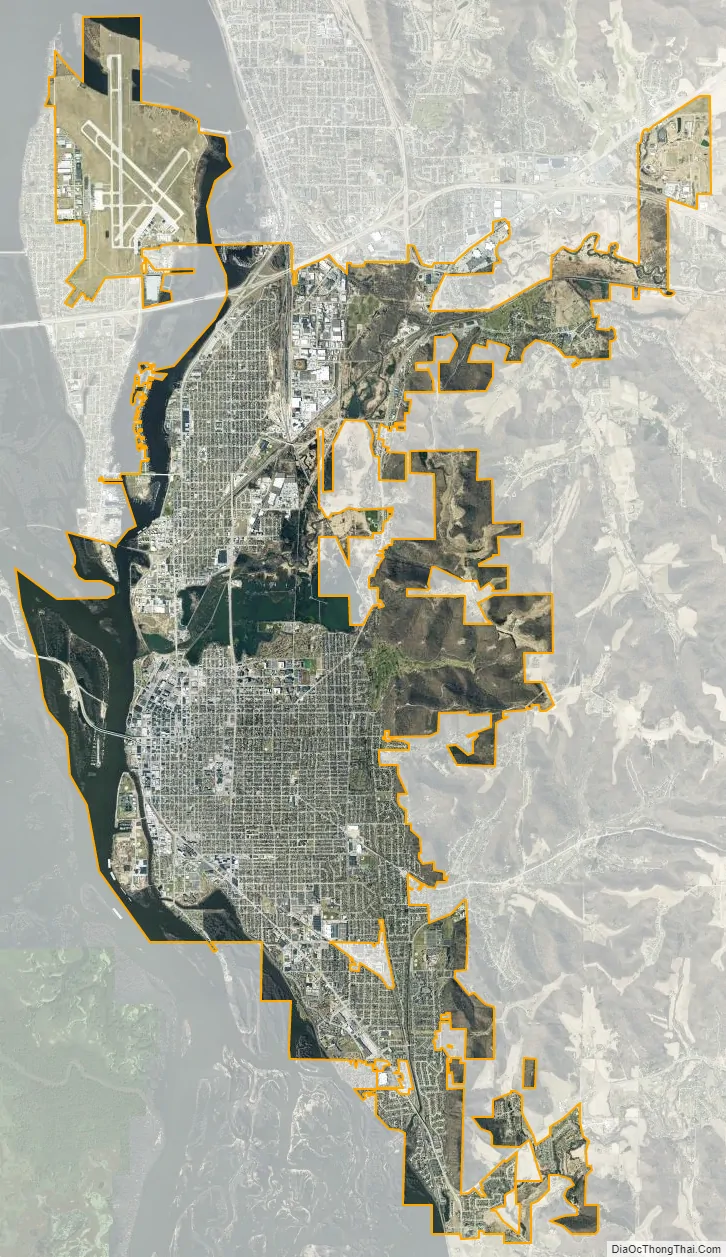
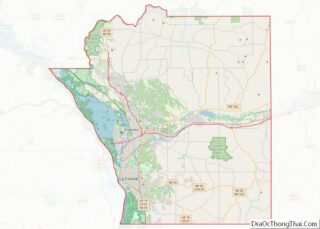
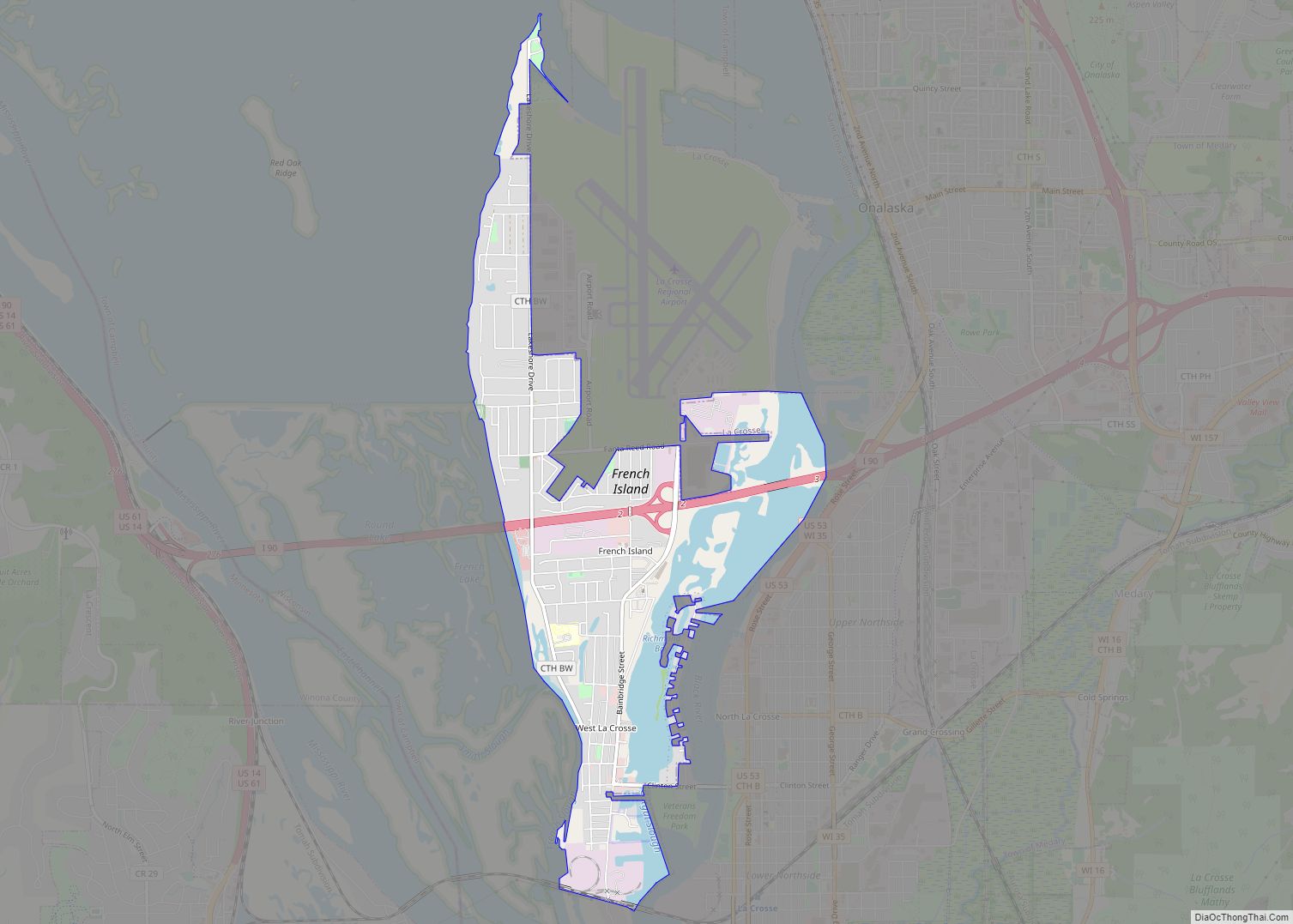
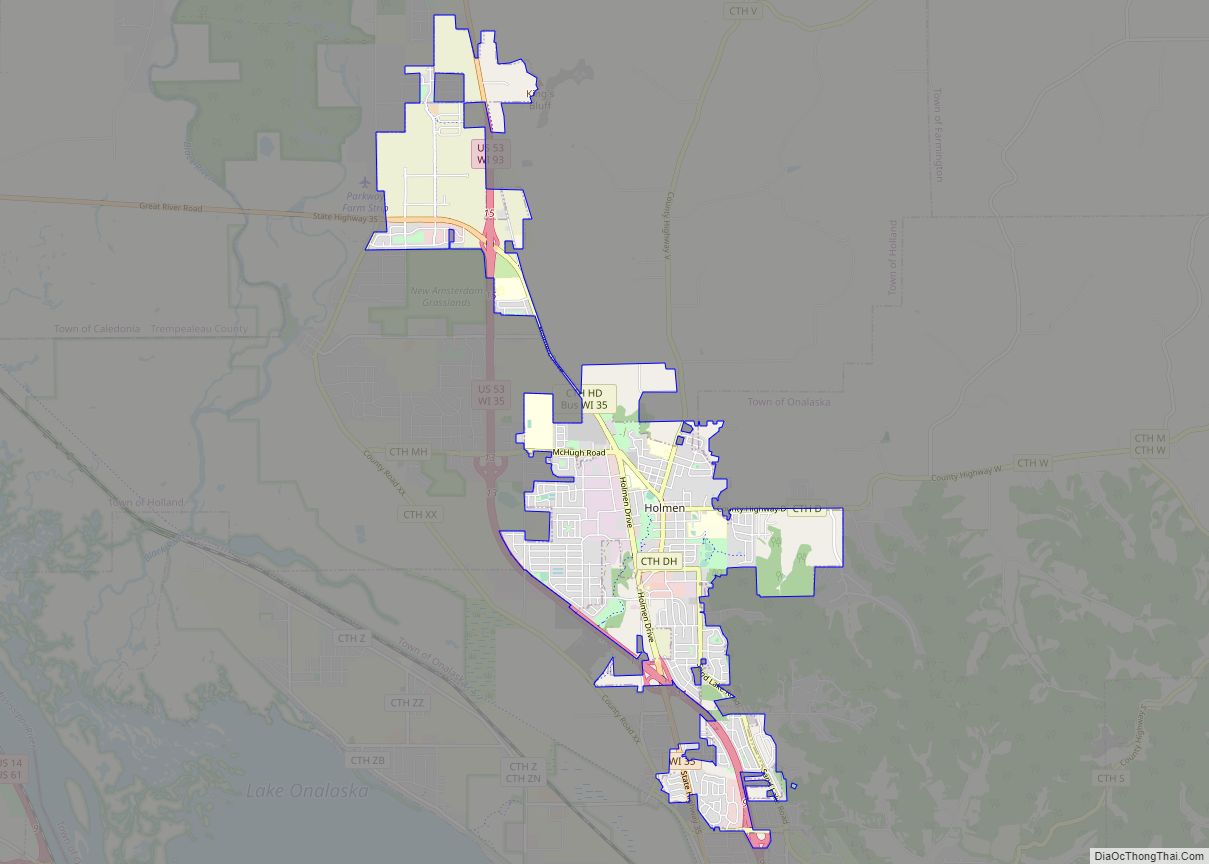
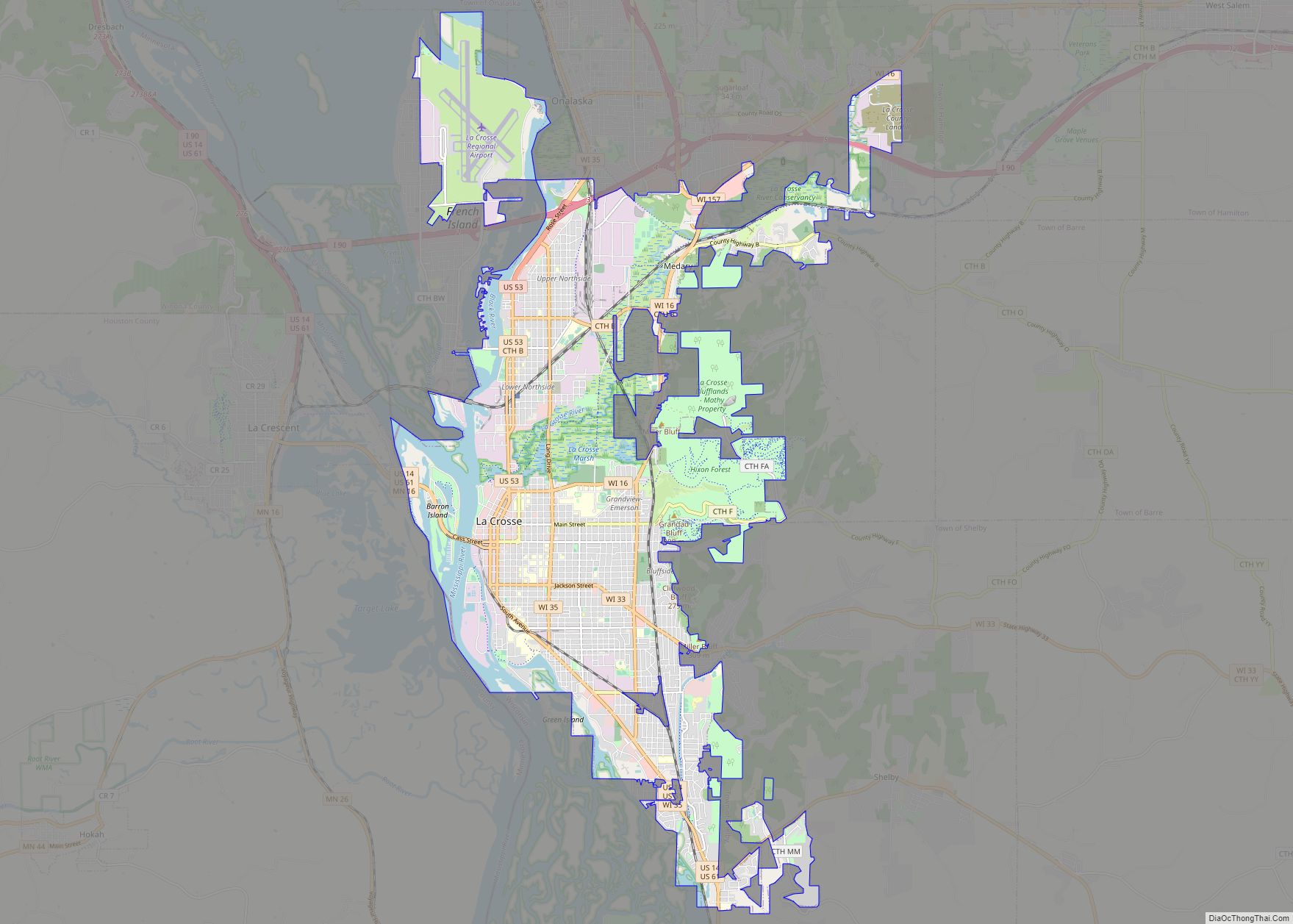
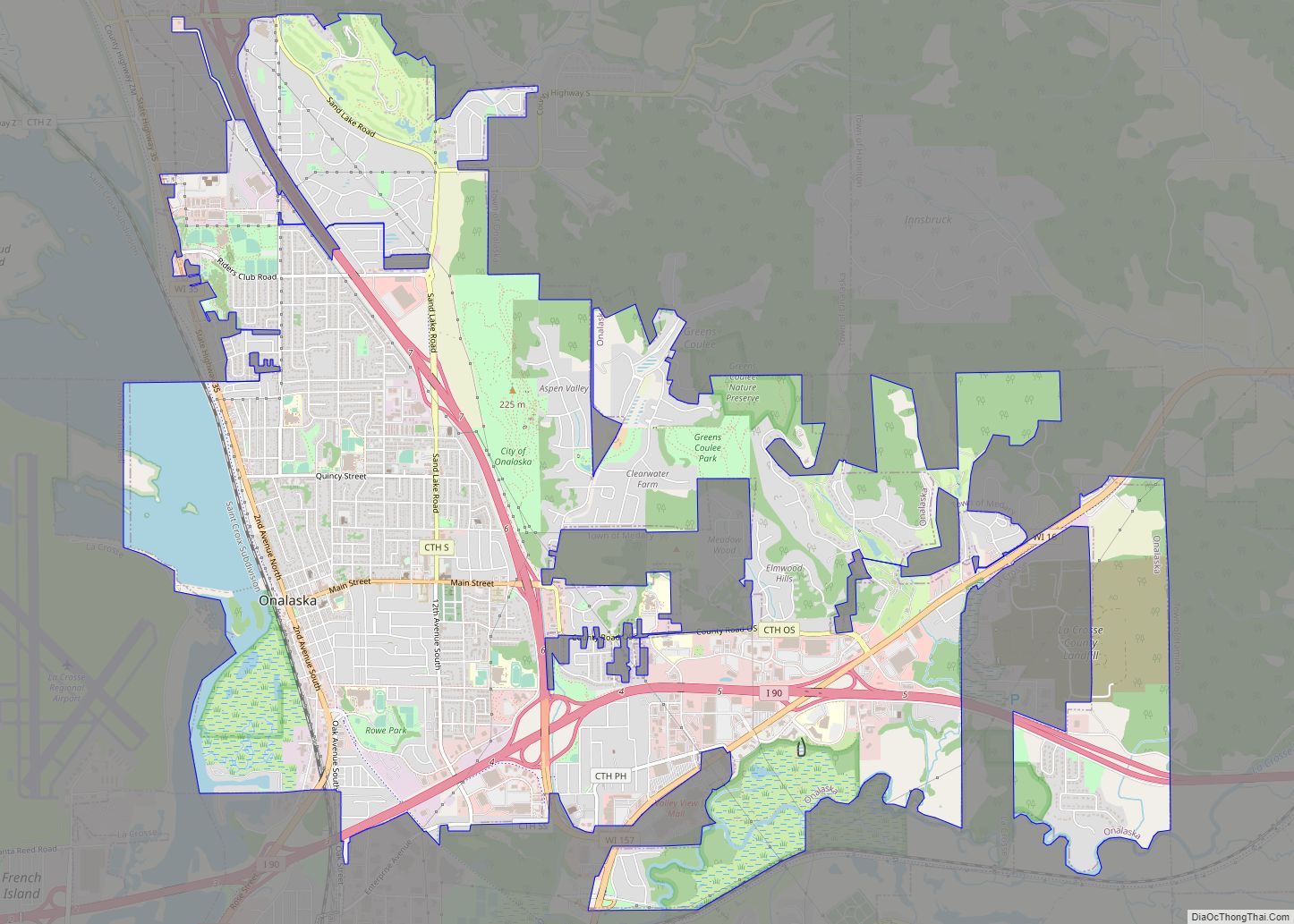
La Crosse is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of La Crosse County. Positioned alongside the Mississippi River, La Crosse is the largest city on Wisconsin’s western border. La Crosse’s population as of the 2020 census was 52,680. The city forms the core of and is the principal city in the La Crosse–Onalaska Metropolitan Area, which includes all of La Crosse County and Houston County, Minnesota, with a population of 139,627.
A regional technology, medical, education, manufacturing, and transportation hub, companies based in the La Crosse area include Organic Valley, Logistics Health Incorporated, Kwik Trip, La Crosse Technology, City Brewing Company, and Trane.
La Crosse is a college town with over 20,000 students and home to the University of Wisconsin-La Crosse, Viterbo University, and Western Technical College.
| Name: | La Crosse city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | Wisconsin |
| County: | La Crosse County |
| Elevation: | 669 ft (204 m) |
| Land Area: | 21.70 sq mi (56.21 km²) |
| Water Area: | 2.08 sq mi (5.40 km²) |
| Population Density: | 2,214.38/sq mi (911.34/km²) |
| Area code: | 608 |
| FIPS code: | 5540775 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1567672 |
| Website: | www.cityoflacrosse.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
La Crosse location map. Where is La Crosse city?
History
The first Europeans to see the region were French fur traders who traveled the Mississippi River in the late 17th century. There is no written record of any visit to the site until 1805, when Lt. Zebulon Pike mounted an expedition up the Mississippi River for the United States. Pike recorded the location’s name as “Prairie La Crosse”. The name originated from the game with sticks that resembled a bishop’s crozier or la crosse in French, which was played by Native Americans there.
In 1841, the first white settlement at La Crosse was established when Nathan Myrick, a New York native, moved to the village at Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin to work in the fur trade. Myrick was disappointed to find that because many fur traders were already well-entrenched there, there were no openings for him in the trade. As a result, he decided to establish a trading post upriver at the then still unsettled site of Prairie La Crosse. In 1841, he built a temporary trading post on Barron Island (now called Pettibone Park), which lies just west of La Crosse’s present downtown. The following year, Myrick relocated the post to the mainland prairie, partnering with H. J. B. Miller to run the outfit.
The spot Myrick chose to build his trading post proved ideal for settlement. It was near the junction of the Black, La Crosse, and Mississippi Rivers. In addition, the post was built at one of the few points along the Wisconsin side of the Mississippi River where a broad plain, ideal for development, existed between the river’s bank and the tall bluffs that line the river valley. Because of these advantages, a small village grew around Myrick’s trading post in the 1840s.
In 1844, a small Mormon community settled at La Crosse, building several dozen cabins a few miles (kilometers) south of Myrick’s post. Although these settlers relocated away from the Midwest after just a year, the land they occupied near La Crosse continues to bear the name Mormon Coulee.
On June 23, 1850, Father James Lloyd Breck of the Episcopal Church said the first Christian liturgy on top of Grandad Bluff. Today, a monument to that event stands atop the bluff, near the parking lot at a scenic overlook.
More permanent development took place closer to Myrick’s trading post, where stores, a hotel, and a post office were constructed during the 1840s. Under the direction of Timothy Burns, lieutenant governor of Wisconsin, surveyor William Hood platted the village in 1851. This opened it up for further settlement, which was achieved rapidly as a result of promotion of the city in eastern newspapers. By 1855, La Crosse had grown in population to nearly 2,000 residents, leading to its incorporation in 1856. The city grew even more rapidly after 1858 with the completion of the La Crosse & Milwaukee Railroad, the second railroad connecting Milwaukee to the Mississippi River.
During the second half of the 19th century, La Crosse grew to become one of the largest cities in Wisconsin. It was a center of the lumber industry, for logs cut in the interior of the state could be rafted down the Black River toward sawmills built in the city. La Crosse also became a center for the brewing industry and other manufacturers that saw advantages in the city’s location adjacent to major transportation arteries, such as the Mississippi River and the railroad between Milwaukee and St. Paul, Minnesota.
Around the turn of the 20th century, the city became a center for education, with three colleges and universities established in the city between 1890 and 1912. Similar to cities across the country, La Crosse saw population stagnation in the latter half of the 20th century as a result of suburbanization. Since 1966, La Crosse has seen its population grow by 10.73%, while its area, miles of sewer, and miles of water mains each grew by more than 50%.
In 2016, Mayor Tim Kabat and former Mayor John Medinger issued a proclamation apologizing for La Crosse’s history as a sundown town that discriminated against African Americans.
La Crosse remains the largest city on Wisconsin’s western border, and the educational institutions in the city have recently led it toward becoming a regional technology and medical hub.
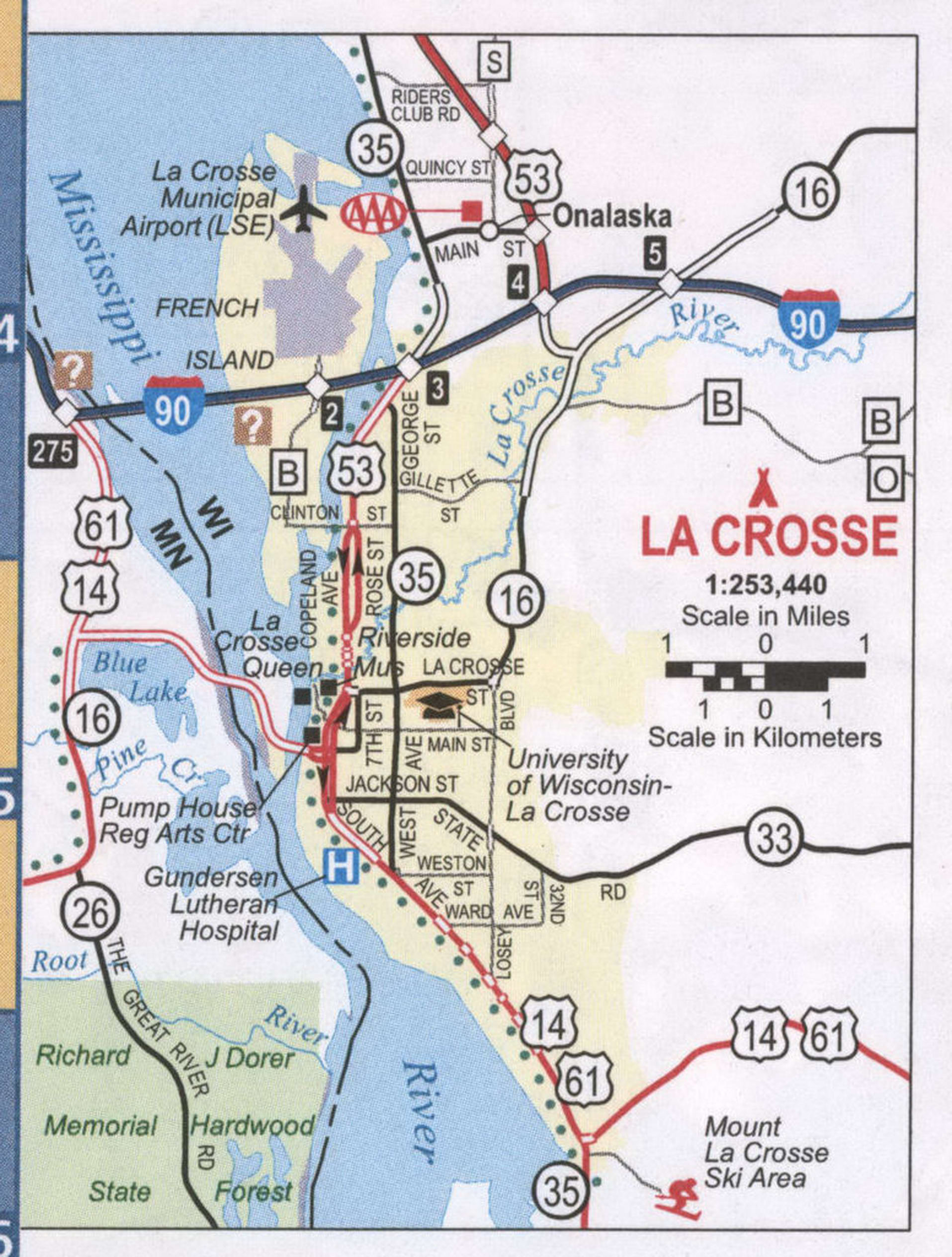
La Crosse Road Map
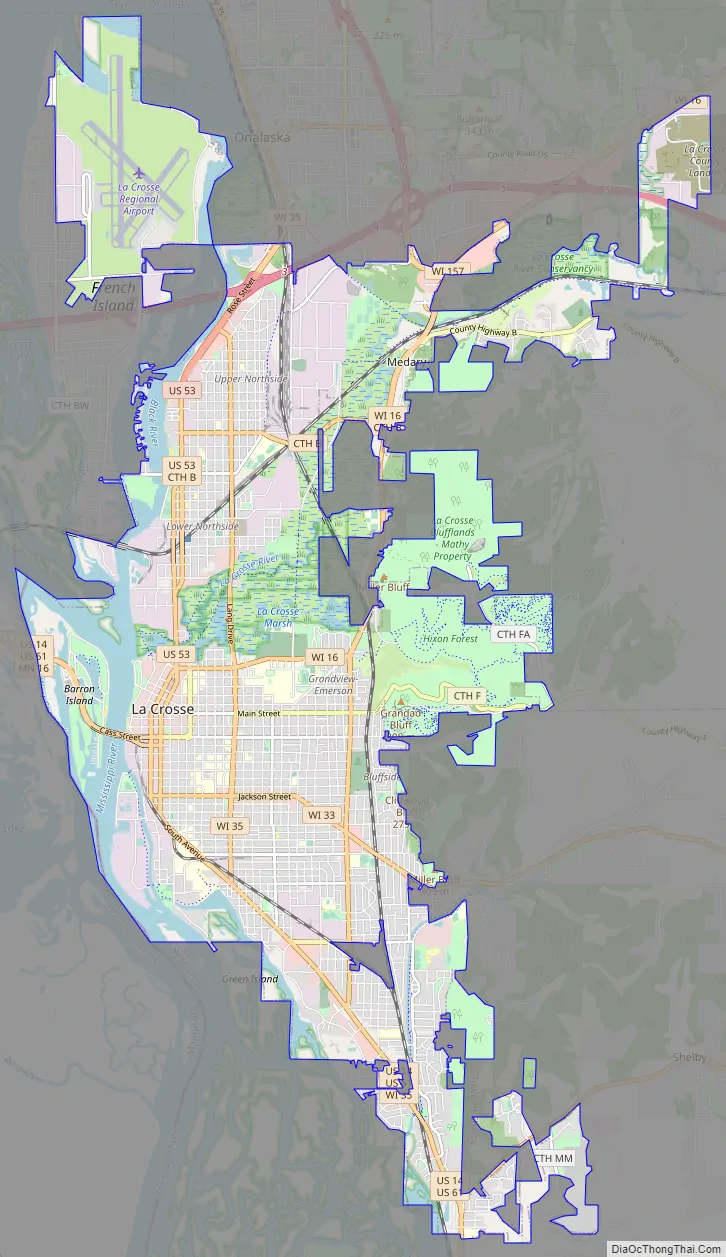
La Crosse city Satellite Map
Geography
La Crosse is located on the western border of the midsection of Wisconsin, on a broad alluvial plain along the east side of the Mississippi River. The Black River empties into the Mississippi north of the city, and the La Crosse River flows into the Mississippi just north of the downtown area. Just upriver from its mouth, this river broadens into a marshland that splits the city into two distinct sections, north and south.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 23.79 square miles (61.62 km), of which, 21.7 square miles (56.20 km) is land and 2.08 square miles (5.39 km) is water.
Surrounding the relatively flat prairie valley where La Crosse lies are towering 500-foot (150 m) bluffs, one of the most prominent of which is Grandad Bluff (mentioned in Life on the Mississippi by Mark Twain), which has an overlook of the three states region. This feature typifies the topography of the Driftless Area in which La Crosse sits. This rugged region is composed of high ridges dissected by narrow valleys called coulees, a French term. As a result, the area around La Crosse is frequently referred to as the “Coulee Region”.
Climate
La Crosse’s location in the United States’ Upper Midwest gives the area a temperate, continental climate. The warmest month of the year is July, when the average high temperature is 84.1 °F (28.9 °C), with overnight low temperatures averaging 63.2 °F (17.3 °C). January is the coldest month, with high temperatures averaging 25.9 °F (−3.4 °C), with the overnight low temperatures around 8.9 °F (−12.8 °C).
Neighborhoods and districts
La Crosse has 13 voting districts (wards). Neighborhoods within the city include:
- Bluffside
- Washburn
- Historic Cass & King
- Powell-Poage-Hamilton
- Historic downtown
- Northside (Upper and Lower) and Old Towne North
- Grandview Emerson
- Weigent Hogan
- Hintgen
- College Park (UW–La Crosse campus district)
- Springbrook Clayton Johnson
Suburbs of the city include: French Island in the Town of Campbell, Holmen, the Town of Medary, City of Onalaska, La Crescent, Minnesota, and the Town of Shelby.
Area
See also
Map of Wisconsin State and its subdivision:- Adams
- Ashland
- Barron
- Bayfield
- Brown
- Buffalo
- Burnett
- Calumet
- Chippewa
- Clark
- Columbia
- Crawford
- Dane
- Dodge
- Door
- Douglas
- Dunn
- Eau Claire
- Florence
- Fond du Lac
- Forest
- Grant
- Green
- Green Lake
- Iowa
- Iron
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Juneau
- Kenosha
- Kewaunee
- La Crosse
- Lafayette
- Lake Michigan
- Lake Superior
- Langlade
- Lincoln
- Manitowoc
- Marathon
- Marinette
- Marquette
- Menominee
- Milwaukee
- Monroe
- Oconto
- Oneida
- Outagamie
- Ozaukee
- Pepin
- Pierce
- Polk
- Portage
- Price
- Racine
- Richland
- Rock
- Rusk
- Saint Croix
- Sauk
- Sawyer
- Shawano
- Sheboygan
- Taylor
- Trempealeau
- Vernon
- Vilas
- Walworth
- Washburn
- Washington
- Waukesha
- Waupaca
- Waushara
- Winnebago
- Wood
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming