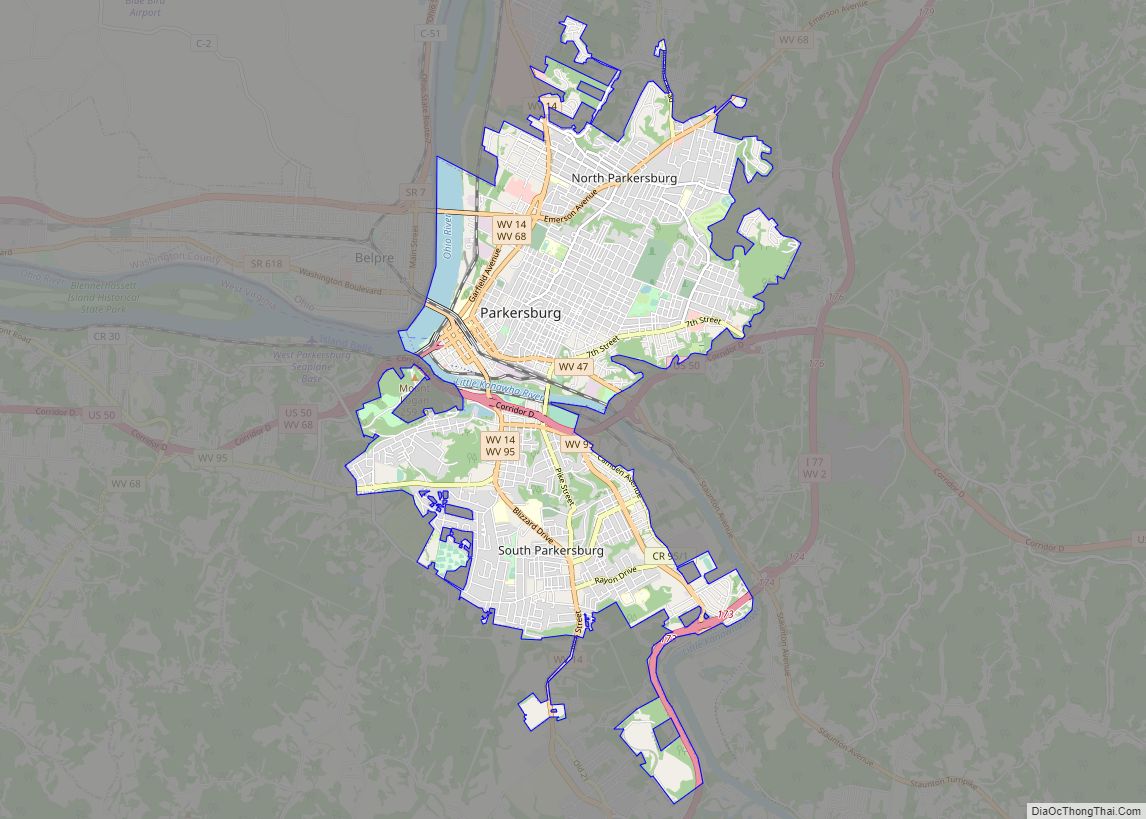
Parkersburg is a city in and the county seat of Wood County, West Virginia. Located at the confluence of the Ohio and Little Kanawha rivers, it is the state’s fourth-largest city and the center of the Parkersburg–Vienna metropolitan area. The city’s population was 29,749 at the 2020 census, and its metro population was 89,490. The city is about 14 miles (23 km) south of Marietta, Ohio.
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad reached Parkersburg in 1857, but lacked a crossing over the Ohio River until after the American Civil War. When the B&O completed the Parkersburg Bridge (CSX) 1868–1870 to Belpre, it was the longest railroad bridge in the world.
The Bureau of the Public Debt, an agency of the U.S. Treasury Department, was relocated from the Washington, D.C. metropolitan area in the late 20th century and headquartered in Parkersburg. In October 2012, it was merged with the Financial Management Service to form the Bureau of the Fiscal Service.
| Name: | Parkersburg city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
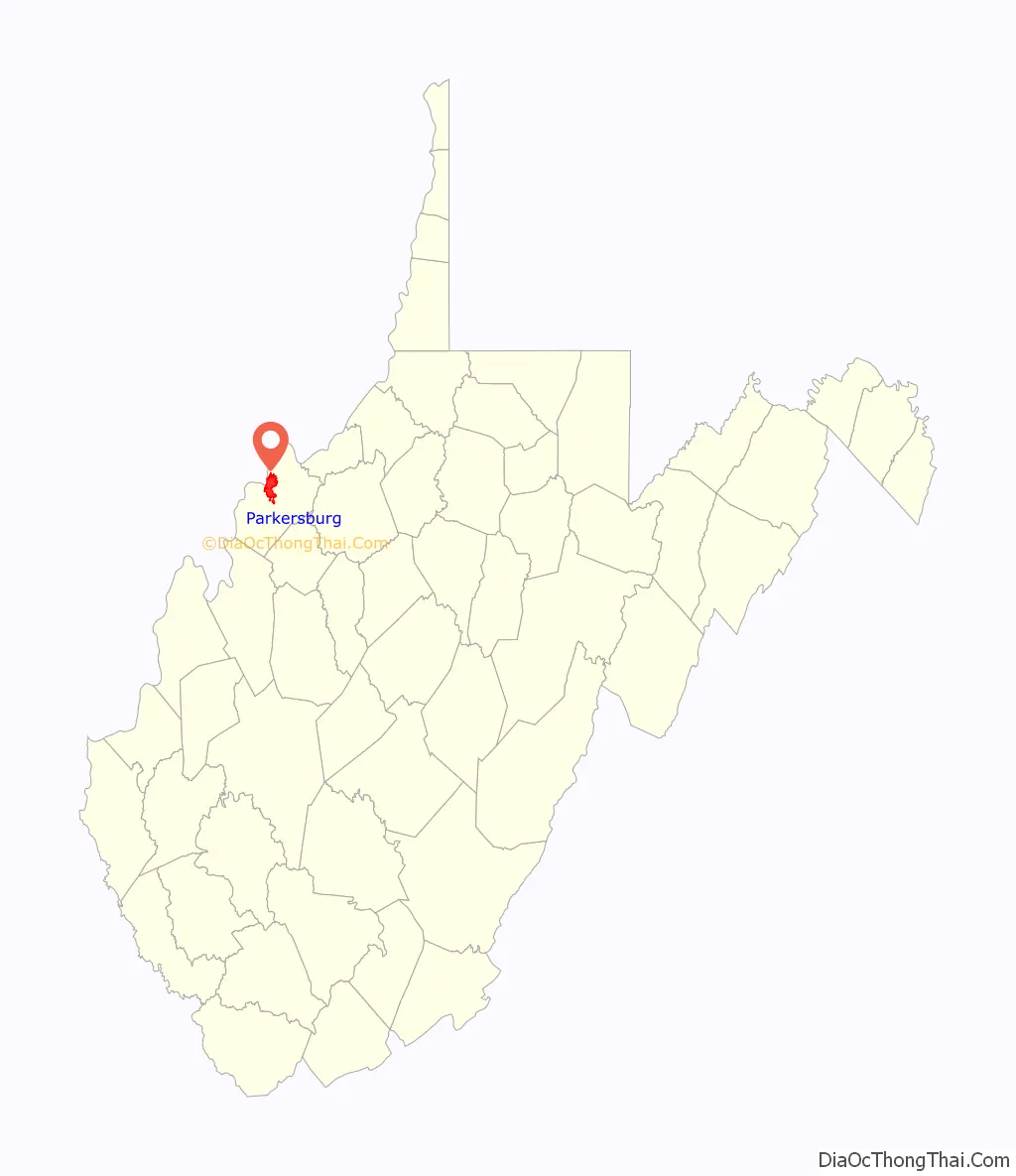
| State: | West Virginia |
| County: | Wood County |
| Incorporated: | 1810 |
| Elevation: | 614 ft (187 m) |
| Land Area: | 11.78 sq mi (30.52 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.55 sq mi (1.43 km²) 4.29% |
| Population Density: | 2,487.35/sq mi (960.34/km²) |
| ZIP code: | 26101, 26102, 26103, 26104, 26105, 26106 |
| Area code: | 304, 681 |
| FIPS code: | 5462140 |
| GNISfeature ID: | 1544587 |
| Website: | parkersburgcity.com |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
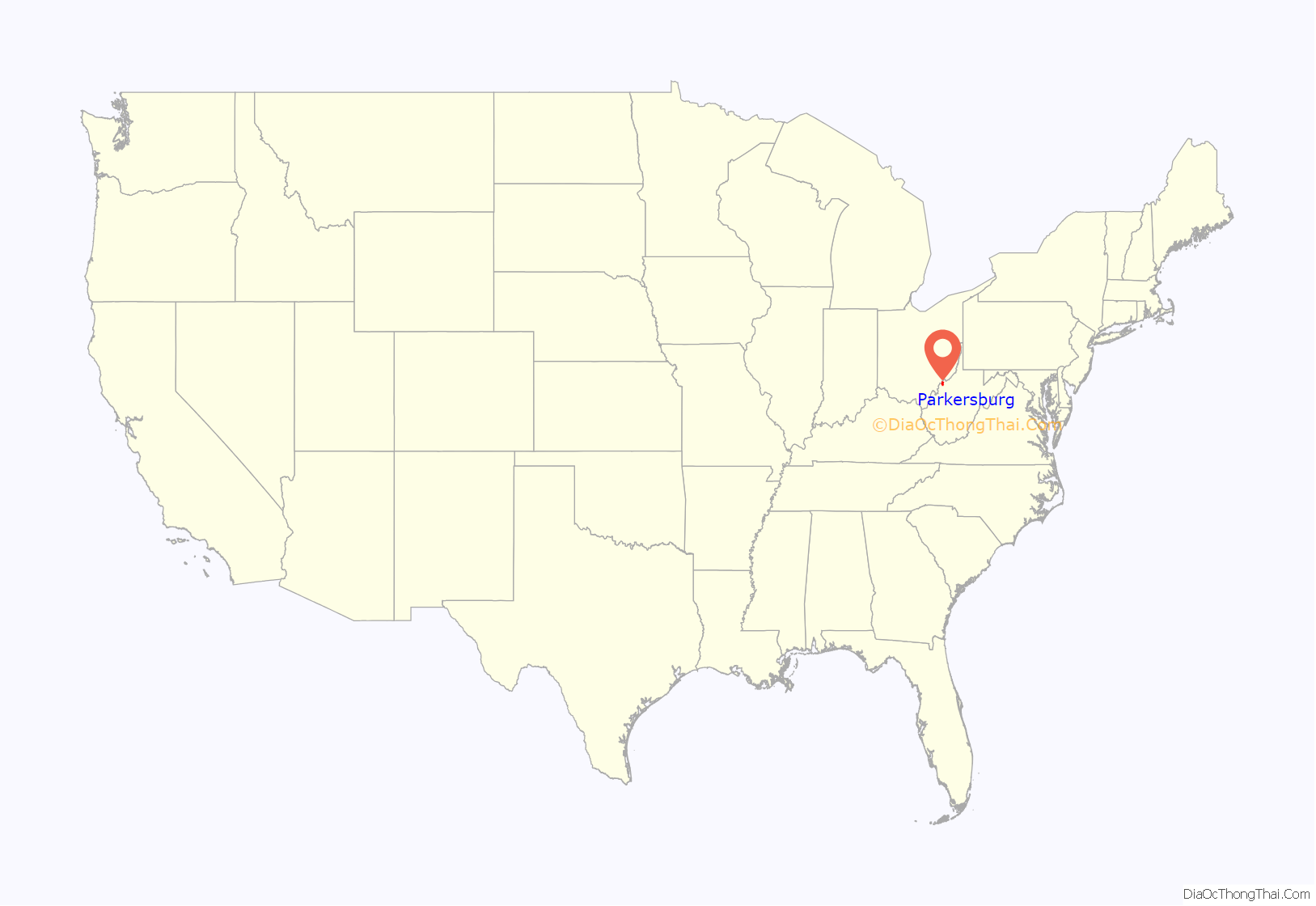
Parkersburg location map. Where is Parkersburg city?
History
Settlers at first named the city Newport when they settled it in the late 18th century following the American Revolutionary War. This was part of a westward migration of settlers from parts of Virginia to the east, closer to the Atlantic Ocean. A town section was laid out on land granted to Alexander Parker for his Revolutionary War service. Virginia made grants of land to veterans for their war service. The title conflicts between Parker and the city planners of Newport were settled in 1809 in favor of his heirs. The town was renamed Parkersburg in 1810. It was chartered by the Virginia General Assembly in 1820. It was rechartered as a city in 1860.
The town was the western terminus of both the Staunton-Parkersburg Turnpike and the Northwestern Turnpike. In 1857 the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad built a branch line south to the town from Wheeling, West Virginia. Travelers wanting to connect with the Ohio Marietta and Cincinnati Railroad, one of the east–west lines along the Ohio River, had to take a steamboat 14 miles north to Marietta, Ohio. Jacob Linville designed the railroad bridge planned by the B&O. It was constructed in 1868–1870 between Parkersburg and Belpre, Ohio, as part of the B&O’s main line from Baltimore to St. Louis, Missouri. This drew traffic and trade from Marietta. Today the structure is known as the Parkersburg Bridge.
Parkersburg served as a transportation and medical center for Union forces during the American Civil War. It developed further as a transportation hub in the gas and oil boom following that war.
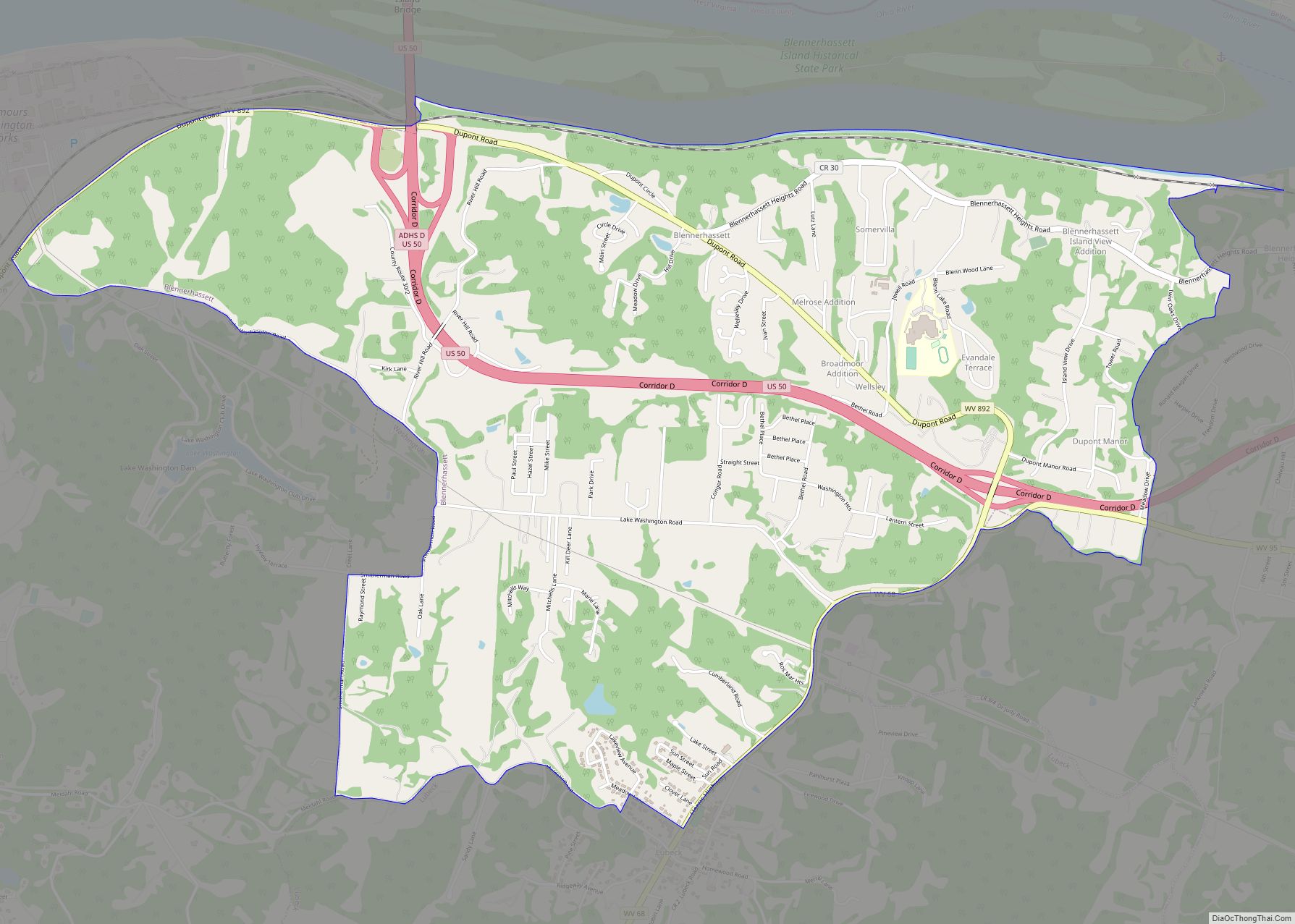
Blennerhassett Island Historical State Park is a historical island located just below Parkersburg.
In the late 19th century, Parkersburg emerged as a major oil refining center serving nearby oilfields at Volcano and Burning Springs. The Camden Consolidated Oil Company, founded in 1866 by future U.S. Senator Johnson Newlon Camden, dominated the refining business and was sold to Rockefeller’s Standard Oil Company in 1875. Camden became a Standard director and vice president and, along with John W. Davis, dominated West Virginia politics until the early 20th century.
In the post-World War II period, Parkersburg became one of the leading industrial centers of the Ohio Valley, producing chemicals, glass, O. Ames tools, textiles (especially American Viscose Company rayon), plastics and polymers, iron, and steel. The Bureau of the Public Debt, an agency of the U.S. Treasury Department, was moved to Parkersburg in 1954 as a location midway between Chicago and Washington, D.C. that would be safe in the event of a national emergency. In October 2012, the Bureau of the Public Debt consolidated with the Financial Management Service to form the Bureau of the Fiscal Service.
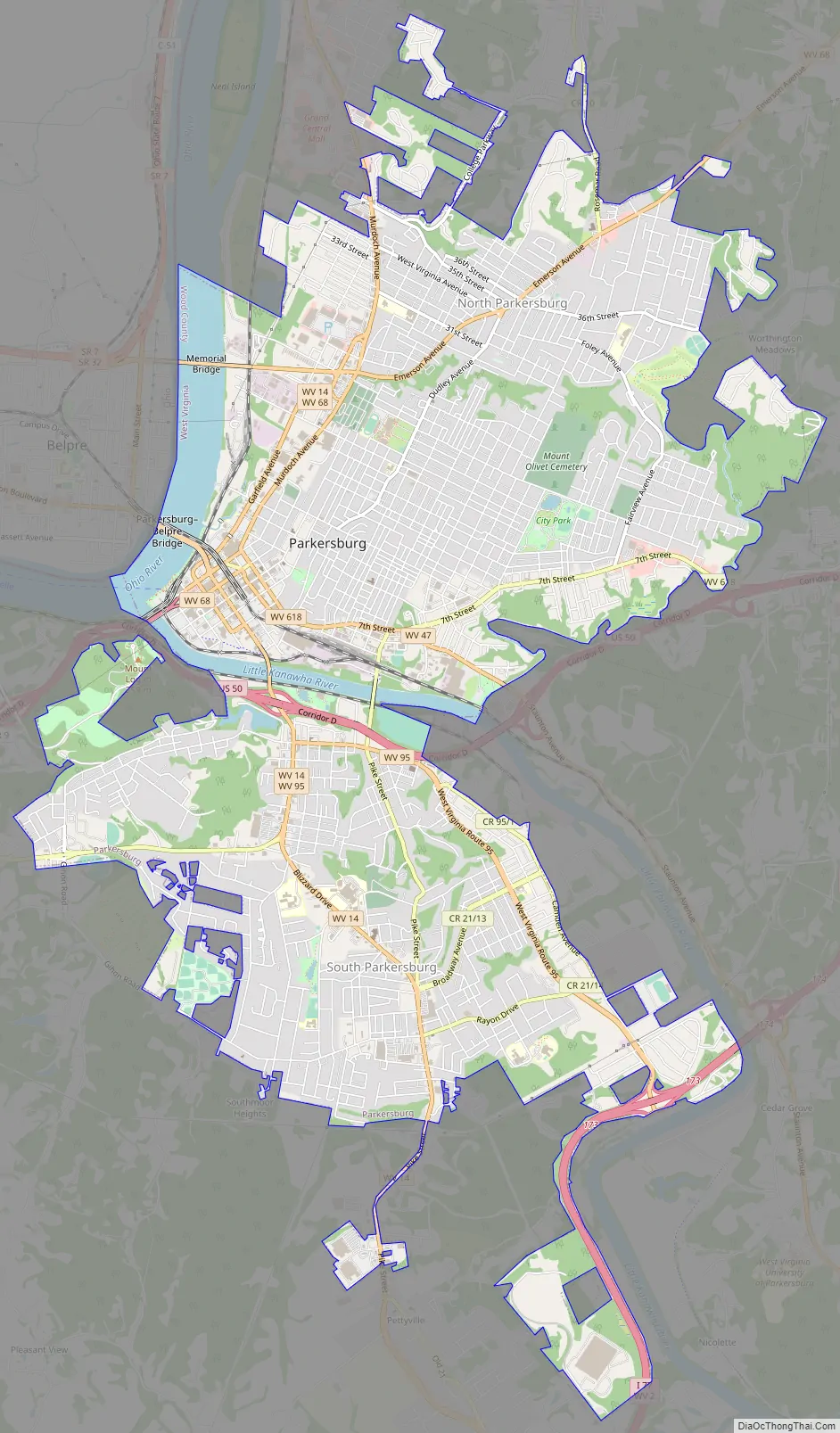
Parkersburg Road Map
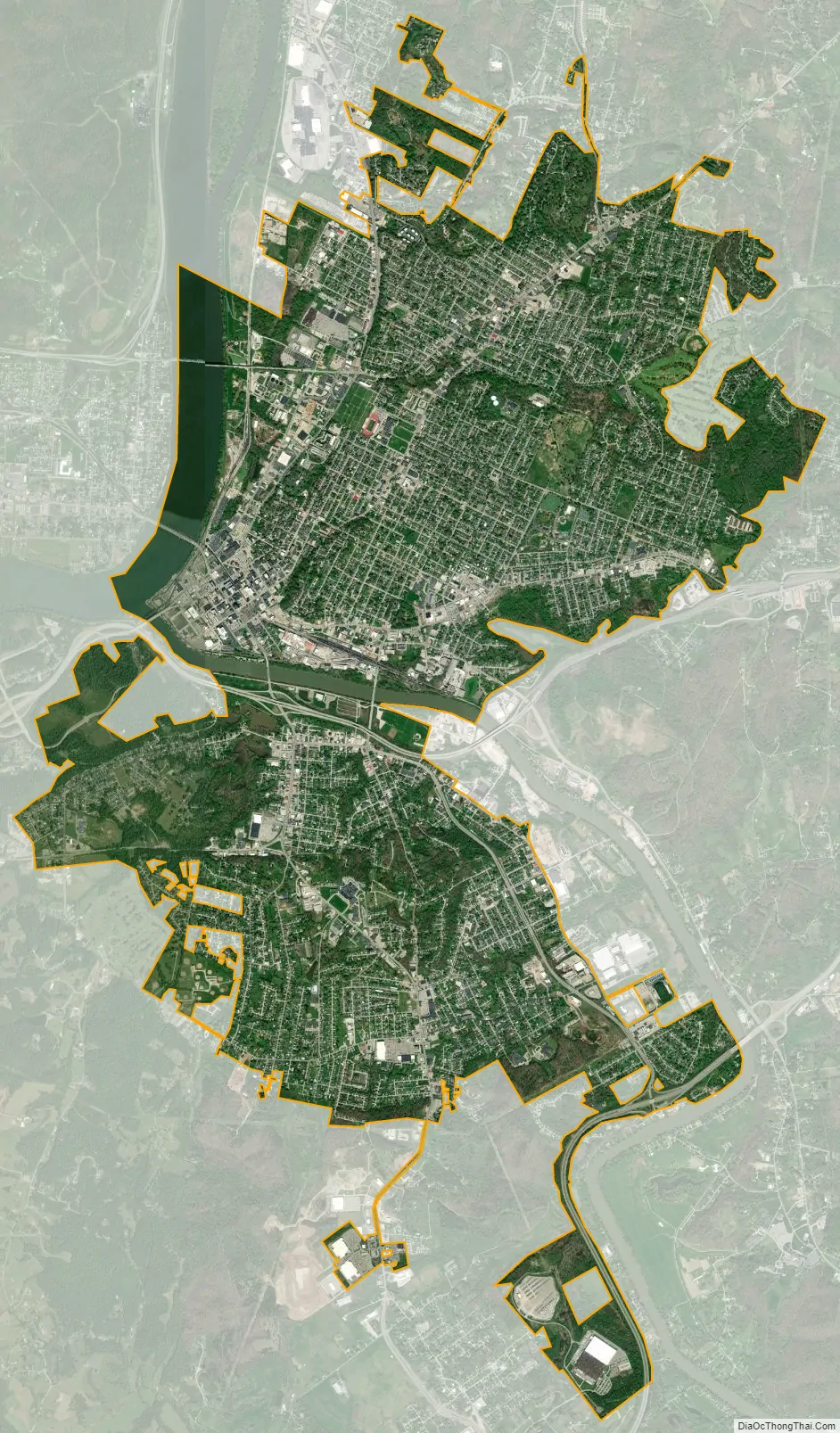
Parkersburg city Satellite Map
Geography
Parkersburg is located at 39°15’58” North, 81°32’32” West (39.266175, −81.542139).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 12.35 square miles (31.99 km), of which 11.82 square miles (30.61 km) is land and 0.53 square miles (1.37 km) is water.
The city is situated at the confluence of the Little Kanawha and Ohio rivers. The Little Kanawha River divides the north and south sides of the city. Worthington Creek, a tributary of the Little Kanawha River, flows through the eastern part of the city.
Neighborhoods
The North End of the city includes the Beechwood, Downtown, Fairview Heights, Granada Hills, Julia-Ann Square, Meadowcrest, Oakwood Estates, Quincy Hill, Riverside, Woodland Park, North End, Worthington, and East End neighborhoods.
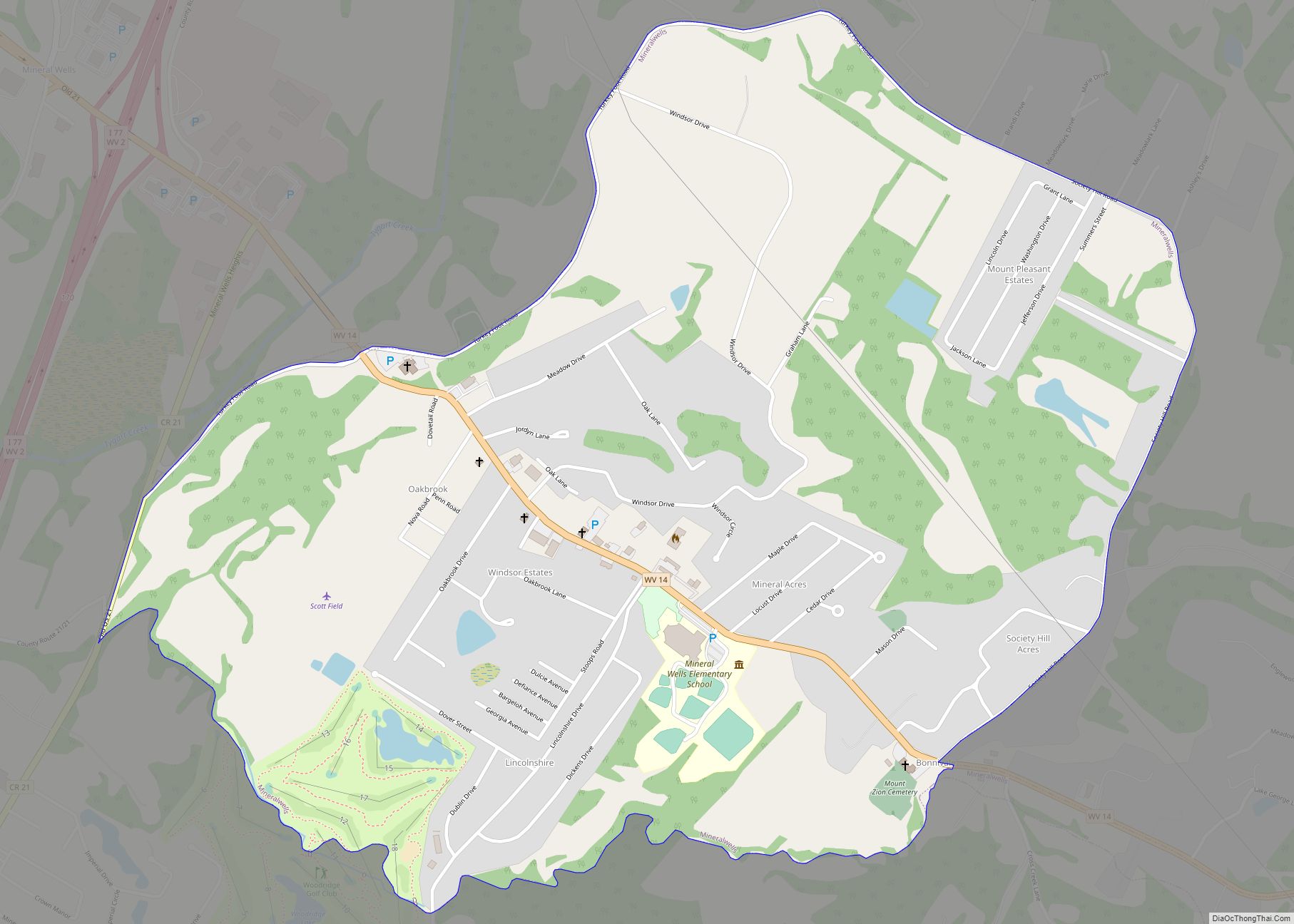
The southern part of the City of Parkersburg, South Parkersburg was a separate city until it became part of Parkersburg in 1950. Suburban parts of southern Wood County include Blennerhassett, Lubeck, and Washington to the southwest, with Mineral Wells located to the southeast.
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers, cold winters and evenly distributed precipitation throughout the year. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Parkersburg has a humid continental climate, abbreviated Dfa on climate maps.
See also
Map of West Virginia State and its subdivision:- Barbour
- Berkeley
- Boone
- Braxton
- Brooke
- Cabell
- Calhoun
- Clay
- Doddridge
- Fayette
- Gilmer
- Grant
- Greenbrier
- Hampshire
- Hancock
- Hardy
- Harrison
- Jackson
- Jefferson
- Kanawha
- Lewis
- Lincoln
- Logan
- Marion
- Marshall
- Mason
- McDowell
- Mercer
- Mineral
- Mingo
- Monongalia
- Monroe
- Morgan
- Nicholas
- Ohio
- Pendleton
- Pleasants
- Pocahontas
- Preston
- Putnam
- Raleigh
- Randolph
- Ritchie
- Roane
- Summers
- Taylor
- Tucker
- Tyler
- Upshur
- Wayne
- Webster
- Wetzel
- Wirt
- Wood
- Wyoming
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming