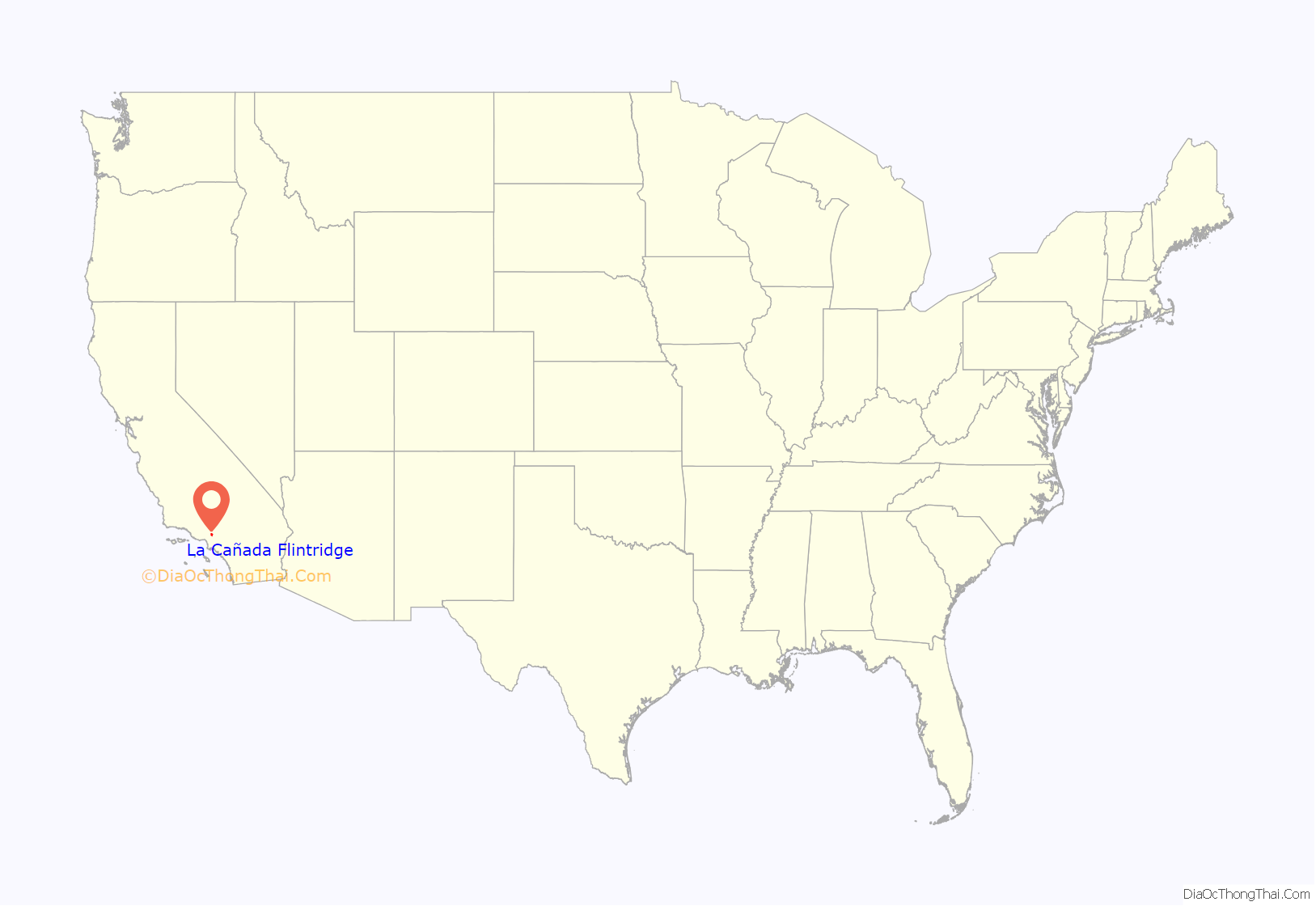
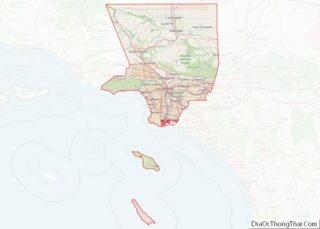
La Cañada Flintridge, commonly known as “La Cañada” (Spanish for “The Canyon”), is a city in the foothills of the Verdugo Mountains in Los Angeles County, California. Located in the Crescenta Valley, in the western edge of Southern California’s San Gabriel Valley, it is the location of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Before the city’s incorporation on November 30, 1976, it consisted of two distinct communities, “La Cañada” and “Flintridge”.
| Name: | La Cañada Flintridge city |
|---|---|
| LSAD Code: | 25 |
| LSAD Description: | city (suffix) |
| State: | California |
| County: | Los Angeles County |
| Incorporated: | November 30, 1976 |
| Elevation: | 1,188 ft (362 m) |
| Total Area: | 8.64 sq mi (22.39 km²) |
| Land Area: | 8.63 sq mi (22.35 km²) |
| Water Area: | 0.02 sq mi (0.04 km²) 0.20% |
| Total Population: | 20,246 |
| Population Density: | 2,318.81/sq mi (895.32/km²) |
| FIPS code: | 0639003 |
| Website: | CityofLCF.org |
Online Interactive Map
Click on ![]() to view map in "full screen" mode.
to view map in "full screen" mode.
La Cañada Flintridge location map. Where is La Cañada Flintridge city?
History
Reference to the entire city is often shortened to just “La Cañada” or seldom to just “Flintridge”. The full city name specifically does not have a hyphen in it, to illustrate unity between the two communities that became one.
La Cañada
During the Spanish and Mexican eras, the area was known as Rancho La Cañada. La Cañada comes from the Spanish word cañada (pronounced [kaˈɲaða]), meaning ‘canyon’, ‘gorge’, or ‘ravine’.
In December 1933 and January 1934, the La Cañada Valley was severely flooded in the Crescenta Valley flood (1933 and 1934).
Flintridge
Flintridge was named after its developer, United States Senator Frank P. Flint.
Flintridge comprises the southern part of the city, covering the northern flank of the San Rafael Hills, but more generally including most areas south of Foothill Blvd. The eastern part, even north of Foothill Blvd, was also originally considered Flintridge and is still home to the Flintridge Riding Club and Flintridge Preparatory School.
Incorporation
On November 30, 1976, the cities of Flintridge and La Cañada were merged into a single incorporated city named “La Cañada Flintridge”.
In a 2015 issue of Forbes, La Cañada Flintridge ranked as the 121st most expensive U.S. city.
La Cañada Flintridge Road Map
La Cañada Flintridge city Satellite Map
Geography
The city is situated in the Crescenta Valley and far western end of the San Gabriel Valley, between the San Gabriel Mountains and Angeles National Forest to the north, and the San Rafael Hills to the south. Most of the city drains southeastward toward the Arroyo Seco area in Pasadena, but the western part of the city (generally west of Alta Canyada Road) drains southward toward Glendale via Verdugo Canyon. Both drainages join the Los Angeles River north of downtown Los Angeles. It is built of the Angeles Crest, the San Rafaels, and the canyon in the middle.
La Cañada Flintridge varies in elevation from about 970 feet (300 m) just below Devil’s Gate Dam in the Arroyo Seco to about 2,400 feet (730 m) at the highest neighborhood, along the mountain front east of Pickens Canyon, at the upper end of Ocean View Blvd. The city limits extend into the San Gabriel Mountains and reach 3,440 feet (1,050 m) along Mount Lukens Road, which follows the crest line well above the developed city.
In August 2009, the city came under threat by the Station Fire. The city is considered a “very high fire hazard severity zone” because of the local topography at the base of the San Gabriel Mountains and abundance of California Live Oak, despite an aggressive fire safety program.
The city is home to Descanso Gardens and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Climate
The climate of La Cañada Flintridge is typical of a Southern California inland valley, with mild winters and hot summers. Spring often has hazy days, in contrast to the more persistently clear weather of fall. On average, the warmest month is August with high temperatures in the low to mid 90s and lows in the low 70s. December and January are the coolest months with typical highs in the low to mid 60s and lows in the low 40s. Rainfall occurs mostly during winter, averaging about 21 inches annually. Rainfall is rare in summer. The moderating influence of the ocean (22 miles, 35 km, away) is limited due to the city’s location inland from the intervening Santa Monica Mountains, the Verdugo Mountains, and the San Rafael Hills. Consequently, summers are generally hotter and winters often cooler than in coastal parts of metropolitan Los Angeles if winds are calm or blowing gently offshore. Occasional strong offshore winds, known as the Santa Ana winds, can bring particularly hot air in summer and fall as air from the desert plateaus crosses the mountains and descends, thus warming further by adiabatic heating. Summer and early fall temperatures are substantially cooler if the prevailing wind is persistently onshore. Occasionally during a winter storm, the upper elevations of the city may see trace amounts of snow. The small ski resorts Mountain High, Mount Baldy, and Mount Waterman are located about 30 miles (48 km) to the northeast.
See also
Map of California State and its subdivision:- Alameda
- Alpine
- Amador
- Butte
- Calaveras
- Colusa
- Contra Costa
- Del Norte
- El Dorado
- Fresno
- Glenn
- Humboldt
- Imperial
- Inyo
- Kern
- Kings
- Lake
- Lassen
- Los Angeles
- Madera
- Marin
- Mariposa
- Mendocino
- Merced
- Modoc
- Mono
- Monterey
- Napa
- Nevada
- Orange
- Placer
- Plumas
- Riverside
- Sacramento
- San Benito
- San Bernardino
- San Diego
- San Francisco
- San Joaquin
- San Luis Obispo
- San Mateo
- Santa Barbara
- Santa Clara
- Santa Cruz
- Shasta
- Sierra
- Siskiyou
- Solano
- Sonoma
- Stanislaus
- Sutter
- Tehama
- Trinity
- Tulare
- Tuolumne
- Ventura
- Yolo
- Yuba
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming