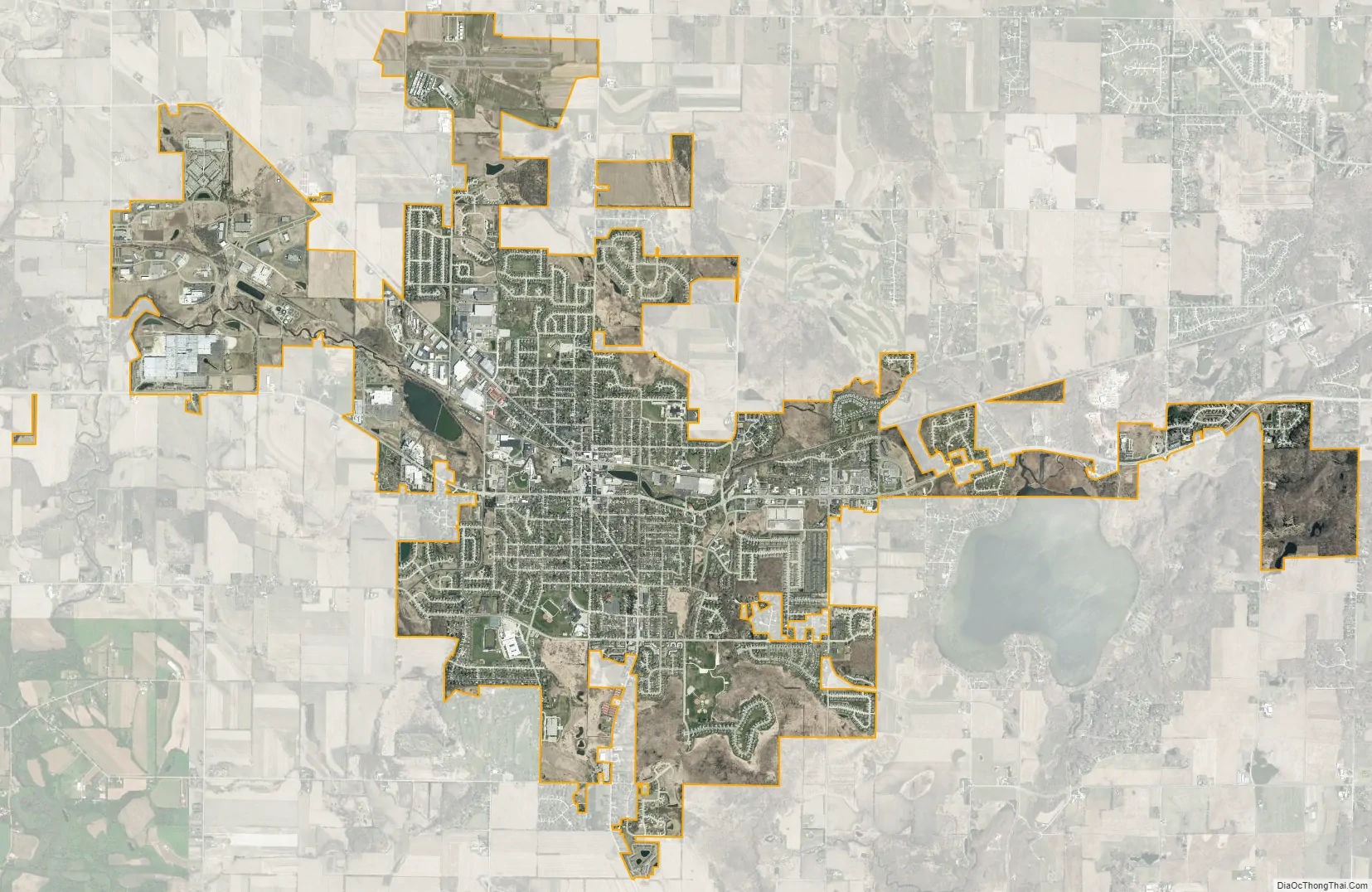
Hartford city Satellite Map
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 8.02 square miles (20.77 km), of which, 7.94 square miles (20.56 km) is land and 0.08 square miles (0.21 km) is water.
Hartford is located within the Kettle Moraine, a large moraine formed when the Green Bay and Lake Michigan Lobes collided. These glacial movements created varied land formations such as kettles, lakes, hills, and kames that distinguish the region.
Tornado of 2006
The city was the site of an F1 tornado on June 18, 2006, which caused minor damage to homes in the area, and major damage on the city’s south side. Lincoln Elementary School and the Silver Bell Motel both suffered roof and structural damage.
See also
Map of Wisconsin State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Ashland
- Barron
- Bayfield
- Brown
- Buffalo
- Burnett
- Calumet
- Chippewa
- Clark
- Columbia
- Crawford
- Dane
- Dodge
- Door
- Douglas
- Dunn
- Eau Claire
- Florence
- Fond du Lac
- Forest
- Grant
- Green
- Green Lake
- Iowa
- Iron
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Juneau
- Kenosha
- Kewaunee
- La Crosse
- Lafayette
- Lake Michigan
- Lake Superior
- Langlade
- Lincoln
- Manitowoc
- Marathon
- Marinette
- Marquette
- Menominee
- Milwaukee
- Monroe
- Oconto
- Oneida
- Outagamie
- Ozaukee
- Pepin
- Pierce
- Polk
- Portage
- Price
- Racine
- Richland
- Rock
- Rusk
- Saint Croix
- Sauk
- Sawyer
- Shawano
- Sheboygan
- Taylor
- Trempealeau
- Vernon
- Vilas
- Walworth
- Washburn
- Washington
- Waukesha
- Waupaca
- Waushara
- Winnebago
- Wood
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming